Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Approaches To Study of Politics
Încărcat de
Andjela Bolta KovacicTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Approaches To Study of Politics
Încărcat de
Andjela Bolta KovacicDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Approaches to study of politics (based on word document to create Notes, 26th lecture) 4 ways of studying Politics, then we go to others
later! Skeptical approach: presumes its beyond comprehension of why politics exists; or how it affects us! Holistic/ Globalistic & Molecular/ Partial approach: uses Case Studies of political systems or of some institutions; or political system to study politics. Consecutive, Concurrent and Fortuitous approach: Consecutive is a dogmatic approach and does not allow its method to be disputed! Concurrent recognizes other approaches that it sees as credible and works with them. Fortuitous approach is made by accident. Now lets look at other approaches for studying Politics. Please remember that this is not the same as the Goals or reason why we study politics!!! But how! The Goals will be briefly commented upon finally! Theleological approach: (for studying Politics!) states that rationality directs society towards a higher goal!! This idea came down form Greek philosophy, and it can create conflict in society when we try to decide what this Goal should be! Statist/ Etatist approach: proposes that the State is greater than all other interests in politics. This approach can lead to authoritarianism as was found in FACISM. Remember Benito Mussolini of Italy! Cratological approach: studies politics as the concentration of power in some political or economic group. This usually leads to dictatorships by theses groups who rule in their interest! Elitist approach: studies politics from their belief that Ancestry, Educational training, or intellectualism is the qualification to rule and direct society. It is usually criticized, but such criticism does not study or consider that there are wider political institutional processes beyond the Elites. Interest Groups approach: of studying politics, examines the competitive actors who try to influence social policy in their groups interest. Social Classes approach: of studying politics, examines economic and class struggle as problems in society. This is found in Marxism! Integrating/ Stabilizing approach: of studying politics, explores the Maintenance of Peace, as; resulting in stability and giving politics legitimacy! There is no need for strict following of any ideology or kind of political system!!
Developmental approach: to study politics, follows the development of former Colonies or States in their development in politics; since the 1960s. Fuctionalist approach: in studying politics, examines the functional distribution of scarce values. Marxist approach: in studying politics, proceeds to view the politics as world systems, where Industrialist States (Nations), keep periphery States economically underdeveloped!! ***Please remember Social Class approach above! Here Marxist approach takes economical inequality to an international level!! Institutional/ Neo-Institutional approach: studies politics from Institutional frameworks which it perceives to be responsible for sustaining democratic structure. It offers that human interactions via institutions lead to rules, norms, and shared strategies. Decisionistic approach: to study politics view Conflicts of interests in society as leading people see the other as an opponent of their ideas or interests. This soon transforms into a political nature or phenomena. I think what this means is that we have decided by our different interests to be politically in competition! and Decisionistic approach presupposes this! Please correct me if Im wrong!! Quickly!! .. Goals, of studying politics are: Cultural & Educational, Adaptive!!, Creative, Democratic & Participative, Rational & Practical, and Professional!!! Like us! Political System Solomon: Jun, what makes up a political system? Jun : Institutional, Behavioral and Normative aspects or parts are what makes up a political system! Solomon: thank you Jun!! Solomon: can anyone explain what these aspects of political system mean? Jelena : legislatures, the Presidency, parties, courts, and civil service, are examples of Institutional aspect of a political system. Bojana : .and!! the behavior of political actors within institutions or Government in the political process is the behavioral aspect!! Jun : lastly, the Normative aspect of political systems is societys values. Their values affect how institutions are created. Their values also determine if they will accept the political system as legitimate!
Professor Zoran asked me to inform you ladies that there are, 6 Types of Political Actors 1. political parties 2. traditional actors: Church, Ethnic groups, tribe, Monarchy! 3. parliamentary institutions 4. functional socio-economic actors : working class, intellectuals, managers (Jelena) 5. person(alistic) or charismatic leaders 6. bureaucratic actors; like civil service, police, military. Questions from Note. Q.1.. same as Q.1 above! (from slides) Q.2 Which approach do you prefer? Why? (meaning approach to studying politics) The Concurrent Approach of studying politics is my preferred approach because it recognizes and uses incorporates other approaches which already have existing knowledge. This existing framework can be built upon by sampling them or building upon them. (what am I talking about!!...help me here!) Q.3 What would be your objections towards functionalist approach? Functionalist approach is deterministic, as it tries to determine who gets what? How? and When? This approach will need a form of authoritarianism for it to function properly. It does not answer the question who is to decide who decides? Q.4 What do you think about marxist approach? Are the economy and the nature of ownership really determining the structure and form of a political system? The Marxist approach does not hold true today. Some countries today like Saudi Arabia have a Capitalist system, yet it has a Sharia political system. And China has what appears to be a capitalist system but operates like a centralized socialist system.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Ficha Tecnica 320D3 GCDocument12 paginiFicha Tecnica 320D3 GCanahdezj88Încă nu există evaluări
- AutoCAD Dinamicki Blokovi Tutorijal PDFDocument18 paginiAutoCAD Dinamicki Blokovi Tutorijal PDFMilan JovicicÎncă nu există evaluări
- SemiDocument252 paginiSemiGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeDocument18 paginiHierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeEmely AlmonteÎncă nu există evaluări
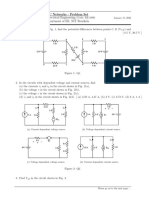
- EE1000 DC Networks Problem SetDocument7 paginiEE1000 DC Networks Problem SetAmit DipankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shopnil Tower 45KVA EicherDocument4 paginiShopnil Tower 45KVA EicherBrown builderÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrganometallicsDocument53 paginiOrganometallicsSaman KadambÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseDocument4 paginiIntelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseBabali MedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bba Colleges in IndiaDocument7 paginiBba Colleges in IndiaSumit GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope: Provisional Method - 1994 © 1984 TAPPIDocument3 paginiScope: Provisional Method - 1994 © 1984 TAPPIМаркус СилваÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Document147 paginiHP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Rinaldo loboÎncă nu există evaluări
- U.S. Pat. 9,514,727, Pickup With Integrated Contols, John Liptac, (Dialtone) Issued 2016.Document39 paginiU.S. Pat. 9,514,727, Pickup With Integrated Contols, John Liptac, (Dialtone) Issued 2016.Duane BlakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Consumer and Business Buyer BehaviorDocument47 paginiUnderstanding Consumer and Business Buyer BehaviorJia LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- KrauseDocument3 paginiKrauseVasile CuprianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.13 Regional TransportationDocument23 pagini3.13 Regional TransportationRonillo MapulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Validation of AnalyticalDocument307 paginiValidation of AnalyticalJagdish ChanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- FBW Manual-Jan 2012-Revised and Corrected CS2Document68 paginiFBW Manual-Jan 2012-Revised and Corrected CS2Dinesh CandassamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Based IVR SystemDocument17 paginiMobile Based IVR SystemIndraysh Vijay [EC - 76]Încă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper: Hygiene, Health and SafetyDocument2 paginiQuestion Paper: Hygiene, Health and Safetywf4sr4rÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPE Cisco LTE Datasheet - c78-732744Document17 paginiCPE Cisco LTE Datasheet - c78-732744abds7Încă nu există evaluări
- Aluminium Extrusion Industry in IndiaDocument3 paginiAluminium Extrusion Industry in Indiakalan45Încă nu există evaluări
- ABB Price Book 524Document1 paginăABB Price Book 524EliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Document6 paginiWHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Dewi PradnyaÎncă nu există evaluări
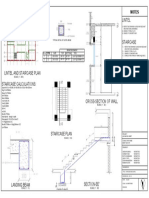
- Staircase and Lintel As-03Document1 paginăStaircase and Lintel As-03Divith B SannakkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygen BarrierDocument20 paginiOxygen BarrierKarina ArdizziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrep Q4 - Module 7Document5 paginiEntrep Q4 - Module 7Paula DT PelitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithm - WikipediaDocument34 paginiAlgorithm - WikipediaGilbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Mining - Exercise 2Document30 paginiData Mining - Exercise 2Kiều Trần Nguyễn DiễmÎncă nu există evaluări
- We Move You. With Passion.: YachtDocument27 paginiWe Move You. With Passion.: YachthatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 Apple Case Study FinalDocument18 paginiWeek 7 Apple Case Study Finalgopika surendranathÎncă nu există evaluări