Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 13 Polarization
Încărcat de
Soorav MlicDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 13 Polarization
Încărcat de
Soorav MlicDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
12/9/2012
Office Hours
Office hours are posted on the website.
Molly: Tuesdays 2-4pm Dr. Keister: Wednesdays 10am-12 Prof. Goldman: Wednesdays 2-3:30pm
All office hours are in the help room downstairs If none of these work and you need extra help before the exam, please email one of us as far in advance as you can
Scattering and Polarization
Adding vectors Polarization by reflection Polarization by scattering 3D movies Polarizers and analyzers
12/9/2012
Adding Vectors
Y Q y-component X x-component
We can decompose any polarization direction into an xcomponent and a y-component
But we dont have to use x and y. We can use any axes that are perpendicular to one another
Adding Vectors
Y Q q-component y-component X x-component p-component P
Now a polarization that was just x in the first set of axes has two components, p and q
12/9/2012
Concept Question
Which polarization has the largest x-component?
A
y
B
y
C
y
Electromagnetic Waves
The polarization is defined as the direction of oscillation of the electric field
Polarized along the z-axis
12/9/2012
Polarizing Filters
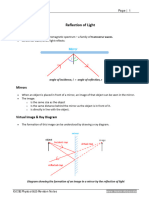
Polarization by Reflection
Review reflection and refraction:
Incident ray
AIR
GLASS
Reflected ray
Transmitted (refracted) ray
12/9/2012
Brewsters Angle
Consider the special case where the transmitted and reflected rays are at right angles to one another
Incident ray
AIR GLASS
Reflected ray
Transmitted (refracted) ray
Brewsters Angle
We can decompose the incident light into two parts: polarized in the plane of the figure, and perpendicular to the figure. We will consider the part in the plane of the figure
Incident ray Electric field oscillation Reflected ray
AIR
GLASS Transmitted (refracted) ray
12/9/2012
Brewsters Angle
The oscillating charges in the glass are what produce the reflected ray. However, they cannot radiate along their direction of travel. Thus there CANNOT be a reflected ray in this special situation.
Incident ray Electric field oscillation Reflected ray AIR GLASS Transmitted (refracted) ray
Brewsters Angle
This special angle of incidence is called Brewsters Angle For light incident at this angle, there is not reflected ray polarized in the plane of the figure.
Thus the reflected light is polarized perpendicular to the plane of the figure
12/9/2012
Brewster Windows
This effect is also used when you have polarized light and you dont want any of it to be reflected Laser light is typically polarized, so this can be used inside a laser to make sure we arent losing energy to surface reflections
Brewster window
Polarizing Sunglasses and Glare
Sunglasses lenses with a polarizer in them can eliminate specular surface reflections
12/9/2012
Polarizing Sunglasses and Glare
The light coming from everywhere else in the scene will be unpolarized Half of it will be transmitted by the glasses
Concept Question
Which polarization should sunglasses reject to eliminate glare from water puddles and other shiny surfaces? Assume the surface is horizontal, as shown in the diagram. A. Sideways B. Up and down
The reflections from the horizontal puddle will be polarized horizontally. So to eliminate glare from this surface, we want to reject the horizontal polarization, thus rejecting the surface reflections
12/9/2012
Polarizing Lenses: Example
Without Polarizing lenses
With Polarizing lenses
Polarizing Camera Filters
12/9/2012
Polarization by Scattering
Consider the following analogy: If we wiggle the rope up and down, a wave is generated in the cross rope If we wiggle the rope sideways, there is no wave generated in the cross rope
Polarization by Scattering
If we wiggle the rope at an angle, the resulting wave in the cross rope will only be Up and down component up and down
Y
Incident wave
Creates new wave in rope X Sideways component Does nothing
The resulting wave will be linearly polarized, even though the incident wave was not
10
12/9/2012
Polarization by Scattering
Light from the sun is unpolarized. It hits particles in the atmosphere, causing them to oscillate The oscillating particles then radiate light
X
Z Y
Polarization by Scattering
There will be no oscillation in the z direction The wave traveling in the y-direction will thus be polarized in the x-direction
X
Z Y
11
12/9/2012
Concept Question
Along which axis will the wave traveling in the xdirection by polarized? (views E3 and E4, circled) A. X B. Y C. Z
Polarization by Scattering
Recall the we see the blue in the sky because of light scattered by the atmosphere The light coming from points in the sky 90from the sun will be linearly polarized
When the sun is overhead, the sky near the horizon will be most polarized
12
12/9/2012
Polarization by Scattering
When the sun is at the horizon, the point of maximum polarization will be straight up in the sky. The part of the sky directly opposite the sun will be unpolarized, as will areas of the sky very near the sun Other areas of the sky will be partially polarized
Camera Filters and the Sky
13
12/9/2012
3D Movie Projection and Viewing
3D movies are actually stereograms, which create the illusion of depth by showing your eyes slightly different images This was originally done using glasses with red and cyan lenses and pictures that looked like this:
3D Movie Projection and Viewing
Modern 3D movies are projected using different polarizations instead of different colors. Without glasses, the images look like this:
14
12/9/2012
3D Movie Projection and Viewing
The two overlapping images are actually projected through a polarizing filter, alternating in rapid succession The glasses separate the polarized light and each eye sees something different, creating the illusion of depth The system actually uses circularly polarized light, so the glasses wont work like your polarized sunglasses
Polarizers and Analyzers
Polarizing filters can also be used to detect the presence of polarized light When used in this way, it is called an analyzer How is this useful?
15
12/9/2012
Polarizers and Analyzers
By changing the relative orientation of the two polarizing filters, the intensity of the light that makes it all the way through can be adjusted
Polarizers and Analyzers
16
12/9/2012
Polarizers and Analyzers
This is useful for adjusting the intensity of light without changing the parameters of the beam An aperture reduces the size of the beam Dimming a light bulb often changes the color temperature Filters are impossible to adjust continuously This is very common way to control laser beam intensity
Next Time
We will do a review, I still havent figured out the exact format I will put together a study guide for the material covered since the last exam I will send out emails with this information, so dont delete them!
17
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Office Hours Are Posted On The WebsiteDocument34 paginiOffice Hours Are Posted On The Websitesamsul bahriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11Document52 paginiChapter 11Mike JingÎncă nu există evaluări
- LightDocument37 paginiLightevanskaranja50Încă nu există evaluări
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Document45 paginiHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Praise NehumambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibrahim OmarDocument50 paginiIbrahim OmarBro OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13Document30 paginiChapter 13Rea Jane PimentelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction 2Document63 paginiReflection and Refraction 2Alaa Asim OsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LightDocument6 paginiLightNishi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- LightDocument12 paginiLightHakim AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics ProjectDocument15 paginiPhysics ProjectRaghvendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument52 paginiNotesSwati SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tom Optics 2012Document60 paginiTom Optics 2012Jasper Catabay UganizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light ReflectionandnrhehrDocument16 paginiLight ReflectionandnrhehrRaghav NegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Science Q2-Week 8 - Properties of MirrorDocument29 paginiG10 Science Q2-Week 8 - Properties of MirrorKarina GentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection of LightDocument8 paginiReflection of LightShivani ChaurasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Points - Section 9 Astrophysics - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument38 paginiKey Points - Section 9 Astrophysics - AQA Physics A-Level4buzarsaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Chapter'sDocument24 paginiLight Chapter'sPratik ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- KS4 Waves: Reflection: © Boardworks LTD 2003Document34 paginiKS4 Waves: Reflection: © Boardworks LTD 2003Isabel Iglesias QuintanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 LensesDocument19 paginiChapter 3 LensesSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optics Section Three For PreseDocument37 paginiOptics Section Three For PreseNahoo BekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter 14 and 15Document5 paginiPhysics Chapter 14 and 15lollypop1288Încă nu există evaluări
- 6 - Geometrical OpticsDocument46 pagini6 - Geometrical OpticsSergio LÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newDocument8 paginiCHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newWan SahirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirrors and Lenses: OpticsDocument28 paginiMirrors and Lenses: OpticsAdrian Paul UgaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpticsDocument84 paginiOpticsNoorzad Khalqi0% (1)
- OpticsDocument56 paginiOpticsahsan shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 paginiWP4 Light Waveswarona letangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 paginiCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScienceDocument5 paginiSciencephilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light - Class 7 - QnA - 2021Document22 paginiLight - Class 7 - QnA - 2021Rahul RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- GNR649 Lecture33 Optics TelescopesDocument36 paginiGNR649 Lecture33 Optics TelescopesR KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 14 LightDocument24 paginiCH 14 LightZainab PeerbuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS 1E Module 13.2 Plane MirrorsDocument29 paginiPHYSICS 1E Module 13.2 Plane MirrorsClaire G. MagluyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials CharacterizationDocument55 paginiMaterials Characterizationmanas sankhlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 5Document29 paginiLecture 7 5mysaustine1Încă nu există evaluări
- Light NotessDocument71 paginiLight NotessShayan RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedDocument20 paginiMirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedJoy Perez100% (1)
- Reflection of LightDocument50 paginiReflection of LightTrixie Nicole CagadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2 LightDocument11 pagini3.2 LightDhanBahadurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirrors and LensesDocument48 paginiMirrors and Lensesayjammo27Încă nu există evaluări
- ReflectionDocument25 paginiReflectionMarilyn Besawen CulanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesDocument28 paginiCBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesPRATUL SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Road Less DiffuseDocument4 paginiThe Road Less DiffusecelinelizabethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection & RefractionDocument50 paginiReflection & Refractionannette.geesiawan1Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 - 2018LDocument115 paginiChapter 9 - 2018LLujainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polarization of LightDocument12 paginiPolarization of LightShrihari DholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinoscope & RetinosDocument41 paginiRetinoscope & RetinosMiriam Mwangi100% (1)
- LightDocument17 paginiLightHunterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffraction of Light: Austen Corbitt and Lindsey StanfieldDocument11 paginiDiffraction of Light: Austen Corbitt and Lindsey StanfieldLokeswara reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TelescopeDocument11 paginiTelescopeapi-279817487Încă nu există evaluări
- Hecht - Chapter 5Document48 paginiHecht - Chapter 5JunHyoung KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 paginiKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Physics Holiday Homewory-Suchith Prabhu (Optics)Document75 paginiPhysics Holiday Homewory-Suchith Prabhu (Optics)Suchith PrabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Mechanical OpticsDocument43 paginiPractical Mechanical OpticsAdelle Katherine R. IntanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021Document61 paginiReflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021abo kooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8K LightDocument84 pagini8K LightaikamileÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 - Plane Mirrors LessonDocument23 pagini6 - Plane Mirrors LessondaregumacalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical OpticsDocument26 paginiPhysical OpticsMuhammad FajriÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesDe la EverandThe Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Visual Elements—Photography: A Handbook for Communicating Science and EngineeringDe la EverandThe Visual Elements—Photography: A Handbook for Communicating Science and EngineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 7 DuttDocument39 pagini2 7 DuttSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto Accouting ExampleDocument29 paginiAuto Accouting ExampleSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atlanta: Presentation To OAUG - SIGDocument15 paginiAtlanta: Presentation To OAUG - SIGSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inter Project BillingDocument8 paginiInter Project BillingSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intercompany Training OAUG Jan06 Vers6Document69 paginiIntercompany Training OAUG Jan06 Vers6vijaykk2447Încă nu există evaluări
- Auto Accouting ExampleDocument29 paginiAuto Accouting ExampleSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 1 GoelDocument37 pagini7 1 GoelSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fed FinancialDocument51 paginiFed FinancialSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goal Setting 2014Document7 paginiGoal Setting 2014Soorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 2 HejnaDocument130 pagini2 2 HejnaSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel Nested IF Formula ExamplesDocument13 paginiExcel Nested IF Formula Exampleseuge_prime2001Încă nu există evaluări
- Oracle Payroll Costing ConceptDocument9 paginiOracle Payroll Costing ConceptSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 1ascp1Document11 pagini4 1ascp1Soorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 1wipDocument7 pagini2 1wipSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onsite Finance Func - Support 1 Finance Func-Integration 1 Project Func - Project 1 HR Func 1 Tech - Func 3 Tech Lead 1 Tech-Func 1 TotalDocument5 paginiOnsite Finance Func - Support 1 Finance Func-Integration 1 Project Func - Project 1 HR Func 1 Tech - Func 3 Tech Lead 1 Tech-Func 1 TotalSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- All PSA Ask IT Incidents 20140707 v114.1Document12.310 paginiAll PSA Ask IT Incidents 20140707 v114.1Soorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDLC EOS CFN Quick GuideDocument2 paginiCDLC EOS CFN Quick Guideyellow_birdÎncă nu există evaluări
- M& A MckinseyDocument5 paginiM& A MckinseySoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 1bomDocument7 pagini1 1bomSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acctg Project in Oracle ReconciliationDocument124 paginiAcctg Project in Oracle ReconciliationSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle NLS SupportDocument31 paginiOracle NLS SupportSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- M& A MckinseyDocument5 paginiM& A MckinseySoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Supplier KPIDocument7 paginiBasic Supplier KPISoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acctg Project in Oracle ReconciliationDocument124 paginiAcctg Project in Oracle ReconciliationSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balaji Sivakumar: Denver, CO. 312.498.0065Document6 paginiBalaji Sivakumar: Denver, CO. 312.498.0065Soorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPM Repetitive CapacityDocument1 paginăPPM Repetitive CapacitySoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source - Bain & Co, 2GC, Balances Scorecard InstituteDocument6 paginiSource - Bain & Co, 2GC, Balances Scorecard InstituteSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPM Risk AnalysisDocument4 paginiPPM Risk AnalysisSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Costing Billing Revenue RecognitionDocument6 paginiCosting Billing Revenue RecognitionSoorav MlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lead at Your Best PDFDocument9 paginiLead at Your Best PDFDivanshu DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 - Factors Affecting Enzymes-1 PDFDocument32 pagini9 - Factors Affecting Enzymes-1 PDFVivek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Balance in Oil ReservoirsDocument6 paginiMaterial Balance in Oil ReservoirsWassef MBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Polymerization ProcessesDocument6 paginiDifferent Polymerization ProcessesMarc Dennis Angelo UgoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explosion Safety in Ethoxylation Reactors: M Braithwaite & A PekalskiDocument19 paginiExplosion Safety in Ethoxylation Reactors: M Braithwaite & A Pekalskikhali54Încă nu există evaluări
- Ab-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFDocument35 paginiAb-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFjie shiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample PDFDocument95 paginiSample PDFRobert EchavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- G 17Document18 paginiG 17Serious ExamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reverse Osmosis ReportDocument25 paginiReverse Osmosis ReportMuhammad Ishfaq100% (1)
- Vapor-Liquid Equilibria Measurements of Methane + 2-Methylpropane PDFDocument7 paginiVapor-Liquid Equilibria Measurements of Methane + 2-Methylpropane PDFTino KhamphasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Assignment - Organic ChemistryDocument7 paginiChemistry Assignment - Organic ChemistryIsaac MapulangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation Note - Tank Rev 1Document3 paginiCalculation Note - Tank Rev 1Steve WanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry in Action Note PackageDocument21 paginiChemistry in Action Note Packageapi-235471411Încă nu există evaluări
- S-H Polarimeter Polartronic-532 Eng - 062015 PDFDocument2 paginiS-H Polarimeter Polartronic-532 Eng - 062015 PDFSuresh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IR - Application - Handbook For Ammonia and CO2 ApplicationsDocument156 paginiIR - Application - Handbook For Ammonia and CO2 ApplicationsJoão Louro Barata100% (1)
- Methanol Production From Biogas: Anita Kovac Kralj and Davorin KraljDocument3 paginiMethanol Production From Biogas: Anita Kovac Kralj and Davorin KraljAndre SyahputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- European Patent Specification: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)Document9 paginiEuropean Patent Specification: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)SarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Slagging and Fouling in Boilers - Thermodyne Engineering Systems PDFDocument3 paginiWhat Is Slagging and Fouling in Boilers - Thermodyne Engineering Systems PDFkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Adsorption Equilibrium of Fructose, Glucose and Sucrose On PDFDocument6 paginiComparison of Adsorption Equilibrium of Fructose, Glucose and Sucrose On PDFDUVAN FELIPE ABRIL BLANCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Last Name, First CHE426:: F 33.54 GPMDocument5 paginiLast Name, First CHE426:: F 33.54 GPMGiancarlo HuertaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts 1Document117 paginiHeterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts 1lotannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lattice Vibrations of Manganese Oxides Part I. Periodic StructuresDocument12 paginiLattice Vibrations of Manganese Oxides Part I. Periodic StructuresMarcelo CalegaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBJEE 2016 Solution Phy ChemDocument24 paginiWBJEE 2016 Solution Phy ChemAnonymous m8oCtJBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Document44 paginiFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315AndrestorpÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Field Guide Tooptica LfiberDocument128 paginiA Field Guide Tooptica LfiberManashkc100% (1)
- Royal Ultra 865MDocument9 paginiRoyal Ultra 865Mjuanfdez42368Încă nu există evaluări
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Document39 paginiX-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Shaba ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsDocument10 paginiSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsAditya Raj SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffusivities Water in Nonpolar Gases: O'Connell, M. D. Gillespie, W. D. Krostek, and J. PrausnitzDocument5 paginiDiffusivities Water in Nonpolar Gases: O'Connell, M. D. Gillespie, W. D. Krostek, and J. PrausnitzBrayan UribeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind Map Angel MeloDocument1 paginăMind Map Angel MeloKARLA CECILIA GARCIA RIOSÎncă nu există evaluări