Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Successful Project Management Chapter 1 Questions
Încărcat de
e0055996Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Successful Project Management Chapter 1 Questions
Încărcat de
e0055996Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1. Define Project.
Is an endeavor to accomplish a specific objective through a unique set of interrelated tasks and the effective utilization of resources. 2. Define the term project objectives, and give some example. It is usually defined in terms of end product or deliverable, schedule, and budget. An example would be finishing a basement to make it a livable space within 6 months on a $5,000 budget. Another example would be a major company wanting to upgrade the computer system with in a 3 month period and a budget of 20,000. 3. List some examples of resources that are used on a project. People, materials, equipment and facilities. 4. What role does a customer have during the project life cycle? They will play different roles, they will part of the initiating process and also if any changes needed to be done in the planning phase. During the performing phase if there needs to be any changes to the work last minute road blocks may need to be addresses and during the closing when the bill gets finalized. Why is it important to satisfy the customer? Customer satisfaction will help grow your business by keeping your clients coming back and for referring new clients. 5. What aspects of a project might involve some degree of uncertainty? Many aspects can have some degree of uncertainty, such as the schedule or the budget. Fires in the plant that you was going to order your lumber from would delay you project because you will now have two locate a new company. Why? Not everything in a project can be planned, scheduled, or budgeted. 6. Define scope, schedule, cost, and customer satisfaction. Scope is all the work that must be done in order to satisfy the customer that the deliverables meet the requirements or acceptance criteria agreed upon at the onset of the project. Cost is the amount the customer has agreed to pay for acceptable project deliverables. The project cost is based on a budget that includes an estimate of the costs associated with the various resources that will be used to accomplish the project. Customer Satisfaction is the level to which the customer is pleased with the end result of the project. Schedule is the timetable that specifies when each activity should start and finish. The project objective usually states the time by which the project scope must be completed in terms of a specific date agreed upon by the customer and the individual or organization performing the work. Why are these considered to be constraints? The objective of any project is to complete the scope within budget by a certain time to the customer's satisfaction. Any of these four factors can put limitations on the final product. 7. List and describe the main phases of the project life cycle. The first is the initiating phase, when projects are identified and selected. They are then authorized, using a document referred to as a project charter. The second phase of the project life cycle is the planning phase and includes defining the project scope, identifying resources, developing a schedule and budget, and identifying risks, all of which make up the baseline plan for doing the project work. In the third phase, the performing phase, the project plan is executed, and work tasks are carried out to produce all the project deliverables and to accomplish the project objective. During this phase, the project progress is monitored and controlled to assure the work
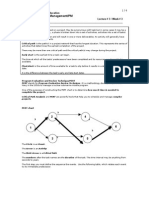
remains on schedule and within budget, the scope is fully completed according to specifications, and all deliverables meet acceptance criteria. Also, any changes need to be documented, approved, and incorporated into an updated baseline plan, if necessary. The final phase of the project life cycle is the closing phase. Project evaluations are conducted, lessons learned are identified and documented to help improve performance on future projects, and project documents are organized and archived. 8. List and describe the steps required to develop a baseline plan. 1. Establish project objective -- clearly define the project objective and have it agreed upon by the sponsor or customer. 2. Define scope -- include customer requirements, define the major work tasks or elements, and provide a list of deliverables and associated acceptance criteria that can be used to verify that the work and deliverables meet specifications 3. Create a work breakdown structure -- divide and subdivide the project scope into pieces or work packages. 4. Assign responsibility - identify the person or organization responsible for each work item in the work breakdown structure 5. Define the specific activities -- develop the list of detailed activities that need to be performed for each work package to produce any required deliverables. 6. Sequence activities -- graphically portray the activities in a network diagram to display the sequence and dependent relationships of the detailed activities. 7. Estimate activity resources -- determine which types and skills or expertise of resources and how many of each resource are needed for each activity with consideration of the availability of the resources. 8. Estimate activity durations -- make a time estimate for how long it will take to complete each activity, based on the estimate of the resources that will be applied. 9. Develop the project schedule -- develop the overall project schedule, including when each activity is expected to start and finish, as well as the latest times that each activity must start and finish in order to complete the project by the project required completion date. 10. Estimate activity costs -- determine the costs for the types and quantities of resources estimated for each activity using the appropriate labor cost rate or unit cost for each type of resource. 11. Determine budget -- aggregate the cost estimates for each activity 9. Why must a manager monitor the progress of a project? A manager must monitor progress to ensure that everything is going according to plan. It is also necessary to measure actual progress and compare it to planned progress. What can be done if a project is not proceeding according to plan? If at any time during the project the comparison of actual to planned progress reveals that the project is behind schedule, overrunning the budget, or not meeting the technical specifications, corrective action must be taken to get the project back on track within the scope, schedule, and budget constraints of the project objective. These actions include adding or changing resources to make up time and get back on schedule.
10. Describe how a global project can be more complex than a project performed within just one country. Global projects have several unique influencing factors such as currency fluctuations and exchange rates, country-specific work codes and regulations, corporate joint ventures and partnerships creating entities with a presence and facilities in multiple countries, political relations between countries, and availability of high-demand workforce skills. How might these elements affect the successful outcome of the global project? Globalization changes the dynamics of the project and adds a layer of complexity that can adversely affect the project outcome if the project participants are not aware of what they might encounter in the way of cultural differences and multinational economic transactions. 11. List some benefits of using project management techniques. The ultimate benefit of implementing project management techniques is having a satisfied customer. Completing the full project scope in a quality manner, on time, and within budget provides a great feeling of satisfaction. It could lead to additional business. Successful projects can expand career opportunities. A feeling of satisfaction comes from being on a winning team. Project management can expand knowledge, enhance skills, and make it easier to undertake more complicated projects.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Improvement and Efforts to Minimize Project DelaysDe la EverandImprovement and Efforts to Minimize Project DelaysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Management HandbookDocument6 paginiProject Management HandbookReza Noor MuinÎncă nu există evaluări
- LN15Document4 paginiLN15DrMohamed MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDP-02-Commencing Project and Scope-LV1Document26 paginiMSDP-02-Commencing Project and Scope-LV1Wavda AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 PDFDocument30 paginiChapter 10 PDFPandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 General: Chabahil Road in Kathmandu District, BagmatiDocument25 pagini1.1 General: Chabahil Road in Kathmandu District, Bagmatienlacer009Încă nu există evaluări
- Determining Activity Durations: PurposeDocument12 paginiDetermining Activity Durations: PurposemanikantanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smooth TransitionsDocument3 paginiSmooth TransitionsfakhroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Intl CPM Constr Scheduling With Asta PowerprojectDocument16 paginiLong Intl CPM Constr Scheduling With Asta PowerprojectTomasz WiatrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Post-Implementation Review ChecklistDocument6 paginiProject Post-Implementation Review ChecklistyogiforyouÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Insert Project Name) : Post Implementation ReviewDocument6 pagini(Insert Project Name) : Post Implementation ReviewTuanHung0% (1)
- CM PMDocument6 paginiCM PMJohnreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acumen FuseDocument4 paginiAcumen FuseLam Thanh HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 Introduction To Industrial EngineeringDocument18 paginiCH 1 Introduction To Industrial EngineeringraynezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appraisal AssignmentDocument15 paginiAppraisal AssignmentNizar AhamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Project Management Solution For Automotive Supplier (Case Study)Document4 paginiIntegrated Project Management Solution For Automotive Supplier (Case Study)Angie Fer.Încă nu există evaluări
- PirgthfgcDocument5 paginiPirgthfgcsruthisharma000Încă nu există evaluări
- Project Scheduling B07K ASSIGNMENT 8Document5 paginiProject Scheduling B07K ASSIGNMENT 8CRAIG JOSEPHÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSBPMG410Document8 paginiBSBPMG410Tanmay JhulkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PGPM 34Document25 paginiPGPM 34vasan_establishmentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjectDocument15 paginiProjecthammad_ali3Încă nu există evaluări
- Pat 252: Construction Project Management: Ts. Mardhiah Farhana BT OmarDocument29 paginiPat 252: Construction Project Management: Ts. Mardhiah Farhana BT Omaradeliene 25Încă nu există evaluări
- An Alternate Approach To Integrating Cost and ScheduleDocument9 paginiAn Alternate Approach To Integrating Cost and ScheduleAcumenÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMBOK Chapter 4 - ScopeDocument52 paginiPMBOK Chapter 4 - ScopelatehoursÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 System ThinkingDocument23 pagini01 System ThinkingNicholas WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument5 paginiProject Management Tools and TechniquesTolera GudisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- p2 AssignmentDocument5 paginip2 AssignmentmulugetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strengths of Primavera P6Document3 paginiStrengths of Primavera P6hashim malikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Monitoring ControlDocument28 paginiProject Monitoring Controlsarah smithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Closeout TemplateDocument6 paginiProject Closeout Templatejeyn100% (1)
- Concept SelectionDocument30 paginiConcept SelectionazroyezettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITPM Assignment 1Document2 paginiITPM Assignment 1Heinrich Le RouxÎncă nu există evaluări
- C4384 - Assignment 2Document26 paginiC4384 - Assignment 2iamaffandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Project Management INDIVIDUALDocument21 paginiAssignment Project Management INDIVIDUALshewameneBegashawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Success Factors in Project ManagementDocument13 paginiCritical Success Factors in Project ManagementSiencia No Enjinaria DitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network DiagramsDocument8 paginiNetwork Diagramscrystal50% (2)
- Project ManagemrntDocument83 paginiProject ManagemrntSandeep Arora0% (1)
- Unit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructureDocument12 paginiUnit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructurebevinjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Scheduling A ProjectDocument63 paginiTime Scheduling A ProjectRavneet S. LoteyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Management CourseworkDocument17 paginiProject Management CourseworkEqui AgbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Managment Lecture NoteChp3Document32 paginiConstruction Managment Lecture NoteChp3ሽታ ዓለሜ100% (1)
- PrimaveraP6 Training - 24hrsDocument1 paginăPrimaveraP6 Training - 24hrsespee29Încă nu există evaluări
- PMLect 3Document4 paginiPMLect 3api-3697776Încă nu există evaluări
- Project Management DISCUSSION QUESTIONS PDFDocument18 paginiProject Management DISCUSSION QUESTIONS PDFsamer iqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nikhilesh 2K10B24 Neena 2K10BFS11 Rohit Kumar 2K1OBFS43Document17 paginiNikhilesh 2K10B24 Neena 2K10BFS11 Rohit Kumar 2K1OBFS43avasthi_ankitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By: Preeti Submitted To: Prof - Tejinder ROLL NO: 18010 Class: Mcom 1StDocument16 paginiSubmitted By: Preeti Submitted To: Prof - Tejinder ROLL NO: 18010 Class: Mcom 1StPreeti100% (1)
- Computer-Aided Project Organization & ManagementDocument62 paginiComputer-Aided Project Organization & ManagementAref MalkawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using PDRI For Project Risk ManagementDocument9 paginiUsing PDRI For Project Risk Management4jawwy markme026Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 - QualityDocument24 paginiAssignment 1 - Qualityfrozenash3sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nicmar Assignment (PGQS 21)Document9 paginiNicmar Assignment (PGQS 21)Soumya SarangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGT601 Assignment SolutionDocument3 paginiMGT601 Assignment SolutionMaafiaa Tal100% (1)
- Does Better Scheduling Drive Execution Success?Document9 paginiDoes Better Scheduling Drive Execution Success?AcumenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Different Types of Tenders, Tender Qualification/ Processing, Quantitative Techniques For Tendering, Planning and Monitoring-A ReviewDocument4 paginiStudy On Different Types of Tenders, Tender Qualification/ Processing, Quantitative Techniques For Tendering, Planning and Monitoring-A ReviewAanchal MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Make Erp Documentation VERSION B1.05.1231Document12 paginiI Make Erp Documentation VERSION B1.05.1231Ahmad Takiyuddin Bin SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Project Management: Course TitleDocument29 paginiSoftware Project Management: Course TitleTALAT GHAFOORÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earned Value ManagementDocument11 paginiEarned Value ManagementAhmadAl-NafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1.6.validate Scope TemplatesDocument2 pagini2.1.6.validate Scope TemplatesAssad AssadÎncă nu există evaluări
- David BirchDocument27 paginiDavid BirchShubham JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICBT HND Quantity Surveying Econ AssignementDocument29 paginiICBT HND Quantity Surveying Econ AssignementAnonymous c0YBLLmQnXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Appraisal: Module 5 Session 6Document19 paginiProject Appraisal: Module 5 Session 6PaulamiDeSarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avanza Xenia Wiring DiagramDocument5 paginiAvanza Xenia Wiring DiagramFazri Putugerah100% (2)
- Eee111 Experiment 4Document6 paginiEee111 Experiment 4Amirul 0205Încă nu există evaluări
- Topics That We Will ExploreDocument135 paginiTopics That We Will ExploreAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sihao Huang Resume 1Document2 paginiSihao Huang Resume 1api-528311148Încă nu există evaluări
- Property Management SystemDocument48 paginiProperty Management SystemAkshay P50% (2)
- Classified 2015 01 19 000000Document7 paginiClassified 2015 01 19 000000sasikalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AICE Milestone04 03.04.2024Document15 paginiAICE Milestone04 03.04.2024kevinkiprotichyegonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deutsche Bank - Cloud Computing. Clear Skies AheadDocument20 paginiDeutsche Bank - Cloud Computing. Clear Skies AheadkentselveÎncă nu există evaluări
- PUMP MMTV Vertical Mixed Flow Multistage Pump With CanisterDocument3 paginiPUMP MMTV Vertical Mixed Flow Multistage Pump With Canisterarondaniel ocampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Informe Practica II Lab de MedidasDocument5 paginiInforme Practica II Lab de MedidasMaria Isabel Martinez NorenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bike Engine: Ricardo 2/4sight - 2 and 4 Stroke EngineDocument6 paginiBike Engine: Ricardo 2/4sight - 2 and 4 Stroke Enginecloudsakthivel89% (9)
- Cosco Fitness Catalogue 2020 - 17778246990Document144 paginiCosco Fitness Catalogue 2020 - 17778246990arpit99990Încă nu există evaluări
- Premier League Season Review 2020 - 21Document9 paginiPremier League Season Review 2020 - 21Iftar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnCase Forensics Edition Primer - Getting StartedDocument37 paginiEnCase Forensics Edition Primer - Getting StartedJason KeysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collaborative Knowledge Networks: Peter Gloor Deloitte ConsultingDocument15 paginiCollaborative Knowledge Networks: Peter Gloor Deloitte ConsultingJona D'johnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alm-Ims-Prc-Si-013 Welding Inspection FDocument11 paginiAlm-Ims-Prc-Si-013 Welding Inspection F123netflix542Încă nu există evaluări
- Education Course Catalog enDocument8 paginiEducation Course Catalog enlipasot781Încă nu există evaluări
- Bhel Summer Training (Industrial Training) ReportDocument35 paginiBhel Summer Training (Industrial Training) ReportAmelia WarnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Study On Marketing Strategies of SamsungDocument64 paginiTo Study On Marketing Strategies of SamsungVaibhav Shah MangalamjobsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Licensing and ActivationDocument46 paginiInstallation Licensing and ActivationnerittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC Twin Rt2 0,7.. 10 kVA: User ManualDocument48 paginiSLC Twin Rt2 0,7.. 10 kVA: User Manualsomae AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC320W01 Sla1Document33 paginiLC320W01 Sla1Robert TocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooling Tower MotorDocument2 paginiCooling Tower MotorDipendraTomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19BCG1077 - Swarup DebDocument1 pagină19BCG1077 - Swarup DebUX ༒CONQUERERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Quality Management PMPDocument47 paginiProject Quality Management PMPnguyen728100% (2)
- CV WiraDocument3 paginiCV WiraNi Komang Utari YulianingsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spreadsheet 2006-2021 Kcse Computer Studies PracticalDocument16 paginiSpreadsheet 2006-2021 Kcse Computer Studies PracticalMakueni Girls ICT StudentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python OS Module - 30 Most Useful Methods From Python OS ModuleDocument5 paginiPython OS Module - 30 Most Useful Methods From Python OS ModuleRajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSL Bochure enDocument17 paginiSSL Bochure enlineylosadagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cut Off Points Private. Ay 2020-2021 AdmissionsDocument6 paginiCut Off Points Private. Ay 2020-2021 AdmissionsRonnie AtuhaireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxDe la EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (156)
- High Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesDe la EverandHigh Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendDe la EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverDe la EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (186)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsDe la EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (57)
- The FBI Way: Inside the Bureau's Code of ExcellenceDe la EverandThe FBI Way: Inside the Bureau's Code of ExcellenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDe la EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEODe la EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (22)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDe la EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2567)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceDe la EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobDe la EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (37)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekDe la EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (142)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0De la EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindDe la EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (276)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolDe la EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (702)
- Everyone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyDe la EverandEveryone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (348)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersDe la EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (151)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessDe la EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (132)
- The Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableDe la EverandThe Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (216)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDe la EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsDe la EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (52)
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersDe la EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (95)
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceDe la EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (22)
- Extreme Ownership by Jocko Willink and Leif Babin - Book Summary: How U.S. Navy SEALS Lead And WinDe la EverandExtreme Ownership by Jocko Willink and Leif Babin - Book Summary: How U.S. Navy SEALS Lead And WinEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (75)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleDe la EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6521)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeDe la EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingDe la EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (211)