Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Experiment No 6 Ce NPN
Încărcat de
Eugene Christina EuniceDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Experiment No 6 Ce NPN
Încărcat de
Eugene Christina EuniceDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EXPERIMENT NO.
6
I. AIM: To obtain common emitter characteristics of NPN transistor II. APPARATUS REQUIRED Power supply, VOM, NPN Transistor, 100 k-ohms and 1k-ohms resistor III. BRIEF THEORY Transistor is three terminal active device having terminals collector, base and emitter. Transistor is widely used in amplifier, oscillator, electronic switch and so many other electronics circuits for variety of applications. To understand operation of the transistor, we use three configurations common emitter, common base and common collector. In this practical, we will understand common emitter configuration. As the name suggest, emitter is common between input and output. Input is applied to base and output is taken from collector. We will obtain input characteristics and output characteristics of common emitter (CE) configuration. We will connect variable DC power supply at V BB and VCC to obtain characteristics. Input voltage in CE configuration is base-emitter voltage Vbe and input current is base current Ib. Output voltage in CE configuration is collector to emitter voltage VCE and output current is collector current Ic. We will use multi-meter to measure these voltages and currents for different characteristics. Collector to emitter junction is reverse biased and base to emitter junction is forward biased. The CE configuration is widely used in amplifier circuits because it provides voltage gain as well as current gain. In CB configuration current gain is less than unity. In CC configuration voltage gain is less than unity. Input resistance of CE configuration is less than CC configuration and more than CB configuration. Output resistance of CE configuration is more than CC configuration and less than CB configuration. IV. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
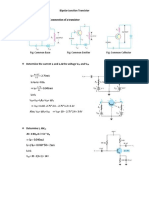
a) Input Characteristics
XMM1 R1 1k
where: XMM1 = Ib XMM2 = Vbe
Q1 R2 100k VBB 12 V XMM2 BJT_NPN_VIRTUAL VCC 12 V
b) Output Characteristics
XMM2
XMM1
R1 1k Q1
R2
XMM3 VCC 12 V
where: XMM1 = Ib XMM2 = Ic XMM3 = Vce
100k BJT_NPN_VIRTUAL VBB 12 V
V. PROCEDURES Input Characteristics 1. Connect circuit as shown in the circuit diagram for input characteristics 2. Connect variable power supply 0-30V at base circuit and collector circuit. 3. Keep Vcc fix at 0V (Or do not connect Vcc) 4. Increase VBB from 0V to 20V, note down readings of base current Ib and base to emitter voltage Vbe in the observation table. 5. Repeat above procedure for Vcc = +5V and Vcc = +10V 6. Draw input characteristics curve. Plot Vbe on X axis and Ib on Y axis. Output Characteristics 1. Connect circuit as shown in the circuit diagram for output characteristics 2. Connect variable power supply 0-30V at base circuit and collector circuit. 3. Keep base current fix (Initially 0) 4. Increase VCC from 0V to 30V, note down readings of collector current Ic and collector to emitter voltage Vce in the observation table. 5. Repeat above procedure for base currents Ib = 5A, 50 A, 100 A. Increase base current by increasing VBB. 6. Draw output characteristics curve. Plot Vce on X axis and Ic on Y axis. VI. OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS
a) Input Characteristics TRANSISTOR : _________________
SR No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
VBB 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 5 10 15 20
VCC = 0V VBE Ib
VCC = 5V VBE Ib
VCC = 10V VBE Ib
b) Output Characteristics TRANSISTOR : ___________________
SR No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
VCC 0 1 2 4 6 8 10 12 15 20
Ib = 0 uA VCE Ic
Ib = 5 uA VCE Ic
Ib = 10 uA VCE Ic
Ib = 100 uA VCE Ic
VII. QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What What What What What is is is is is Common Emitter configurations? the input impedance you obtain in this practical? the output impedance you obtain in this practical? the DC voltage gain you obtain in this practical? the DC current you obtain in this practical?
VIII. CONCLUSIONS
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Laboratory 2 - Diode Characteristics - Don Bernard D. MijaresDocument14 paginiLaboratory 2 - Diode Characteristics - Don Bernard D. MijaresDon Bernard MijaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode Characteristics PDFDocument16 paginiDiode Characteristics PDFJOECELLE ABLEGINAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Part 1 StudentDocument4 paginiFinal Exam Part 1 StudentRJ Balbedina100% (1)
- Lab Manual All ExperimentDocument62 paginiLab Manual All ExperimentLIFE of PSÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDocument24 paginiECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument29 paginiTransformergolu100% (1)
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifier Phase Control: ObjectivesDocument4 paginiSilicon-Controlled Rectifier Phase Control: ObjectivesSTO. TOMAS SHAIRA FRESCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3,4 and 5Document10 paginiExperiment 3,4 and 5airaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: E B CE CBDocument18 paginiBipolar Junction Transistor: E B CE CBMohammadAshraful100% (1)
- Experiment 1Document6 paginiExperiment 1Jomel JomelÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Tutorial ProblemsDocument63 paginiDC Tutorial ProblemsKenneth Paul Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clippers and ClamersDocument15 paginiClippers and ClamersThilaga MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP6 Clipper and Clamper CircuitDocument4 paginiEXP6 Clipper and Clamper CircuitMohammed Dyhia Ali100% (2)
- Lista 5Document22 paginiLista 5vsabioniÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT Practice Questions PDFDocument5 paginiBJT Practice Questions PDFDustin BentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocument62 paginiZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEC LAB REPORT-08 (Familiarization With The 555 Timer)Document11 paginiDEC LAB REPORT-08 (Familiarization With The 555 Timer)Mazumder OliveÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT 3 4 and 5 - LINGAODocument9 paginiEXPERIMENT 3 4 and 5 - LINGAOairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode ApplicationsDocument3 paginiEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode Applicationsdonatello84Încă nu există evaluări
- Mdefbod Quiz 1Document1 paginăMdefbod Quiz 1Heiro KeystrifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.diode Clipper and ClamperDocument12 pagini2.diode Clipper and ClamperMounika AllagaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac Single Phase First PartDocument32 paginiAc Single Phase First PartreyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 1 Group 4 DraftDocument35 paginiExp 1 Group 4 DraftJERUSHA ANNE RETARDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsDocument6 paginiMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument8 paginiSilicon Controlled RectifierTrisha Camille NerieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switching RealizationDocument25 paginiSwitching Realizationferdad4realÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 BJT Biasing and Thermal StabilizationDocument74 paginiChapter 5 BJT Biasing and Thermal Stabilizationshubhankar palÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open-Circuit or No-Load TestDocument13 paginiOpen-Circuit or No-Load TestNANDHAKUMAR AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 DiodeApplicationDocument4 paginiLab 1 DiodeApplicationAlissandra ClaveriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment #01 (Measurement of AC Voltage With An Oscilloscope)Document9 paginiExperiment #01 (Measurement of AC Voltage With An Oscilloscope)NeilChristianBonillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MachinesDocument20 paginiDC MachinesRaeniel SoritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Repot 5 - TransistorDocument8 paginiLab Repot 5 - TransistorUmmu Umar Wa Aisyah100% (1)
- Emitter FollowerDocument8 paginiEmitter FollowerjerlineprincyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 (Nodal Analysis)Document8 paginiLab 3 (Nodal Analysis)anon_938313424Încă nu există evaluări
- LAB Experiment 1 GROUP NO.7Document6 paginiLAB Experiment 1 GROUP NO.7Janpherson BellecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Document3 paginiThe Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Tim Picar100% (1)
- Types of Armature WindingDocument2 paginiTypes of Armature WindingCastello Akar100% (1)
- Series Type Voltage RegulatorDocument4 paginiSeries Type Voltage RegulatorErika VistanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thevenin's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferDocument26 paginiThevenin's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferNathaniel PanganibanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDocument22 paginiBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRHiếu Dương100% (1)
- Lab Report 8Document8 paginiLab Report 8Nebil YisuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP. 2-Voltage MultiplierDocument3 paginiEXP. 2-Voltage MultiplierJohn RatillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDocument4 paginiExperiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDenisse Torizo Olan100% (1)
- Zener DiodeDocument15 paginiZener DiodeTawki BakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems To Chapter 02 (Singh)Document7 paginiSolved Problems To Chapter 02 (Singh)Julie Hurley100% (1)
- Cap 5Document29 paginiCap 5deberes ucacueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3 Synchronous Motor PSDocument10 paginiActivity 3 Synchronous Motor PSReinz 0429Încă nu există evaluări
- AC Machines Alternators 2Document10 paginiAC Machines Alternators 2Vanvan BitonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5TH Topic in 3 Phase AlternatorDocument22 pagini5TH Topic in 3 Phase AlternatorAlban Ronel D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Document34 paginiElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Mst557Document13 paginiLab Report Mst557hyebibie0% (1)
- Transformer 1 2Document94 paginiTransformer 1 2Tobi AQWÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsDocument4 pagini02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsntldvlaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Test On DC Series MotorDocument3 paginiLoad Test On DC Series Motorramniwas123Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 AlternatorsDocument34 paginiModule 1 AlternatorsIan Guieb100% (1)
- Common Base Transistor ProjectDocument5 paginiCommon Base Transistor ProjectNihanth Charan50% (12)
- Transistor Common - Base ConfigurationDocument5 paginiTransistor Common - Base ConfigurationSunitha JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE Out XticsDocument5 paginiCE Out XticsDenis OdhiamboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No: 4-Characteristics of BJT in CE Configuration AimDocument6 paginiExperiment No: 4-Characteristics of BJT in CE Configuration AimGANESH KUMAR B eee2018100% (2)
- Basic Electronics Lab Report Fall Semester 2021: Course Code: Bece101PDocument17 paginiBasic Electronics Lab Report Fall Semester 2021: Course Code: Bece101PSoumyojyoti Saha 21BEC2076Încă nu există evaluări
- C9 Game Guide For VIPsDocument62 paginiC9 Game Guide For VIPsChrystyanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Label MatrixDocument66 paginiTutorial Label MatrixLuisa Adriana Perez GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BDM DriverDocument16 paginiBDM DrivervolvodiagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Bombas Pozo e ImpulsionDocument112 paginiManual Bombas Pozo e ImpulsionFernando PuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Solver Platform ReferenceDocument247 paginiRisk Solver Platform Referencemj_davis04Încă nu există evaluări
- HVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsDocument5 paginiHVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsReddyvari Venugopal0% (1)
- BextexDocument14 paginiBextexBishawnath RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFD Cable Selection Guide: NEC Allowable Conductor Ampacity Regulatory CodesDocument1 paginăVFD Cable Selection Guide: NEC Allowable Conductor Ampacity Regulatory Codescarlos ortizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 LPC2103 Microcontroller: 2.1.1 FeaturesDocument18 pagini2.1 LPC2103 Microcontroller: 2.1.1 FeaturesBhaskar Rao PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Files - Pumps - Turbo Pumps - Pfeiffer TMH 071 Turbo Pump ManualDocument25 paginiFiles - Pumps - Turbo Pumps - Pfeiffer TMH 071 Turbo Pump ManualOséias Maciel SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adicionando Mais Um Disco (VG) HPUXDocument4 paginiAdicionando Mais Um Disco (VG) HPUXVinicius SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wyche Bridge 2000Document12 paginiWyche Bridge 2000BhushanRajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acord and IAADocument4 paginiAcord and IAABHASKARA_20080% (1)
- Scan 0001Document1 paginăScan 0001ochiroowitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Learning 1 Quiz 1Document3 paginiAssessment of Learning 1 Quiz 1imalwaysmarked100% (4)
- Tiger SharkDocument2 paginiTiger Sharkstefanpl94Încă nu există evaluări
- SM PC300 350 LC 8Document1.025 paginiSM PC300 350 LC 8dedy imranÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Voice: and The Musical InstrumentsDocument12 paginiThe Voice: and The Musical InstrumentsnireadaetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 AcrotechDocument32 pagini2006 Acrotechkaniappan sakthivelÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Universe - Rogues Testament by Steve MillerDocument281 paginiX-Universe - Rogues Testament by Steve MillerRoccoGranataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vessel Maneuverability Guide E-Feb17Document111 paginiVessel Maneuverability Guide E-Feb17KURNIAWAN100% (1)
- Karcher Quotation List - 2023Document12 paginiKarcher Quotation List - 2023veereshmyb28Încă nu există evaluări
- A White Paper On IExpense Features in R12Document17 paginiA White Paper On IExpense Features in R12Balaji ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differences Between Huawei ATCA-Based and CPCI-Based SoftSwitches ISSUE2.0Document46 paginiDifferences Between Huawei ATCA-Based and CPCI-Based SoftSwitches ISSUE2.0Syed Tassadaq100% (3)
- Acid CleaningDocument32 paginiAcid Cleaningsekhar_ntpcÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOE Cooling Catalogue 2017Document164 paginiDOE Cooling Catalogue 2017Rashaad SheikÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Impact Presentation SkillsDocument5 paginiHigh Impact Presentation SkillsMohd AqminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statement of Purpose China PDFDocument2 paginiStatement of Purpose China PDFShannon RutanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Recorder (Paperless) MDR290Document4 paginiCourse Recorder (Paperless) MDR290Jay SanchaniyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sell Sheet Full - Size-FinalDocument2 paginiSell Sheet Full - Size-FinalTito BustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări