Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Intersection of Surfaces
Încărcat de
rashik072Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Intersection of Surfaces
Încărcat de
rashik072Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
61
Intersection of Surfaces
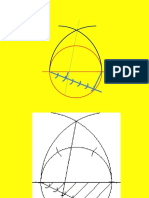
Introduction Ducts, pipe joints, smoke stacks, boilers, containers, machine castings etc., involve intersection of surfaces. Sheetmetal work required for the fabrication of the above objects necessitates the preparation of the development of the joints/objects. Orthographic drawings of lines and curves of intersection of surfaces must be prepared first for the accurate development of objects. Methods of obtaining the lines and curves of intersection of surfaces of cylinder and cylinder, prism and prism are shown to introduce the subject. Figure shows intersection of two cylinders.
Intersection of cylinder and cylinder Example A horizontal cylinder of diameter 40 mm penetrates into a vertical cylinder of diameter 60 mm. The axes of the cylinders intersect at right angles. Draw the curves of intersection when the axis of the horizontal cylinder is parallel to the VP. Construction 1. Draw the top and front views of the cylinders. 2. Draw the left side view of the arrangement. 3. Divide the circle in the side view into number of equal parts say 12. 4. The generators of the horizontal cylinder are numbered in both front and top views as shown.
62
5. Mark point m, where the generator through 1 in the top view meets the circle in the top view of the vertical cylinder. Similarly mark m2, .m12. 6. Project m7 to m1 on the generator 1 1 in the front view. 7. Project m7 to m7 on 77. Similarly project all the point. 8. Draw a smooth curve through m1 ....... m7 This curve is the intersection curve at the front. The curve at the rear through m4, m8 -------m12 coincides with the corresponding visible curve at the front. Since the horizontal cylinder penetrates and comes out at the other end, similar curve of intersection will be seen on the right also. 9. Draw the curve through n1 ...... n7 following the same procedure. The two curves m1 - m7 and n1 - n7 are the required curves of intersection.
Intersection of prism and prism When a prism penetrates another prism, plane surface of one prism intersects the plane surfaces of another prism and hence the lines of intersection will be straight
63
lines. In these cases, lines on the surface of one of the solids need not necessarily be drawn as it is done with cylinders. Instead, the points of intersections of the edges with the surface are located by mere inspection. These points are projected in the other view and the lines of intersection obtained. Example A square prism of base side 60 mm rests on one of its ends on the HP with the base sides equally inclined to the VP. It is penetrated fully by another square prism of base side 45 mm with the base side equally inclined to the HP. The axes intersect at right angles. The axis of the penetrating prism is parallel to both the HP and the VP. Draw the projections of the prisms and show the lines of intersection. Construction 1. Draw the top and front view of the prisms in the given position.
2. Locate the points of intersection of the penetrating prism with the surfaces of the vertical prism in the top view by inspection. Here, the edges 2-21 of the horizontal prism intersects the edge point of the vertical prism at m 2 in the top view. n4
64
corresponds to the edge 4-41, and the immediately below m2, m1 and m3 relate to 1-11 and 3-31 respectively. 3. Similarly locate points n1, n2, n3, and n4 4. Project m1 onto 1-11 in the front view as m1. Similarly project all other points. m3 coincides with m1 and n3 coincides with n1 5. Join m2, m1 and m1 m4 by straight lines. Join n2 n1 and n1 n4 also by straight lines. Exercises on drawing sheet 1. A square prism with a base side of 60mm and a height of 100mm rests on the
base on the HP with a face inclined at 30 to the VP. Another horizontal square prism with a base side of 60mm and a length of 130mm, a face of which is inclined at 30 to the HP, penetrates the vertical prism completely. The axes of the two prisms are offset at 15mm with their midpoints coinciding in FV. Draw the three views of the prisms showing LOI 2. Two equal triangular prisms with a base side of 45mm and an axis length of
100mm intersect centrally at right angles. A rectangular face of each prism is on the VP. One of the prisms is vertical. Draw FV and SV of the prisms. Draw an auxiliary TV on an AIP inclined at 60 to the HP. 3. A cylinder with a 60mm diameter and a 100mm length has axis perpendicular
to the VP. Another cylinder with a 44mm diameter and a 120mm length penetrates the first cylinder. The axis of the penetrating cylinder is parallel to the HP, inclined at 150 to the VP and 8mm away from the axis of the first cylinder. Draw the two views of the cylinders showing COI 4. Two cylinders, each of 60mm base diameter and 120mm length of axis,
intersect each other in such a way that an extreme generator of each passes through the midpoint of the others axis. One of the cylinders is vertical while the other is horizontal. Draw the two views showing COI.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Intersection of SolidsDocument6 paginiIntersection of Solidsrkadiraj7011Încă nu există evaluări
- Intersection of Solids: ME 111 Engineering DrawingDocument18 paginiIntersection of Solids: ME 111 Engineering DrawingtadesseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Industrial Engineering: Thapathali Campus, KathmanduDocument33 paginiDepartment of Industrial Engineering: Thapathali Campus, KathmanduMaxwell ChikaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safi Ss1 l9 Bolted Connections 26-03-2022Document86 paginiSafi Ss1 l9 Bolted Connections 26-03-2022esamalnhari77Încă nu există evaluări
- Model Paper Sainik School Class 6Document2 paginiModel Paper Sainik School Class 6AbcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing: Mechanical Engineering Department L.J. PolytechnicDocument40 paginiEngineering Drawing: Mechanical Engineering Department L.J. PolytechnicTufel NooraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fitter Semi C Its QBDocument62 paginiFitter Semi C Its QBPrashank100% (1)
- ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF SECTIONS AND DEVELOPMENTDocument26 paginiENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF SECTIONS AND DEVELOPMENTAditya NagÎncă nu există evaluări
- SS1 PresentationDocument43 paginiSS1 PresentationAdoga EdwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compression Test On MS and CI RevisedDocument7 paginiCompression Test On MS and CI Revisedafzal taiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel BasicsDocument13 paginiExcel BasicsKapongola NganyanyukaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Engineering Drawing in Chem. Engg.Document3 paginiApplication of Engineering Drawing in Chem. Engg.ArslanQureshi0% (1)
- Lesson 6. Welding SymbolsDocument37 paginiLesson 6. Welding SymbolsJay-r MiñozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LatheDocument74 paginiLatheChandrakantha K100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Question - pdf-21Document14 paginiEngineering Drawing Question - pdf-21gidlavinayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Lateral SurfacesDocument8 paginiDevelopment of Lateral SurfacesDeva RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENG2068 SampleofcontentsDocument10 paginiENG2068 SampleofcontentsKlich77Încă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For The Conduct of AISSEE - 2021: Date of Exam: 07 February 2021Document101 paginiGuidelines For The Conduct of AISSEE - 2021: Date of Exam: 07 February 2021DrAjay SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture07-Sections of SolidsDocument95 paginiLecture07-Sections of SolidsKajal KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Tech Test PaperDocument7 paginiConcrete Tech Test PaperatulqweÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME-109 Engineering DrawingDocument40 paginiME-109 Engineering DrawingHaadin ZamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-5 Engineering Drawing II Auto CADDocument231 pagini2-5 Engineering Drawing II Auto CADMuhammad Noerdiansyah100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing 1Document49 paginiEngineering Drawing 1Thorne Adam Danor100% (1)
- Mechanical Drafting and DesignDocument21 paginiMechanical Drafting and DesignVinod BhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Important Terms:: Isometric Axes, Lines and PlanesDocument10 paginiSome Important Terms:: Isometric Axes, Lines and PlanesAnand BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study centre lathe single point cutting tool geometryDocument4 paginiStudy centre lathe single point cutting tool geometryTanmay Warde100% (1)
- MosDocument42 paginiMosSajjan Kumar100% (2)
- CTS FitterDocument37 paginiCTS Fitterrajum465100% (1)
- ME232Geometric Tolerancing Classnotes: An Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ConceptsDocument6 paginiME232Geometric Tolerancing Classnotes: An Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ConceptsEngineernadeemshahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 9 Development of Surfaces - IDocument12 paginiLesson 9 Development of Surfaces - IAKSHANSH MATHURÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Question Paper Mechanical Engineering MeasurementsDocument4 paginiSample Question Paper Mechanical Engineering MeasurementsAbhishek SakatÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Theory of Engineering DrawingDocument370 paginiThe Theory of Engineering Drawingcocotess100% (1)
- Engineering Graphics: Course No. 6Document12 paginiEngineering Graphics: Course No. 6vic70r9Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Part OneDocument78 paginiLecture 1 Part Onewubied100% (1)
- Welding Electrodes - Understanding The SMAW Electrode SymbolsDocument5 paginiWelding Electrodes - Understanding The SMAW Electrode SymbolsRobert DelafosseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Graphics: Course No. 5Document13 paginiEngineering Graphics: Course No. 5vic70r9Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing Form 4 (Quadrilaterals)Document14 paginiEngineering Drawing Form 4 (Quadrilaterals)farah sakinah100% (1)
- Caesar Ii: Training SyllabusDocument1 paginăCaesar Ii: Training SyllabusJason ChongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Orthographic ProjectionDocument61 pagini3 - Orthographic ProjectionaliffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Assembly DrawingsDocument87 paginiChapter 6 - Assembly DrawingsAnonymous ohCM2ktv100% (1)
- Engineering Graphics Syllabus and ConceptsDocument68 paginiEngineering Graphics Syllabus and ConceptsSUSHIL SUSHILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 03 Orthographic ProjectionDocument46 paginiChapter 03 Orthographic Projectionmusiomi2005Încă nu există evaluări
- .NG Mec 224 Properties of Mat TheoryDocument73 pagini.NG Mec 224 Properties of Mat TheoryYusuf taiwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsDocument9 paginiEngineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsJithesh.k.sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Principles of WeldingDocument23 paginiTeknologi Dan Rekayasa: Principles of WeldingBouzaida MaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Project: Sections of SolidsDocument13 paginiMicro Project: Sections of Solidsomkar digamabar sononeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping DrawingDocument36 paginiPiping DrawingmansurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Technical DrawingDocument41 paginiIntroduction To Technical Drawingnormanjames966Încă nu există evaluări
- DEMONSTRATION - Const. of A HelixDocument2 paginiDEMONSTRATION - Const. of A HelixNitin B maskeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step and V-FittingDocument11 paginiStep and V-FittingME Rgukt100% (1)
- RivetsDocument28 paginiRivetsMS JAMWALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smithy & Forging ShopDocument24 paginiSmithy & Forging Shopashok junapudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering DrawingDocument1 paginăEngineering DrawingDreamtech PressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing & WorkshopDocument126 paginiEngineering Drawing & WorkshopAtthapol YuyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intersection of SolidsDocument19 paginiIntersection of SolidsNitin Maske100% (1)
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 2Document6 paginiDrawing 2 Book-Ch 2Yasser Abd-ElrazekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 3Document7 paginiDrawing 2 Book-Ch 3Yasser Abd-ElrazekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intersection of SurfacesDocument12 paginiIntersection of SurfacesNipun HarshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09A10491 Engg DrawingDocument8 pagini09A10491 Engg DrawingSaquib SalahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Paper-Based Assays For Urine Analysis) A. Types of Paper and Other Porous SubstratesDocument8 pagini(Paper-Based Assays For Urine Analysis) A. Types of Paper and Other Porous Substratesrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Chap03 001Document22 paginiHeat Chap03 001rashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Lucas-Washburn Equation-Based Modeling of Capillary-Driven Flow in Porous SystemsDocument2 paginiLucas-Washburn Equation-Based Modeling of Capillary-Driven Flow in Porous Systemsrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- (Paper-Based Microfluidic Point-Of-Care Diagnostic Devices) WaxpatterningDocument5 pagini(Paper-Based Microfluidic Point-Of-Care Diagnostic Devices) Waxpatterningrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 01Document84 paginiCH 01fang7591100% (4)
- Armand VDocument11 paginiArmand Vrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Apple PuddingDocument1 paginăApple Puddingrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Ese 17Document3 paginiEse 17rashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Butter ChickenDocument1 paginăButter Chickenrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument40 paginiQuality Function Deploymentrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Mech Conv II IesDocument15 paginiMech Conv II IesSue WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument5 paginiChapter 1 Introductionrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Quality and TQMDocument11 paginiQuality and TQMrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Taguchi's Steps To Carry Out The Experimental Design and Offline Control. Product Life Cycle Characteristics Curve Three Magic Wands of Japanese ManagementDocument1 paginăTaguchi's Steps To Carry Out The Experimental Design and Offline Control. Product Life Cycle Characteristics Curve Three Magic Wands of Japanese Managementrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer MCQs - Mechanical Engineering Objective QuestionsDocument27 paginiHeat Transfer MCQs - Mechanical Engineering Objective Questionsrashik072100% (2)
- Hydraulic and Fluid Machines Multiple ChoiceDocument64 paginiHydraulic and Fluid Machines Multiple Choicerashik072100% (1)
- Thermal Degradation Behavior of Inconel 617 AlloyDocument5 paginiThermal Degradation Behavior of Inconel 617 Alloyrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 paginiFluid Mechanics Multiple Choice Questionsrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Degradation Behavior of Inconel 617 AlloyDocument5 paginiThermal Degradation Behavior of Inconel 617 Alloyrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of Sheet Processing On The Microstructure, Tensile, and Creep Behavior of INCONEL Alloy 718Document14 paginiThe Effect of Sheet Processing On The Microstructure, Tensile, and Creep Behavior of INCONEL Alloy 718rashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 ReferencesDocument2 paginiChapter 6 Referencesrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Cryogenic Properties of Some Cutting Tool Materials PDFDocument10 paginiCryogenic Properties of Some Cutting Tool Materials PDFrashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of Sputtered Inconel 617Document5 paginiCharacterization of Sputtered Inconel 617rashik072Încă nu există evaluări
- Solving Radical PuzzlesDocument7 paginiSolving Radical PuzzlesPaula MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Questions Maxima MinimaDocument4 paginiJEE Questions Maxima MinimalucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Primary CheckpointDocument16 paginiCambridge Primary CheckpointNordie RemegioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Sol Crosswalk 01 09Document22 paginiMath Sol Crosswalk 01 09mschaferÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Area ComputationDocument22 pagini7 Area ComputationIshtiaq hussain0% (1)
- CH 1 SimilarityDocument309 paginiCH 1 SimilarityRavi Kumar Chaurasia80% (5)
- Applied Mechanics Chapter 2: Laws of Forces: Tushar Kiran Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument25 paginiApplied Mechanics Chapter 2: Laws of Forces: Tushar Kiran Department of Mechanical EngineeringTushar KiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- (S3) Test-Midterm 20230315Document10 pagini(S3) Test-Midterm 20230315gurnoorkaur sandhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- APMO 2018 Math Olympiad ProblemsDocument2 paginiAPMO 2018 Math Olympiad ProblemsSiddhiksha ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PL PDFDocument3 paginiPL PDFalmas0% (1)
- CAT Quant Questions PDFDocument65 paginiCAT Quant Questions PDFSuryansh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roll No.: 31 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2014Document10 paginiRoll No.: 31 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2014vatsalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2D and 3D ShapesDocument3 pagini2D and 3D ShapesvirusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 51 Identifying and Describing Triangles MarvietblancoDocument28 paginiLesson 51 Identifying and Describing Triangles MarvietblancoMarinette LayaguinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 4Document245 paginiPart 4Nageswar MakalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAT G9 - Congruence and SimilarityDocument43 paginiMAT G9 - Congruence and SimilarityEtha CantikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To Textbook Engineering Graphics With AutoCADDocument90 paginiSolutions To Textbook Engineering Graphics With AutoCADNanda Kumar63% (8)
- MPM2D0 REVIEW ADocument6 paginiMPM2D0 REVIEW ARuby Kabouke100% (1)
- Review Exercise 2Document19 paginiReview Exercise 2eventra bangladeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elements of Stat S L Sidney L (Ebooksread - Com)Document523 paginiThe Elements of Stat S L Sidney L (Ebooksread - Com)Sanjay SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 ReviewDocument4 paginiChapter 5 Reviewapi-232613595Încă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Syllabus For 2013 WACEDocument79 paginiMathematics Syllabus For 2013 WACEDaniel PushpanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euclidean Plane and Its Relatives - Anton Pretunin PDFDocument166 paginiEuclidean Plane and Its Relatives - Anton Pretunin PDFRaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Quality Testing TechniquesDocument29 paginiSoftware Quality Testing TechniqueschandimacpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 9 Mathspace ExtensionDocument624 paginiYear 9 Mathspace ExtensioncrawIey100% (3)
- Exercise 1 PDFDocument5 paginiExercise 1 PDFAnurag KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHSMEDocument5 paginiAHSMENathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Geometry Notes and Questions For SAT:GRE PDFDocument32 paginiAdditional Geometry Notes and Questions For SAT:GRE PDFAnshul WadhwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Topics: Paper 1 Past Paper Questions - Sorted by TopicDocument198 paginiList of Topics: Paper 1 Past Paper Questions - Sorted by TopicEbs TamÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJOPCM (Vol 5 4 3 D 12)Document9 paginiIJOPCM (Vol 5 4 3 D 12)Fustei BogdanÎncă nu există evaluări