Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit 25 Selection and Applications of Programmable Controllers
Încărcat de
Yellaji AllipilliTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit 25 Selection and Applications of Programmable Controllers
Încărcat de
Yellaji AllipilliDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Unit 25:
NQF Level 3:
Selection and Applications of Programmable Logic Controllers
BTEC National
Guided learning hours: 60
Unit abstract
The automation of machines, process control and conveyor lines has resulted in the ever-increasing consistency of quality, speed and cost savings within complex processes. Consumers have come to expect high standards of quality in the manufactured goods they use, but to an engineer these are the challenges that make the profession interesting. This unit will consider programmable logic controllers (PLCs), control devices which aid the automation of these processes. The capabilities of PLCs have developed over the years, with performance, reliability and operational resilience being key attributes to their continued success. In order to achieve automated monitoring and control, these devices can be used on their own or in conjunction with others through communication systems/links, which are themselves becoming more versatile. The unit will introduce learners to the use and applications of PLCs, the hardware and software that makes up a PLC and the interaction needed between the component parts. Learners will develop their ability to use programming techniques to produce programs for modern PLCs. They will also gain an understanding of the different types of communication media used to link larger numbers of PLCs together, the networking architecture used and the associated standards and protocols.
Learning outcomes
On completion of this unit a learner should: 1 2 3 4 Understand the selection, hardware and software requirements of a programmable controller Be able to use programming techniques to produce a program for a modern programmable controller Understand complex programmable controller applications Understand data communications media and networks used with modern programmable controllers.
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Unit content
Understand the selection, hardware and software requirements of a programmable controller Programmable controller selection: criteria eg cost, versatility and scanning time; internal architecture eg central processing unit (CPU), arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), flags, registers, memory and types (volatile, non-volatile); scan cycle (self-test, input/logic/output scans) System hardware and software requirements: manufacturers specification of input/output (I/O) units (digital and analogue); power supply; use of operating system; configuration of inputs and outputs; number systems eg binary, octal, hexadecimal, binary-coded decimal (BCD); input/output devices; mechanical switch relays (electromechanical and solid state); transducers eg temperature, pressure, flow, smart sensors, simple motors and drives
Be able to use programming techniques to produce a program for a modern programmable controller Programming method: eg ladder and logic diagrams, statement listing, functional diagrams, graphical programming languages, mimic diagrams, sequential function charts (SFCs) Produce, store and present program: human computer interface (HCI) eg handheld input pad, personal computer, text, graphical touch screens; use of system software to write, edit, delete, save, restore, create reports, load/unload, search; use of fault diagnostic indicators; print copies of program; storage eg scanning, memory organisation, continuous updating, back-up copies, supervisor control and data acquisition (SCADA) Instruction types: production of program using relay, bit, branch, timer/counter, comparison, logical, arithmetic instructions; proportional integral derivative (PID) controller loops
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Understand complex programmable controller applications Program documentation: hardware considerations (environmental, operational, maintainability); instruction types; documentation for testing eg software debug instructions, diagnostic indicators, data monitors, search, force facilities; complex engineering applications eg machine, process control, conveyor Health and safety with programmable controller: safe working practices for personnel and with equipment eg tools and equipment risk assessment, job safety analysis (JSA), housekeeping practices for work areas, personal protective equipment (PPE), restriction of non-participants from areas; health and safety standards (local, national, international) eg local safety agreements between employees and employers, Health and Safety Executive (HSE), Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, regulations for the use of display screens; avoiding haphazard operations eg risk management, planning considerations, testing (usability, unit, component, acceptance), what If scenarios, commissioning
Understand data communications media and networks used with modern programmable controllers Communication media: selection criteria, description of features, frequency ranges, technology eg analogue, digital, wireless; media types (cable eg twisted pairs, coaxial, fibre-optic, shielded/unshielded, categories, operational lengths; connector eg Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNC), registered jack (RJ-45), straight tip (ST), universal serial bus (USB) type A and type B; opto-isolator eg photodiode, phototransistor, thyristors, triacs) Network: network architecture (fieldbus, distributed intelligence, open communications networks); network standards/protocols eg International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO), Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE), Manufacturing Automation Protocol (MAP), Electronics Industry Association (EIA - 485), Factory Instrumentation Protocol (FIP)
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Grading grid
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that they can meet all of the learning outcomes for the unit. The criteria for a pass grade describe the level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Grading criteria To achieve a merit grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to: M1 select and describe the benefits and limitations of a programmable controller for a specific application justify the choice of a specific programming method and the methods used to produce, store and present the program compare two different networks used for a modern programmable controller system. D2 D1 To achieve a distinction grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to: evaluate program documentation used to control an automated machine/process and make recommendations for improvement compare the current capabilities and limitations of a programmable controller and identify possible areas of future development.
To achieve a pass grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to:
P1
describe the selection criteria and a practical application for a unitary, a modular and a rack-mounted programmable controller M2
P2
explain the system hardware and software requirements for a programmable controller application M3
P3
use a programming method to produce, store and present a program that demonstrates the full range of instruction types
P4
explain the program documentation that has been used for a complex engineering application
P5
describe the importance of health and safety when working with programmable controlled equipment
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Grading criteria To achieve a merit grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to: To achieve a distinction grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to:
To achieve a pass grade the evidence must show that the learner is able to:
P6
explain how one example of each of the three types of communication media would be selected for a specific programmable controller application
P7
describe a network and relevant standards and protocols used for a modern programmable controller system.
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Essential guidance for tutors
Delivery This unit could be delivered as a stand-alone unit or be integrated with other units such as Unit 61: Construction and Application of Digital Systems and Unit 68: Principles and Applications of Microcontrollers. An integrated approach to delivery will give learners an opportunity to consider the wider aspects of hardware and software development within modern integrated applications. Delivery and learning will be maximised through a strong, practically based learning programme. PLC capabilities and their range of uses within the control industry has grown considerably over recent years, meaning that there is a wide variety of PLCs available. However, it is important that learners recognise the limitations of earlier models (in terms of hardware and software) and the potential of newer models for longer life cycles and advanced characteristics and features. In order to ensure breadth of learning, centres should ideally work with employers to introduce real work-based applications of PLC technology. Educational visits to appropriate events such as exhibits, trade fairs and system manufacturers are an important method to inspire learning. Practical work should ensure that learners can recognise a range of PLC units, interfaces and connections, programming techniques and large system integration, for both existing and future demands. This will enable them to appreciate how the various aspects fit together to produce an efficient, reliable and safe control method that is capable of fitting within a range of operational environments. In some cases, this will include the need for portability and an operationally sustainable energy source. Appropriate attention must be given to health, safety and welfare arrangements throughout the delivery of this unit. Note that the use of eg in the content is to give an indication and illustration of the breadth and depth of the area or topic. As such, not all content that follows an eg needs to be taught or assessed. Assessment PLCs involve a complex mixture of computer technology, communication interfaces and software programming techniques. The assessment strategy for this unit should consist of a mix of written technical reports and hands-on practical work. Annotated photographic evidence could also be a valuable tool to capture on-site information and support learners written work. Where the grading criteria refer to an application this is intended to mean a realworld situation wherever possible. Although a different application could be used for different criteria it would be reasonable to use the same or closely related applications throughout.
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
P1 and P2 are closely linked. P1 requires learners to describe the selection criteria and a practical application for a unitary, a modular and a rack-mounted programmable controller. In doing so, learners need to demonstrate their ability to recognise the different approaches to PLC operational activities. In describing the selection criteria learners should consider things such as cost, versatility and scanning time, together with relevant descriptions of the internal architecture (eg central processing unit (CPU), arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) etc) and a practical application of each. For P2, a comprehensive range of hardware and software requirements should be considered. For example, the power supply available may have quite different consequences for an application involving a field monitoring system as opposed to an installation in a factory. The amount of coverage of content for this criterion will be determined by the actual programmable controller application considered but it is expected that the learner should have at least four or five system hardware and software requirements indicated and explained. P3 requires learners to use a programming method to produce, store and present a program that demonstrates the full range of instruction types. Learners are not expected to be fully competent programmers but their programs should be printed out, annotated where appropriate and stored. The explanation required for P4 needs to cover all the related unit content including hardware considerations, instruction types and documentation for testing. A complex engineering application in this context is intended to mean some form of machine, a manufacturing process control operation or a conveyor system based on a real-life situation. Learners will need to provide some details of the complex application and go on to explain the documentation, for example the program instructions, testing documentation and forced facilities etc associated with it. Ideally this would be a work-based application, although learners could be provided with a case study of a complex application. P5 requires learners to describe the importance of health and safety when working with programmable controlled equipment. A range of what if scenarios for various applications could be used to cover the full requirements of the unit content. P6 requires learners to explain how one example of each of the three types of communication media (cable, connector, opto-isolator) would be selected for a specific programmable controller application. The key point here is for learners to recognise the media, understand how each one is selected, describe the main features and consider aspects such as frequency ranges and the technology to which they are being applied. For P7, there is a possibility that the description of a network and relevant standards and protocols could become overly complex and involve a wide range of issues. Therefore, learners need to be restricted to describing just the general network architecture of perhaps an Ethernet, and provide details of the associated standards and what they generally imply. M1 builds on the work carried out for pass criteria P1 and P2, as learners need to consider a specific application and apply their understanding of the selection criteria already used. The important point is that they can demonstrate ability in selecting an appropriate PLC type and have knowledge as to why it is an appropriate choice.
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
M2 can be clearly linked to pass criteria P3 and P4. To achieve M2, learners need to reflect on their choice of programming methods. In their justification learners should identify why one programming method has been chosen and make it clear why the others have been rejected. M3 builds on the work undertaken to achieve P7 and P8. It requires learners to compare two different networks used for a modern programmable controller system. This should include details of the networks, standards and key differences. Learners need to demonstrate that they realise the important differences between networks and how they may influence the associated PLC systems. To achieve D1, learners must consider the wider implications of the work carried out for P4 and M2. Learners need to be able to appraise the material and suggest improvements. These improvements should not simply be related to the amount of material documentation. Learners should also consider the documentation in light of their ability to recognise the hardware considerations, work with the range of instruction types and use the documentation for testing. As with the related pass criterion, this must be set within a complex engineering application. Finally, D2 requires learners to reflect on the unit as a whole. The comparison could include aspects such as memory capacity, the types of PLC available, the growing development in networking technologies (eg wireless implications), the use of smart sensors and how this may impair the programme and feedback loops, how processor power may influence the programming method etc. Satisfactory achievement of this criterion will require learners to have considered the range of issues covered by the unit content and undertaken some independent research of trends and potential benefits. Links to National Occupational Standards, other BTEC units, other BTEC qualifications and other relevant units and qualifications This unit can be linked with Unit 61: Construction and Application of Digital Systems and Unit 68: Principles and Applications of Microcontrollers. The unit also links with the SEMTA Level 3 National Occupational Standards in Engineering Technical Support, particularly: Unit 30: Loading and Proving Computer Control Programs Unit No 32: Producing Off-line Programs for Programmable Logic Controller Equipment. Essential resources Centres will need access to a range of PLCs, communication media and interface devices. Software packages and tools should also be available to permit programming and implementation of device/applications for circuit performance and debugging. Learners will require access to a range of relevant manuals, reference data and manufacturers information. Indicative reading for learners Bolton W Programmable Logic Controllers (Newnes, 2006) ISBN 0750681128 Hooper J Introduction to PLCs (Carolina Academic Press, 2004) ISBN 0890893896
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Key skills
Achievement of key skills is not a requirement of this qualification but it is encouraged. Suggestions of opportunities for the generation of Level 3 key skill evidence are given here. Staff should check that learners have produced all the evidence required by part B of the key skills specifications when assessing this evidence. Learners may need to develop additional evidence elsewhere to fully meet the requirements of the key skills specifications.
Communication Level 3 When learners are: carrying out research into system hardware and software, programming methods and applications of programmable controllers preparing technical reports on programmable controllers features, characteristics and applications. They should be able to develop the following key skills evidence: C3.2 Read and synthesise information from at least two documents about the same subject. Each document must be a minimum of 1000 words long. C3.3 Write two different types of documents each one giving different information about complex subjects. One document must be at least 1000 words long.
Information and communication technology Level 3 When learners are: carrying out research into system hardware and software, programming methods and applications of programmable controllers using ICT to prepare and present technical reports and to program. They should be able to develop the following key skills evidence: ICT3.1 Search for information, using different sources, and multiple search criteria in at least one case. ICT3.2 Enter and develop the information and derive new information. ICT3.3 Present combined information such as text with image, text with number, image with number.
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
UNIT 25: SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Problem solving Level 3 When learners are: using a programming method to produce, store and present a program that demonstrates the full range of instruction types. They should be able to develop the following key skills evidence: PS3.1 PS3.2 PS3.3 Explore a problem and identify different ways of tackling it. Plan and implement at least one way of solving the problem. Check if the problem has been solved and review your approach to problem solving.
10
Edexcel Level 3 BTEC Nationals in Engineering Issue 1 May 2007 Edexcel Limited 2007
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Safe Use of Smart Devices in Systems Important to Safety in Nuclear Power PlantsDe la EverandSafe Use of Smart Devices in Systems Important to Safety in Nuclear Power PlantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing SCADA Application Software: A Practical ApproachDe la EverandDesigning SCADA Application Software: A Practical ApproachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 25 Selecting and Using Programmable Controllers PDFDocument12 paginiUnit 25 Selecting and Using Programmable Controllers PDFahmed357Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 62 Microprocessor Systems and ApplicationsDocument11 paginiUnit 62 Microprocessor Systems and ApplicationsPaul Jensen Umali SatimbreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Aided Manufacturing 2Document10 paginiComputer Aided Manufacturing 2engrodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Classification Framework For Automated Control Code GenerationDocument26 paginiA Classification Framework For Automated Control Code Generation曾升为Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 11648 J Ajrs 20170505 11Document9 pagini10 11648 J Ajrs 20170505 11sweet boy play boyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harmonizing Programmable Logic Controller Programming To IEC 61131-3 On A Multi-Axes Pneumatic Educational TrainerDocument8 paginiHarmonizing Programmable Logic Controller Programming To IEC 61131-3 On A Multi-Axes Pneumatic Educational TrainerInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Validation of Industrial Distributed Control SystemsDocument6 paginiDesign and Validation of Industrial Distributed Control SystemsPriyatham GangapatnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Generation of PLC Automation PDocument2 paginiAutomatic Generation of PLC Automation Pkaddour78Încă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Generation of PLC Automation Projects From Component BasedDocument14 paginiAutomatic Generation of PLC Automation Projects From Component BasedAweSome, ST,MTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1-Basic Concepts of Measurements-09Document21 paginiChapter1-Basic Concepts of Measurements-09azrurezuan100% (1)
- Embedded Steer-by-Wire System DevelopmentDocument7 paginiEmbedded Steer-by-Wire System DevelopmentkeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- On The Suitability of Modeling Approaches For Engineering Distributed Control SystemsDocument6 paginiOn The Suitability of Modeling Approaches For Engineering Distributed Control SystemsPriyatham GangapatnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pias 2020-18earc302Document23 paginiPias 2020-18earc302Deepak KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 1Document19 pagini6 1Zubair AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control Trainer Project Report - Original1Document42 paginiProcess Control Trainer Project Report - Original1Augustine paulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 A Mechatronics Educational Laboratory Programmable Logic Controllers and Material Handling ExperimentsDocument9 pagini2007 A Mechatronics Educational Laboratory Programmable Logic Controllers and Material Handling ExperimentsnileshsawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rohit ReportDocument37 paginiRohit ReportRohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- EIT Course PLCs SCADA Systems CAU BrochureDocument3 paginiEIT Course PLCs SCADA Systems CAU Brochuresukhbir24Încă nu există evaluări
- PID Controllers and Algorithms: Selection and Design Techniques Applied in Mechatronics Systems Design - Part IIDocument13 paginiPID Controllers and Algorithms: Selection and Design Techniques Applied in Mechatronics Systems Design - Part IITI Journals PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Automation and Control Systems - Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of MeasurementsDocument21 paginiIndustrial Automation and Control Systems - Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of MeasurementsHasan IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICAS3121B Administer Network PeripheralsDocument5 paginiICAS3121B Administer Network PeripheralsCoenie HumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCSDocument14 paginiDCSkemmazamcfcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Challenges Fieldbus SystemDocument14 paginiApplication Challenges Fieldbus SystemMericatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Automation CertificationDocument1 paginăIndustrial Automation CertificationAndhika Kumara DjaffriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Specification: Se425 Distributed Control SystemDocument10 paginiCourse Specification: Se425 Distributed Control SystemAmmar AlkindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual InstrumentationDocument18 paginiVirtual Instrumentationroshi478Încă nu există evaluări
- Safety-Critical Systems in Rail TransportationDocument5 paginiSafety-Critical Systems in Rail TransportationRăzvan PopaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modulo de Bajo Costo para Probar Algoritmos de ControlDocument15 paginiModulo de Bajo Costo para Probar Algoritmos de ControlBrayan Espinoza GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Automation Train in IngDocument11 paginiIndustrial Automation Train in IngGopala KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Name IA03Document2 paginiCourse Name IA03Amaldev ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of A Project-Based Embedded System Laboratory Using LPC1768Document8 paginiDesign and Development of A Project-Based Embedded System Laboratory Using LPC1768Bảo BìnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30 MN423 Instrumentation Measurement and ControlDocument2 pagini30 MN423 Instrumentation Measurement and ControlLeonidas PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE2MksIvyrESys PDFDocument27 paginiECE2MksIvyrESys PDFRithi VishwanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Framework of Multi-Microcontroller Evaluation Tool For A Use of Academic EnvironmentDocument6 paginiFramework of Multi-Microcontroller Evaluation Tool For A Use of Academic EnvironmentrajeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCBI - WholeDocument10 paginiPCBI - WholeSucharitha PathipatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Towards A Seamless Development Process For Automotive Engine Control SystemDocument10 paginiTowards A Seamless Development Process For Automotive Engine Control SystemMuhidin ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial AutomationDocument4 paginiIndustrial AutomationNarayanan IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- (294100910) Art - 3A10.1007 - 2Fs11265-013-0767-xDocument10 pagini(294100910) Art - 3A10.1007 - 2Fs11265-013-0767-xAdriana Saltos IbarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme of Work 2013Document56 paginiScheme of Work 2013OsamaRahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Integration EngineerDocument10 paginiEnterprise Integration Engineergabiacu123Încă nu există evaluări
- 1-Basic Concept of Measurement SystemsDocument51 pagini1-Basic Concept of Measurement SystemsWan HarrazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Software For Nuclear Reactors: 11 Years of Field Experience AnalysisDocument5 paginiCritical Software For Nuclear Reactors: 11 Years of Field Experience Analysishamkam2003Încă nu există evaluări
- Efforts To Improve Programmable Logic Controller Programming Competence and Its Application On Vocational High SchoolDocument9 paginiEfforts To Improve Programmable Logic Controller Programming Competence and Its Application On Vocational High Schoolrullyhimawan.tmmjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kant 2 New PrintDocument68 paginiKant 2 New PrintTushar KantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test SocDocument133 paginiTest SocjeevithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEC 61850: Role of Conformance Testing in Successful IntegrationDocument12 paginiIEC 61850: Role of Conformance Testing in Successful IntegrationDuško TovilovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unknown - Unknown - Advanced - Tools - Control - Industry - 4.0Document6 paginiUnknown - Unknown - Advanced - Tools - Control - Industry - 4.0gesmarjuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASE STUDY SahanaDocument8 paginiCASE STUDY SahanaVishnu .SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Standards and Specifications Process Control Package Rev01Document10 paginiProject Standards and Specifications Process Control Package Rev01Ahmad EmamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Based Calculation of Capacity Outage of Generating UnitsDocument5 paginiSoftware Based Calculation of Capacity Outage of Generating UnitsVIVA-TECH IJRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece Embed Ed SystemDocument27 paginiEce Embed Ed SystemlakshmigajendranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2Document110 paginiCH 2delinquent_abhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechatronics Course OutlineDocument3 paginiMechatronics Course OutlineRoss Mel Bautista LingonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC2Document8 paginiPLC2William BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Successfully Designing Integrated Substations: NtroductionDocument12 paginiSuccessfully Designing Integrated Substations: NtroductionHassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ing Reqs Reft05postwsDocument16 paginiIng Reqs Reft05postwsjgonzalezsanz8914Încă nu există evaluări
- STG Etg v1.0 PDFDocument158 paginiSTG Etg v1.0 PDFcosmin75Încă nu există evaluări
- R41024112018 JNTUK Question PaperDocument2 paginiR41024112018 JNTUK Question PaperYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent Trends in Power Electronics Applications in Smart Grid, Electric Vehicles and Renewable EnergyDocument2 paginiRecent Trends in Power Electronics Applications in Smart Grid, Electric Vehicles and Renewable EnergyYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- JNTUK Question PaperDocument2 paginiJNTUK Question PaperYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategies and Ict Tools For Power Conversion Technologies & ApplicationsDocument2 paginiStrategies and Ict Tools For Power Conversion Technologies & ApplicationsYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDP ProposalDocument2 paginiFDP ProposalYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDSJFGHSDGBV KJLSDG Gjkhsag SDD GSD BVGHKJSDGF VKDLSG DSG BDHJG JKDHSGH D G SDJKG JKG G KG KGV DG HJGKHH L GDocument1 paginăFDSJFGHSDGBV KJLSDG Gjkhsag SDD GSD BVGHKJSDGF VKDLSG DSG BDHJG JKDHSGH D G SDJKG JKG G KG KGV DG HJGKHH L GYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- KLFDGBJHNKF HGJNF'D HDF /H DF'HNDF DF HFDNH FDH FDH LFDHJ' DFGJH FDSGH JFH X H Xjobnh XCHBDocument1 paginăKLFDGBJHNKF HGJNF'D HDF /H DF'HNDF DF HFDNH FDH FDH LFDHJ' DFGJH FDSGH JFH X H Xjobnh XCHBYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZJBJDSGJSDDocument1 paginăZJBJDSGJSDYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hisgjsh JH KSH K GKGHK H HKHGKH'KL GK' HBFDSH LJ' LHJFDHJ' GHL'D KHKDSH DFH Ksda K Fs H Lafhkl H AkkscDocument1 paginăHisgjsh JH KSH K GKGHK H HKHGKH'KL GK' HBFDSH LJ' LHJFDHJ' GHL'D KHKDSH DFH Ksda K Fs H Lafhkl H AkkscYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- G J KJKL JB LKJLN N L HKH J, JH H JLH NKJ HLJ KJ HMJKL HLDocument1 paginăG J KJKL JB LKJLN N L HKH J, JH H JLH NKJ HLJ KJ HMJKL HLYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
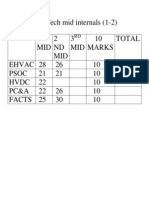
- M.tech Internals (1-2) MarksDocument1 paginăM.tech Internals (1-2) MarksYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Course Calender Very UsefulDocument4 pagini2014 Course Calender Very UsefulYellaji AllipilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equal Cost Multipath Routing in IP Netwo PDFDocument97 paginiEqual Cost Multipath Routing in IP Netwo PDFFederacion Hip Hop DominicanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aveva System Platform,: Formerly WonderwareDocument6 paginiAveva System Platform,: Formerly WonderwareArturÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using em Quest Viewer SupplementDocument15 paginiUsing em Quest Viewer SupplementMarcos CarnevaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title Revision No. Issued Date::: Sm-90 / Sm-500 Specification List 13 3 JAN 2003Document26 paginiTitle Revision No. Issued Date::: Sm-90 / Sm-500 Specification List 13 3 JAN 2003Newlin NievesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carestream Imaging Software ManualDocument2 paginiCarestream Imaging Software ManualTONDERAI0% (1)
- SF DumpDocument32 paginiSF DumpporelitomaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacity PlanningDocument11 paginiCapacity PlanningaleenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class XII Boolean Algebra: + B) .C. (A+B) (X' +Z) + ( (Y' +Z) - (X' +y) ) ' 1Document3 paginiClass XII Boolean Algebra: + B) .C. (A+B) (X' +Z) + ( (Y' +Z) - (X' +y) ) ' 1Srijan JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRS Car Price PredictionDocument18 paginiSRS Car Price Predictionali mughalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Systems CheatsDocument32 paginiMaster Systems CheatsBoki NovakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintenance by Garr BhuwaDocument8 paginiMaintenance by Garr BhuwaejazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 96mar Coyne PDFDocument103 pagini96mar Coyne PDFdanto yuliardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robot Welding TipsDocument50 paginiRobot Welding Tipscentaury20130% (1)
- 1) Develop An Application That Uses GUI Components, Fonts and ColorsDocument56 pagini1) Develop An Application That Uses GUI Components, Fonts and ColorsKirti AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco ExamDocument109 paginiCisco ExamBart WetzelsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 90203-1104DEC E Cont Operations PDFDocument414 pagini90203-1104DEC E Cont Operations PDFelmacuarro5Încă nu există evaluări
- CMMS D-FW 2014-04 8034520g1Document246 paginiCMMS D-FW 2014-04 8034520g1Nelson KempÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows HardeningDocument36 paginiWindows Hardeningomarelmoktar19869795Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual MillerDocument44 paginiManual MillerIsai MixiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topo ReportDocument18 paginiTopo ReportOlaitan RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Pcnsa: IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!Document35 paginiExam Pcnsa: IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!Diego Fernando Bedoya CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MD5 and SHA 1Document6 paginiMD5 and SHA 1Syed SalmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOLA NotesDocument22 paginiTOLA NotesSam TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Cost Accounting Sohail Afzal With SolutionDocument2 paginiFree Cost Accounting Sohail Afzal With SolutionHafizUmarArshad50% (18)
- Magic Cube enDocument2 paginiMagic Cube enCoreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBRA Full Membership Form Inscribable - 01-2020Document2 paginiIBRA Full Membership Form Inscribable - 01-2020Vijay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jochen Hartmann, Juliana Huppertz, Christina Schamp, Mark HeitmannDocument19 paginiJochen Hartmann, Juliana Huppertz, Christina Schamp, Mark Heitmann23520017 Widya Puteri AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 30 Companies in India (Sectorwise) - 23.4.2012Document34 paginiTop 30 Companies in India (Sectorwise) - 23.4.2012Gogol SarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBCDG 100Document210 paginiCBCDG 100Tatjana GligorijevicÎncă nu există evaluări