Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tutorial 4
Încărcat de
Rajkamal NayakDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tutorial 4
Încărcat de
Rajkamal NayakDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
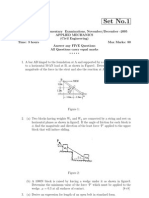
Tutorial Sheet 4
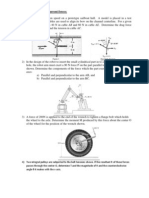
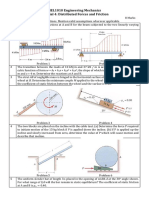
PROBLEM 8.10 The 20 N block A hangs from a cable as shown. Pulley C is connected by a short link to block E which rests on a horizontal rail. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between block E and the rail is 0.35 and neglecting the weight of the block E and the friction in the pulleys, determine the maximum allowable value of if the system is to remain in equilibrium. PROBLEM 8.12 The coefficients of friction are S = 0.40 and k = 0.30 between all surfaces of contact. Determine the force P for which motion of the 30-kg block is impending if cable AB (a) is attached as shown, (b) is removed. PROBLEM 8.16 A packing crate of mass 40 kg is pulled by a rope as shown. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.35. If =40 , determine (a) the magnitude of the force P required for impending motion of the crate, (b) whether sliding or tipping is impending. PROBLEM 8.20 A cord is attached to and partially wound around a cylinder of weight W and radius r that rests on an incline as shown. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the cylinder and the incline is 0.35, find (a) the smallest allowable value of if the cylinder is to remain in equilibrium, (b) the corresponding value of the tension in the cord. PROBLEM 8.23 End A of a slender, uniform rod of weight W and length L bears on a horizontal surface as shown, while end B is supported by a cord BC of length L. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction is 0.40, determine (a) the value of for which motion is impending, (b) the corresponding value of the tension in the cord. PROBLEM 8.25 The shear shown is used to cut and trim electronic-circuit-board laminates. Knowing that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the blade and the vertical guide is 0.20, determine the force exerted by the edge E of the blade on the laminate. PROBLEM 8.27 The friction tongs shown are used to lift a 750-N casting. Knowing that h = . 9 m, determine the smallest allowable value of the coefficient of static friction between the casting and blocks D and D.
PROBLEM 8.29 A child having a mass of 18 kg is seated halfway between the ends of a small, 16-kg table as shown. The coefficient of static friction is 0.20 between the ends of the table and the floor. If a second child pushes on edge B of the table top at a point directly opposite to the first child with a force P lying in a vertical plane parallel to the ends of the table and having a magnitude of 66 N, determine the range of values of for which the table will (a) tip, (b) slide. PROBLEM 8.31 A pipe of diameter 60 mm is gripped by the Stillson wrench shown. Portions AB and DE of the wrench are rigidly attached to each other and portion CF is connected by a pin at D. If the wrench is to grip the pipe and be selflocking, determine the required minimum coefficients of friction at A and C. PROBLEM 8.43 Blocks A, B, and C having the weights shown are at rest on an incline. Denoting by S the coefficient of static friction between all surfaces of contact, determine the smallest value of S for which equilibrium is maintained. PROBLEM 8.50 The elevation of the end of a steel beam supported by a concrete floor is adjusted by means of the steel wedges E and F. The base plate CD has been welded to the lower flange of the beam, and the end reaction of the beam is known to be 90 KN. The coefficient of static friction is 0.30 between the two steel surfaces and 0.60 between the steel and the concrete. If the horizontal motion of the beam is prevented by the force Q, determine (a) the force P required for impending upward motion of the beam, (b) the corresponding force Q. PROBLEM 8.51 The elevation of the end of a steel beam supported by a concrete floor is adjusted by means of the steel wedges E and F. The base plate CD has been welded to the lower flange of the beam, and the end reaction of the beam is known to be 90 KN. The coefficient of static friction is 0.30 between the two steel surfaces and 0.60 between the steel and the concrete. If the horizontal motion of the beam is prevented by the force Q, determine (a) the force P required for impending upward motion of the beam, (b) the corresponding force Q. PROBLEM 8.53 A 16 wedge A of negligible weight is placed between two 175-N blocks B and C which are at rest on inclined surfaces as shown. The coefficient of static friction is 0.40 between both the wedge and the blocks and block C and the incline. Determine the magnitude of the force P for which motion of the wedge is impending when the coefficient of static friction between block B and the incline is (a) 0.40, (b) 0.60.
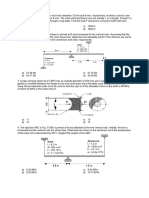
PROBLEM 8.56 A 12 wedge is to be forced under the corner B of the 250-N quarter cylinder shown. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the cylinder and the wedge is 0.35 and 0.50 between the wedge and the floor, determine the magnitude of the force P required for impending motion of the wedge. PROBLEM 8.58 A conical wedge is placed between two horizontal plates that are then slowly moved toward each other. Indicate what will happen to the wedge (a) if s = 0.20, (b) if s = 0.30. Problem 8.67: The square-threaded worm gear shown has a mean radius of 1.5 in. and a lead of 0.375 in. The larger gear is subjected to a constant clockwise couple of 7.2 kip-in. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the two gears is 0.12, determine the couple that must be applied to shaft AB to rotate the large gear counterclockwise. Neglect friction in the bearings at A, B, and C. PROBLEM 8.68 In Prob. 8.67, determine the couple that must be applied to shaft AB to rotate the gear clockwise. PROBLEM 8.70 The position of the automobile jack shown is controlled by a screw ABC that is single-threaded at each end (righthanded thread at A, left-handed thread at C). Each thread has a pitch of 2 mm and a mean diameter of 7.5 mm. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.15, determine the magnitude of the couple M that must be applied to raise the automobile. PROBLEM 8.71 For the jack of Prob. 8.70, determine the magnitude of the couple M that must be applied to lower the automobile. PROBLEM 8.72 The vise shown consists of two members connected by two double-threaded screws of mean radius 6 mm and pitch 2 mm. The lower member is threaded at A and B (S = 0.35), but the upper member is not threaded. It is desired to apply two equal and opposite forces of 540 N on the blocks held between the jaws. Determine (a) which screw should be adjusted first, (b) the maximum couple applied in tightening the second screw. PROBLEM 8.73 Solve part b of Prob. 8.72 assuming that the wrong screw is adjusted first. PROBLEM 8.96 A 1000 N machine base is rolled along a concrete floor using a series of steel pipes with outside diameters of .127 m Knowing that the coefficient of rolling resistance is .0006 m between the pipes and the base and .0015 m between the pipes and the concrete floor, determine the magnitude of the force P required to slowly move the base along the floor. PROBLEM 8.107 In the pivoted motor mount shown, the weight W of the 175-N motor is used to maintain tension in the drive belt. Knowing that the coefficient
of static friction between the flat belt and drums A and B is 0.40, and neglecting the weight of platform CD, determine the largest couple which can be transmitted to drum B when the drive drum A is rotating clockwise. PROBLEM 8.108 Solve Prob. 8.107 assuming that the drive drum A is rotating counterclockwise. PROBLEM 8.115 The drum brake shown permits clockwise rotation of the drum but prevents rotation in the counterclockwise direction. Knowing that the maximum allowed tension in the belt is 4.5 kN, determine (a) the magnitude of the largest counterclockwise couple that can be applied to the drum, (b) the smallest value of the coefficient of static friction between the belt and the drum for which the drum will not rotate counterclockwise (self locking). PROBLEM 8.117 A cord is placed over two 100-mm diameter cylinders. Knowing that the coefficients of friction are S = 0.30 and k = 0.25, determine the largest mass m that can be raised when cylinder B is rotated slowly and cylinder A is kept fixed. PROBLEM 8.120 A cable passes around three .05 m-radius pulleys and supports two blocks as shown. Pulleys C and E are locked to prevent rotation, and the coefficients of friction between the cable and the pulleys are S = 0.20 and k = 0.15. Determine the range of values of the weight of block A for which equilibrium is maintained (a) if pulley D is locked, (b) if pulley D is free to rotate. PROBLEM 8.121 A cable passes around three 05 m.-radius pulleys and supports two blocks as shown. Two of the pulleys are locked to prevent rotation, while the third pulley is rotated slowly at a constant speed. Knowing that the coefficients of friction between the cable and the pulleys are S = 0.20 and k = 0.15, determine the largest weight WA which can be raised (a) if pulley C is rotated, (b) if pulley E is rotated. PROBLEM 8.126 The strap wrench shown is used to grip the pipe firmly without marring the surface of the pipe. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction is the same for all surfaces of contact, determine the smallest value of S for which the wrench will be selflocking when a = 200 mm, r = 30 mm, and = 65 . PROBLEM 8.136 A window sash having a mass of 4 kg is normally supported by two 2-kg sash weights. Knowing that the window remains open after one sash cord has broken, determine the smallest possible value of the coefficient of static friction. (Assume that the sash is slightly smaller than the frame and will bind only at points A and D.) PROBLEM 8.140 The ends of two fixed rods A and B are single-threaded screws of mean radius .0076 m and pitch .0025 m Rod A has a right-handed thread, and rod B has a left-handed thread. The coefficient of static friction between the rods and the threaded sleeve is 0.12. Determine the magnitude of the couple that must be applied to the sleeve to draw the rods closer together.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocument18 paginiQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- Equivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsDocument14 paginiEquivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsYun RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction and Forces in Mechanics ProblemsDocument11 paginiFriction and Forces in Mechanics Problemsprem19999Încă nu există evaluări
- FINITE ELEMENT 18ME73 ASSIGNMENTSDocument10 paginiFINITE ELEMENT 18ME73 ASSIGNMENTSFOODIE USÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question BankDocument9 paginiQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Tutorials 1 5Document7 paginiTutorials 1 5faizankhan260690Încă nu există evaluări
- Question Sheet2 PDFDocument15 paginiQuestion Sheet2 PDFSaumyak RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- ES 13 Problem Set 1 SolutionsDocument2 paginiES 13 Problem Set 1 SolutionsSammy Marquez100% (1)
- Strema 102Document4 paginiStrema 102Hazel VidallonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practise Problems Set01Document7 paginiPractise Problems Set01rohit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Body 3D AnsDocument23 paginiRigid Body 3D AnsSyed ShaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Solution for Torque Between Magnetic DipolesDocument5 paginiAnalytic Solution for Torque Between Magnetic DipolesLee Kar Huo22% (9)
- Tutorial 5Document4 paginiTutorial 5Kumar ShivamÎncă nu există evaluări
- MiniFrac Test Analysis Reveals Formation PropertiesDocument32 paginiMiniFrac Test Analysis Reveals Formation Propertiesgodrich1Încă nu există evaluări
- The Selection of Cyclone Classifiers, Pumps and Pump Boxes For Grinding CircuitsDocument28 paginiThe Selection of Cyclone Classifiers, Pumps and Pump Boxes For Grinding CircuitsRosemarie Blanche Villanueva100% (1)
- Applied Mechanics Problems & SolutionsDocument4 paginiApplied Mechanics Problems & SolutionsBuddhisagar BastolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Project ExamplesDocument49 paginiFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesDocument5 paginiProblem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesClint Charles P. BrutasÎncă nu există evaluări
- BME - MOD I QuestionsDocument4 paginiBME - MOD I QuestionsGaurav ThakareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Questions For PracticeDocument4 paginiModel Questions For PracticeRohan SahanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 paginiAssignment For IPEAbirHasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 paginiStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics: Review MaterialDocument30 paginiEngineering Mechanics: Review MaterialVon Eric DamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Body 3DDocument6 paginiRigid Body 3DSyed ShaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering MechanicsDocument8 paginiEngineering MechanicsNanna ShivuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress - ProblemsDocument13 paginiStress - ProblemsMilaj YuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics Tutorial on FrictionDocument3 paginiEngineering Mechanics Tutorial on FrictiondummyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Material 2Document6 paginiStrength of Material 2viv_1971Încă nu există evaluări
- The tutorial problems have been highlightedDocument14 paginiThe tutorial problems have been highlighteddarkknightoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial5 FrictionDocument4 paginiTutorial5 FrictionTapan BadheiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equilibrium Problems Solved for Forces and ReactionsDocument15 paginiEquilibrium Problems Solved for Forces and ReactionsSivaprasad DusiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06Document12 pagini06Meliza AnalistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 212-Chpt 8Document5 pagini212-Chpt 8zainabcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 paginiLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages4 41 To 52 PDFDocument12 paginiPages4 41 To 52 PDFIsmael de PabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction (MEC 107)Document2 paginiFriction (MEC 107)Piyush JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Diagrams, Stress Analysis, and Material BehaviorDocument7 paginiPhase Diagrams, Stress Analysis, and Material BehaviorMOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz No 1Document2 paginiQuiz No 1Tris ZackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 paginiScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5Document7 paginiTutorial 5A SкÎncă nu există evaluări
- CENG198 CE Competency Appraisal III Static and Dynamics ProblemsDocument4 paginiCENG198 CE Competency Appraisal III Static and Dynamics ProblemsJeric DinglasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME101 Tutorial 03 PDFDocument2 paginiME101 Tutorial 03 PDFalex albÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument3 paginiStrength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsNEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut 05Document3 paginiTut 05Ashutosh RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 고체역학 문제집Document41 pagini고체역학 문제집Michael MeashoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document4 paginiAssignment 1TanmayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4Document2 paginiTutorial 4nageshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document3 paginiTutorial Chapter 1ACC SHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. TechDocument7 paginiSecond Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. Techlatendra kumar srivastavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 paginiTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me218 Fa15 W3 HoDocument10 paginiMe218 Fa15 W3 HonhiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prob SheetDocument20 paginiProb SheetAditya ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Document2 paginiSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Kamini GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2017 Tutorial ProblemsDocument2 paginiSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2017 Tutorial ProblemsMihir Kumar MechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank - DMEDocument6 paginiQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sebellino StaticsDocument3 paginiSebellino StaticsJoby Jobzz SebellinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment04 (2:11:14)Document2 paginiAssignment04 (2:11:14)Gabriel SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 2 - Shear and Bearing Stresses CalculationsDocument5 paginiProblem Set 2 - Shear and Bearing Stresses CalculationsLynx101Încă nu există evaluări
- nov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂Document14 pagininov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂badboy_rockssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDe la EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityDe la EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column Buckling: (Eccentric Loaded)Document9 paginiColumn Buckling: (Eccentric Loaded)Muhammad sheryarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave Propagation in Solids and FluidsDocument10 paginiWave Propagation in Solids and FluidsjohnsgdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velocity Definitions GuideDocument8 paginiVelocity Definitions GuideSani TipareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Overhead Monor PDFDocument5 paginiDesign and Development of Overhead Monor PDFFiroz PawaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- De-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDocument2 paginiDe-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDahanyakage WickramathungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture - Material TechnologyDocument18 paginiFracture - Material TechnologyayushdbcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Fields and Electric CurrentDocument11 paginiMagnetic Fields and Electric CurrentRaghav MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series Test-Ii November - 2021: Ilm College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument2 paginiSeries Test-Ii November - 2021: Ilm College of Engineering & TechnologyHOD ILM aeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation For: CalculationsDocument2 paginiCalculation For: CalculationsShivendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rectilinear Motion ExplainedDocument22 paginiRectilinear Motion ExplainedJamie MedallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document7 paginiAssignment 1debabrata chowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13.702 Mechatronics: Module - IDocument105 pagini13.702 Mechatronics: Module - ISahad MkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Spectrum Method-Based Stress Analysis For Oil Pipelines in Earthquake Disaster AreasDocument24 paginiFrequency Spectrum Method-Based Stress Analysis For Oil Pipelines in Earthquake Disaster AreasNTRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec15 PDFDocument7 paginiLec15 PDFRohan sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Chemistry Impq Ch02 Structure of Atom KvsDocument11 pagini11 Chemistry Impq Ch02 Structure of Atom KvsshubhammukriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Construction of A Torsion Fatigue Machine: Torsion Fatigue Tests On Two Industrial Aluminum AlloysDocument15 paginiDesign and Construction of A Torsion Fatigue Machine: Torsion Fatigue Tests On Two Industrial Aluminum AlloysAyberk TürkÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE8301-SOM-I-By WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFDocument128 paginiCE8301-SOM-I-By WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFMadhu shivaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8 of Tropical MeteorologyDocument22 paginiLecture 8 of Tropical MeteorologyMelvin BadonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Throttling Characteristics of Multi-Hole Orifice in Multi Stage AssemblyDocument13 paginiThrottling Characteristics of Multi-Hole Orifice in Multi Stage AssemblyGuglielmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Pattern Cumulative Test-3 (Act-3) : Paper-2Document31 paginiAdvanced Pattern Cumulative Test-3 (Act-3) : Paper-2Tushar Kant0% (1)
- Revision Tutorial- A2 Physics Key ConceptsDocument4 paginiRevision Tutorial- A2 Physics Key ConceptsjayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum Deflection of Beams Using Moment Area MethodDocument5 paginiMaximum Deflection of Beams Using Moment Area Methodpmali2Încă nu există evaluări
- Mike WeaverDocument35 paginiMike WeavervilukÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Resultant ForceDocument30 pagini1.1 Resultant ForceLim Yan JoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of The Wavelet Transform in The Generation and Analysis of Spectrum-Compatible RecordsDocument27 paginiApplications of The Wavelet Transform in The Generation and Analysis of Spectrum-Compatible Recordsfernando CanizaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMRDocument30 paginiNMRBharatula Suryamani Shankar ee19b013Încă nu există evaluări