Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
0001 0003
Încărcat de
Anonymous FigYuONxuuTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
0001 0003
Încărcat de
Anonymous FigYuONxuuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tetrahedron Letters, No, 8, pp.l-3,1959.Pergemon PressLtd. Printedin Great Britain.
ORI~ATIO~ IN TRE REACTION OF ~I~I~~~
~-~STITCTED PYRIDINEES
R, A. Abramovitch, A. D, Notation and Giam Choo Sex@ Chemistry Department, University of Seekztohewan, Saskatoon, Sazkstchewan (Reaeived 4 June 1959)
A STKDYof the addition of phenyllithimn to 3-substituted pyridinez m.z undertaken to detemine the orientatfon of the entering phenylgroup,
.
While thiswork was in progrees W&leg et al*' reported that the reaction of 3-phenylpyridine I(R - C H ) with phenyllithium II wag aelective in giving 65 The formation of 2,3_diph~i2,+iiphenylpyridine III(R- C&) exolusively. pyridine IV(R = C H f, which%iley et al, regardaz less probable,
65 ma
not observed.
The
addition of othernucleophilic reagent8 such az aodzmide 2*3 and butyl-
' R. R. Wiley,C. H. Jarboe, P. X. Callzhan and J, T, Nielsen, J. Org. Ch@, 2, 780 (1958), m L E. Plazek,A. Mzrcinikov znd Ch, Stammer, Rocm. Chem,1;& 365 (1935); mm. Abstr,& 1377 (1936). 3 E. Eerdegger and E. Nfklez,Helv. Chim.Aota 2, 5Ofi (1956).
Orientationin the reaction of phenyllithium
lithium4 to j-substituted pyridines indicated the preferentialformatinn of the 2,3-isomer in such reactions.Since our results with phenyllithiumalso show this trend we report some of our observations. With 3-picoline,II gave P-phenyl-3-picoline IV(R - CH3), b.p. 154156'/18 mm, (picrate,m.p. 165-166'),and 6-phenyl-3-picoline III(R = CH3), b.p. 162-164'/20mm, (picrate,m.p, 181-183'),the relative yields of IV and III being in the ratio of 8:l respectively,The structure of the main
product was proved by permanganate oxidation to 2-phenylpyridine-3-carboqlic acid IV(R = COOH), m.p. 168-169' (1it.5 m.p, 168-169')which was converted 6 via the acid chloride into 4-aeafluorenone, m.p. 139.5-141.5',by AlC13 in light petroleum.When the acid chloride was treated with AlC13 in benzene 3-benzoyl-2-phenylpyidine IV(R - C6H5CO), b.p. 155-160/15mm, picrate, was obtained.The structure of 2-phenyl-3-picoline was m.p. 137.5-138.5', confirmed by direct comparisonwith a specimen obtained unambiguouslyby Ishiguro et a1,,5 the IR spectra of the products and their picrates being identical and a mixed melting point of the picrates being undepressed.The NMR spectrum of the product was also consistentwith its formulationas 2-phenyl-3-picoline. The structureof III(R = CH3) was similarly proved by oxidation to 2-phenylpyridine-5-carboxylic acid, m.p. 232-233' (1ite7 m.p. 233'). A dimethyldipyridyl, characterized as the dipicrate,m.p. 2O4206' (decomp.),was isolated as a byproduct of the reaction and shown to
4 N. J. Leonard and B. L. Ryder, J. Org. Chem, ig, 596 (1953). 5 T. Ishiguro, Y. Morita and K. Ikushima, Yalcugaku Zasshi 12, 220 (1958); Chem. Abstr, 22, 118468 (1958). 6 Z. Skraup and A. Cobenzl,Monatsh, 4, 436 (1883), report m.p. 140-141' for 4-azafluorenone. 7 N. Nienburg, Chem. Ber, 51, 874 (1934).
Orientationin the reaction of phenyllithium
be different from j,j'-dimethyland 5,5'-dimethyl-2,2'-dipyridyl by a comparison of the picrates. The structure of this byproduct was not investigated further at this stage. 1 In view of the results of Wiley et al, the possible steric effect of the 5-substituent upon the orientationof the entering phenyl groups was investigatedin the reaction of II with nicotine. The product was shown to be a 1:l mixture of 2-phenyl- IV(R - 4-C H NCR ) and 6-phenylnicotine 47 3 III(R = -a-C B NCH ) by vapour phase chromatography. The two isomers were 47 3 separated by preparativevapour phase chromatography giving 2_phenylnicotine, b.p. 145/0.7 mm, picrate, b.p. 165/0.6mm, m.p. 211-213' and 6_phenylnicotine,
picrate, m.p, 170-171O.The structuresof the isomers were assigned on the basis of their infrared spectra (characteristic bands at 1610-1570 cm-') and by oxidation of the second fraction to 2-phenylpyridine-5-carboqylic acid. Addition of II and of other nucleophilicreagents seems to occur preferentiallyat the P-positionbut the j-substituent, if sufficiently bulky, may exert a steric effect resulting in appreciable addition at the 6-positionalso, The exclusive formation of 2,5_diphenylpyridine' might be attributed to steric inhibitionof coplanarityin the transitionstate in the formation of the 2,j-isomer, Acknowledgements - The authors wish to thank Dr. Ishiguro for samples of P-phenyl-j-picoline and its picrate, and Varian Associates for the NMR spectrum of 2-phenyl-3-picoline and its interpretation. This work was supported by a National Research Council of Canada grant.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Erosion of Limestones Under Soil AND Vegetation Systems On LimestoneDocument11 paginiThe Erosion of Limestones Under Soil AND Vegetation Systems On LimestoneAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masthead (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document1 paginăMasthead (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stability of Minels in Ring Reaneral Thchemical Approach (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document8 paginiStability of Minels in Ring Reaneral Thchemical Approach (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Of of of of 9% For: Short CommunicationsDocument1 paginăOf of of of 9% For: Short CommunicationsAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Al Stream Relationships - A Case Study in The Westend Basin of The Southern Pennines, England (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document7 paginiAl Stream Relationships - A Case Study in The Westend Basin of The Southern Pennines, England (Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Scree Slope Rockfa (Esses, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document20 paginiA Scree Slope Rockfa (Esses, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedological Feeability of Hillydale, Yorire (, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document14 paginiPedological Feeability of Hillydale, Yorire (, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Surface Processes, Vol. 39, Issue 5Document1 paginăEarth Surface Processes, Vol. 39, Issue 5Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ground State Oi The Bose Gas By: AbstractDocument16 paginiThe Ground State Oi The Bose Gas By: AbstractAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrograph Peakedness and Basin Area (Es, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Document4 paginiHydrograph Peakedness and Basin Area (Es, Vol. 1, Issue 1) (1976)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iterated Crossed Box Diagram in The Complex Angular Momentum Plane and Bethe-Salpeter EquationDocument15 paginiIterated Crossed Box Diagram in The Complex Angular Momentum Plane and Bethe-Salpeter EquationAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communications in Maths&Physics 6-13Document8 paginiCommunications in Maths&Physics 6-13Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- On The Connection Between The LSZ and Wightman Quantum Field TheoryDocument17 paginiOn The Connection Between The LSZ and Wightman Quantum Field TheoryAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Theorem Concerning The Positive Metric: Derek W. Robi NsonDocument6 paginiA Theorem Concerning The Positive Metric: Derek W. Robi NsonAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- On The Vacuum State in Quantum Field Theory. II: H. J. BorchersDocument23 paginiOn The Vacuum State in Quantum Field Theory. II: H. J. BorchersAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divergence of Perturbation Theory For Bosons: ArthurDocument23 paginiDivergence of Perturbation Theory For Bosons: ArthurAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhomogeneous: SL (N, C)Document9 paginiInhomogeneous: SL (N, C)Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communications in Math&Physics 49-56Document8 paginiCommunications in Math&Physics 49-56Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Andlower Limitsforthe Number Ofbound States in A Given Central PotentialDocument9 paginiUpper Andlower Limitsforthe Number Ofbound States in A Given Central PotentialAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Go Game Records For Prediction of Player AttributesDocument7 paginiEvaluating Go Game Records For Prediction of Player AttributesAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communications in Math&Physics 1-5Document5 paginiCommunications in Math&Physics 1-5Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communications in Math&Physics14-48Document35 paginiCommunications in Math&Physics14-48Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Photoelectric Method The Phosphorus': For DeterminationDocument3 paginiA Photoelectric Method The Phosphorus': For DeterminationAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jou Chem of SaltsDocument1 paginăJou Chem of SaltsAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Ozonizer: LaboratoryDocument1 paginăSimple Ozonizer: LaboratoryAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measurement Distensibilitv Organic Finishes: NE Is A of A TDocument4 paginiMeasurement Distensibilitv Organic Finishes: NE Is A of A TAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 44 GÇô45Document2 pagini44 GÇô45Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Improved Semi-Micro and Micro-Carius Determination: HE L. and of A and ToDocument2 paginiAn Improved Semi-Micro and Micro-Carius Determination: HE L. and of A and ToAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 46 GÇô47Document2 pagini46 GÇô47Anonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Vehicle Films Free of Supporting Foundation: Semi-MicromethodDocument1 paginăPreparation of Vehicle Films Free of Supporting Foundation: Semi-MicromethodAnonymous FigYuONxuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Shendy Rulida SCIENCE 9 - Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes (Part 1)Document4 paginiShendy Rulida SCIENCE 9 - Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes (Part 1)Shendy RulidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry (Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument30 paginiOrganic Chemistry (Some Basic Principles and TechniquesNaveen SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2022-23 by Physics LinxDocument18 paginiClass 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2022-23 by Physics LinxRudar MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biennial Report 2003-05Document227 paginiBiennial Report 2003-05dangchihienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of DibenzalacetoneDocument7 paginiPreparation of DibenzalacetoneHaiqal AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- AldehydeDocument3 paginiAldehydelapÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEET Syllabus 2021Document6 paginiNEET Syllabus 2021chandanaa sriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kimia OrganikDocument32 paginiKimia OrganikFitria Salsabila100% (1)
- Science Grade 10: Quarter 4 - Biomolecules: Protein S & Nucleic AcidsDocument14 paginiScience Grade 10: Quarter 4 - Biomolecules: Protein S & Nucleic AcidsMernalyn Deximo Inot100% (1)
- Polyester PolyolsDocument5 paginiPolyester PolyolsWSERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covennatone Line Notation PDFDocument5 paginiCovennatone Line Notation PDFifiokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kumaun University Programme of M. Sc. (Previous & Final) Main Examination - 2011Document4 paginiKumaun University Programme of M. Sc. (Previous & Final) Main Examination - 2011Mukesh BishtÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDU BIOCHEMISTRY Structure of Triacylglycerols WorksheetDocument2 paginiCDU BIOCHEMISTRY Structure of Triacylglycerols WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook: EpoxyDocument36 paginiHandbook: EpoxyBelarbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Percubaan STPM 2019 Semester 3 Chemistry Upper 6Document4 paginiSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Percubaan STPM 2019 Semester 3 Chemistry Upper 6AlyciaLeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind Map ChemistryDocument3 paginiMind Map ChemistryTheesha SophieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers) (Answers) Topic:-Miscellaneous QuestionDocument2 paginiCbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers) (Answers) Topic:-Miscellaneous QuestionShreyash KolekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee Mains: Highlights of JEE Main ExaminationDocument1 paginăJee Mains: Highlights of JEE Main Examinationvidya sagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Project Updated 2Document80 paginiFinal Project Updated 2Abdulwahid SultanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of LipidDocument11 paginiStructure of LipidAfrah Alatas100% (1)
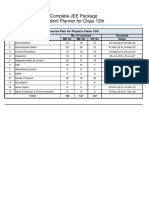
- JEE Lecture Plan - 12th PackageDocument3 paginiJEE Lecture Plan - 12th PackageAman KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xliv "A. Corbella" International Summer School On Organic Synthesis - Isos 2019 Gargnano (BS), Palazzo Feltrinelli, 9 - 13 June 2019Document1 paginăXliv "A. Corbella" International Summer School On Organic Synthesis - Isos 2019 Gargnano (BS), Palazzo Feltrinelli, 9 - 13 June 2019SonjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 111-2-2023Document71 paginiCH 111-2-2023mirnadeem2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Postlab8 9Document3 paginiPostlab8 9Niño Sandro Jocson MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetDocument15 paginiAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetSankar KumarasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- M1 W01 Ans PDFDocument4 paginiM1 W01 Ans PDFnelson100% (2)
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument119 paginiAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benzimidazole Acidhydrazide DerivativesDocument6 paginiBenzimidazole Acidhydrazide DerivativesGopal Krishna PadhyÎncă nu există evaluări
- (C6H6) CHM 112 Isomers and IsomerismDocument37 pagini(C6H6) CHM 112 Isomers and IsomerismHezekiah DanelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4Document59 paginiCHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4fatin harrisÎncă nu există evaluări