Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Mohr Circle1
Încărcat de
Kenny Ruiz0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
43 vizualizări14 paginiMohr
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentMohr
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
43 vizualizări14 paginiMohr Circle1
Încărcat de
Kenny RuizMohr
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 14
Mohrs Circle Plane Stress
Mohrs Circle Plane Stress
sn s nn
n x
]2 [
[ ]2 [
]2 ]2
[c, 0]
nn
sn
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
[avg, -max]
[yy, -xy]
[22, 0] a) Principal stresses 2s [xx,xy] [c, 0] 2p
[11, 0]
[avg, max] b) Maximum in-plane stress
p - s =45o
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point. Specify the orientation of the element in each case.
a) Principal stresses
30MPa 45MPa
60MPa b) Maximum in-plane stress
14.9o
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point. Specify the orientation of the element in each case. 60MPa 30MPa 1) Mohrs circle 45MPa
2) Principal stresses
[avg, -max] [-60, -30] 2p2 [22, 0] [11, 0] nn
[c, 0]
3) Maximum in-plane stress
[avg, max]
2p1
2s
[45, 30]
sn
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point. Specify the orientation of the element in each case. 60MPa 30MPa 1) Mohrs circle 2) Principal stresses 45MPa
3) Maximum in-plane stress
[avg, -max] [-60, -30] [11, 0] [22, 0] 14.9o 30.1o 60.5 MPa 7.5 MPa [avg, max] [c, 0] 2p1 nn
4) Draw infinitesimal elements
2s
[45, 30]
sn
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example A point on a thin plate is subjected to two successive states of stress as shown. Determine the resulting state of stress with reference to an oriented as shown on the bottom.
50 kPa
II
45 kPa
30o
50o
18 kPa
xy xx
yy
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example A point on a thin plate is subjected to two successive states of stress as shown. Determine the resulting state of stress with reference to an oriented as shown on the bottom. Step 1: the resulting stresses from part I xy xx
1) Mohrs circle
50 kPa
30o
yy
[yy1, -xy1]
2) Plane Stress Transformation
[kPa] [0, 0] [kPa] [kPa] sn [c, 0] 60o [50, 0]
nn
[xx1, xy1]
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example A point on a thin plate is subjected to two successive states of stress as shown. Determine the resulting state of stress with reference to an oriented as shown on the bottom. Step 2: the resulting stresses from part II
1) Mohrs circle
45 kPa
II
xy xx
50o
18 kPa
yy
[0,-45]
2) Plane Stress Transformation
[yy2, -xy2]
[c, 0]
100o
nn [xx2, xy2]
[-18, 45]
sn
Mohrs Circle Principal Stresses & Maximum In-Plane Shear Stress
Example A point on a thin plate is subjected to two successive states of stress as shown. Determine the resulting state of stress with reference to an oriented as shown on the bottom. Step 3: the total resulting stresses the resulting stresses from part I
[kPa]
50 kPa
45 kPa
II 50o
18 kPa
[kPa]
[kPa]
30o
the resulting stresses from part II
22.69 kPa the total resulting stresses 74.38 kPa
42.38 kPa
State of Stresses Caused by Combined Loads
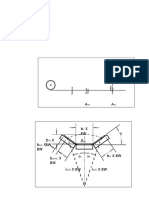
8-57 The 25 mm diameter rod is subjected to the loads shown. Determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at point B. (p. 460) y x Step 1: Internal loads at section b-b Step 2: Stresses at point B caused by internal loads (stress distribution) Step 3: State of stresses
400 N
B z
y B
Step 4: Mohrs circle
Step 5: Principal stresses & maximum in-plane shear stress
x b-b b B y x xx
xy
State of Stresses Caused by Combined Loads
Example: The 25 mm diameter rod is subjected to the loads shown. Determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at point B (week 9) Fx= 375N y Step 1: Internal loads at section b-b Fy; My Fy= -400N x Step 2: Stresses at point B caused by internal loads Fx; Tx Fz= 500N Tx= -30 Nm My= 71.875 Nm Mz= 80 Nm B
Fz; Mz
Step 3: State of stresses
State of Stresses Caused by Combined Loads
8-57 The 25 mm diameter rod is subjected to the loads shown. Determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at point B. (p. 460)
Step 1: Internal loads at section b-b
Step 2: Stresses at point B caused by internal loads Step 3: State of stresses y
B
46.12 MPa 10.87 MPa
x
[-10.87, -46.12]
Step 4: Mohrs circle
[c, 0] nn
[0, 10.87] sn
State of Stresses Caused by Combined Loads
8-57 The 25 mm diameter rod is subjected to the loads shown. Determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at point B. (p. 460)
Step 1: Internal loads at section b-b
Step 2: Stresses at point B caused by internal loads Step 3: State of stresses y
B
46.12 MPa 10.87 MPa
Step 4: Mohrs circle
[avg, -max]
Step 5: Principal stresses & maximum in-plane shear stress
[22, 0] [c, 0] nn [11, 0]
[avg, max]
sn
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Socket Base Connections With Precast Concrete Columns PDFDocument11 paginiSocket Base Connections With Precast Concrete Columns PDFAc2140100% (5)
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 paginiWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welding Joint Design and Welding SymbolsDocument67 paginiWelding Joint Design and Welding SymbolsAdhanom G.Încă nu există evaluări
- Moment of Resistance For Doubly Reinforced SectionsDocument32 paginiMoment of Resistance For Doubly Reinforced SectionsWanda Beasley100% (3)
- MECH4450 Introduction To Finite Element Methods: Basic PrinciplesDocument24 paginiMECH4450 Introduction To Finite Element Methods: Basic PrinciplesMayank KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Door Hinge StressesDocument15 paginiDoor Hinge Stressesnargissuhail100% (3)
- EPRI Field Guide For Boiler Tube FailuresDocument215 paginiEPRI Field Guide For Boiler Tube FailuresGurugubelli DeekshitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Cause AC Motor Failure Analysis With Focus On Shaft FailuresDocument43 paginiRoot Cause AC Motor Failure Analysis With Focus On Shaft Failuresharshal161987100% (1)
- Exercise 09 Hertz ContactDocument30 paginiExercise 09 Hertz ContactFernando Salles100% (1)
- Design For Antenna Tower Group 2Document75 paginiDesign For Antenna Tower Group 2amantz91Încă nu există evaluări
- Opensees Geotechnical Capabilities and ApplicationsDocument31 paginiOpensees Geotechnical Capabilities and ApplicationsMahmoud ElkhedrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideDocument238 paginiCondmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideKenny Ruiz67% (6)
- Introduction To Continuum MechanicsDocument162 paginiIntroduction To Continuum MechanicsMichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Elements For Modeling Bridge ComponentsDocument83 paginiFinite Elements For Modeling Bridge ComponentsK KajeenthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Design of Conveyor PulleysDocument10 paginiThe Design of Conveyor PulleysJam BabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Report - RawanDocument23 paginiPartial Report - RawanKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Equipment Dossier R0Document50 paginiEquipment Dossier R0Kenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- WE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelDocument1 paginăWE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spherical Valve Technical DescriptionDocument12 paginiSpherical Valve Technical Descriptionpavankumar001100% (6)
- Annexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeDocument3 paginiAnnexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Hydraulic FracturingDocument213 paginiSimulation of Hydraulic Fracturingnaqueel100% (1)
- Successful Solution: To The Challenge ofDocument2 paginiSuccessful Solution: To The Challenge ofKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- SketchsDocument1 paginăSketchsKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mba ZC417Document4 paginiMba ZC417Kenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fly AcDocument7 paginiFly AcKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Properties of Solar CellsDocument8 paginiElectrical Properties of Solar CellsKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book-I Chapter 1: Input DataDocument3 paginiBook-I Chapter 1: Input DataKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaDocument6 paginiTest Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- cdk1 Coal B-EDocument1 paginăcdk1 Coal B-EKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- VB 29 - 10Document5 paginiVB 29 - 10Kenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 148 FPDocument2 pagini148 FPKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 139 FPDocument7 pagini139 FPKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 142 EaDocument3 pagini142 EaKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameDocument2 paginiList of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameKenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 paginiCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- IIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialDocument4 paginiIIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 paginiEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastic Beams in Three Dimensions: Lars Andersen and Søren R.K. NielsenDocument104 paginiElastic Beams in Three Dimensions: Lars Andersen and Søren R.K. NielsenAnonymous hprsT3WlPÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 6 - (Design of Compression Members)Document35 paginiMODULE 6 - (Design of Compression Members)TobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 - Losses in PSDocument12 paginiLecture 4 - Losses in PSLexi BarcelonÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Proceeding ICSEM 2013 PDFDocument887 paginiE-Proceeding ICSEM 2013 PDFMehar Babu RavulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.pore Pressure From Seismic PDFDocument10 pagini10.pore Pressure From Seismic PDFSudip RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me6503 Dme Unit 4 Study Notes 2015Document29 paginiMe6503 Dme Unit 4 Study Notes 2015Bala MuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traditional Methods For The Design of Radial-Axial Hydraulic Turbines With Verification in CFD SimulationDocument15 paginiTraditional Methods For The Design of Radial-Axial Hydraulic Turbines With Verification in CFD SimulationЖивотаЛазаревићÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mom Ii IaDocument2 paginiMom Ii IaKIRAN H SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Undergrad Course DescriptionsDocument212 paginiUndergrad Course DescriptionsRickÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Problem Solving With 3dec: Section 3.1 Sections 3.2 3.10Document126 pagini3 Problem Solving With 3dec: Section 3.1 Sections 3.2 3.10Nguyen Huu CuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course-Earth Pressure On Retaining Walls PDFDocument37 paginiCourse-Earth Pressure On Retaining Walls PDFnoussnoussaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz QuestionnaireDocument3 paginiReinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz QuestionnaireIRISHÎncă nu există evaluări
- AghajaniDelavarDocument6 paginiAghajaniDelavarArunkumar sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop Homework ProblemsDocument41 paginiWorkshop Homework ProblemsKemoHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature ReviewDocument3 paginiLiterature ReviewAkshay MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări