Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
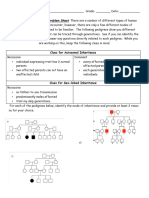
Pedigrees Assignments 2014 Students
Încărcat de
booDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pedigrees Assignments 2014 Students
Încărcat de
booDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Christie Elaine Tam UID: 20125251 !
BBMS2003 Human Genetics "e#i$ree %nal&sis' %((licati)ns
1* +)u are stu#&in$ c&stic ,i-r)sis .C/0* 1hile l))2in$ at a (e#i$ree &)u n)tice that the C/ (hen)t&(e is n)t (resent in a set ), (arents' -ut )ne )ut ), their ,i3e chil#ren has C/* 1hat can &)u c)nclu#e a-)ut C/4 a* The trait is 56lin2e#* -* The trait is aut)s)mal #)minant* c. The trait is autosomal recessive. #* 1e #) n)t ha3e en)u$h #ata t) c)nclu#e an&thin$* 2* +)u are stu#&in$ %le7an#er #isease* %ll (re3i)us (e#i$ree #ata in#icates that this #isease is an aut)s)mal #)minant trait* H)8e3er' &)u n)tice that in )ne instance the trait s2i(s a $enerati)n* I, %le7an#er #isease is aut)s)mal #)minant' 8hat is a li2el& e7(lanati)n as t) 8h& it s2i((e# a $enerati)n this )ne time4 a* S2i((in$ $enerati)ns is c)mm)n in aut)s)mal #)minant traits* -* %le7an#er #isease must -e 1009 (enetrant* c. A new mutation must have been introduced causing Alexander disease. #* :) e7(lanati)ns c)ul# e7(lain this* %le7an#er #isease cann)t -e aut)s)mal #)minant* 3* In stu#&in$ an 56lin2e# #)minant trait' &)u e7amine a ,amil& 8ith se3en chil#ren* :)ne ), the three s)ns has the trait an# all ,)ur #au$hters ha3e the trait* 1hat is a li2el& c)nclusi)n a-)ut the (arents4 a* The m)ther has the 56lin2e# #)minant trait* -* B)th m)ther an# ,ather ha3e the 56lin2e# #)minant trait* c* This mutati)n li2el& ar)se #urin$ mei)sis ), either (arent* d. The father has the X-linked dominant trait. e* 1e #) n)t ha3e en)u$h #ata t) c)nclu#e an&thin$* ;* +6lin2e# #)minant traits are #i,,erent ,r)m )ther #)minant traits -ecause the& are inherite#: a* ,r)m m)thers t) #au$hters )nl&* -* ,r)m m)thers t) s)ns )nl&* c* ,r)m ,athers t) #au$hters )nl&* d. from fathers to sons only. e* -& mechanisms n)t c)m(letel& un#erst))#*
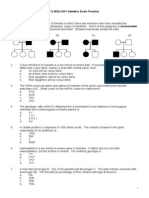
Christie Elaine Tam UID: 20125251 ! True/False
BBMS2003 Human Genetics
1. When both parents are heterozygous for an autosomal recessive trait, neither show the trait, but of their children will. T 2. A Y lin!ed trait will affect only males, appear in every generation "as long as there are sons#, and is always passed from a father to a son. T $. An % lin!ed recessive trait is never seen in females and affects of all the sons of a female carrier. F &. A proband is the first affected person that comes to the attention of a geneticist and from whom a pedigree is initiated. T
Short Answer '. (ist three characteristics of human autosomal recessive traits. the disease tends to s!ip generations) pattern of inheritance is horizontal both se*es are affected roughly 1+& of the offspring of an affected parent are affected
,. (ist four characteristics of % lin!ed recessive traits. affect mostly males) females can be affected but in a milder way than males females don-t usually e*press the condition unless the fre.uency for the mutant allele is high pattern of inheritance is diagonal or criss cross there is no direct male to male transmission
7. Use the following information for questions 21 22. Ability to roll the tongue is caused by a dominant allele. A woman is a roller, but one of her parents is not. What is the woman-s genotype/ a. homozygous dominant b. heterozygous c. homozygous recessive d. cannot be determined from this information 0he woman is e*pecting a child with a man who is a 1nonroller.2 What is the probability that their child will be a 1roller2/ a. 1+& b. 1+$
Christie Elaine Tam UID: 20125251 ! c. $+& d. 1/2 e. 2+$
BBMS2003 Human Genetics
3. 4uggest a mode of inheritance for the trait shown in the pedigree below.
autosomal dominant
5. 4everal members of a family have a very rare form of hearing disorder. You construct the following pedigree. 6ropose a li!ely mode of inheritance and 7ustify your reasoning.
autosomal dominant dominant because inheritance is in every generation) an affected individual has at least one affected parent the condition affects both se*es the mode of inheritance is not * lin!ed dominant because if it is * lin!ed dominant, every daughter of an affected male would be affected, but as the red arrows indicate, this is not the case
18. 9se the following information to draw a pedigree. :uliet and ;ob have two children, :ac! and <orma. <o one in this family is red green color blind, although :uliet sometimes has difficulty passing the color vision part of the driving test. <orma has a color blind son with 0om, who is not color blind.
Christie Elaine Tam UID: 20125251 !
BBMS2003 Human Genetics
Write their genotype for the red green color blindness gene, using % B for the normal allele and Xb for the color blindness allele. :uliet= % %b ;ob= % Y :ac!= % Y <orma= % %b 0om= % Y 4on of <orma and 0om= %bY
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Exercise 6 Pedigree Analysis 1Document10 paginiExercise 6 Pedigree Analysis 1neil gutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedigree WorksheetDocument4 paginiPedigree Worksheetleister.hidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PedigreeDocument5 paginiPedigreeEnter tainmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Genetics Problems - AnswersDocument11 paginiSolving Genetics Problems - AnswersGonzalo Estrán Buyo0% (1)
- Chapter 14: Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument4 paginiChapter 14: Mendel and The Gene IdeaBello NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- SF3 AnswersDocument24 paginiSF3 AnswersBrenda LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank 1Document36 paginiGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank 1kristygonzalezqsizobcfrj100% (22)
- En 12 Research PaperDocument13 paginiEn 12 Research PaperRozyyleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Biology Genetics Exam Practise With AnswersDocument8 pagini12 Biology Genetics Exam Practise With AnswersBrooke Gooding100% (1)
- Exe - 6Document8 paginiExe - 6Wasim HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument12 paginiPedigree AnalysisNeha PathaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 (Teacher)Document19 paginiChapter 2 (Teacher)ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFallison.young656100% (15)
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument11 paginiPedigree Analysismzunl25476Încă nu există evaluări
- GC Roadshow BioSTPM PrintDocument12 paginiGC Roadshow BioSTPM PrintazharsarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 29 12 Monohybrid Practice and Dihybrid CrossesDocument12 pagini11 29 12 Monohybrid Practice and Dihybrid CrossessandalailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Solution Manual Chapter 2Document21 paginiGenetics Solution Manual Chapter 2amarka01Încă nu există evaluări
- The Human RaceDocument26 paginiThe Human RaceJuan Carlos Medina SantanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Pedigree Problem Set1Document5 paginiAP Biology Pedigree Problem Set1Shilpa IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 2 F01Document4 paginiExam 2 F01Matin Ahmad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10A - Bio - All - Worksheets - Quizzes 4Document49 pagini10A - Bio - All - Worksheets - Quizzes 4Farzad FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 221 Final 2012Document17 pagini221 Final 2012Gizem OsmanogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch24 Answer KeyDocument9 paginiCh24 Answer Keymrmr92Încă nu există evaluări
- Embryology BY DRDocument58 paginiEmbryology BY DRshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Similarity and VariationDocument36 paginiGenetics Similarity and VariationLuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics - Human Genetic Traits LabDocument4 paginiGenetics - Human Genetic Traits Labapi-2398846040% (1)
- Quiz On Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 paginiQuiz On Mendelian GeneticsslytheraineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Escape Room 3Document6 paginiEscape Room 3jenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14Document11 paginiChapter 14homamunfatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chendi's GeneDocument10 paginiChendi's GeneGbenga AjibikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeredityDocument72 paginiHereditySein Hla KyawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Gen Inherit LabDocument4 paginiBiology Gen Inherit LabMasOom Si ChuRailÎncă nu există evaluări
- My TraitsDocument14 paginiMy Traitsapi-283922467Încă nu există evaluări
- Prob PDFDocument12 paginiProb PDFwallace120Încă nu există evaluări
- CD38 Adolescence-ParentingDocument9 paginiCD38 Adolescence-ParentingTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedigree ProblemsDocument7 paginiPedigree ProblemsImrana Iqbal0% (1)
- Introduction To GeneticsDocument10 paginiIntroduction To GeneticsZoul HasleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument21 paginiPedigree Analysischoryn modinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian Genetics 2Document35 paginiMendelian Genetics 2Joshua RaipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concussion Care: Simple Strategies, Big PayoffsDocument17 paginiConcussion Care: Simple Strategies, Big PayoffsCiiFitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics A Conceptual ApproachDocument11 paginiGenetics A Conceptual ApproachAffan HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case StudiesDocument10 paginiInquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case Studiesapi-394564312Încă nu există evaluări
- Ministry of Education of The Republic of MoldovaDocument6 paginiMinistry of Education of The Republic of MoldovaEugenia PlescaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applying Mendel's Principles: Lesson ObjectivesDocument4 paginiApplying Mendel's Principles: Lesson ObjectivesTae McLoughlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 971 Quantification and SI StudentsDocument12 pagini971 Quantification and SI StudentsMikhael O. SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Pedigree AnalysisDocument48 pagini4 Pedigree AnalysisBiologistAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 15 16Document19 pagini3 15 16api-293006069Încă nu există evaluări
- GeneticsDocument76 paginiGeneticsDonovan JenkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Advanced Test 01 Answer KeyDocument1 paginăSolutions Advanced Test 01 Answer Keyanjabeat43% (7)
- LSM1102 - Pract 7 Genetic Pedigree Analysis ExerciseDocument6 paginiLSM1102 - Pract 7 Genetic Pedigree Analysis Exercisegivena2ndchanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- The PresentDocument138 paginiThe Presentarion777Încă nu există evaluări
- The PresentDocument138 paginiThe PresentjamesosulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen AllDocument23 paginiGen Allkenma fugeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week1PodcastTranscript (Updated 1-6)Document3 paginiWeek1PodcastTranscript (Updated 1-6)dulexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Handouts (Group 12)Document7 paginiGenetics Handouts (Group 12)cianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stargenetics Tutorial 1 Ver6 PDFDocument5 paginiStargenetics Tutorial 1 Ver6 PDFdegcppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Men or Women Make Better Leaders? The Science Behind LeadershipDocument10 paginiDo Men or Women Make Better Leaders? The Science Behind LeadershipsridwieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B JordeDocument36 paginiTest Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B Jordeconsistaestivaljnajk100% (38)
- Sapiens A Graphic History The Birth of Humankind Vol 1 by Yuval NoahDocument381 paginiSapiens A Graphic History The Birth of Humankind Vol 1 by Yuval NoahSepti sawandi69% (26)
- Parts of Speech BulletinDocument10 paginiParts of Speech BulletinVino Buenaventura VersozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Hygiene Rules: Never On The Floor Chairs After Each Class and Leave To DryDocument2 paginiImportant Hygiene Rules: Never On The Floor Chairs After Each Class and Leave To DrybooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poscc TRMDocument67 paginiPoscc TRMbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Psychology Ninth EditionDocument614 paginiBiological Psychology Ninth EditionAikido Euroget100% (15)
- A Smart Girl's Guide To BoysDocument116 paginiA Smart Girl's Guide To BoysbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSocSc MH - 2021 22Document1 paginăMSocSc MH - 2021 22booÎncă nu există evaluări
- Super Minds American English Level2 Flashcards Pack Of103 Sample PagesDocument10 paginiSuper Minds American English Level2 Flashcards Pack Of103 Sample PagesbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAGC (Poly-U)Document4 paginiMAGC (Poly-U)booÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kindergarten ProgrammeDocument2 paginiKindergarten ProgrammebooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kids Box American English Level1 Students Book Sample Pages PDFDocument3 paginiKids Box American English Level1 Students Book Sample Pages PDFboo100% (1)
- Kids Box American English Level1 Students Book Sample Pages PDFDocument3 paginiKids Box American English Level1 Students Book Sample Pages PDFboo100% (1)
- Job Components QuestionaireDocument5 paginiJob Components QuestionaireKwaku OwusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- TH THDocument11 paginiTH THFista Divi AmesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACRRM PESCI Application FormDocument6 paginiACRRM PESCI Application FormChenthanKrishÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAURODONTISMDocument23 paginiTAURODONTISMDr.Neethu SalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ophthalmic Surgeon in HKDocument4 paginiOphthalmic Surgeon in HKJOHAYNIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examen Ingles Vocabulario Medico/presente SimpleDocument2 paginiExamen Ingles Vocabulario Medico/presente SimpleCesarIslasÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB - Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument51 paginiOB - Normal Labor and DeliveryJosh Matthew Rosales33% (3)
- Suck Training PDFDocument2 paginiSuck Training PDFomboÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnseDocument31 paginiAnseAndreea MihaelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover LetterDocument1 paginăCover Letterapi-405172309Încă nu există evaluări
- Pediatrician Power Point 1Document11 paginiPediatrician Power Point 1Ashley100% (1)
- Parkway Group HotelsDocument11 paginiParkway Group HotelsAryan GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSU11011Document8 paginiMSU11011Michael TarverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Appendicitis in Children - Diagnostic Imaging - UpToDateDocument28 paginiAcute Appendicitis in Children - Diagnostic Imaging - UpToDateHafiz Hari NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logic TreesDocument19 paginiLogic TreesKenneth E. LibreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laor FootDocument77 paginiLaor FootTrandafir LacramioaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shortt TaylorDocument2 paginiShortt Taylorapi-351549200Încă nu există evaluări
- C Shaped Canals in Mandi 2nd MolarsDocument4 paginiC Shaped Canals in Mandi 2nd MolarsPriya ChandnaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- You'reDocument7 paginiYou'reyihengcyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Sales Executive Consultant in Sarasota FL Resume Gail BoyerDocument2 paginiPharmaceutical Sales Executive Consultant in Sarasota FL Resume Gail BoyerGailBoyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodontal Microsurgery: Home Mcq's Discussions ContactDocument8 paginiPeriodontal Microsurgery: Home Mcq's Discussions Contactdileep9002392Încă nu există evaluări
- Competition RatiosDocument4 paginiCompetition RatiosAkshit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFSC Guide - CGO Perspectives PDFDocument225 paginiAFSC Guide - CGO Perspectives PDFAlex Clancy ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- GuideDocument58 paginiGuideNasir MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing in Australia 2010Document40 paginiNursing in Australia 2010david_haratsis50% (2)
- Job Design of Govt. HospitalDocument7 paginiJob Design of Govt. HospitalRayeshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wounds and Scars in Amputees An Overview: Sanzida HoqueDocument35 paginiWounds and Scars in Amputees An Overview: Sanzida HoqueRandi SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Practitioner Curriculum VitaeDocument2 paginiMedical Practitioner Curriculum VitaesamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MiscarriageDocument1 paginăMiscarriageJen BallesterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 008 Uk Geoff Knight Riva Star v2 1Document2 pagini008 Uk Geoff Knight Riva Star v2 1api-240710651Încă nu există evaluări