Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science Blog 13.4 Chason, Thanu
Încărcat de
thanusshmanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science Blog 13.4 Chason, Thanu
Încărcat de
thanusshmanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
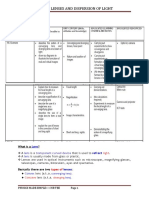
Science Blog Project 13.
The Lens Equations Chason C, Thanu P
The lenses of todays technology include plane, converging (Convex) and diverging (concave). There are two ways to determine the characteristics of image formed by lens. The two ways are by using ray diagrams or algebra. Ray diagrams method allows you to find the general size. Algebra method allows you determine the exact size. These lens types manipulate the rays of light that pass through them in different ways. The main way results in a reflected and refracted ray coming off the lens. But this blog is going to take a large step towards math as being very helpful in making accurate measurements.
The thin lens equation is
E.g
The following symbols mean Hi, Ho, F, Di, and Do. H represents height from principle axis, D represents distance from lens, i represents image, o represents object, and F represents distance from lens to Focus. Magnification is the number affiliated with the charge of the image. When you compare the size of the image with the size of the object is finding the magnification of the lens. The last symbol needed for this chapter is the M, which as you guessed it represents the magnification. Always remember of the image is upright it is positive number, inverted image it is a negative number. The magnification equation is
E.g
What is difference between Converging lens and Diverging lens? Converging lens are when parallel rays come and converge and cross at a focal point. The lens that is thickest in the middle and that causes incident parallel light rays to converge trough a single point after refraction. A converging lens (convex lens) is curved on both sides. A converging lens is has positive focal length. Converging lens causes exiting rays to be more convergent coming out than they were entering the lens. Diverging lens are parallel rays diverge after refraction from the lens. Diverging lens have a negative focal length. A diverging lens is thinnest in the middle. It causes incident parallel light rays to spread apart after refraction.
Converging lens
Diverging lens
Links For further information on chapter 13.4 I encourage you to visit the sights I am providing for below. -http://emmybella.wordpress.com/the-lens-equations/themagnification-equation/ https://www.boundless.com/physics/geometricoptics/lenses/the-thin-lens-equation-and-magnification/ Now to summarize chapter 13.4 I have found a video of an enthusiastic teacher explaining the equations. Enjoy it by clicking link >http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pi02n_lteXA Just to clarify he uses the letter S in Si and So instead of H making them Hi and Ho.
Magnification Formula video that a professor explain really well http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ORUGwPP-mb4 Concave and Convex Lens teaches how to draw them. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9-XAolo9xz8 Citations: "The Thin Lens Equation and Magnification." Boundless. SmartNotes, n.d. Web. 06 Feb. 2014. <https://www.boundless.com/physics/geometricoptics/lenses/the-thin-lens-equation-and-magnification/>. Emma. "Simplified Physics." Emmas ExplanationThe Physics of It All. N.p., n.d. Web. 06 Feb. 2014. <http://emmybella.wordpress.com/the-lens-equations/themagnification-equation/>. "Lens Equation." YouTube. YouTube, 10 Sept. 2010. Web. 06 Feb. 2014. <http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pi02n_lteXA>. "Physics 2020 Lab 4: Pre-Lab Questions."Physics 2020 Lab 4: Pre-Lab Questions. Colorado, 6 Nov. 2012. Web. 8 Feb. 2014. <http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys20>. Simanek, Donald. "Lens Basics." Lens Basics. lhup, n.d. Web. 8 Feb. 2014. <http://www.lhup.edu/~dsimanek/scenari>.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Detailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesDocument9 paginiDetailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesCyril Cauilan100% (1)
- LensesDocument31 paginiLensesDejaunae LawsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument27 paginiPhysicsshlokpandey0202Încă nu există evaluări
- Lens PowerpointDocument28 paginiLens Powerpointdarellbarnes450Încă nu există evaluări
- Spherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesDocument18 paginiSpherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesPrinceNeilCedrickCastro100% (1)
- My FileDocument7 paginiMy Fileمؤمل فاضلÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument30 paginiPhysicsshlokpandey0202Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Document14 paginiLearning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Daniel Angelo Esquejo ArangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science10 Q2 Mod5 v4Document6 paginiScience10 Q2 Mod5 v4Kim TaehyungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Document5 paginiScience 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Jess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 paginiRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirrors and Lenses ReviewerDocument9 paginiMirrors and Lenses ReviewerVannie MonderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plane and Spherical MirrorsDocument9 paginiPlane and Spherical Mirrorschinkayaby16Încă nu există evaluări
- Capstone ProjectDocument29 paginiCapstone ProjectJohn RemzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 paginiScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Q.2. Srlu W3 G10Document6 paginiQ.2. Srlu W3 G10Pamela IndosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 4.4Document15 paginiLesson 4.4alexandriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E112 - AgustinDocument19 paginiE112 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDocument22 paginiSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- COT PresentationDocument42 paginiCOT PresentationCedric BaldozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReflnDocument20 paginiReflnDaniel Boenfie100% (1)
- Lenses and EYE WorksheetDocument17 paginiLenses and EYE WorksheetarjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27Document29 pagini27physicsdocs0% (2)
- Science10 q2 w7 CALADODocument18 paginiScience10 q2 w7 CALADOGabriel SakayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 2Document11 paginiPhysics 2bort kortÎncă nu există evaluări
- g10 Ntot Physics LightDocument44 paginig10 Ntot Physics Lightapi-283862617100% (5)
- Physics - Geometric-Optics Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiPhysics - Geometric-Optics Lesson PlanBeing MotivatedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thin LensesDocument37 paginiThin LensesVianca Rein MilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeaDocument24 paginiLIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeanidharshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lens & MirrorsDocument219 paginiLens & MirrorsChandra ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUARTER 2 - A4Document3 paginiQUARTER 2 - A4Monique MangubatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science - Grade 10: Reflection of Light in A Curved MirrorDocument16 paginiScience - Grade 10: Reflection of Light in A Curved MirrorJames AlforteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 paginiNotes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionShardul SumantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Convex LensDocument15 paginiPhysics - Convex LensdivyapriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 31.1-Mariam Jameela Jutar-WrittenReport7Document6 paginiPhysics 31.1-Mariam Jameela Jutar-WrittenReport7Jameela JutarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 paginiLIGHT Physics Form 4Amrita KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirror NotesDocument6 paginiMirror Notesmarife gupaal100% (1)
- Image Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving MirrorsDocument75 paginiImage Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving Mirrorsjohn charles garalde100% (1)
- Lens PresentationDocument40 paginiLens PresentationNayeem HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- LENSESDocument9 paginiLENSESmafiamain160Încă nu există evaluări
- Optics Lenses and DispersionDocument23 paginiOptics Lenses and DispersionHomok NokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomedical Equipment 1Document21 paginiBiomedical Equipment 1benardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Make Your Own ProjectorDocument9 paginiMake Your Own ProjectorswapnasridharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometric Opti CS: Ariel C. LalisanDocument26 paginiGeometric Opti CS: Ariel C. LalisanTrishia PradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometric Opti CS: Ariel C. LalisanDocument26 paginiGeometric Opti CS: Ariel C. LalisanTrishia PradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LensesDocument13 paginiLenseshelmi_tarmiziÎncă nu există evaluări
- E402 Part 1Document3 paginiE402 Part 1Ralph Evidente100% (2)
- Geometric OpticsDocument8 paginiGeometric OpticsSerge Mandhev SwamotzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astrophsics Option ADocument87 paginiAstrophsics Option AAlex KingstonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0971physics Form 4 Notesa7638e67Document59 pagini0971physics Form 4 Notesa7638e67Philemon KeitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of LightDocument10 paginiProperties of LightKesanam SpÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE Grade 10: Quarter 2 - Module 6Document16 paginiSCIENCE Grade 10: Quarter 2 - Module 6P. Brucoy100% (1)
- SCIENCE Grade 10: Quarter 2 - Module 6Document15 paginiSCIENCE Grade 10: Quarter 2 - Module 6Nadzbalyn BallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Quarter 2 - Module 4: Uses of Mirrors and Lenses (REVIEWER)Document4 paginiScience 10 Quarter 2 - Module 4: Uses of Mirrors and Lenses (REVIEWER)Ella AuriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S10 Q2 Week-7Document10 paginiS10 Q2 Week-7Aiphrell Anne D. MoradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science - Grade 10: Mirror and Lens EquationDocument16 paginiScience - Grade 10: Mirror and Lens EquationJames Alforte100% (3)
- 3.2 LightDocument11 pagini3.2 LightDhanBahadurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6Document9 paginiModule 6chef curryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Today's Agenda: Death Rays. Refraction at Spherical Surfaces.: Concave and Convex Lenses,, Solving The Lens EquationDocument6 paginiToday's Agenda: Death Rays. Refraction at Spherical Surfaces.: Concave and Convex Lenses,, Solving The Lens EquationOmar DoskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesDe la EverandThe Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesÎncă nu există evaluări