Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Water Flow Tutorials
Încărcat de
Falahiah JudgeDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Water Flow Tutorials
Încărcat de
Falahiah JudgeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
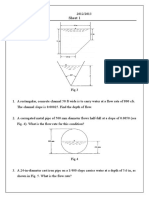
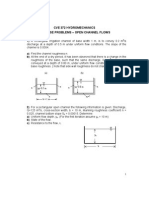
TUTORIALS - Chapter 3 1. Find the water depths if 1.0 m3/s of water that flow in a 1.
8 m-wide rectangular channel has a specific energy of 1.2 m. Water flow at a rate of 30 m3/s in a rectangular channel of 5 m width. Find (a) critical depth, and (b) critical velocity, if Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.030. Water flow at a rate of 25 m3/s in a trapezoidal channel with side slope m = 2.2, bottom width b = 3 m and Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.020. Find the critical depth, critical velocity and critical slope. Water flow with discharge of 8 m3/s in a triangular channel with side slope m = 2 and Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.020. Find the critical depth, critical velocity and critical slope. Find the diameter of a semi-circular channel that conveys 15.0 m3/s of water at critical state. A trapezoidal channel with bottom width of 3 m, side slope 1(v) : 1.5(h) and Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.012 carries a discharge of 50 m3/s. Draw the specific energy curve for water depths from y = 0 to y = 5 m at intervals of 0.25 m. Water flows in a rectangular channel at a rate of 7 m3/s/m and normal depth of 2 m. Find the maximum height of the weir to be built in the channel to produce critical flow above it. A trapezoidal channel has a side slope of 1(v) : 3 (h), bottom width = 2 m, bottom slope = 0.008 and Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.013. Water flows in the channel at a normal depth of 0.5 m. Find the minimum height of a broad-crested weir that produces critical flow above it. A long rectangular channel with width = 2.6 m has Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.015 and bottom slope So = 0.0008. Water flows at the rate of 10 m3/s. If a 0.7 m-high weir is built in the channel, find the depth of water upstream and downstream of the weir. Sketch the flow profile. Water flows with a normal depth of 1 m in a 3 m-wide rectangular channel. A weir is built which causes the sub-critical flow at upstream becomes super-critical at downstream. If the water depth above the weir is 0.76 m and discharge coefficient is 0.66, find the discharge. Water flows in a 2.5 m-wide rectangular channel at a rate of 5.3 m3/s/m and normal depth = 2 m. Find the maximum constriction width that is allowed in the channel without causing backwater at upstream. A long 2.6 m-wide rectangular channel with Manning roughness coefficient n = 0.015 and bottom slope = 0.0008 conveys water at 9.8 m3/s. If constriction is made with a width of 2.4 m, find the depth of water upstream and downstream of the constriction. Sketch the flow profile.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
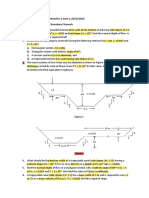
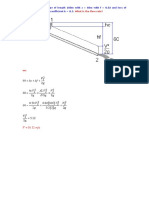
An open channel with a constant width has a broad-crested weir of 6 m height installed. If the depth of water behind the weir is 50 m, find the velocity of water if (i) the depth of water is reduced by 8 cm, and (ii) the depth of water is increased by 8 cm. Assume no energy loss. Also, find the critical depth and sketch the flow profile for the two conditions. A rectangular channel of 3 m width has a flow rate of 5 m3/s and water depth = 2 m. Find the critical depth at: i. above the broad crested weir with z = 30 cm, installed in the middle of the channel, ii. constriction section (without broad-crested weir) where the constriction width = 2.5 m, and iii. contriction section with broad-crested weir.
14.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Open Channel ProblemsDocument21 paginiOpen Channel ProblemsMangam Rajkumar100% (4)
- Chapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Document15 paginiChapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Jerle ParondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment on Channel Flow CalculationsDocument1 paginăFluid Mechanics Assignment on Channel Flow CalculationsKochuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPDocument8 paginiUce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPkarthickaryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixed TopicDocument105 paginiMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS3Document2 paginiPS3Syrille Lubigan AlarconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowDocument7 paginiNumericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowCristiano Omega RalteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller 2 - 2P-2020Document1 paginăTaller 2 - 2P-2020Yoel LobeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 3Document2 paginiQuiz 3acurvz2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Rapidly Varied Flow Tutorial ProblemsDocument1 paginăRapidly Varied Flow Tutorial ProblemsfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems Open Channel FlowDocument3 paginiProblems Open Channel Flow8986103t100% (1)
- Compre Hydraulics PSDocument5 paginiCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Open-Channel Flow ExamplesDocument7 paginiOpen-Channel Flow ExamplesAlfatah muhumedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MoF I, MoF 2 TutorialsDocument8 paginiMoF I, MoF 2 TutorialsDr. Pratheesh KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems On Channel ControlsDocument2 paginiProblems On Channel Controlswacotc2163Încă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Hydraulics Module 1: Key Concepts of Open Channel FlowDocument4 paginiAdvanced Hydraulics Module 1: Key Concepts of Open Channel FlowRajendra Kore100% (1)
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics IIDocument3 paginiHydraulics IIZerihun Ibrahim0% (1)
- Tutorial 2Document1 paginăTutorial 2Haniza SahudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uniform Flow Channel Hydraulics ProblemsDocument2 paginiUniform Flow Channel Hydraulics ProblemsADELLINNE NATASYA BINTI ROSDI / UPMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Channel Hydraulics WorksheetDocument5 paginiOpen Channel Hydraulics WorksheetLemi100% (2)
- Sheet 1Document11 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidraulica de Canales AbiertosDocument3 paginiHidraulica de Canales AbiertosLauren AndrewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document2 paginiAssignment 2mustefa kelilÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 141 Hydraulic EngineeringDocument7 paginiCE 141 Hydraulic EngineeringAngelo Mathew ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDocument7 paginiCVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDorry Magdy100% (1)
- Assignment No. 1: Course: Hydraulic Engineering I&D-501 Due Date: 12 March 2021Document2 paginiAssignment No. 1: Course: Hydraulic Engineering I&D-501 Due Date: 12 March 2021Aarish MaqsoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce142p-2 Q3-B A2Document1 paginăCe142p-2 Q3-B A2Jemuel FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller Flujo Gradualmente VariadoDocument9 paginiTaller Flujo Gradualmente VariadoFelipe Ferrin VilladaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecw301 Asgmt 3Document1 paginăEcw301 Asgmt 3eijal11Încă nu există evaluări
- 19 1 PDFDocument6 pagini19 1 PDFآكوجويÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment and WorksheetDocument3 paginiAssignment and WorksheetHMAN OROMOÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringDocument9 paginiCE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringSivarajSivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 3135 Sample Problems On WeirsDocument11 paginiCE 3135 Sample Problems On WeirsDave Robin Olanga Bobier100% (6)
- Hydraulics Weir Problems AssignmentDocument1 paginăHydraulics Weir Problems AssignmentGerrold RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsDocument7 paginiFluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsPraveen SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CvaDocument2 paginiCvaZaid HadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test On Fluid MechanicsDocument11 paginiTest On Fluid MechanicsJonathan GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question BankDocument9 paginiCE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question Banksankaran sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics Assignment Open Channel Flow ProblemsDocument3 paginiHydraulics Assignment Open Channel Flow ProblemsChanako Dane100% (1)
- Pipe Flow Rate CalculationDocument146 paginiPipe Flow Rate Calculationmalditaako66% (47)
- Hydraulics Geotech2Document101 paginiHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Rate Calculation for PipeDocument146 paginiFlow Rate Calculation for PipeKarl Anne DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics, Soil Mechanics, and Hydraulics ProblemsDocument3 paginiFluid Mechanics, Soil Mechanics, and Hydraulics ProblemsStudent555Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment FM 2Document2 paginiAssignment FM 2KrijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 paginiProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- Open Channel Hydraulics Worksheet 2Document4 paginiOpen Channel Hydraulics Worksheet 2Yasin Mohammad Welasma100% (1)
- Question No 1:: AnswerDocument11 paginiQuestion No 1:: AnswerShaheer RizwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4 - Open Channel FlowDocument4 paginiTutorial 4 - Open Channel Flowumaluxman kanagasingamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet OpcDocument2 paginiWorksheet OpcnewayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visit: Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument9 paginiVisit: Civildatas - Blogspot.insankaran sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsDe la EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Melbourne's Water Catchments: Perspectives on a World-Class Water SupplyDe la EverandMelbourne's Water Catchments: Perspectives on a World-Class Water SupplyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A World of Rivers: Environmental Change on Ten of the World's Great RiversDe la EverandA World of Rivers: Environmental Change on Ten of the World's Great RiversEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 497, July 11, 1885De la EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 497, July 11, 1885Încă nu există evaluări
- The Water Supply of the El Paso and Southwestern Railway from Carrizozo to Santa Rosa, N. Mex. American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, No. 1170De la EverandThe Water Supply of the El Paso and Southwestern Railway from Carrizozo to Santa Rosa, N. Mex. American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, No. 1170Încă nu există evaluări
- SpanDocument9 paginiSpanFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory+3+ +Point+Load+TestDocument6 paginiLaboratory+3+ +Point+Load+TestFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slope StabilityDocument28 paginiSlope Stabilityzzany86100% (2)
- STAIRSDocument46 paginiSTAIRSKannamma Dorairaj50% (2)
- 2.0 Analysis and Design: 2.2 Structural ElementsDocument29 pagini2.0 Analysis and Design: 2.2 Structural ElementsFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 (Color)Document56 paginiChapter 5 (Color)Falahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 4 ConcreteDocument43 paginiCHAPTER 4 ConcreteFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 7 - Other MaterialsDocument80 paginiCHAPTER 7 - Other MaterialsFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 5 - Woods at TimberDocument37 paginiCHAPTER 5 - Woods at TimberFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- April 13 East Grand Forks Roundabout or Street Rebuild MaterialsDocument19 paginiApril 13 East Grand Forks Roundabout or Street Rebuild MaterialsJoe BowenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop ProceedingsDocument71 paginiWorkshop ProceedingsAndualem TadesseÎncă nu există evaluări
- If X Is A Limit Point of A Set S, Then Every Open Ball Centered at X Contains Infinitely Many Points of S?Document1 paginăIf X Is A Limit Point of A Set S, Then Every Open Ball Centered at X Contains Infinitely Many Points of S?naoto_somaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-3-Control Strategies For Environmental RisksDocument30 paginiChapter-3-Control Strategies For Environmental Riskswaleedsalama1Încă nu există evaluări
- EEG - Brainbit-SpecificationDocument2 paginiEEG - Brainbit-SpecificationSergio OlivieriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design & Optimization of Bed Material Screening Machine For AFBC BoilerDocument11 paginiDesign & Optimization of Bed Material Screening Machine For AFBC BoilermansukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Item Analysis MPSDocument14 paginiItem Analysis MPSRose AspirasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cblephpl 04Document9 paginiCblephpl 04Srikanth G.RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trent 700 - tcm92-5733Document4 paginiTrent 700 - tcm92-5733arabysadekÎncă nu există evaluări
- CisplatinDocument3 paginiCisplatinRicey MelegritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- As 60068.2.61-2003 Environmental Testing Tests - Test Z ABDM - Climate SequenceDocument8 paginiAs 60068.2.61-2003 Environmental Testing Tests - Test Z ABDM - Climate SequenceSAI Global - APACÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miconium Ctac29: Quaternary Ammonium SaltDocument1 paginăMiconium Ctac29: Quaternary Ammonium Saltanon_993394650Încă nu există evaluări
- EMI and Cable's Role in EMC ComplianceDocument3 paginiEMI and Cable's Role in EMC Compliancekrishna_ScrbidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicaments & DefinitionDocument32 paginiPredicaments & DefinitionGisselle PauloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feast of Tabernacles Part 1Document45 paginiFeast of Tabernacles Part 1marcdhaynesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Marks QA MOMDocument11 pagini2 Marks QA MOMvasanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bill of Lading PDFDocument2 paginiBill of Lading PDFSushant Pai60% (5)
- How To Make A Simple DC MotorDocument1 paginăHow To Make A Simple DC MotorQuen AñanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10th Grade Vocabulary Matching ExerciseDocument2 pagini10th Grade Vocabulary Matching ExerciseDinara İbrahim QızıÎncă nu există evaluări
- History & Physical Examination in Obstetrics and Gynecology: Dr. Getamesay M. (MD)Document64 paginiHistory & Physical Examination in Obstetrics and Gynecology: Dr. Getamesay M. (MD)Chara ZerihunÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITP - Data & Telephone InstallationDocument6 paginiITP - Data & Telephone InstallationGultom Juliana LiliesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentinel EventsDocument14 paginiSentinel EventsNatasha BhasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRONICS Grade10 Quarter1 Module6 Week6 PDFDocument5 paginiELECTRONICS Grade10 Quarter1 Module6 Week6 PDFxander isonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utilization of Waste Materials As A Partial Replacement of BitumenDocument65 paginiUtilization of Waste Materials As A Partial Replacement of BitumenVenkatram PrabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notam For LGGGDocument42 paginiNotam For LGGGAPOSTOLOS KATSIONISÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kultura at Tradisyon NG Mga HAPONDocument1 paginăKultura at Tradisyon NG Mga HAPONJullianMarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument14 paginiArt Appreciation ReviewerRon RealinÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHWRDocument2 paginiPHWRNoraishah Syahirah AzharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fanuc 16i 210i Ts AlarmsDocument109 paginiFanuc 16i 210i Ts AlarmstugskulÎncă nu există evaluări