Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Interrogative Forms: Basic Question Structure
Încărcat de
Niuerb BeibreDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interrogative Forms: Basic Question Structure
Încărcat de
Niuerb BeibreDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interrogative Forms
Basic Question Structure:
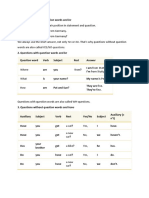
Yes or no questions. Use the verbs be, have and do along with helping (also called Auxiliary) verbs such as can, will and should when you ask these questions. The helping verb comes before the subject, the main one comes after the subject. The verb to be also comes before the subject when it is an ordinary verb rather than a helping verb ( ii, v ).
Helping verb
i) ii) iii) iv) v)
Subject you they you she this
Main verb like doing finished come soccer? their homework? your meal? with us? your seat?
Do Are Have Will Is
Inversion: Auxiliary verbs are inverted with the subject in a question:
Statement:
Subject I Auxiliary verb Am
Auxiliary verb am Subject I
doing it right.
Question:
doing it right?
Question-word Questions:
Question words what, which, who (sometimes whom), whose, when, where and how are used to ask for information. The verbs be, have and do, and helping verbs such as can, will and should are also used in these questions. The helping verb comes before the subject.
Question word Where When What When
Auxiliary verb are do have will
Subject you you you we
Main verb going? get married? got meet?
there?
Question word What Where Some more examples:
i) ii)
Auxiliary verb is do
Subject your name? the birds
Main verb
go
when it rains?
Which house do you live in? What date is it today?
In these cases the subject is still after the helping verb (in example ii is is used as a main verb). Sometimes the wh-word (who, which, etc.) itself is the subject of the sentence. In this case, dont use do to form questions.
iii) iv)
Who wants to come with me? What caused the accident?
Question Tags:
Sometimes people finish what they are saying with a short question called question tag to know if the person they are speaking to agrees with them: The weather is lovely today, isnt it? The main part of the sentence is positive, but the question tag is negative. You expect the answer to a negative question tag to be yes. Use a helping verb and the subject of the sentence to make the question tag. Notice that the subject has been replaced by a pronoun in the example sentences. The pronoun in the question tag refers to the subject in bold. Tom is older than you, isnt he? Sally has got a dog, hasnt she? Anna and I can go by train, cant we? Peter and David should leave now, shouldnt they? If the main part of the sentence has I am in it, use arent I in the question tag: Im your best friend, arent I? Im taller than John, arent I? If the main part of the sentence is negative, the question tag is positive. You expect the answer to a positive question tag to be no: These questions arent very difficult, are they? You havent read this book, have you? Peter isnt as tall as I am, is he? She isnt eight yet, is she? There arent many clouds in the sky, are there? There isnt much wind today, is there? There werent any emails for me, were there?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Aqua FarmDocument32 paginiAqua FarmMehrdad SorouraminiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Letters: Mrs. Holt's IBT ClassDocument20 paginiBusiness Letters: Mrs. Holt's IBT ClassDarlyn BucayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Talent Acquisition: An OverviewDocument10 paginiTalent Acquisition: An OverviewPulin PathnejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liming and Fertilization of Brackishwater Shrimp PondsDocument17 paginiLiming and Fertilization of Brackishwater Shrimp PondslestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Plankton in Aquaculture and The Benefits of Ecoplankt-AquaDocument7 paginiImportance of Plankton in Aquaculture and The Benefits of Ecoplankt-AquaRai Abdur RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forms of Verbal CommunicationDocument5 paginiForms of Verbal CommunicationAmandaIndahKusumaPertiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of Nonverbal CommunicationDocument20 paginiFunctions of Nonverbal CommunicationNany Gómez TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease Prevention in Shrimp - Nutriad - Animal Feed AdditivesDocument8 paginiDisease Prevention in Shrimp - Nutriad - Animal Feed AdditivesSuprapto NsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liming Ponds AquacultureDocument7 paginiLiming Ponds Aquacultureristiawan nugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immune Response in ShrimpDocument16 paginiImmune Response in ShrimpKhair KadimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liming and Its Principles in Aquaculture: The Advantages of Liming AreDocument5 paginiLiming and Its Principles in Aquaculture: The Advantages of Liming Areristiawan nugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Quality and Partial Mass Budget in Extensive Shrimp Ponds in BangladeshDocument11 paginiWater Quality and Partial Mass Budget in Extensive Shrimp Ponds in BangladeshFaisal AzmeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salary Cirtificate SHAKTIDocument1 paginăSalary Cirtificate SHAKTIsachin patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Leg Shrimp - Litopenaeus Vannamei PDFDocument27 paginiWhite Leg Shrimp - Litopenaeus Vannamei PDFdevarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Communication: by Maria Moten Mba (Iobm, CBM)Document35 paginiBusiness Communication: by Maria Moten Mba (Iobm, CBM)beena100% (1)
- Presentation AquaParkDocument74 paginiPresentation AquaParkHafez MabroukÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCDA Prawn Hatchery (Financial Feasibility) - 20july2013 - FinalDraftDocument57 paginiCCDA Prawn Hatchery (Financial Feasibility) - 20july2013 - FinalDraftTaskin ShakibÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Growth of Microalgae in Shrimp Hatchery: Impact of Environment On Nutritional ValuesDocument8 paginiThe Growth of Microalgae in Shrimp Hatchery: Impact of Environment On Nutritional ValuesIOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissolved Oxygen Budget For Pacifi C White Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) Culture in Earthen PondsDocument8 paginiDissolved Oxygen Budget For Pacifi C White Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) Culture in Earthen PondsHiral PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PI - Standard - Feed Mill Standard - Issue 2.1 - 23-May-2017 PDFDocument29 paginiPI - Standard - Feed Mill Standard - Issue 2.1 - 23-May-2017 PDFRomy Bennouli TambunanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naresh Surya Mitra-ProjectDocument75 paginiNaresh Surya Mitra-ProjectSaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shrimp Farm Wastewater ManagementDocument6 paginiShrimp Farm Wastewater ManagementFIdaa BRidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business CommunicationDocument33 paginiBusiness Communicationasadguy2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood Bank Management System: Guided byDocument27 paginiBlood Bank Management System: Guided byPRATIKKUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyuthi T1237 PDFDocument224 paginiDyuthi T1237 PDFsubhadeep pramanickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquaculture Asia Pacific NewsletterDocument49 paginiAquaculture Asia Pacific NewsletterfdlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Blood Bank Management SystemDocument6 paginiOnline Blood Bank Management SystemAnish MateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live Feeds in AquaDocument5 paginiLive Feeds in Aquakamei321Încă nu există evaluări
- AquaCulture Asia Pacific Jan - Feb 18 - FA - LR174 PDFDocument72 paginiAquaCulture Asia Pacific Jan - Feb 18 - FA - LR174 PDFJoanna MordenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Nursery Anil Pages From Aqua Culture Asia Pacific - Mar Apr 18 Fa lr-5Document8 pagini8 Nursery Anil Pages From Aqua Culture Asia Pacific - Mar Apr 18 Fa lr-5api-412305171Încă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Improvement in Aquatic Food Production SystemsDocument6 paginiSustainable Improvement in Aquatic Food Production SystemsJerome Earl AmarantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good Aquaculture Practices PDFDocument5 paginiGood Aquaculture Practices PDFvikasbnsl1Încă nu există evaluări
- Business CommunicationDocument28 paginiBusiness Communicationamityscribd0% (2)
- Vannamei Shrimp FeedDocument3 paginiVannamei Shrimp Feednaturalle herbalprawnfeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqua News PDFDocument16 paginiAqua News PDFZoo BearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Quality For FishDocument2 paginiWater Quality For FishzulfiqaralimalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shrimp Feed ManagmentDocument8 paginiShrimp Feed ManagmentMohammad AhmadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Management Case Studies Two Example PDFDocument2 paginiTime Management Case Studies Two Example PDFSalman T Ghani100% (1)
- Godrej Agrovet IC Jan18Document49 paginiGodrej Agrovet IC Jan18S KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Call Letter.. PDFDocument3 paginiInterview Call Letter.. PDFswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LiptoCitro - Phytobiotics and Prebiotics: A New Alternative For Sustainable Aquaculturephytobiotics and PrebioticsDocument4 paginiLiptoCitro - Phytobiotics and Prebiotics: A New Alternative For Sustainable Aquaculturephytobiotics and PrebioticsInternational Aquafeed magazineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkalinity Management in Shrimp PondDocument3 paginiAlkalinity Management in Shrimp Pondly minh quanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination and Comparative Study of Water Quality Parameters in Shrimp Culture PondsDocument6 paginiDetermination and Comparative Study of Water Quality Parameters in Shrimp Culture PondsIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business CommunicationDocument38 paginiBusiness CommunicationAdil ChaudhryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sgeb53 Farm-Raised ShrimpDocument75 paginiSgeb53 Farm-Raised ShrimpbyrongaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkalinity and Hardness in Production PondsDocument4 paginiAlkalinity and Hardness in Production PondsWisnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probiotics in AquacultureDocument7 paginiProbiotics in AquaculturemoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquaculture Facility Certification: Finfish, Crustacean and MolluskDocument36 paginiAquaculture Facility Certification: Finfish, Crustacean and MolluskAnonymous xv5fUs4AvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Letter+ EmailDocument13 paginiBusiness Letter+ EmailAkhter AzanumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business CommunicationDocument11 paginiBusiness CommunicationMehediÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsDocument26 paginiBUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsKeshalini Perambalam0% (1)
- Organic Agriculture PDFDocument14 paginiOrganic Agriculture PDFLucky TraderÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effects of Using Seaweed On The Quality of Asian NoodlesDocument4 paginiThe Effects of Using Seaweed On The Quality of Asian NoodlesTrần Tâm PhươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Fish CultureDocument10 paginiComposite Fish CulturevickÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Institute of Engineering Computer Science EngineeringDocument32 paginiUniversity Institute of Engineering Computer Science EngineeringHimanshu NishalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Water Chemistry in FreshwasterDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Water Chemistry in FreshwasterpomodoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- AgriFutures Australia Final Report Template 2017 PDFDocument182 paginiAgriFutures Australia Final Report Template 2017 PDFNookala Raghu RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shrimp ImmunostimulantsDocument27 paginiShrimp ImmunostimulantsSyed Omer AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Make QuestionsDocument6 paginiHow To Make QuestionsKarla LintuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 2020-08-20 5f3ec1a6250aeDocument7 pagini15 2020-08-20 5f3ec1a6250aeBo Theingi ChitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Parts of SpeechDocument15 paginiThe Parts of Speechsummer wheelerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in English 10 - COT2Document6 paginiLesson Plan in English 10 - COT2Angel Rose Timtim100% (3)
- 4 Semantic RoleDocument3 pagini4 Semantic RoleNesia Riyana Cot0% (1)
- A Grammar of The Ithkuil LanguageDocument129 paginiA Grammar of The Ithkuil LanguageLeonardo Pereira VianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of EnglishDocument37 paginiStructure of Englishkyla quilicolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentence Structure TypesDocument45 paginiSentence Structure TypesMohammad Yasser MakilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toefl Module For Structure Part 1Document39 paginiToefl Module For Structure Part 1Leandro VieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument9 paginiBasic Sentence PatternsRevan GallihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yes No Questions WorkshopDocument7 paginiYes No Questions WorkshopCAROLINA DUQUE PÉREZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resumen IN Tema 12Document10 paginiResumen IN Tema 12Daniel Arana100% (1)
- Lista Verbelor NeregulateDocument14 paginiLista Verbelor NeregulateMada LinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Speaking Rules You Need To Know!: 1. Don't Study Grammar Too MuchDocument131 pagini5 Speaking Rules You Need To Know!: 1. Don't Study Grammar Too MuchUditha Wedage100% (1)
- What Is ConcordDocument6 paginiWhat Is ConcordAjisafe Jerry T-moneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1-3 LessonDocument24 paginiWeek 1-3 LessonsalditoskriiusyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEnglish - Grade 1Document204 paginiIEnglish - Grade 1Acel San JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadcast Journalism: Basics Broadcast Sentence-StructureDocument37 paginiBroadcast Journalism: Basics Broadcast Sentence-StructureMahan LagadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject-Verb Agreement IIDocument30 paginiSubject-Verb Agreement IIJayson Donor ZabalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sat Practice Test 2 Writing and Language Assistive TechnologyDocument88 paginiSat Practice Test 2 Writing and Language Assistive TechnologyAgungdeAngeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test 7 A&E PDFDocument31 paginiPractice Test 7 A&E PDFSivasaiManyapu100% (1)
- Toaz - Info b1 Participate in Workplace Communication PRDocument83 paginiToaz - Info b1 Participate in Workplace Communication PRYohannes BushoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tagmemics Analysis of Using Language Linguistic Data of BanyuwangiDocument6 paginiTagmemics Analysis of Using Language Linguistic Data of BanyuwangiDenzel Mark Arreza CiruelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject-Verb Agreement ModuleDocument16 paginiSubject-Verb Agreement Modulekhairulrasyid100% (1)
- CLASS 10 FinalDocument63 paginiCLASS 10 FinalSheyla CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senin - Ikoma Program ClassDocument17 paginiSenin - Ikoma Program ClassUmmaMarwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noun Clause NewDocument22 paginiNoun Clause NewDeyan lisyo RamadhayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 7 Directions: Read The Questions Carefully and Select The Correct AnswerDocument8 paginiEnglish 7 Directions: Read The Questions Carefully and Select The Correct AnswerDafchen Nio MahasolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relative Clauses: What Is A Relative Clause?Document11 paginiRelative Clauses: What Is A Relative Clause?EnaDumitrascuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing GuideDocument11 paginiWriting Guideanhquang151087Încă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Preparation For The TOEFL Test - New Third Edition - TextDocument613 paginiCambridge Preparation For The TOEFL Test - New Third Edition - TextFERNANDO AYALA PEREZ100% (2)
- Session Plan - ENGPLUS - Grammar & CompositionDocument7 paginiSession Plan - ENGPLUS - Grammar & Compositionmhel20010Încă nu există evaluări