Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Marketing Management Notes For Module 8
Încărcat de
Aniruddh ChavanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Marketing Management Notes For Module 8
Încărcat de
Aniruddh ChavanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
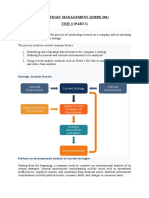
MARKETING MANAGEMENT Sub Code: 10MBA16 MODULE 8 (6 Hours) Marketing Planning: Meaning, Concepts of Marketing plan, Steps involved
in planning. Marketing Organisation: Evolution of Modern Marketing department, Factors influencing the size of the marketing organisation, various types of marketing structures/organisation Marketing Audit: Meaning, Features of marketing audit, various components of marketing audit. Planning is a managerial activity which is a basic requirement for all organizations. Key elements of planning activity1. Timing 2. Tasks 3. Responsibility 4. Follow-up 5. Budgeting Levels of Planning Strategic Planning Marketing Planning Tactical Planning Basic elements of Strategic Planning 1. Mission 2. Strategic Business Units 3. Objectives 4. Strategic Planning Tools 5. Marketing Plans General Electric (GE) Portfolio of SBUs 1. 2. 3. 4. GE Appliances 5. GE Lighting GE Aircraft engines 6. GE Plastics GE Capital 7. GE Transportation Systems GE Global Services 8. GE Medical Systems
Marketing Planning A marketing plan is a written document containing the guidelines for the business centres marketing programmes and allocations over the planning period. Objectives of a Marketing Plan1. To define the current situation facing the product. 2. To define problems and opportunities facing the business. 3. To establish objectives.
4. 5. 6. 7.
To define the strategies and programmes necessary to achieve the objectives. To pinpoint responsibility for achieving product objectives. To encourage careful and disciplined thinking. To establish a customer-competitor orientation.
Steps in Marketing Planning
Analysis of the market situation
Developing marketing objectives
Formulation of marketing strategies
Preparing action programmes and Budgets
Developing Control Procedures
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Components of Marketing Plan Executive summary Situation analysis Threats and opportunities analysis Objectives Marketing strategy Marketing action programmes Budget allocation Monitors and controls Annual Marketing Planning
It is the blueprint for a years marketing activity for a specified organizations division, department, a brand, a product line or a SBU. Purpose of the Annual Plan 1. It summarizes the marketing strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve specified objective in the coming year.
2. The annual plan also points to what needs to be done regarding the other steps in the management process. 3. The annual plan outlines who is responsible for which activities, when they are to be carried out, and how much time and money can be spent.
SWOT Analysis
Strategic Business Unit (SBU) It is a single business or collection of related businesses that can be planned separately from the rest of the company. It has its own set of competitors. It has a manger who is responsible for strategic planning & profit performance & who controls most of the factors affecting profit. BCG Model Growth-share matrix Market growth rate on the vertical axis indicates the annual growth rate of the market in which the business operates. Market growth serves as proxy for industry attractiveness. Relative market share (horizontal axis) refers to the SBUs market share relative to that of its largest competitor. Market share serves as proxy for competitive advantage. Growth-share matrix is divided into 4 cells, each indicating a different type of business.
Cash cows are units with high market share in a slow-growing industry. These units typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the business. They are regarded as staid and boring, in a "mature" market, and every corporation would be thrilled to own as many as possible. They are to be "milked" continuously with as little investment as possible, since such investment would be wasted in an industry with low growth. Dogs, or more charitably called pets, are units with low market share in a mature, slowgrowing industry. These units typically "break even", generating barely enough cash to maintain the business's market share. Though owning a break-even unit provides the social benefit of providing jobs and possible synergies that assist other business units, from an accounting point of view such a unit is worthless, not generating cash for the company. They depress a profitable company's return on assets ratio, used by many investors to judge how well a company is being managed. Dogs, it is thought, should be sold off. Question marks (also known as problem child) are growing rapidly and thus consume large amounts of cash, but because they have low market shares they do not generate much cash. The result is a large net cash consumption. A question mark has the potential to gain market share and become a star, and eventually a cash cow when the market growth slows. If the question mark does not succeed in becoming the market leader, then after perhaps years of cash consumption it will degenerate into a dog when the market growth declines. Question marks must be analyzed carefully in order to determine whether they are worth the investment required to grow market share. Stars are units with a high market share in a fast-growing industry. The hope is that stars become the next cash cows. Sustaining the business unit's market leadership may require extra cash, but this is worthwhile if that's what it takes for the unit to remain a leader. When growth slows, stars become cash cows if they have been able to maintain their category leadership, or they move from brief stardom to dogdom.
Marketing organization Evolution: 1. Simple sales department 2. Sales department with ancillary marketing functions VP (Sales) hires a MR Manager or a Marketing Director to manage marketing functions 3. Separate marketing department CEO appoints a VP (Marketing) - so VP (Sales) & VP (Marketing) both report to CEO 4. Modern marketing department/marketing organization VP (Marketing & Sales) heads both sales & marketing departments to reduce friction between Marketing & Sales. Reports to CEO Organizing Marketing Dept. Types of Marketing Organizations 1. 2. 3. 4. Functional organization Product-oriented organization Geographic (territory)- OR market oriented organization Complex organization
Functional organization: Functional specialists reporting to a Marketing VP, who coordinates their activities. Specialists will include: 1. Marketing admin. Manager 2. A & SP Manager 3. Sales Manager 4. MR Manager 5. Product Manager Geographic organization: NSM will have RSM, who in turn will have ASM reporting to them. Sales reps will report to ASM. Most common form in India. There could be some Regional Marketing Managers too, to provide local marketing expertise. Brand Management Organization Tasks of Brand Managers: 1. Developing long range/competitive strategy for products 2. Preparing annual marketing plan & sales forecast 3. Working with ad agencies 4. Stimulating product support amongst sales force & distributors 5. Gathering market intelligence 6. Initiating product improvements Complex organization: Many large companies that produce many products flowing into many different geographic and customer markets usually employ some combination of the functional, geographic, product and market organization forms.
MARKETING AUDIT: A comprehensive, periodic, independent, & systematic examination of a companys environment, objectives, strategies and activities to determine problem areas & to recommend a plan of action to improve the companys marketing performance. It is a major tool for strategic control. FEATURES OF MARKETING AUDIT: Comprehensive Systematic Independent Periodic Components of Marketing Audit I. Marketing Environment Audit II. Marketing Strategy Audit III. Marketing Organization Audit IV. Marketing Systems Audit V. Marketing Productivity Audit VI. Marketing Function Audit Marketing Environment Audit Macro environment Demographic Economic Environmental Technological Political Cultural Micro environment Markets Customers Competitors Channels Suppliers Facilitators / Marketing Firms Publics
Marketing Strategy Audit Business Mission Marketing Objectives and Goals Strategy Marketing Organization Audit Formal Structure Functional Efficiency Interface Efficiency
Marketing Systems Audit Marketing Information Systems Marketing Planning Systems Marketing Control System New Product Development System Marketing Productivity Audit: this audit examines the profitability of different marketing and the cost effectiveness of different marketing expenditures.
Profitability Analysis
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Marketing Function Audit Products Prices Distribution Integrated Marketing Communications Sales Force END OF MODULE 8
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- G12 ABM Marketing Lesson 3 HandoutsDocument11 paginiG12 ABM Marketing Lesson 3 HandoutsLeo SuingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winning Market Through Market Oriented Strategic PlanningDocument25 paginiWinning Market Through Market Oriented Strategic PlanningKafi Mahmood NahinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM Unit 4Document27 paginiSM Unit 4mohammadimran4310Încă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionDe la EverandMarketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (7)
- Marketing Management - Module 2Document20 paginiMarketing Management - Module 2Genner RazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Plan Final 1201071514114303 4Document46 paginiMarketing Plan Final 1201071514114303 4KaziRafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding The ToolDocument4 paginiUnderstanding The ToolSaratha KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module PrinciplesOfMarketing Chapter2 120304Document9 paginiModule PrinciplesOfMarketing Chapter2 120304Kaye PauleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 MMDocument34 paginiUnit 2 MMmonishajai8336Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7Document27 paginiUnit 7Pawan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.developing Markeing Strategies and PlansDocument9 pagini2.developing Markeing Strategies and PlanspremiumelecgadgetsÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG growth-share matrix analysis toolDocument7 paginiBCG growth-share matrix analysis toolchienÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Marketing Process: Marketing Process Is The Process of Analyzing Market Opportunities, Selecting Target MarketsDocument4 paginiThe Marketing Process: Marketing Process Is The Process of Analyzing Market Opportunities, Selecting Target MarketsJamyang Palmu KatukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Three: Winning The Market Though Market Oriented Strategic PlanningDocument29 paginiChapter Three: Winning The Market Though Market Oriented Strategic Planningalazar suffaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Analysis Tools and TechniquesDocument10 paginiStrategic Analysis Tools and TechniquesANKUR CHOUDHARYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Government College Women University FaisalabadDocument20 paginiGovernment College Women University FaisalabadMaryam SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Marketing For Marketing 2018 19th Edition Pride Test Bank PDFDocument36 paginiDwnload Full Marketing For Marketing 2018 19th Edition Pride Test Bank PDFsintochenge62100% (10)
- Chapter 2 Strategic Marketing PlanningDocument19 paginiChapter 2 Strategic Marketing PlanningMuhammad AbubakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Planning and Marketing Process ClassDocument42 paginiStrategic Planning and Marketing Process ClassGaurav gusaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 - 1668854523Document6 paginiAssignment 2 - 1668854523Ridhi GambhirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Plan Final 1201071514114303 4Document46 paginiMarketing Plan Final 1201071514114303 4Arindini PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- MKTG 2400 CH 2 NotesDocument11 paginiMKTG 2400 CH 2 NotesDawson TeagueÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG Matrix PDFDocument5 paginiBCG Matrix PDFPravish KhareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Planning and Marketing Process GuideDocument24 paginiStrategic Planning and Marketing Process GuideRahul SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19.-Strategic-marketing-for-Sampath-BankDocument9 pagini19.-Strategic-marketing-for-Sampath-Bankanjalikadeshani39Încă nu există evaluări
- Developing Marketing Strategies & Plans: Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering To Build Customer RelationshipsDocument38 paginiDeveloping Marketing Strategies & Plans: Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering To Build Customer RelationshipsMarisol DulceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 POMDocument6 paginiChapter 2 POMMeghnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Build Customer RelationshipDocument7 paginiBuild Customer RelationshipBurcuÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between A Marketing Mix and A Promotional Mix?Document18 paginiWhat Is The Difference Between A Marketing Mix and A Promotional Mix?rubal0468Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolDocument12 paginiUNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolNishath NawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing PlanDocument7 paginiMarketing PlanStephanie BissessurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 SummaryDocument3 paginiChapter 2 SummaryeudamnboredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-2: Marketing Strategies & PlanningDocument36 paginiChapter-2: Marketing Strategies & PlanningPiyush LoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Marketing (Chapter 2)Document28 paginiPrinciples of Marketing (Chapter 2)Salman Preeom100% (5)
- Chapter - 3 Nature, Importance and Scope of Strategic PlanningDocument7 paginiChapter - 3 Nature, Importance and Scope of Strategic PlanningTino AlappatÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Marketing Research Process Define The Problem and Research ObjectivesDocument4 paginiThe Marketing Research Process Define The Problem and Research ObjectivesSsneha DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG Matrix: The Growth Share Matrix Was Created in 1968 by BCG's Founder, Bruce HendersonDocument4 paginiBCG Matrix: The Growth Share Matrix Was Created in 1968 by BCG's Founder, Bruce HendersonRuhul Amin Rasel100% (1)
- Growth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enDocument6 paginiGrowth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enBlack EyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2 Handout PDFDocument15 paginiWeek 2 Handout PDFkiks fernsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Marketing ModelDocument7 paginiTypes of Marketing ModelBlack EyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Planning ProcessDocument11 paginiMarketing Planning ProcessShilpy Ravneet KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document9 paginiChapter 2melodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understand the BCG growth-share matrix with this guideDocument5 paginiUnderstand the BCG growth-share matrix with this guideChanthini VinayagamÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG Matrix SWOT and Porter Model-April 2011Document12 paginiBCG Matrix SWOT and Porter Model-April 2011Kavudham ASÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG MatrixDocument4 paginiBCG MatrixAJEET893032100% (1)
- Marketing PlanDocument40 paginiMarketing PlanKapeel LeemaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG Matrix and GE Nine Cells MatrixDocument15 paginiBCG Matrix and GE Nine Cells MatrixBinodBasnet0% (1)
- Chapter ThreeDocument28 paginiChapter ThreeBethlehem BirukÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Format For Marketing StrategyDocument4 paginiA Format For Marketing StrategyTushar RohatgiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market AnalysisDocument32 paginiMarket AnalysisLennyson MachigereÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMU A S: Marketing ManagementDocument19 paginiSMU A S: Marketing ManagementGYANENDRA KUMAR MISHRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG MatrixDocument6 paginiBCG MatrixSpandana AchantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimality in Marketing ResearchDocument5 paginiOptimality in Marketing ResearchEmanuele TaglioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comsa Institute Information Technolor, (IslamabadDocument13 paginiComsa Institute Information Technolor, (Islamabadusmanbhatti86Încă nu există evaluări
- Winning Markets Through Strategic PlanningDocument8 paginiWinning Markets Through Strategic PlanningRodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 1 Marketing & Business PlanDocument26 paginiSession 1 Marketing & Business Planprabs9869Încă nu există evaluări
- Marketing PalnDocument2 paginiMarketing PalnRuth Ngina MulwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand Forcasting: Abinaya Afshaan Aishwarya Akhila Altamash Anita Aniruddh ArindhumDocument11 paginiDemand Forcasting: Abinaya Afshaan Aishwarya Akhila Altamash Anita Aniruddh ArindhumAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Value Chain Analysis ExplainedDocument15 paginiPorter's Value Chain Analysis ExplainedAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6 Notes - Marketing ManagementDocument11 paginiModule 6 Notes - Marketing ManagementAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Features for Organization, Tone & ReadabilityDocument1 paginăWriting Features for Organization, Tone & ReadabilityAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContextDocument7 paginiContextAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT's Role in Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 paginiIT's Role in Supply Chain ManagementAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- India BudgetDocument89 paginiIndia BudgetsurendragiriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 8 CKM VtuDocument15 paginiModule 8 CKM VtuAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT's Role in Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 paginiIT's Role in Supply Chain ManagementAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DynamicDocument30 paginiDynamicAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply ChainDocument20 paginiSupply ChainAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Value Chain Analysis ExplainedDocument15 paginiPorter's Value Chain Analysis ExplainedAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumerism & Consumer Act of 1986Document11 paginiConsumerism & Consumer Act of 1986Aniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selling & Buying Styles & Selling SkillsDocument16 paginiSelling & Buying Styles & Selling SkillsAniruddh Chavan100% (1)
- Rural MarketingDocument7 paginiRural MarketingAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Change and Knowledge ManagementDocument6 paginiChange and Knowledge ManagementAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blake and Mouton's GridDocument20 paginiBlake and Mouton's GridAniruddh ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selling & Buying Styles & Selling SkillsDocument16 paginiSelling & Buying Styles & Selling SkillsAniruddh Chavan100% (1)
- 01 Equity MethodDocument41 pagini01 Equity MethodAngel Obligacion100% (1)
- Welingkar Institute of ManagementDocument2 paginiWelingkar Institute of ManagementanandnikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real EstateDocument38 paginiReal EstateRHEA19100% (3)
- PD WakalahDocument22 paginiPD WakalahDavid CartellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Design Models and MethodsDocument22 paginiSupply Chain Design Models and MethodssankofakanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guardians of GoodDocument27 paginiGuardians of GoodKadaeuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSEP Audited Financial Stmts 2018Document21 paginiHSEP Audited Financial Stmts 2018Fallon FischerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sector Report Real EstateDocument14 paginiSector Report Real EstateDawit SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counterparty LimitDocument413 paginiCounterparty Limitmuhammad firmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark ZuckerbergDocument2 paginiMark Zuckerbergapi-379733075Încă nu există evaluări
- Group Assignment 2 - DraftDocument4 paginiGroup Assignment 2 - Draftsumeet kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinMod 2022-2023 Tutorial 2 Exercise + AnswersDocument41 paginiFinMod 2022-2023 Tutorial 2 Exercise + AnswersjjpasemperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship ReportDocument51 paginiInternship ReportUmi Izhar75% (4)
- Indiareit Domestic Fund IV PresentationDocument28 paginiIndiareit Domestic Fund IV PresentationChetan Mukhija100% (1)
- Technology Transfer in IndiaDocument9 paginiTechnology Transfer in IndiaMehak Bhargava100% (1)
- Abdhini Biswas Product CannibalisationDocument45 paginiAbdhini Biswas Product Cannibalisationabdhini biswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel GCE Accounting Paper January 2007 Mark SchemeDocument11 paginiEdexcel GCE Accounting Paper January 2007 Mark Schemecara_rebelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMO Script PDFDocument5 paginiSMO Script PDF『SHREYAS NAIDU』Încă nu există evaluări
- CRM challenges in investment banking and financial marketsDocument16 paginiCRM challenges in investment banking and financial marketssarferazul_haqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFM Nov 20Document20 paginiSFM Nov 20ritz meshÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Invest in Gold: Spot Markets, Futures, ETFs, Bars and CoinsDocument5 paginiHow to Invest in Gold: Spot Markets, Futures, ETFs, Bars and CoinsLeonard NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBS Xccry Basis Swaps StratDocument7 paginiRBS Xccry Basis Swaps StratJolin Majmin100% (2)
- Contributed CapitalDocument2 paginiContributed CapitalNiño Rey LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thomson Reuters Eikon BrochureDocument5 paginiThomson Reuters Eikon BrochureIvon BacaicoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graeme Roustan - Johnstown Tribune Democrat - News Articles - The War Memorial Arena and The Departure of The Johnstown ChiefsDocument135 paginiGraeme Roustan - Johnstown Tribune Democrat - News Articles - The War Memorial Arena and The Departure of The Johnstown ChiefsJim JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 17Document62 paginiChapter 11 17Melissa Cabigat Abdul KarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Markets Quiz 1Document8 paginiFinancial Markets Quiz 1Aingeal DiabhalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finra Claim in Securities America CaseDocument9 paginiFinra Claim in Securities America CaseDealBook100% (1)
- 17 PHD Directory F LRDocument16 pagini17 PHD Directory F LRchetanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument34 paginiIntroduction To Financial ManagementKevin OnaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurDe la Everand12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldDe la Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (19)
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoDe la Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (20)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffDe la Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (11)
- Summary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:De la EverandSummary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelDe la EverandThe Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (51)
- Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (38)
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDe la EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (85)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDe la EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingDe la EverandHow to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (28)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItDe la EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (150)
- Summary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureDe la EverandSummary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (100)
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistDe la EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeDe la EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (88)
- Creating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsDe la EverandCreating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveDe la EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (153)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeDe la EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (276)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDe la EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Without a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatableDe la EverandWithout a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatableEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (23)
- Ca$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneDe la EverandCa$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (114)
- Anything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurDe la EverandAnything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (46)
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"De la EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (163)
- The Tipping Point by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: How Little Things Can Make a Big DifferenceDe la EverandThe Tipping Point by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: How Little Things Can Make a Big DifferenceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Summary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (10)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldDe la EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Your Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyDe la EverandYour Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (794)
- Summary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesDe la EverandSummary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (99)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindDe la EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (272)