Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Energy Ans
Încărcat de
kevinamyDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Energy Ans
Încărcat de
kevinamyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
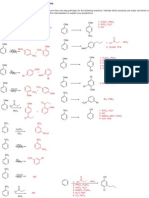
CHEM211 Problem Set
Reaction Energetics
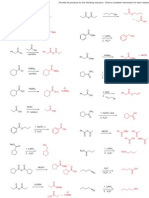
1) For the molecules below:
a) Draw the most stable and least stable conformations.
b) Calculate the difference in energy between the conformations.
c) Calculate the equilibrium constant (Keq) for conversion between the conformations at room
temperature (70 oF, 21 oC, 294 K).
OH
(H3C)2HC CH3 H3CH2C CH(CH3)2
t-Bu Cl
H3CH H CH3
H H3C H HH CH3 H H CH3
OH
H H H3C H Cl
H3C HH CH3 H3C HCH3 CH3 t-Bu
Cl
CH3
H3C H HCH3 H3C CH3 H3CCH3 t-Bu
H H
H3CH HH H CH3 HH H3C H
H HCH3 H CH3 OH
CH3
4 + 6 + 6 = 16 kJ/mol 11 - 4 = 7 kJ/mol 2x(11.4) - 4x(3.8) 2x(1.0) + 2x(2.1)
= 7.6 kJ/mol = 6.2 kJ/mol
∆Go = -RT lnKeq Keq = 5.7 x 10 -2
Keq = 1.4 x 10 -3 Keq = 4.46 x 10 -2 Keq = 7.92 x 10 -2
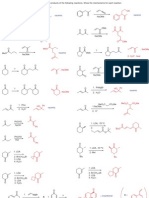
2) Sketch an energy diagram to match each of the following descriptions:
a) Fast reaction; ∆Go = -120 kJ/mol.
b) Slow reaction; ∆Go = 20 kJ/mol.
c) Very slow reaction; Keq = 1.36×10 –3.
d) Fast reaction; Keq = 3.0.
e) A two step reaction; first step is fast; second step is slow; ∆Go = -80 kJ/mol.
f) ∆G1‡ = 200 kJ/mol; ∆G2‡ = 50 kJ/mol; ∆Go = -40 kJ/mol.
TS
E TS E
∆G
SM
∆ Go ∆G
= -120
P
SM ∆ Go
P = +20
reaction coordinate reaction coordinate
TS
E ∆G E TS
∆G
P SM
P
∆Go = 16 o
∆G = -2.7
SM
reaction coordinate reaction coordinate
TS1
TS2
TS2 ∆G2 = 50
I
∆ G2
TS1 ∆ G1
I E = 200
E
∆ G1
SM
SM
∆ Go
= -80 ∆ Go
= -40
P P
reaction coordinate reaction coordinate
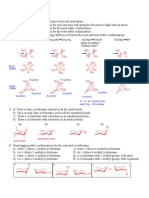
3) For each energy diagram in (2), lable starting material(s) (SM), product(s) (P), intermediate(s) (I),
transition state(s) (TS‡), activation energy(s) (∆
∆G‡) and free energy (∆
∆Go).
4) For the reactions below, calculate ∆Go, ∆Ho and ∆So.
290 K 19
Br2 Br Keq = 1.24 x 10
Br
∆Go = -RT lnKeq = -(8.315 J/K mol)(290K) ln (1.24×1019) = -106,000 J/mol = -106 kJ/mol
∆Ho = ∆Hf bonds broken – ∆Hf bonds formed = ∆Hf C=C + ∆Hf Br-Br – 2(∆Hf C-Br) – ∆Hf C-C =
611 + 193 – 2(285) – 376 = -142 kJ/mol
∆Go = ∆Ho – T∆So
∆So = - (∆Go – ∆Ho)/T = - (-106 – (-142))/290 = -0.124 kJ/K mol = -124 J/K mol
HBr Keq = 3.96 x 10 15
Br
∆Go = -RT lnKeq = -(8.315 J/K mol)(290K) ln (3.96×1019) = -87,000 J/mol = -87 kJ/mol
∆Ho = ∆Hf C=C + ∆Hf H-Br – ∆Hf C-H – ∆Hf C-Br – ∆Hf C-C =
611 + 366 – 420 – 285 – 376 = -104 kJ/mol
∆So = - (∆Go – ∆Ho)/T = - (-87 – (-104))/290 = -0.060 kJ/K mol = -60 J/K mol
Br Br Keq = 0.13
O OH
∆Go = -RT lnKeq = -(8.315 J/K mol)(290K) ln (0.13) = 4900 J/mol = 4.9 kJ/mol
∆Ho = ∆Hf C-H + ∆Hf C-Br + ∆Hf C-C – ∆Hf O-H – ∆Hf C=C =
420 + 285 + 376 – 437 – 611 = 33 kJ/mol
∆So = - (∆Go – ∆Ho)/T = - (4.9 – 33)/290 = 0.097 kJ/K mol = 97 J/K mol
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionDe la EverandElectron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- T1-1 TDocument30 paginiT1-1 TFRENCHONLYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haloalkanes PDFDocument6 paginiHaloalkanes PDFthc8477Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 108M Final Exam Practice 1Document8 paginiChemistry 108M Final Exam Practice 1Norma Leticia RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes PDFDocument40 paginiChapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes PDFSam0% (1)
- Exp.06 Preparation of P-Bromo AcetanilideDocument3 paginiExp.06 Preparation of P-Bromo AcetanilideAnanda VijayasarathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semi-Empirical Methods: CHEM 430Document42 paginiSemi-Empirical Methods: CHEM 430chama_gozÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2.1 Enthalpy ChangesDocument9 pagini3.2.1 Enthalpy ChangesSofia YÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caieee04fisica PDFDocument15 paginiCaieee04fisica PDFRafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document3 paginiAssignment 1Andrew_Wong_8492Încă nu există evaluări
- Reactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationDocument8 paginiReactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationMarc RitzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cy 101 Uv-Vis and Ir NewDocument66 paginiCy 101 Uv-Vis and Ir NewSomesh MohapatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11chemistry OMEGA PDFDocument96 pagini11chemistry OMEGA PDFChirAgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioinorganic HandoutDocument63 paginiBioinorganic HandoutAL__52Încă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzeneDocument44 paginiAromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzenePaarijat DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The S-Block Elements: The Elements in Which Last Electron Enters The S-Subshell Are Called As S-Block ElementsDocument36 paginiThe S-Block Elements: The Elements in Which Last Electron Enters The S-Subshell Are Called As S-Block ElementstheDarknight2050 (Karthik Sunil)Încă nu există evaluări
- CHE 229 Lab Report 1Document7 paginiCHE 229 Lab Report 1Stephanie CarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical-Kinetics Rate Part2Document29 paginiChemical-Kinetics Rate Part2AribazChemÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 August Mock TestDocument65 pagini12 August Mock Testapi-26674800Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermochemistry Answers RemovedDocument11 paginiThermochemistry Answers Removedapi-327309463Încă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 2Document2 paginiSheet 2Ahmed Rabie Abd Elazeem100% (1)
- Register of Pesticides May 2010Document15 paginiRegister of Pesticides May 2010MarvinGarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnolateansDocument1 paginăEnolateanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectros PDFDocument28 paginiSpectros PDFbalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Brochure PDFDocument12 paginiPhysics Brochure PDFKatrina PanaliganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2kevinamy100% (1)
- Practical Organic Chemistry (I) : October 2017Document44 paginiPractical Organic Chemistry (I) : October 2017NUR ALOMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Test 2 Drug ListDocument33 paginiPharmacology Test 2 Drug ListSHRIKANTÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)Document4 paginiCH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)伊貝P-Încă nu există evaluări
- Redox RxnsDocument30 paginiRedox RxnsJolaine ValloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organometallic ChemistryDocument31 paginiOrganometallic ChemistrySadiaKhan100% (1)
- TEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 paginiTEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocument17 paginiNotes Organic Chemistry and Alkanessrk78Încă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 3Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 3kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic 6 CDocument26 paginiOrganic 6 CDr.Rajarshi PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1 Solns KineticsDocument10 paginiHW1 Solns Kineticsapb91781Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 Grand Canonical EnsembleDocument12 pagini10 Grand Canonical EnsembleAnonymous FRKcnDx7Încă nu există evaluări
- Isomerism in Coordination Compounds PDFDocument7 paginiIsomerism in Coordination Compounds PDFmf720383270100% (1)
- Chapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDDocument93 paginiChapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDyonggyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkyl HalidesDocument20 paginiAlkyl HalidesShivam Gupta0% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocument23 paginiChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Goc Revision Notes QuizrrDocument145 pagini13 Goc Revision Notes QuizrrRohit sharma100% (1)
- CH 19-AminasDocument40 paginiCH 19-Aminasmelg16Încă nu există evaluări
- Maths QuesDocument2 paginiMaths QuesKunalSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlyDocument9 paginiOrganic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlybrookÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Solid State EDocument1 pagină01 Solid State EKunalSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Org Chem Final ReviewerDocument7 paginiOrg Chem Final ReviewerblessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organometallic CompoundsDocument66 paginiOrganometallic CompoundsJon Ho100% (1)
- Hyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. EvansDocument12 paginiHyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. Evansomkar9996767Încă nu există evaluări
- Solid State-1Document31 paginiSolid State-1ChirAgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocument14 pagini02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wade 18 PowerpointDocument55 paginiWade 18 PowerpointKosygin Leishangthem100% (2)
- Lecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 paginiLecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsSHUBHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aldehydes Ketones HaccDocument66 paginiAldehydes Ketones HaccRammohan VaidyanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13B Heat of FusionDocument8 pagini13B Heat of FusionManish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLS AN 107 ChemCompPlasticDocument1 paginăCLS AN 107 ChemCompPlasticPim ChaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsDocument8 pagini03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsJant Erbert GarbosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Formula SheetDocument3 paginiPhysics Formula SheetCalvin NickiforÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pagini5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 3Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 3kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH211 ALKYNES Problem Set 1. Provide The Products For TheDocument1 paginăCH211 ALKYNES Problem Set 1. Provide The Products For ThekevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2kevinamy100% (1)
- Condensation 1 AnsDocument1 paginăCondensation 1 AnskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 5Document1 paginăChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 5kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarboxylicansDocument1 paginăCarboxylicanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condensation 2 AnsDocument1 paginăCondensation 2 AnskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkane Stereochemistry 1) For The Molecules Below: A) Provide ADocument3 paginiAlkane Stereochemistry 1) For The Molecules Below: A) Provide AkevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 2Document1 paginăChem 212 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 2kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Condensation Reactions 3Document1 paginăChem 212 Condensation Reactions 3kevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 212 Provide The Products For The Following Reactions. BeDocument1 paginăChem 212 Provide The Products For The Following Reactions. BekevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM211 Problem Set Functional Groups and Reaction Types These AnswersDocument4 paginiCHEM211 Problem Set Functional Groups and Reaction Types These AnswerskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnolateansDocument1 paginăEnolateanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stereochemistry Problem Set 1) Indicate Whether The Following Structures AreDocument1 paginăStereochemistry Problem Set 1) Indicate Whether The Following Structures ArekevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSansDocument2 paginiMSanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naming Alkanes AnsDocument1 paginăNaming Alkanes AnskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMRansDocument1 paginăNMRanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giao Ly For KidsDocument2 paginiGiao Ly For KidskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpecansDocument2 paginiSpecanskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthesis 3 AnsDocument1 paginăSynthesis 3 AnskevinamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expdb DorkDocument3 paginiExpdb Dorkhdr kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto Plin Schema Zapojeni Prepinace Autronic As 101Document28 paginiAuto Plin Schema Zapojeni Prepinace Autronic As 101Tom TalicniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Vibratory Cockles Grading MachineDocument23 paginiDesign and Development of Vibratory Cockles Grading MachinehalizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E5263 - M4A87TD EVO PDFDocument76 paginiE5263 - M4A87TD EVO PDFLeandro Henrique AgostinhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Databook Continental Agri 2006 PDFDocument0 paginiDatabook Continental Agri 2006 PDFdanilo3073Încă nu există evaluări
- Relationship of EN 954-1 and IEC 61508 Standards PDFDocument2 paginiRelationship of EN 954-1 and IEC 61508 Standards PDFfitasmounirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Item 103 Structure ExcavationDocument3 paginiItem 103 Structure ExcavationGerry Velicaria100% (1)
- DC Rectifier - OrionDocument12 paginiDC Rectifier - OrionLimbagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raymond Scott - Cindy ElectroniumDocument2 paginiRaymond Scott - Cindy ElectroniumJen HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFDocument2 paginiScania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFMehmet ErenÎncă nu există evaluări
- I J E C B S Issn (O) : 2230-8849: Cloud Computing: An AnalysisDocument15 paginiI J E C B S Issn (O) : 2230-8849: Cloud Computing: An AnalysisnoddynoddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veritas™ Volume Manager Administrator's Guide Solaris - VXVM - Admin - 51sp1 - SolDocument614 paginiVeritas™ Volume Manager Administrator's Guide Solaris - VXVM - Admin - 51sp1 - Solakkati123Încă nu există evaluări
- PQP FormatDocument10 paginiPQP FormatMichael TeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITC Guide For Thesis PreparationDocument26 paginiITC Guide For Thesis PreparationPanha MenhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vray Material Settings: COMP 423: Cadd For ArchitectureDocument18 paginiVray Material Settings: COMP 423: Cadd For ArchitectureMarvin GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mining and Earthmoving: Estimating Production Off-the-Job Grade Resistance Total Resistance TractionDocument4 paginiMining and Earthmoving: Estimating Production Off-the-Job Grade Resistance Total Resistance Tractionali alilouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminium - Copper AlloysDocument3 paginiAluminium - Copper AlloysRex RusselÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dielectric HeatingDocument2 paginiDielectric HeatingPallavi JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acoustics in Religious BuildingsDocument31 paginiAcoustics in Religious Buildingsrusydi.dpikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company ProfileDocument6 paginiCompany ProfileFaidzil ChabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE-Acoustic & Fire DoorsDocument6 paginiHSE-Acoustic & Fire DoorsInterior ProjectsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrument and Control Designer Rev01Document5 paginiInstrument and Control Designer Rev01masilamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traction Motors E WebDocument16 paginiTraction Motors E WebMurat YaylacıÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load Calculation As Per ASCE 7 10Document8 paginiWind Load Calculation As Per ASCE 7 10ani145yadav100% (1)
- Copperacetate Ammonium Nitrate Oxidation of Benzoin To BenzilDocument12 paginiCopperacetate Ammonium Nitrate Oxidation of Benzoin To BenzilDillon TrinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEC StdsDocument65 paginiSEC Stdserson1981Încă nu există evaluări
- 20v4000enDocument266 pagini20v4000enMario MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senior Piping DesignerDocument2 paginiSenior Piping Designerapi-77709853Încă nu există evaluări
- Important RCC Questions-Short and LongDocument15 paginiImportant RCC Questions-Short and LongmailjoelsamuelÎncă nu există evaluări