Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TOOLS USED TO OVERCOME HUMAN LIMITATIONS
Încărcat de
Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TOOLS USED TO OVERCOME HUMAN LIMITATIONS
Încărcat de
Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TOOLS USED TO OVERCOME HUMAN LIMITATIONS
NAME: MOHAMMAD ZIMAM RIFKY BIN MOHDTARMIZI CLASS: 2 DINAMIK SUBJECT: SCIENCE
BINOCULAR:
Binoculars, field glasses or binocular telescopes are a pair of identical or mirror-symmetrical telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point accurately in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal mounted military models. Many different abbreviations are used for binoculars, including glasses, nocs, binocs, noculars, binos and bins. Unlike a (monocular) telescope, binoculars give users a three-dimensional image: for nearer objects the two views, presented to each of the viewer's eyes from slightly different viewpoints, produce a merged view with an impression of depth.
MICROSCOPE:
The function of a microscope is to enlarge the visual image of small objects (a telescope, on the other hand, is enlarges the image of distant objects). More specifically, microscopes enlarge the image of objects too small to be seen by the naked eye.
TELESCOPE:
Most people would say that the main function of a telescope is to make things look larger. But in fact, the most important function is to make things look brighter! This is called itslight-gathering power. If you enlarge an object, it gets fainter because you are spreading the light over a larger image, so any telescope has a limit to how much magnification it can comfortably deliver. Another important function of the telescope is resolving power. This measures how well you can separate two objects, and of course this is related to how sharp the image looks. Both of these functions, light gathering power and resolving power, depend only on the size of the telescope (called the aperture). The light gathering power depends on the area of the main element (the objective), while the resolving power depends on the diameter
ULTRASOUND:
An ultrasound scan, also referred to as a sonogram,diagnostic sonography, and ultrasonography, is a device that uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of some part of the inside of the body, such as the stomach, liver, heart, tendons, muscles, joints and blood vessels. Experts say that as sound waves, rather than radiation are used, ultrasound scans are safe. Obstetric sonography is frequently used to check the baby in the womb. Ultrasound scans are used to detect problems in the liver, heart, kidney or the abdomen. They may also be useful in helping the surgeon when carrying out some types of biopsies. The word "ultrasound", in physics, refers to all sound with a frequency humans cannot hear. In diagnostic sonography, the ultrasound is usually between 2 and 18 MHz. Higher frequencies provide better quality images, but are more readily absorbed by the skin and other tissue, so they cannot penetrate as deeply as lower frequencies. Lower frequencies can penetrate deeper, but the image quality is inferior.
X-RAY:
The German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895. "X-ray beams can pass through your body, but they are absorbed in different amounts depending on the density of the material they pass through," according to the Mayo Clinic. Physicians have used X-rays, also known as medical imaging, since 1896, and they continue to be their most popular diagnostic method. The use of X-rays proves helpful in other areas as well, including airport security and space studies
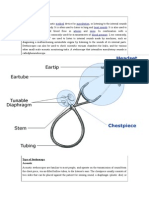
STETHOSCOPE:
The stethoscope is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to the internal sounds of an animal or human body. It is often used to listen to lung and heart sounds. It is also used to listen to intestinesand blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used for measurements of blood pressure. Less commonly, "mechanic's stethoscopes" are used to listen to internal sounds made by machines, such as diagnosing a malfunctioning automobile engine by listening to the sounds of its internal parts. Stethoscopes can also be used to check scientific vacuum chambers for leaks, and for various other smallscale acoustic monitoring tasks. A stethoscope that intensifies auscultatory sounds is called phonendoscope.
HEARING AIDS:
A hearing aid is an electroacoustic device which is designed to amplify sound for the wearer, usually with the aim of making speech more intelligible, and to correct impaired hearing as measured by audiometry. In the United States, Hearing aids are considered medical devices and are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Ordinary small audio amplifiers or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids". Earlier devices, known as ear trumpets or ear horns,[1][2] were passive funnel-like amplification cones designed to gather sound energy and direct it into the ear canal. Similar devices include the bone anchored hearing aid, and cochlear implant.
EAR PHONE:
An earphone device having composite functions at least has an earphone shell body, a loudspeaker, and an adjustment component. Several outer sound holes are disposed on the outer side of the earphone shell body. The loudspeaker is fixed in the earphone shell body. The loudspeaker is arranged outwards. The adjustment component is disposed on the earphone shell body. There are several adjustment holes corresponding to the outer sound holes of the earphone shell body on the adjustment component. The adjustment holes of the adjustment component can be controlled to be opposite to or be staggered with the outer sound holes of the earphone shell body. The earphone device is comfortable for use and can reduce pathological changes in ear and hearing decay to keep the human body healthy. Moreover, the earphone device has the functions of earphone, sound amplifier, and sound box.
THANK YOU
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Atlas of Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound: With Anatomic and MRI CorrelationDe la EverandAtlas of Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound: With Anatomic and MRI CorrelationÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroscopeDocument6 paginiMicroscopeLucas ComptonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limitations of sight and hearing overcome with devicesDocument11 paginiLimitations of sight and hearing overcome with devicesLim Yung KienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devices To Overcome The Limitations of Sight and HearingDocument18 paginiDevices To Overcome The Limitations of Sight and Hearingyihanwong100% (1)
- A Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerDocument7 paginiA Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerBryan WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devices Used To Overcome Limitation of Sight and HearingDocument6 paginiDevices Used To Overcome Limitation of Sight and HearingTing Hui CheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Auscultation Heart Sounds Intestines Arteries Veins Sphygmomanometer Blood PressureDocument3 paginiMedical Auscultation Heart Sounds Intestines Arteries Veins Sphygmomanometer Blood Pressure李炫苇Încă nu există evaluări
- Devices To Overcome The Limitations of Sight (Adik)Document11 paginiDevices To Overcome The Limitations of Sight (Adik)Saridah IshakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology For Engineers Module 3Document40 paginiBiology For Engineers Module 3moaaz ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is UltrasoundDocument5 paginiWhat Is UltrasoundEva VictoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology For Engineers, Unit-IVDocument33 paginiBiology For Engineers, Unit-IVtharunn6364Încă nu există evaluări
- Listening to the Body with a StethoscopeDocument1 paginăListening to the Body with a StethoscopeAnggis SarjonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound Imaging Explained: Uses and Applications of Medical UltrasoundDocument19 paginiUltrasound Imaging Explained: Uses and Applications of Medical UltrasoundAli AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- General UltrasoundDocument114 paginiGeneral Ultrasoundgilbert centerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Us PhysicsDocument7 paginiUs PhysicsRathi TanusreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Ultrasound WorksDocument6 paginiHow Ultrasound WorksDoc AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group #1 UltrasoundDocument10 paginiGroup #1 UltrasoundAbdul RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentasi Dan Teknologi KedokteranDocument51 paginiInstrumentasi Dan Teknologi KedokteranalfianhasbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buku Scrap Science Form 2Document10 paginiBuku Scrap Science Form 2Faizah FizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 - BIOLOGYDocument36 paginiModule 4 - BIOLOGYPunith PuniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working of The UltrasoundDocument8 paginiWorking of The UltrasoundRagnar RagnarsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- المستندDocument11 paginiالمستندNoor S NajemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Member Bibliographic Studies on Medical Imaging TechniquesDocument6 paginiMember Bibliographic Studies on Medical Imaging TechniquesArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 AnyphyDocument3 pagini101 AnyphyJonah SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- B-Scan Part 1Document41 paginiB-Scan Part 1Aisha TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sainstechnological Devices Which Are Suitable For Overcoming The Limitations of Sight and HearingDocument32 paginiSainstechnological Devices Which Are Suitable For Overcoming The Limitations of Sight and HearingAthirah YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument4 paginiBiologykirosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Diagnostic InstrumentsDocument32 paginiBasic Diagnostic InstrumentsBethelhem HabtamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21BE45 - Module 4 - Study MaterialDocument29 pagini21BE45 - Module 4 - Study MaterialEdu techÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Biomedical Instruments and Their UsesDocument12 paginiTypes of Biomedical Instruments and Their Usesgzb0120% (2)
- Folio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and HearingDocument19 paginiFolio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and HearingMohamad Rizal MukhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Electronic StethoscopeDocument85 paginiProject Report On Electronic StethoscopeMohit Rana87% (23)
- Medical ImagingDocument7 paginiMedical ImagingAlejandra AlfaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is General Ultrasound ImagingDocument12 paginiWhat Is General Ultrasound Imagingfatah.ozilÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS MANUAL MEDICAL-WPS OfficeDocument5 paginiTUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS MANUAL MEDICAL-WPS OfficeYanti Puspita SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology ProjectDocument13 paginiBiology ProjectHome MarufÎncă nu există evaluări
- What is sonar and ultrasound scanningDocument17 paginiWhat is sonar and ultrasound scanningalias_acaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mikayla Reeves Phys 1010Document6 paginiMikayla Reeves Phys 1010api-316339123Încă nu există evaluări
- SP 4f – Ultrasound (Notes)Document2 paginiSP 4f – Ultrasound (Notes)nisalielisha rodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Diagnostic ProcedureDocument26 paginiRespiratory System Diagnostic Procedurejefroc75% (4)
- BAB IIRadiology Is A Specialty That Uses Medical Imaging To Diagnose and Treat Diseases Seen Within The BodyDocument7 paginiBAB IIRadiology Is A Specialty That Uses Medical Imaging To Diagnose and Treat Diseases Seen Within The BodySupian Ats-tsauriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound Fact Sheet 508Document2 paginiUltrasound Fact Sheet 508CuuzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound Imaging Basics ExplainedDocument14 paginiUltrasound Imaging Basics Explainedpriyadharshini100% (1)
- Nama: Saifullah Ali NPM: 720621444 Kelas: 2B: How Ultrasound WorksDocument3 paginiNama: Saifullah Ali NPM: 720621444 Kelas: 2B: How Ultrasound WorksSaifullah AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- UltrasonographyDocument4 paginiUltrasonographyapi-242647312Încă nu există evaluări
- The Astonishing Acupuncture System The Chinese OverlookedDocument21 paginiThe Astonishing Acupuncture System The Chinese OverlookedLuiz AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound - Pelvis: What Is Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging?Document8 paginiUltrasound - Pelvis: What Is Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging?Trandafir LacramioaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Reflection of Sound and Applications of UltrasoundDocument9 paginiMultiple Reflection of Sound and Applications of UltrasoundEkashmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. John Stuart ReidENDocument2 paginiDr. John Stuart ReidEN刘育楠100% (1)
- KymographDocument11 paginiKymographJolene Keigh HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Dynamics Sound Applications: Name: Mohamed Mostafa Elsaid Salem Sec: 10Document8 paginiGas Dynamics Sound Applications: Name: Mohamed Mostafa Elsaid Salem Sec: 10mohamed352Încă nu există evaluări
- Technological Devices Which Are Suitable For Overcoming TheDocument11 paginiTechnological Devices Which Are Suitable For Overcoming TheNur Ckin AshiqinÎncă nu există evaluări
- PBLDocument35 paginiPBLSerena LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory and Motor SystemDocument12 paginiSensory and Motor SystemrobertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Boston Ear Maps Orthopaedic Organ Heart WebDocument8 pagini06 Boston Ear Maps Orthopaedic Organ Heart WebWilliam Tell100% (2)
- 06 Boston Ear Maps Orthopaedic Organ Heart Web PDFDocument8 pagini06 Boston Ear Maps Orthopaedic Organ Heart Web PDFYouvanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound Lecture NotesDocument13 paginiUltrasound Lecture NotesLauren Temple100% (1)
- Acoustic PaperDocument4 paginiAcoustic PaperAhmed El SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasunetele ReferatDocument5 paginiUltrasunetele ReferatAde75% (8)
- SMK Sultan Ibrahim 1 Tingkatan 1 Amanah 2017 Student ListDocument1 paginăSMK Sultan Ibrahim 1 Tingkatan 1 Amanah 2017 Student ListMohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kertas 1 F4Document22 paginiKertas 1 F4Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Electric MotorDocument2 paginiSimple Electric MotorMohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skema Physics p123 SPM 2013 MRSMDocument21 paginiSkema Physics p123 SPM 2013 MRSMMohd Tarmizi Mohd Nor0% (1)
- Phy 2Document0 paginiPhy 2Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Messi: The Greatest Football Player TodayDocument8 paginiMessi: The Greatest Football Player TodayMohd Tarmizi Mohd Nor0% (1)
- Minit Sains 3 2010Document4 paginiMinit Sains 3 2010Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kertas 1 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2010 - SoalanDocument27 paginiKertas 1 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2010 - SoalanMuhamad FarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramah Kimia 2012Document85 paginiCeramah Kimia 2012Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cam Module 5 RomDocument28 paginiCam Module 5 Romnamitha rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apple Group 4Document18 paginiApple Group 4Rumbidzaishe MunyanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- L) Screen Printing: Document 2, Health and Safety: Pages 6-7Document10 paginiL) Screen Printing: Document 2, Health and Safety: Pages 6-7GeorgiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hose Fittings and Adapters CatalogDocument40 paginiHose Fittings and Adapters CatalogBk TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precast Mix Design 2020Document2 paginiPrecast Mix Design 2020Dilhara WickramaarachchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration PDFDocument12 paginiIntegration PDFMd. Raihan Habib Rafi Mazumder 191-35-2768Încă nu există evaluări
- Modular Simulation Software Development For Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines Based On MATLAB SimulinkDocument7 paginiModular Simulation Software Development For Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines Based On MATLAB SimulinkĐinh Quốc TríÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drone PilotDocument1 paginăDrone PilotHIKAYAT PICTURESÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Heads Weekly Accomplishment Report RosendoDocument20 paginiSchool Heads Weekly Accomplishment Report RosendoROSELLE NEVADOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indo Asian Retail Price List 2019Document32 paginiIndo Asian Retail Price List 2019vinay kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ekinops PM - Lc5-Mp4-D: 500G Line Module For ETS Compact ChassisDocument2 paginiEkinops PM - Lc5-Mp4-D: 500G Line Module For ETS Compact ChassisBhargav SomepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accenture Coding HandoutDocument94 paginiAccenture Coding HandoutAishwarya km 4GW19CS003100% (2)
- Script 1isp Ega ChanelDocument3 paginiScript 1isp Ega Chanelyama yamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 BCP-DCPDocument19 pagini6 BCP-DCPWriter CourseÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument3 paginiReadmepavelscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- WAT530 04r3Document18 paginiWAT530 04r3Comptoir ChromatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LISTA DE PRECIOS 2020 ActualizadaDocument10 paginiLISTA DE PRECIOS 2020 ActualizadaPaulino BuenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPS Baldor IDLC2000-2M GensetDocument4 paginiGPS Baldor IDLC2000-2M GensetJuvencio MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenges and Applications of Large Language Models: Desi GN BehaviorDocument72 paginiChallenges and Applications of Large Language Models: Desi GN BehaviorAlex DiermeierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Account Usage and Recharge Statement From 02-Dec-2021 To 08-Dec-2021Document2 paginiAccount Usage and Recharge Statement From 02-Dec-2021 To 08-Dec-2021Kartik Jain ASCO, NoidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windpower Engineering and Development February 2022Document52 paginiWindpower Engineering and Development February 2022João BrazãoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Kafka PDFDocument58 paginiIntro To Kafka PDFBarathÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTS - The Virtual Self PDFDocument2 paginiUTS - The Virtual Self PDFSHAIRA PAMAYLAONÎncă nu există evaluări
- File Input-Output in CPPDocument68 paginiFile Input-Output in CPPEsubalew ChekolÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM in BanksDocument31 paginiCRM in Banksauthori71% (7)
- AI Automates Mundane Legal Tasks But Can't Replace Human LawyersDocument5 paginiAI Automates Mundane Legal Tasks But Can't Replace Human LawyersKartikey Gupta100% (1)
- ABREVIAÇÃO DE PINOS - PinAbbreviationsDocument9 paginiABREVIAÇÃO DE PINOS - PinAbbreviationsjampcarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unified Library Application Unit 5Document11 paginiUnified Library Application Unit 5charan vedantamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infiltrated Heat Load (RSH+LSH) KW 14.38527 0.89785488959Document2 paginiInfiltrated Heat Load (RSH+LSH) KW 14.38527 0.89785488959RamKumarSharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ewp Lab QPDocument2 paginiEwp Lab QPHarimadhavareddy YenireddyÎncă nu există evaluări