Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fats and Oils Are Esters of Non
Încărcat de
pantatbolongDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fats and Oils Are Esters of Non
Încărcat de
pantatbolongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fats and oils are esters of non- polar compounds are not soluble in water , which is produced by plants
and animals . In food processing , fats and oils have some important function , namely as a source of energy , contribute to the formation of texture and sensory quality of food products , heat transfer medium in the frying process , as well as a solvent for essential fat-soluble vitamins ( A , D , E and K ) .
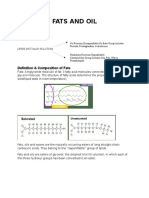
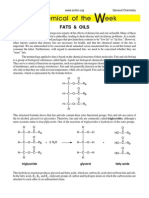
Fats and oils are lipid- simple groups of glycerol esters prepared by fatty acid and glycerine . In the structure of fats and oils , glycerin molecule binds three fatty acid chains to form ester compounds which are non-polar . The length of the molecular structure of fats and oils depending on the type of fatty acids attached to the glycerol . Below we can see the chemical structure of fats / oils .
And , finally we are back to the original question , " What is the difference between fats and oils itself? "
As a student of food technology , I often get questions about it . As we know , the difference lies in its form at room temperature , solid fats and liquid oils otherwise at room temperature . However , what causes the difference in the physical ? ? The difference is caused by the physical composition of the constituent fatty acids . Fats contain more saturated fatty acids , while the oil contains unsaturated fatty acids that much more . Since the melting point is higher in saturated fat than the fat unsaturated fats tend to be solid , while oil is liquid at room temperature .
The melting point ( melting point) is the physical properties of the essential fatty acids . The melting point indicates the temperature at which the fat / oil change phase from solid phase into the liquid phase . The melting point of fatty acids will determine the melting and crystallization properties of fat formulation . The melting point of fatty acids is influenced by the carbon chain length , number of double bonds and cis and trans configurations .
Number of Carbon Atoms The melting point of fatty acids will further increase with increasing number of carbon atoms are bonded . In the same number of carbon atoms , the melting point of fatty acids with unsaturated bonds is higher than the unsaturated fatty acids .
The number of double bonds The more the number of unsaturated bonds ( double bonds ) then the lower the melting point . For example , the melting point of the fatty acids C 18:0 , C 18:1 , C 18:2 , C 18:3 dam row is as follows 70 C , 16 C , -5 C and -11 C .
Cis and trans configurations Unsaturated fatty acid isomers with ciss configuration has a lower melting point than the trans configuration , for example, oleic acid ( cis - 9 - octadecanoic ) has a melting point of 14 C , whereas elaidic acid ( trans - 9 - octadecanoic ) at 43.7 C.
Finally, the physical properties of fats and oils from different sources generally differ because of differences in the proportions of their constituent fatty acids and chemical structure of each triglyceride
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Oils & Fats - 3Document25 paginiOils & Fats - 3Aleem AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Acids and Fats ExplainedDocument2 paginiFatty Acids and Fats ExplainedNica mapeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022-23 Lecture LipidsDocument68 pagini2022-23 Lecture LipidsStudent 365Încă nu există evaluări
- BP301T Poc Unit IiiDocument15 paginiBP301T Poc Unit IiiSUBHASISH DASHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochem AssignmentDocument4 paginiBiochem AssignmentNicola Faye BronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats and OilDocument67 paginiFats and OilShivam KansaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Compopsition of The CellDocument14 paginiChemical Compopsition of The Cellmarwani mat nasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- FatsDocument45 paginiFatsManshad AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids PDFDocument25 paginiLipids PDFTiara AndhitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceDocument3 paginiSekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceherrisenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats and Oils - PRNT193Document65 paginiFats and Oils - PRNT193Joddie LoplopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On LipidsDocument3 paginiNotes On LipidsKyrá BadayosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids 1Document41 paginiLipids 1Nosheen BashirÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument23 paginiLipidsRukhsar JabbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15 Questions and Problems For TextbookDocument4 paginiChapter 15 Questions and Problems For TextbookSara KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Fats: Properties and Food SourcesDocument15 paginiSaturated vs Unsaturated Fats: Properties and Food SourcesMacapodi Nurul-anna100% (1)
- 1A (111) LipidsDocument4 pagini1A (111) Lipidsenakshi perusingheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fat vs Oil: Key DifferencesDocument2 paginiFat vs Oil: Key DifferencesArif MahmudÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT 8. Solubility, Specific Gravity, and Refractive IndexDocument4 paginiEXPERIMENT 8. Solubility, Specific Gravity, and Refractive IndexLykaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument22 paginiLipidsAhmed AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of LipidDocument11 paginiStructure of LipidAfrah Alatas100% (1)
- Chemical Changes and Protective Measures of Fat During Deep FryingDocument11 paginiChemical Changes and Protective Measures of Fat During Deep FryingSyed Ali Akbar BukhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Dietary Fats on HealthDocument2 paginiEffects of Dietary Fats on HealthMollakarn KaewsarehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats and OilsDocument15 paginiFats and OilsNoor AishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fat - WikipediaDocument29 paginiFat - WikipediaWaqar AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids Nomenclature and FunctionsDocument15 paginiLipids Nomenclature and FunctionsDoreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- MF203 Fhs LNT 003Document53 paginiMF203 Fhs LNT 003PikuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fat Acids: "Vasile Alecsandri" High SchoolDocument10 paginiFat Acids: "Vasile Alecsandri" High SchoolCristian NegruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats and oilDocument2 paginiFats and oilAyesha AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions of Oils, Fats and Their ProductsDocument50 paginiChemical Reactions of Oils, Fats and Their ProductsJai MurugeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palm OilDocument8 paginiPalm OilHadiBiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturated and Unsaturated FatsDocument5 paginiSaturated and Unsaturated FatsKhor Z ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choe and Min, 2007Document10 paginiChoe and Min, 2007Julio Mauricio Vidaurre-RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidDocument30 paginiLipidsima mhammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Chemistry 1Document102 paginiLipid Chemistry 1queenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty AcidsDocument2 paginiFatty AcidsSteven4654Încă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry MidreviewerDocument21 paginiBiochemistry MidreviewerLexa CyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title: Aim: Date: Name: Matriculation Number: Serial Number: Group: Experiment Number: Level: Course Code: Instructor'S NameDocument14 paginiTitle: Aim: Date: Name: Matriculation Number: Serial Number: Group: Experiment Number: Level: Course Code: Instructor'S NameJim0% (1)
- Chemistry of Lipid-IDocument38 paginiChemistry of Lipid-Idj77djcqy7Încă nu există evaluări
- Lipids: An Overview of Their Classes, Structures and FunctionsDocument68 paginiLipids: An Overview of Their Classes, Structures and FunctionsakintunjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Chemistry of Biodiesel: A Curriculum For Agricultural ProducersDocument38 paginiBasic Chemistry of Biodiesel: A Curriculum For Agricultural ProducersVano NonikashviliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument5 paginiSaturated and Unsaturated Fatty AcidsNindya BadzlinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids Answered Review F 07Document7 paginiLipids Answered Review F 07song flamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Lipids Mam BarramedaDocument16 paginiNotes On Lipids Mam Barramedasshh bartolata100% (1)
- 06 Fat AnalysisDocument18 pagini06 Fat AnalysisADINDA DYAH MUKHLASINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids: Student Activity GuideDocument18 paginiLipids: Student Activity GuideShyra Mae PajarillagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Basic Oil ChemistryDocument19 pagini2 Basic Oil ChemistryAndrés Gutiérrez RicardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document65 paginiChapter 1maya adamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats and Oils: Classification, Structure and PropertiesDocument65 paginiFats and Oils: Classification, Structure and PropertiesNaveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of Lipids PDFDocument37 paginiPhysical Properties of Lipids PDFDania SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frying OilsDocument10 paginiFrying OilsSuryadi XuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document6 paginiAssignment 1Asia AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry LipidsDocument62 paginiBiochemistry LipidsDianne Joy100% (1)
- Oil ReviewerDocument7 paginiOil ReviewerAbbygale Therese LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 15 - LipidsDocument46 paginiLecture 15 - LipidsZain AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Chemistry Fat and OilsDocument10 paginiFood Chemistry Fat and OilsSHAFIKANOR3661Încă nu există evaluări
- Lipids: What Are Fatty Acids?Document7 paginiLipids: What Are Fatty Acids?Jeff MorrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Enhanced Recovery Methods for Heavy Oil and Tar SandsDe la EverandIntroduction to Enhanced Recovery Methods for Heavy Oil and Tar SandsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantDe la EverandSoap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantÎncă nu există evaluări
- What is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksDe la EverandWhat is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksÎncă nu există evaluări