Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nuclear Physics
Încărcat de
azamtoorDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nuclear Physics
Încărcat de
azamtoorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nuclear Physics Radioactivity Nuclear reactions
Radioactivity: Phenomenon in which a heavy, unstable nucleus, like uranium, gives out radiations i.e. , and is called radioactivity. Radioactive element: Elements which gives/emits nuclear radiation Discovering , and radiations: Naturally radioactivity radiations emitted by naturally occurring elements. Artificial radioactivity Element/Nucleus of certain elements can be made radioactive such radioactivity is called artificial radioactivity. FIG When radioactive element is exposed to photographic film, installed in a vacuum chamber provided with electric and magnetic fields mutually perpendicular, as shown in the diagram above. After exposing over a period, when the film is developed, there spots are obtained on the film. i. ii. a spot towards ve end of the film, indicating that the spot is due to +vely charged radiations called Alpha radiations they are positively charged symbols . Another spot formed towards the +ve end of the film, indicating that the spot is due to vely charged radiations called Beta radiations they are negatively charged Symbol Third spot is formed right in front of the radioactive source indicating that they are not deflected by electricity and magnetic fields, hence are neutral. These radiations are called Gamma radiations Symbol ()
iii.
Characteristics of radiations/particles: i. Nature: Alpha radiations are positively charged particles with charge equal to twice the charge of proton, and mass equal to four times the mass of hydrogen atom (or nucleus). Hence particle is taken as helium nucleus i.e. ++2He4 FIG
ii. iii. iv. v. vi.
They carry energy. They move at about one tenth of speed of light. They are highly ionizing i.e. they ionize the gas through which they pass. Least penetrating, can travel a maximum distance of 5 cm in air. They can be blocked/absorbed by the sheet of paper. They show deflection in electric and magnetic fields. FIG
vii. viii.
They produce fluorescence effect on striking fluorescent coated surface. They are harmful radiations which cause skin diseases.
Characteristics of Beta particles/Radiation: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. They cue negatively charged particles and has same charge and mass as that of an electrons, hence they are taken to be fast moving electrons. They carry energy. They move almost at the same speed of light. They are less ionizing than alpha particles/ they have less ionizing power than Alpha particles. They are more penetrating than Alpha particles. They can be blocked by few inns, thick aluminum sheet. They show deflection in Electric and magnetic field. FIG viii. ix. They produce fluorescence effect on striking fluorescent coated surface. They are harmful radiations, cause skin diseases.
Characteristics of rays/radiation: i. ii. iii. iv. Gamma rays are electrically neutral and carry no mass. Hence, they are electromagnetic radiations. Carry energy. They move at the speed of light. They are least ionizing.
v. vi. vii. viii.
They are highly penetrating and can be blocked/absorbed by few cm thick lead sheet. They dont show deflection electric and magnetic fields. They produce fluorescence effect on striking fluorescent coated surface. They are harmful radiations, cause skin disease.
Radiation Detector: GM Tube: FIG GM Tube: A device used to detect nuclear radiations. It consists of a metal cylinder fitted with a axial rod, which is insulated from the cylinder. The rod acts as anode and metal cylinder acts as cathode. Some inert gas is trapped in it, and a mica window is fitted at its outer end. Working: When radiations from the radioactive source enter this tube, they produce ionization in the gas trapped in it. The ions so formed, more towards corresponding electrodes. These moving charges develop weak current in the circuit, this current is fed to amplifier which enlarges this current, and the scalar shows deflection on Ammeter. Whereas the counter records the No. of particles/radiations, entering the tube.
Discussion
Alpha more current as more ionizing Beta less current as less ionizing
Nuclear Physics! Radioactivity: FIG Traces of ionized paths in alcohol vapors at low pressure due to nuclear radiations observed in cloud chamber. Continuous bold tracks in alcohol vapors represent strongly ionizing/heavy particles or radiation i.e. Alpha. Broken, discontinuous zigzag paths show weaker ionization caused by Beta particles/radiations. Distant clots observed due to weakest ionization caused by gamma radiations.
Fluorescent coated screen can be used to detect nuclear radiations.
more energy
more effect
more energy so shows most effects weaker than alpha weakest affect Randomness (related to type) and spontaneity (related to time) of radiations: It is no possible/impossible of predict the time and type of emission of nuclear radiation. This phenomenon is called randomness and spontaneous behavior/effect. Uranium is a radioactive source, it gives all three radiations. The type and time of radiations cant be predicted. For any radioactive nucleus the type + type cant be emitted.
RADIOACTIVE DECAY: The transformation of parent nucleus into daughter nucleus by emitting Alpha, Beta and gamma radiations (nuclear radiations) is called nuclear decay. Parent Nucleus: Which emits radiations Daughter Nucleus: After emitting radiations
- Parent
+ daughter + alpha
There are three types of nuclear decays Alpha Decay Beta Decay Gamma Decay ALPHA DECAY (): Emission of Alpha particle from a radioactive nucleus During decay, parent nucleus transforms into daughter nucleus according to following equation.
2He 4
(Parent)
()
decay (Beta): Emission of beta particles from a radioactive nucleus
N P
P N
P e Emitted out as
-1 +
z (-1) (z + 1) Q. If emits 2 and 2 Electron doesnt take part in mass exchange as its mass is negligible.
If emits 2
During a decay, a neutron changes into an electron and proton. Electrons cant stay in So is emitted out Gamma Decay: () Emission of gamma radiations from radioactive nucleus When Emits and it has gaps between as a jar filled with something need to be shaken to fill the gaps differ the thrown (in) of fillings. FIG
The nucleus in this state is known as excited nucleus.
When this shuffles gamma are emitted. Half Life: Duration/Time in which half of the radioactive parent nuclei transforms into daughter nuclei by emitting radiation , and . OR Time in which current falls to half if its initial (original) value. OR Time in which count rate falls to half of its original value. OR Time in which half of the original mass decays by emitting radiations. OR Time in which activity of the radioactive substance falls to half of its original value. FIG * *
Remaining Activity = ( ) x original activity Where n = No. of half lives
Find the mass after 8 days, given that half life is 2 days.
n=4 ( ) = x 800
R.M = 50 gm
Count rate of certain radioactive element falls to one eighth of its initial value, given that half life of the element is 5 years. Calculate the duration in which activity falls to the given value. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
n=3
TP = 15 Back ground Radiations: Radiations coming from surrounding environment Source of Back ground radiations: Sun Earth Crust Nuclear waste
Background Count Rate: Count Rate due to back ground radiations i.e. without any sources exposed to GM tube. Background count rate is always there it can never be eliminated.
A certain radioactive substance when exposed to GM tube, the count rate recorded on GM tube is 900 counts/hours given that background count rate is 100 counts/hour. If half life of the elements is 10 days. Calculate a) Count rate of the element after 2 months
b) Count rate recorded by GM tube after 2 months
n=6 Remaining count rate = ( ) =( ) =( ) = 12.5 (b) element = 12.5 Count rate = 100 + 12.5 = 112.5 count/hr
Activity of a certain element falls to one sixteenth of its initial value in 2 years. Calculate the half life of the element. ( ) ( ) ( ) n=4 Radioactive Isotopes: Atoms of the same element having same number of protons but different number of neutrons Same charge number, different mass no. 1) Uses of Radioactive Isotopes:
Industrial Use: To check the thickness of metal sheets (thin) FIG
To ensure quantity of liquids in packs To detect leakages and cracks in pipes etc.
FIG
FIG
The water contaminated with radioactive is passed through the pipe and GM tube is moved all around the pipe, variations are observed. Count rate increase leakage , count rate shoots crack
2) Carbon Dating: Archeologists use C-14 isotope of carbon which is an essential part of every living matter for a living body, the amount of C-14 almost remains constant, whereas after the death of the living matter C-14 starts decaying.
3) Agriculture and medical use: GM tube if radiations detected then not affected used to check nutrition and fertilizer use
Water + radioactive Gamma, long half life
MEDICINE: Is contaminate with RA isotope, GM is moved against targeted area, detection in count rate indicates that medicine is reaching the target area hence on behalf of relief to the patient quality can be improved.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- 101 Last Days Prophecies (The End Times, Anarchy, ViolenceDocument38 pagini101 Last Days Prophecies (The End Times, Anarchy, ViolenceAshangelV1Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Year 9 Science Yearly NotesDocument5 paginiYear 9 Science Yearly NotesAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM D6938 15 Nuclear Densitometer PDFDocument9 paginiASTM D6938 15 Nuclear Densitometer PDFculicha23100% (1)
- Extrusion and Injection Molding of PolymersDocument6 paginiExtrusion and Injection Molding of PolymersazamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument8 paginiNuclear Physics NotesCai Peng Fei100% (1)
- Edexcel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 6 Test 16 - 17 With Mark SchemeDocument18 paginiEdexcel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 6 Test 16 - 17 With Mark SchemePaul BurgessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astronomy - Chapter 14 TestDocument28 paginiAstronomy - Chapter 14 TestJ. R. SilveyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UP - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument18 paginiUP - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryKate Evangelista100% (1)
- Drivers of Supply Chain ManagementDocument39 paginiDrivers of Supply Chain ManagementazamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 Gamma Ray LogDocument39 paginiLecture 7 Gamma Ray LogNaser Khan100% (2)
- Refractory MaterialsDocument8 paginiRefractory Materialskaran nirmala gajanan shindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PersonalityDocument5 paginiPersonalityazamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation and Performance: Prof. Sidra Lecture#5Document19 paginiMotivation and Performance: Prof. Sidra Lecture#5azamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Labor in Pakistan As PresentationDocument15 paginiChild Labor in Pakistan As PresentationazamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetism 1Document25 paginiMagnetism 1azamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Management: Sunil Chopra (3rd Edition)Document29 paginiSupply Chain Management: Sunil Chopra (3rd Edition)azamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology InventoryDocument1 paginăBiology InventoryazamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leads Academy SAT1Document23 paginiLeads Academy SAT1azamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 1Document1 paginăBook 1azamtoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial Paper SPM 2019Document26 paginiTrial Paper SPM 2019Christian AdkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miss Rabia Najam: Nuclear PHYSICS Presentation Submitted ToDocument13 paginiMiss Rabia Najam: Nuclear PHYSICS Presentation Submitted ToWajeeha IftikharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure Timeline: 400 BC, Scientist: Democritus (Greek Philosopher)Document13 paginiAtomic Structure Timeline: 400 BC, Scientist: Democritus (Greek Philosopher)Anthony BasantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution:: 7.2.5 Photoelectric EffectDocument7 paginiSolution:: 7.2.5 Photoelectric EffectIka Fitria WatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Document29 paginiChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Korey PrestonÎncă nu există evaluări
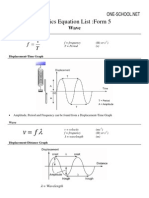
- WWW - One School - Net Notes Physics SPM Physics Formula List Form5Document9 paginiWWW - One School - Net Notes Physics SPM Physics Formula List Form5Adam Chew Lip WeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Chemistry and Radioactivity: Stable ParticlesDocument48 paginiNuclear Chemistry and Radioactivity: Stable ParticlesAdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skills Iit Jee ChemistryDocument22 paginiSkills Iit Jee Chemistrysiddharth95480% (1)
- Deleted Portion Physics - 042 Class XiDocument3 paginiDeleted Portion Physics - 042 Class XiRounak SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GenPhysics2 Q2-Module-6 RemovedDocument19 paginiGenPhysics2 Q2-Module-6 RemovedJasmin SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhyiscsDocument38 paginiPhyiscsLo CtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paul Brown Nuclear Battery Patent 1989 PDFDocument10 paginiPaul Brown Nuclear Battery Patent 1989 PDFЛето Жаркое100% (1)
- Radiation Production and Characteristics Lecture2021 22Document188 paginiRadiation Production and Characteristics Lecture2021 22Lei ClamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monte Carlo Simulations of Radioactivity Using PythonDocument12 paginiMonte Carlo Simulations of Radioactivity Using PythonHarsh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GenMath Q1 M4 Exponential FunctionsDocument23 paginiGenMath Q1 M4 Exponential FunctionsJoanna Marie RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms Molecules IonsDocument36 paginiAtoms Molecules IonsGraciella Anne LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 DENSITY LOG RevDocument26 pagini8 DENSITY LOG RevRiska Indah0% (1)
- Nuclear Stability Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument20 paginiNuclear Stability Radioactivity and Half LifeKris Carl QuirapasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Science G11 Q1 W6 GeologicalHistoryEarthDocument9 paginiEarth and Life Science G11 Q1 W6 GeologicalHistoryEarthAna CristinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coach Ally Open School Physics Paper 1 Form FourDocument5 paginiCoach Ally Open School Physics Paper 1 Form FourJuma BwaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- JSU SAINS FORM 4 PPT 2018Document12 paginiJSU SAINS FORM 4 PPT 2018Nadiya NedyÎncă nu există evaluări