Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Gas Lift Dual
Încărcat de
Mikhaelrams RamsDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Gas Lift Dual
Încărcat de
Mikhaelrams RamsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Slim hole completions are often used in lower productivity wells.
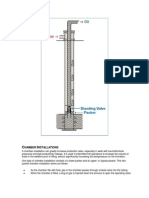
These normally use a string of 2-3/8 to 31/2-inch OD pipe as the production casing. Smaller size tubing, (e.g., 1 to 1-1/2-inches in diameter) is then run inside this casing (Figure 8: Slim hole gas lift completion).
Figure 8
Slim hole completions are especially useful for producing from two or more zones without commingling. Production rates for continuous gas lift will depend on the ID of the tubing, but can range from 150 B/D for 3/4-inch tubing to 900 B/D for 1 1/2-inch ID tubing. The rates for intermittent injection in slim hole wells are considerably lower.
DUAL INSTALLATIONS
Gas lift wells, like flowing wells, can be designed with parallel or concentric dual tubing strings (Figure 9: Dual gas lift installations). The two most common configurations are (1) parallel strings of 2 3/8-inch OD tubing inside 7-inch casing and (2) parallel strings of 3 1/2-inch OD tubing inside 9 5/8-inch casing (API RP 11V8, 2003).
Figure 9
Gas is supplied through the tubing-casing annulus, and injected into two separate tubing strings. The zones may be produced using the same type of lift method (i.e., both on continuous or both on intermittent lift), or the two methods may be used in combination (e.g., one zone is on intermittent lift while the other is on continuous lift). For a dual installation to work, the valves must be spaced to prevent interference between the two zones, and selected so that the desired amounts of gas are injected for each zone.
COILED TUBING INSTALLATIONS
Coiled tubing can be used to convert a flowing well to gas lift without having to pull the main production tubing string, simply by placing conventional gas lift mandrels at the appropriate depths on the coiled tubing string and then running it inside the production tubing. The smaller diameter of the coiled tubing restricts its use to lower-productivity wells.
ANNULAR FLOW INSTALLATIONS
In most gas lift operations, production is confined to the tubing because of safety issues, regulatory requirements and company operating policies. This is especially true offshore. In some areas, however such as the Middle East, where wells produce at rates up to 80,000 B/D operators use annular flow gas lift. In this process, gas is injected down the tubing and production is from the annulus. A bull plug is placed at the bottom of the tubing to contain the injected gas. A small-bore orifice or check valve can also be used for this purpose.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- BASIC Wireline (Narong T)Document54 paginiBASIC Wireline (Narong T)Tiwakorn DarajitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Gas Lift Camco ManualDocument86 paginiGas Lift Camco ManualJorge Alberto Quiza Polania100% (8)
- Completions and Workovers 1.9Document46 paginiCompletions and Workovers 1.9Maqbool Ahmad67% (3)
- PCR 2022 PIPESIM COURSE Fundamentals Final PDFDocument96 paginiPCR 2022 PIPESIM COURSE Fundamentals Final PDFAndres MerloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Petrobras - DeepWater Gas LiftDocument36 pagini1 - Petrobras - DeepWater Gas LiftNisar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ankleshwar Asset-ONGCDocument116 paginiAnkleshwar Asset-ONGCyash saragiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haggis Exercise - Prosper - Updated 2007Document11 paginiHaggis Exercise - Prosper - Updated 2007Anonymous 3TyM2U3U4eÎncă nu există evaluări
- Completion TheoryDocument74 paginiCompletion TheoryHKHKBOOKSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Integrity MaintenanceDocument164 paginiWell Integrity MaintenanceZool Hilmi100% (1)
- Gas LiftDocument66 paginiGas LiftWahyu NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lease Pumper Handbook PDFDocument552 paginiLease Pumper Handbook PDFWahyu YanuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Camco Gas Lift Product Catalog 1987Document93 pagini13 Camco Gas Lift Product Catalog 1987Cluis KeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas LiftBestPracticesDocument80 paginiGas LiftBestPracticesRaed fouad100% (1)
- PIPESIM 2019: Steady-State Multiphase Flow SimulatorDocument32 paginiPIPESIM 2019: Steady-State Multiphase Flow SimulatorHafiz AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gap & Prosper WorkshopDocument60 paginiGap & Prosper WorkshopWael FaragÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of Artificial Lift MethodDocument5 paginiSelection of Artificial Lift MethodAngel David Ponce OropezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 3 Presentation PTC Barrier PhilosophyDocument19 pagini1 3 Presentation PTC Barrier Philosophyuserscribd2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift Valve InjDocument3 paginiGas Lift Valve InjMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipesim Project2Document151 paginiPipesim Project2sugiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- I 8 API Standards For Gas Lift Slide DeckDocument27 paginiI 8 API Standards For Gas Lift Slide DeckalrqyshyaydhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selecting An Artificial Lift MethodDocument62 paginiSelecting An Artificial Lift MethodSiddiq MahyildinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water FracDocument1 paginăWater FracMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resin Coated SandDocument1 paginăResin Coated SandMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water FracDocument1 paginăWater FracMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- What If The Fracs Are NOT Longitudinal?Document1 paginăWhat If The Fracs Are NOT Longitudinal?Mikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resin Coated SandDocument1 paginăResin Coated SandMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- What If The Fracs Are NOT Longitudinal?Document1 paginăWhat If The Fracs Are NOT Longitudinal?Mikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic ProppantsDocument2 paginiCeramic ProppantsMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift PrincDocument2 paginiGas Lift PrincMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proppand ConductivityDocument1 paginăProppand ConductivityMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift StarDocument4 paginiGas Lift StarMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift StarDocument4 paginiGas Lift StarMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift ValvDocument2 paginiGas Lift ValvMikhaelrams Rams0% (1)
- Mohr Circle ADocument3 paginiMohr Circle AMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift Val InjDocument2 paginiGas Lift Val InjMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift SurfaceDocument4 paginiGas Lift SurfaceMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift PrincDocument2 paginiGas Lift PrincMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift PrincDocument2 paginiGas Lift PrincMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift OperDocument3 paginiGas Lift OperMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift Valve MechDocument4 paginiGas Lift Valve MechMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift DesingDocument5 paginiGas Lift DesingMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift InterDocument7 paginiGas Lift InterMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift Valve ContDocument5 paginiGas Lift Valve ContMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift ChamberDocument3 paginiGas Lift ChamberMikhaelrams Rams100% (1)
- Gas Lift DownDocument6 paginiGas Lift DownMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift Valve DomoDocument2 paginiGas Lift Valve DomoMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift ValvesDocument7 paginiGas Lift ValvesMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift ValvesDocument7 paginiGas Lift ValvesMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift DownDocument6 paginiGas Lift DownMikhaelrams RamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Side Pocket Mandrels PsDocument2 paginiSide Pocket Mandrels PsEmad JamshidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SzakmDocument50 paginiSzakmAhmed AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIPESIM Brochure Licenses ModuleDocument6 paginiPIPESIM Brochure Licenses ModuleKarolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Mandrel SpacingDocument17 paginiSimple Mandrel SpacingJulian UribeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Completation Inteligent RevistaDocument9 paginiCompletation Inteligent RevistaGabriel Castellon HinojosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocw - Utm.my File - PHP 12 Chapter 7-OCWDocument44 paginiOcw - Utm.my File - PHP 12 Chapter 7-OCWRahul Gupta100% (1)
- Zdocs - Tips Pipesim GuiaDocument644 paginiZdocs - Tips Pipesim GuiaFernando Ledesma SolaecheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Lift SystemDocument12 paginiGas Lift SystemCamilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Api Spec 6D: API - The American Petroleum InstituteDocument3 paginiApi Spec 6D: API - The American Petroleum Institutenrd9771100% (1)
- Stabilization of Gas Lifted WellsDocument6 paginiStabilization of Gas Lifted WellsEzequias MattosÎncă nu există evaluări