Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Medical-Surgical Nursing (Gastrointestinal)
Încărcat de
アンナドミニクDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Medical-Surgical Nursing (Gastrointestinal)
Încărcat de
アンナドミニクDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
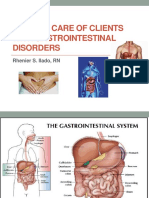
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING (GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM) I. Introduction A. Anatomy 1. Mouth 2. Esophagus: passes through the diaphragmatic hiatus. 3.
Stomach: 1500 ml Gastroesophageal junction: inlet Chyme a. Cardia b. Fundus c. Body d. Pylorus Pyloric sphincter 4. Small intestine: secretion & absorption (primary function). Segmental contraction: mixing wave; churning motion Intestinal peristalsis: propel Villi (finger-like projections): produce digestive enzymes & absorbs nutrients a. Duodenum Sphincter of Oddi (confluence of common bile duct & duodenum): control bile flow. Ampulla of Vater Nutrients, Mg, PO4, K. b. Jejunum: process of absorption begins Fats, chon, cho, Na, Cl, Mg, PO4, K. c. Ileum Terminal ileum Ileocecal valve: prevents bacterial reflux into the s.i. B12, bile salts, Mg, PO4, K. 5. Large intestine Primary purpose: absorb water and electrolytes Bicarbonate: neutralize Mucus: protect from fecal adhesion Cecum o Appendix a. Ascending colon b. Transverse colon c. Descending colon d. Sigmoid colon e. Rectum f. Anus Internal sphincter: ANS External sphincter: cerebral cortex 6. Portal venous System a. Superior mesenteric vein (s.i., cecum, ascending & transverse colon) b. Inferior mesenteric vein c. Gastric splenic d. Cystic veins e. Vena portae (enters the liver) Gastric Artery Superior mesenteric artery Inferior mesenteric artery B. Physiology 1. Digestion Enzyme/Secretion Source Carbohydrates
Salivary glands Pancreas & intestinal mucosa Intestinal mucosa Intestinal mucosa Intestinal mucosa Protein Pepsin Gastric mucosa Trypsin Pancreas Aminopeptidase Intestinal mucosa Dipeptidase Intestinal mucosa Hydrochloric acid Gastric mucosa Fat (Triglycerides) Pharyngeal lipase Pharynx mucosa Steapsin Gastric mucosa Pancreatic lipase Pancreas Bile Liver & Gallbladder Medulla oblongata: swallowing center Intrinsic factor (from gastric mucosa): combine with vitamin B12 to be absorbed in the ileum. 2. Absorption 3. Elimination Brown feces: breakdown of bile by colonic bacteria Gases: methane, hydrogen sulfide, & ammonia C. Diagnostics 1. Stool tests Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) 2. Breath tests Hydrogen Breath Test: cho absorption Urea Breath Test: carbon labeled urea, H. pylori presence 3. Abdominal Ultrasonography Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS): 8-12 hrs fasting; fat-free meal (gb studies); Ba studies after utz. 4. DNA Testing 5. Imaging Studies a. UGIT Study BaSO4: radiopaque Double-contrast studies: thick Ba suspension, give CO2 tabs in H2O after Enteroclysis: 500-1000ml of thin BaSO4 suspension into the s.i. through a duodenal tube, infuse methylcellulose in the tube after Clear liquids, NPO post mn, bowel prep b. LGIT Studiy Ba enema Double contrast/Air contrast: thicker Ba enema H2O soluble: H2O soluble iodinated contrast (gastrografin) Low residue diet 1-2 days before; clear liquids, laxatives, NPO post mn; cleansing enema @ am. c. Computed Tomography Check allergies to seafoods, serum crea, HCG levels. d. Magnetic Resonance Imaging No ferromagnetic objects, metals, jewelry; NPO 6-8 hrs;assess claustrophobia e. Positron Emission Tomography Carbon-11, fluorine-18, oxygen-15, nitrogen-13 f. Scintigraphy (Radionuclide testing) Radioactive isotopes g. Gastrointestinal Motility Studies
Ptyalin (Salivary amylase) Amylase Maltase Sucrase Lactase
6.
7.
8.
9.
Scintiscanner p.c.: measures rate of passage of radioactive substance. Colonic transit studies: capsule with 20 radionuclide markers Abd XR q 24 hrs until all markers are passed. Endoscopic procedures a. UGI Fibroscopy/Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) PillCam ESO: pill-sized instrument with 2 cameras Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): common bile, hepatic, and pancreatic ducts via ampulla of vater 8 hrs NPO; Midazolam (sedate); Atropine (reduce secretions); Glucagon (relax smooth muscles); Left lateral position b. Fiberoptic Colonoscopy Virtual colonoscopy/CT colonography Laxatives for 2 nights; fleets/saline enema @ am; polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage; clear liquids starting noon before; oral lavage solutions @ intervals over 3-4 hrs; Midazolam, Glucagon; Left fetal position c. Anoscopy, Proctoscopy, Sigmoidoscopy Warm tap H2O/fleet enema; Comfortable in left side lying with right leg bent and placed anteriorly d. Small Bowel Enteroscopy Small-caliber transnasal endoscope Push & pull endoscope methods e. Endoscopy through Ostomy Manometry & Electrophysiologic Studies Changes in intraluminal pressure & coordination of muscle activity Esophageal Manometry: esophageal motility studies; 8-12 hrs NPO; No medications that affect motility 24-48 hrs Anorectal Manometry: phosphor-soda/saline cleansing enema 1 hr prior; prone/lateral position Rectal Sensory Function Studies Electrogastrography a. Defecography Anorectal function; very thick Ba paste; fluoroscopy Gastric analysis, Gastric acid Stimulation test, pH monitoring 8-12 hrs NPO; No medications that affect gastric secretions for 24-48 hrs; no smoking @ am; Gastric samples aspirated q 15 minutes for the next hour via NGT. Histamine/Pentagastrin subQ to stimulate gastric secretions Collect gastric specimen q 15 minutes for 1 hr. Ambulatory pH monitoring: 6 hrs NPO; no medications affecting gastric secretions 24-36 hrs; probe inserted via the nares and into position 5 in above lower esophageal sphincter connected to external recording device worn for 24 hrs; Dx GERD Bernstein test: HCL via feeding tube in esophagus; evaluate complaint of acid-related pain. Laparoscopy (Peritoneoscopy) Creation of pneumoperitoneum & incision lateral to the umbilicus.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- M Vanguardia-McnpDocument11 paginiM Vanguardia-Mcnpmark OrpillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NORMAL OB-emergency-assessmentDocument3 paginiNORMAL OB-emergency-assessmentJo Hn VengzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Exam CIDocument9 paginiMaternal Exam CIRyojie RetomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtireviewDocument163 paginiAtireviewGlory Mimi0% (1)
- Goal 3: Good Health and Well-: Placed in The Center of The Public Health BagDocument26 paginiGoal 3: Good Health and Well-: Placed in The Center of The Public Health BagHed KcamÎncă nu există evaluări
- GI Practice Exam With AnswersDocument3 paginiGI Practice Exam With AnswerskcpuffsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca1 Nursing Care Management 102Document8 paginiCa1 Nursing Care Management 102raul nino MoranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Adjustment and Nursing EthicsDocument13 paginiProfessional Adjustment and Nursing EthicsGaea Angela MACATANGAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESEARCH LM - Toprank ReviewDocument34 paginiRESEARCH LM - Toprank ReviewAnna Mateo De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal Nursing Test BanksDocument2 paginiGastrointestinal Nursing Test BanksNorhana Manas50% (6)
- Review MSDocument8 paginiReview MSPatrycyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 106-Post Concept Exam: A. B. C. DDocument3 paginiNCM 106-Post Concept Exam: A. B. C. DAraw GabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NP3 ExamDocument14 paginiNP3 ExamArnie Jude CaridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CD 1Document13 paginiCD 1Don MarcusÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 31112L Midterm Exams: RationalizationDocument202 paginiNCM 31112L Midterm Exams: RationalizationWen SilverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Previous BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Document10 paginiPrevious BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Tom CuencaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gi NclexDocument8 paginiGi NclexDerek Scott Tripp67% (3)
- Recalls 7 CompilationDocument117 paginiRecalls 7 CompilationReka LambinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof Ad ch1-3Document3 paginiProf Ad ch1-3Daisy Ann IñigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compre F&EDocument6 paginiCompre F&EArcon AlvarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHN ReviewerDocument12 paginiCHN ReviewerArvi GayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoparDocument4 paginiCopar.fayefen100% (4)
- GastrointestinalDocument69 paginiGastrointestinalRodney MacansantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Patients with Neurosensory DisordersDocument18 paginiCare of Patients with Neurosensory DisordersSIJIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maladaptive Exam 1Document20 paginiMaladaptive Exam 1Wen SilverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Imbalances ExamDocument24 paginiFluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Imbalances ExamAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Nle Notes MCNDocument33 paginiNle Notes MCNjosephmary09Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Coaching - Primary Health Care - StudentDocument13 paginiFinal Coaching - Primary Health Care - StudentAshley Ann FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- GitDocument23 paginiGitHannah Meriel Del MundoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNLE IV For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part 2)Document23 paginiPNLE IV For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part 2)ASDF ASDFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Fundamentals Questions With RationaleDocument2 paginiNursing Fundamentals Questions With Rationalemae7777Încă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health & Psychiatric Nursing - QuizDocument29 paginiMental Health & Psychiatric Nursing - QuizChy ChyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingDocument22 paginiGrand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingEsarpy (Nana)Încă nu există evaluări
- OB Sample QuizDocument2 paginiOB Sample QuizYaj CruzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia ExamDocument7 paginiPedia Examefermin_lovelyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jam RodriguezDocument14 paginiJam RodriguezSandra GabasÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument18 paginiUntitledstuffednurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNLE III For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsDocument10 paginiPNLE III For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsANGELINE PALATINO100% (1)
- Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. Mark Only One Answer byDocument7 paginiInstruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. Mark Only One Answer byEden Marie FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Compre Exam Key AnswersDocument14 paginiFinal Compre Exam Key Answersmj CanilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro Post TestDocument4 paginiNeuro Post TestAhrisJeannine EscuadroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toprank Cardio Hema Post TestDocument5 paginiToprank Cardio Hema Post TestJoyce ObraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Test ArellanoDocument11 paginiPost Test ArellanoMho Pimentel VanguardiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registered Nurse Rushed to Help Injured Elderly Woman Hit by MotorcycleDocument26 paginiRegistered Nurse Rushed to Help Injured Elderly Woman Hit by MotorcycleNina OaipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing History and ConceptsDocument15 paginiNursing History and ConceptsEm IdoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Delivery Systems GuideDocument6 paginiNursing Care Delivery Systems GuideMho Pimentel VanguardiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Item Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test Drill With RationaleDocument11 pagini50 Item Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test Drill With Rationalemayal100% (1)
- TRA Psychiatric NursingDocument10 paginiTRA Psychiatric NursingGil GanibanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Practice IVDocument11 paginiNursing Practice IVapi-3718174100% (1)
- CA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Document6 paginiCA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Esmareldah Henry SirueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Care of The Patients With Altered MetabolismDocument6 paginiGastrointestinal Disorders: Care of The Patients With Altered MetabolismHazel BandayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership MGTDocument30 paginiLeadership MGTJay-Dee Evangelista PacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- NP5 Recalls5Document9 paginiNP5 Recalls5AhrisJeannine EscuadroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Text: Clear My ChoiceDocument13 paginiQuestion Text: Clear My ChoiceLylibette Anne H. CalimlimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Np2 Recalls 4Document7 paginiNp2 Recalls 4AhrisJeannine EscuadroÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Learning Midterm BSN-IV 1Document18 paginiE-Learning Midterm BSN-IV 1Ahmad BaolayyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medsurg Gi AnaphysioDocument13 paginiMedsurg Gi AnaphysioNermeen Mudsol100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing The Gastro-Intestinal System Nurse Licensure Examination Review By: John Mark B. Pocsidio, RN, Usrn, MSNDocument22 paginiMedical Surgical Nursing The Gastro-Intestinal System Nurse Licensure Examination Review By: John Mark B. Pocsidio, RN, Usrn, MSNjm_pocsidio8213Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument228 paginiNursing of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersLane Mae Magpatoc Noerrot100% (1)
- Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination May 2014 Requirements and RemindersDocument2 paginiPhilippine Nursing Licensure Examination May 2014 Requirements and RemindersアンナドミニクÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric NursingDocument2 paginiPsychiatric NursingアンナドミニクÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment and Management of Anemia - Teaching PlanDocument4 paginiTreatment and Management of Anemia - Teaching Planアンナドミニク100% (2)
- Acute Pain - Nursing Care PlanDocument9 paginiAcute Pain - Nursing Care Planアンナドミニク89% (37)
- "Is There a Role for Acupuncture in the Symptom Management of Patients Receiving Palliative Care for Cancer? A Pilot Study of 20 Patients Comparing Acupuncture with Nurse-led Supportive Care" - Journal ReactionDocument4 pagini"Is There a Role for Acupuncture in the Symptom Management of Patients Receiving Palliative Care for Cancer? A Pilot Study of 20 Patients Comparing Acupuncture with Nurse-led Supportive Care" - Journal ReactionアンナドミニクÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molar Pregnancy - Case PresentationDocument7 paginiMolar Pregnancy - Case Presentationアンナドミニク100% (1)
- Classification of Seizure and Its TypesDocument6 paginiClassification of Seizure and Its TypesアンナドミニクÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assistive Devices For Walking, Casts, and Traction CareDocument7 paginiAssistive Devices For Walking, Casts, and Traction Careアンナドミニク100% (1)
- Infection Control - Teaching PlanDocument3 paginiInfection Control - Teaching Planアンナドミニク100% (4)
- Deep Breathing and Coughing Exercises - Teaching PlanDocument3 paginiDeep Breathing and Coughing Exercises - Teaching Planアンナドミニク80% (5)
- Bariatric Case StudyDocument11 paginiBariatric Case Studyapi-346620455100% (3)
- Science8 Q4 SLM2Document14 paginiScience8 Q4 SLM2Joel Villegas33% (3)
- Bill Nye Digestions Video WorksheetDocument2 paginiBill Nye Digestions Video WorksheetDaniel EffingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates LaboratoryDocument5 paginiCarbohydrates LaboratoryJhoevina Dulce CapicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0610 w19 QP 42 PDFDocument24 pagini0610 w19 QP 42 PDFrachitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomical Atlas, Illustrative of The Structure of The Human BodyDocument386 paginiAnatomical Atlas, Illustrative of The Structure of The Human BodyAmaterasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checkpoint Biology RevisionDocument133 paginiCheckpoint Biology RevisionAngeline Ngou100% (4)
- Lesson Plan - AlcoholismDocument11 paginiLesson Plan - AlcoholismSimran Josan100% (4)
- Git PathologyDocument113 paginiGit PathologyanggitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric mucus thickness chronic gastritis fucoidanDocument6 paginiGastric mucus thickness chronic gastritis fucoidanmelz_mocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- You Are What You EatDocument31 paginiYou Are What You Eatapi-356444313Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 22 - The Digestive TractDocument32 paginiLecture 22 - The Digestive TractCarl Agape DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOTECH - 1 - Nutrition - 2013 - 1 - .PPT Filename UTF-8''BIOTECH 1 Nutrition 2013Document71 paginiBIOTECH - 1 - Nutrition - 2013 - 1 - .PPT Filename UTF-8''BIOTECH 1 Nutrition 2013Rico EdureseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Digestion Chart Nutrition 1aDocument1 paginăProtein Digestion Chart Nutrition 1aapi-242487781Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology: University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelDocument36 paginiBiology: University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Levellfwjfw;fwjf;fjÎncă nu există evaluări
- The health benefits of Islamic prayerDocument3 paginiThe health benefits of Islamic prayerrosidin_551390Încă nu există evaluări
- Review Digestive SystemDocument7 paginiReview Digestive Systemcaryl james faith abrenicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical TerminologyDocument2 paginiMedical TerminologyChrystel Mae PañaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healing Foods by Walter LastDocument29 paginiHealing Foods by Walter LastXavier Guarch100% (6)
- Shatavari - Benefits, Precautions and DosageDocument13 paginiShatavari - Benefits, Precautions and Dosagenvenkatesh485Încă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Procedures PDFDocument6 paginiPediatric Procedures PDFSanjida Mithila100% (1)
- Shackelford S Surgery of The Alimentary Tract Yeo 8 Ed 2019Document2.400 paginiShackelford S Surgery of The Alimentary Tract Yeo 8 Ed 2019Shuler007193% (29)
- Digestion and Absorption: A Summary of the 5 StagesDocument5 paginiDigestion and Absorption: A Summary of the 5 StagesRocio Guadalupe Lopez BlandonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Practice WorksheetsDocument20 paginiBiology: Practice Worksheetsদেবব্রত মন্ডলÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastritis Nursing AssistanceDocument10 paginiGastritis Nursing AssistancedirzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Digestive System ExplainedDocument33 paginiThe Digestive System ExplainedGulAwezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Ana and PhysioDocument360 paginiGen Ana and Physioanadelavega96Încă nu există evaluări
- Digestion and Absorption NotesDocument2 paginiDigestion and Absorption NotesHyazen E. DELOS SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stomach CancerDocument61 paginiStomach Cancerisaco1531012Încă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism 7th Edition Gropper Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Download Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism 7th Edition Gropper Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdatiscincnidariak6y549100% (10)