Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Test 4: Electronic Structure and Periodic Table
Încărcat de
Dai Fei PohDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Test 4: Electronic Structure and Periodic Table
Încărcat de
Dai Fei PohDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TEST 4: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE and PERIODIC TABLE 3.
1 The diagram sho)s the energy level diagram for an atom. <ra) all the possi#le electron jumps from e&cited states leading to the emission of light. <ra) the line spectrum you )ould e&pect to see indicating the direction of increasing frequency.
4.1
The energy of the line at the convergence limit of the Lyman series in the H-atom spectrum corresponds to the largest energy jump on the energy level diagram. This energy is equal to the ionisation energy for the H-atom: the energy needed to remove an electron from an isolated atom forming an H ! ion. "f the frequency of the line is found to #e 3.$% & 1'1( s-1 calculate the energy associated )ith it using the formula: E=hx )here *lanc+,s constant h - ...3 & 1'-34 / s0 1vogadro constant - ..'$ & 1'$3
2onvert your ans)er to +/ and multiply #y 1vogadro,s constant to give your ans)er in +/ mol-1. 1.1 a. 3sing o&ygen atom as an e&le e&plain the follo)ing: i. Hund,s 4ule ii. *auli 5&clusion *rinciple. 6rite do)n the electronic configuration of the iron atom 7e and the iron8""9 ion 7e$!. 1 cation A2+ has the follo)ing electronic configuration: 1s$ $s$ $p. 3s$ 3p. a. 5&plain the term :cation,. #. Ho) many electrons )ould atom A consist of;
1
1.3 1.(
c. 6rite do)n the electronic configuration for atom A. d. 5&plain )hy atom A forms an ion )ith a charge of !$. e. "dentify element A. $.1 $.$ 1.1 1.3 $.1 a. <escri#e the general trend in electrical conductivity across *eriod $. #. <oes *eriod 3 sho) the same trend; Ho) does the trend in electrical conductivity across a period relate to the structure of the elements; <escri#e the general trend in melting points across *eriods $ and 3. The atoms in diamond and in o&ygen are joined #y covalent #onds. 6hy is there such a huge difference in melting point #et)een these t)o elements; a. The si=e of the atoms decreases across each of the periods. 6hy does this happen; #. The 1st ionisation energy of magnesium is greater than that of sodium in the same period #ut smaller than that of #eryllium in the period a#ove it. 5&plain this considering the proton num#er and electronic configuration in these atoms.
The diagram a#ove sho)s the valence electronic configuration of an element in the ground state. a. "dentify the element and state its proton num#er. #. 6rite similar diagrams to sho) the valence electronic configuration of the ion formed )hich has a charge of !3. 3.$ >ive an e&planation for each of the o#servations regarding the ioni=ation energies of the d-#loc+ elements from ?candium 8?c9 to @inc 8@n9. a. There is little change in the ionisation energy of the elements from titanium to copper. #. The second ionisation energy of copper is higher than e&pected. c. 2r has the highest $nd ionisation energy An has the highest 3rd ionisation energy and 7e has the highest 4th ionisation energy of the elements from ?c to @n. d. The 3rd ionisation energy of 7e is lo)er than e&pected.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsDe la EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesDe la EverandAmorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Physics Unit 1lecture Notes PhysicsDocument33 paginiLecture Notes Physics Unit 1lecture Notes PhysicsAlex PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voltage and CurrentDocument92 paginiVoltage and CurrentDominique Tuble EcleoÎncă nu există evaluări
- III The Sommerfeld Free Electron Theory of Metals 2000 Solid State PhysicsDocument25 paginiIII The Sommerfeld Free Electron Theory of Metals 2000 Solid State PhysicsChristian Julian ForeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document19 paginiLecture 3John Wanyoike MakauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electron ConfigurationDocument9 paginiElectron ConfigurationShuganthi MasilamanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem1 1 - Atomic StructureDocument5 paginiChem1 1 - Atomic Structureapi-247243068Încă nu există evaluări
- 02 Bonding (1, A)Document16 pagini02 Bonding (1, A)Pramudith LiyanageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 1 Revision Guide Atomic StructureDocument5 paginiMod 1 Revision Guide Atomic StructurePascal Indy EmeryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electron Configuration 123Document34 paginiElectron Configuration 123Gelo AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electron ConfigurationDocument30 paginiElectron ConfigurationShiela Dianne Caliwanagan100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Chemical BondingDocument10 paginiChapter 4: Chemical BondingdanielmahsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Unit 2 Notes ChemDocument81 paginiComplete Unit 2 Notes ChemJack jacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical BondingDocument12 paginiChemical Bondingrockworld009Încă nu există evaluări
- ChemLab - Chemistry 6 - Spectrum of The Hydrogen Atom - Chemistry & BackgroundDocument13 paginiChemLab - Chemistry 6 - Spectrum of The Hydrogen Atom - Chemistry & BackgroundAt TanwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 3Document2 paginiTutorial 3AbhinavJainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ionisation Energy PDFDocument28 paginiIonisation Energy PDFAinthu IbrahymÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - I P-N Junction Diode 1Document23 paginiUnit - I P-N Junction Diode 1Sandeep Babu VannempalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronegativity and Relativistic EffectsDocument13 paginiElectronegativity and Relativistic Effectsadley35Încă nu există evaluări
- Free Electron TheryDocument7 paginiFree Electron TheryRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microwave Semiconductor Device Technologies 4. Energy Bands and Charge CarrierDocument11 paginiMicrowave Semiconductor Device Technologies 4. Energy Bands and Charge Carriersushil4056Încă nu există evaluări
- Unidad 1. Tabla PeriodicaDocument17 paginiUnidad 1. Tabla PeriodicaAlrisha6Încă nu există evaluări
- Honors Electrons Activity Worksheet: Part One-Orbital NotationDocument2 paginiHonors Electrons Activity Worksheet: Part One-Orbital NotationYungxLWM0% (1)
- Atom ThryDocument6 paginiAtom ThrySumathi SrinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
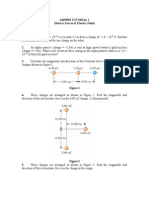
- Asp0503 Tutorial 1 Electric Forces & Electric Fields Coulomb's Law 1Document3 paginiAsp0503 Tutorial 1 Electric Forces & Electric Fields Coulomb's Law 1airatkemuningÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lectron Iffraction: PhysicsDocument13 paginiLectron Iffraction: PhysicsZeen MajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 1311 Problem Set 1Document5 paginiChemistry 1311 Problem Set 1qabusalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Periodic Table Note 1Document24 paginiThe Periodic Table Note 1Thuran NathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 AnlatDocument17 paginiCH 1 Anlatmusa ozanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure WorksheetsDocument5 paginiAtomic Structure WorksheetsYến Nhi LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Chem Target Sheet U 1Document7 paginiEdexcel Chem Target Sheet U 1Ruwan BandaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document32 paginiLecture 2John Wanyoike MakauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semi ConductorDocument50 paginiSemi ConductorVibhor KaushikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che 126 - (Prof Woods and Dr. Omoreghie's Part)Document541 paginiChe 126 - (Prof Woods and Dr. Omoreghie's Part)BishopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matriculation Physics Electric Current and Direct Current CircuitDocument118 paginiMatriculation Physics Electric Current and Direct Current Circuitiki292Încă nu există evaluări
- Periodic PropertiesDocument22 paginiPeriodic Propertiessecondary twoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material de Clase 3 PDFDocument57 paginiMaterial de Clase 3 PDFPiero ZeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edited - Riah Kim - Investigating Periodic Trends Through GraphsDocument5 paginiEdited - Riah Kim - Investigating Periodic Trends Through Graphsapi-342226911Încă nu există evaluări
- Synchrotron NotesDocument10 paginiSynchrotron NotesjarjarbrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material 2Document22 paginiMaterial 2zeekumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bohr 3 - PhilMag 1913Document19 paginiBohr 3 - PhilMag 1913Dr. John BeveridgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure: ObjectivesDocument20 paginiAtomic Structure: Objectivesgeoboom12Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Electronic ConfigurationDocument28 pagini2 Electronic ConfigurationCarlo James SablanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr ModelDocument13 paginiThe Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr Modeljuso_jusicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Exercises: Sections 9.7Document9 paginiHomework Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Exercises: Sections 9.7BettyxhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Les 1. Basic Concepts. AbstractDocument29 paginiLes 1. Basic Concepts. AbstractRojin KaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuracion ElectronicaDocument3 paginiConfiguracion ElectronicaKmilo OspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Sample of Iron From A Meteorite Was Found To Contain The Isotopes 54fe, 56fe and 57feDocument5 paginiA Sample of Iron From A Meteorite Was Found To Contain The Isotopes 54fe, 56fe and 57feJithesh ParambathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro-Chemical Reaction Engineering: Electrode ReactionsDocument28 paginiElectro-Chemical Reaction Engineering: Electrode ReactionsJyothsna AnnepuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument14 pagini2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureAdwaar HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Chapter 7 PMRDocument10 paginiScience Chapter 7 PMRSuntharan MuniandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM.2. Charge To Mass Ratio of The Electron: 1. Purpose: 2. ApparatusDocument5 paginiIM.2. Charge To Mass Ratio of The Electron: 1. Purpose: 2. ApparatusZeen MajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- POGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsDocument11 paginiPOGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsCrumb BanditÎncă nu există evaluări
- POGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsDocument10 paginiPOGIL Electron Configuration and Orbitals776pmsfq2fÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical ElectronicsDocument9 paginiPhysical Electronicsatem assane jean jacquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity: Solution of Intext Questions (NCERT Book) Part:-1Document4 paginiElectricity: Solution of Intext Questions (NCERT Book) Part:-1jots2Încă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Geometry Lab 12 6 12 Tenure PortfolioDocument5 paginiMolecular Geometry Lab 12 6 12 Tenure Portfolioapi-249441006Încă nu există evaluări
- Early Quantum PhenomenaDocument5 paginiEarly Quantum PhenomenaJonathan Briones Mses MsphyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 5Document2 paginiTest 5Dai Fei PohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 2: State of Matter (Gas) and Electrochemistry (Ans)Document7 paginiTest 2: State of Matter (Gas) and Electrochemistry (Ans)Dai Fei PohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 3: State of Matter (Liquid and Solid) and Rate of Reaction (Ans)Document5 paginiTest 3: State of Matter (Liquid and Solid) and Rate of Reaction (Ans)Dai Fei PohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDocument4 paginiTest 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDai Fei PohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1: Matter and ThermochemistryDocument4 paginiTest 1: Matter and ThermochemistryDai Fei PohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geochemistry IntroductionDocument25 paginiGeochemistry Introductionkristiano97100% (1)
- Klimov Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactors PDFDocument417 paginiKlimov Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactors PDFHarry SmartÎncă nu există evaluări
- MKUn - CHE 101.6 - 101.18 - Fall 2022Document3 paginiMKUn - CHE 101.6 - 101.18 - Fall 2022Sne HaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subatomic StructuresDocument18 paginiSubatomic StructuresArlyn RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Examination 2021-2022-CombinedDocument15 paginiAnnual Examination 2021-2022-CombinedElectronic4 Arts3Încă nu există evaluări
- Science (Physics, Chemistry) : Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument16 paginiScience (Physics, Chemistry) : Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelKelvin BwalyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science ScrapbookDocument13 paginiScience ScrapbookAbbi Nelson50% (2)
- Engineering Materials: Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bounding Dr. Aneela Wakeel (Lec-2)Document42 paginiEngineering Materials: Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bounding Dr. Aneela Wakeel (Lec-2)Jawad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Let's Explore Electricity Basics!: Instructor GuideDocument10 paginiLet's Explore Electricity Basics!: Instructor GuiderezhabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISC Chemistry XI RevisedDocument10 paginiISC Chemistry XI RevisedShashvita RatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure Basic Information FullDocument45 paginiAtomic Structure Basic Information FullSai KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Atomic Structure 2018 Tut Soln LMSDocument17 paginiH2 Atomic Structure 2018 Tut Soln LMScalebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter2 Review BDocument12 paginiChapter2 Review Bapi-235052534Încă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint: Science 1113/01Document20 paginiCambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint: Science 1113/01Mazanda YalinduaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clarisa Unit 2Document10 paginiClarisa Unit 2Noviana TevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Important Questions and Answers, Entrance Exam, Study Material and Notes For All Subject - BrainKartDocument24 paginiPhysics - Important Questions and Answers, Entrance Exam, Study Material and Notes For All Subject - BrainKartKali Thaash100% (1)
- CH 10 WorksheetsDocument4 paginiCH 10 Worksheetsadaglio001Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry F4 C2Document9 paginiChemistry F4 C2nicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The History of Science From 1946 To The 1990sDocument196 paginiThe History of Science From 1946 To The 1990sBert LievrouwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Energy, Gravity and The AetherDocument17 paginiFree Energy, Gravity and The AetherCarlita MontrossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paddington Academy: Topic 1 Test Mark SchemeDocument5 paginiPaddington Academy: Topic 1 Test Mark SchemeRahi FurqanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kertas 1 Pat 2023Document15 paginiKertas 1 Pat 2023Nazirah binti HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life The Science of Biology 9th Edition Sadava Test BankDocument35 paginiLife The Science of Biology 9th Edition Sadava Test Banknitrymediceanpgyt5100% (21)
- Chemistry: Textbook For Class XIDocument10 paginiChemistry: Textbook For Class XIrekha_1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Spectroscopy & ChromatographyDocument23 paginiSpectroscopy & ChromatographyKamrul Alam MasumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Longman RedDocument28 paginiLongman ReddinopatilauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mature Student AssessmentDocument26 paginiMature Student AssessmentPankaj Mandal100% (1)
- The Electronic Structure of An Atom: Chapter 2Document18 paginiThe Electronic Structure of An Atom: Chapter 2Syamimi MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 Most Important Chemistry and Biology Questions For CDS ExamDocument322 pagini300 Most Important Chemistry and Biology Questions For CDS Exam3021 Akash joshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Atom Class 11Document74 paginiStructure of Atom Class 11Komal VermaÎncă nu există evaluări