Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
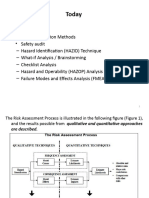
Simplified Risk Analysis LOPA 7
Încărcat de
CH1253Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Simplified Risk Analysis LOPA 7
Încărcat de
CH1253Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AIChE 2002 National Meeting Paper 281a
Page 5 of 6
Beyond LOPA. Some scenarios or groups of scenarios are too complex for LOPA. A more detailed risk assessment tool such as event tree analysis, fault tree analysis, or quantitative risk analysis is needed. Some examples where this might be true include: o A system that has shared components between the initiating event and candidate IPLs, and no cost effective way of providing independence. This system violates the LOPA requirement for independence between initiating event and IPLs. o A large complex system with many LOPA scenarios, or a variety of different consequences impacting different populations. This system may be more effectively analyzed and understood using quantitative risk analysis. Risk Criteria. Implementation of LOPA is easier if an organization has defined risk tolerance criteria. It is very difficult to make risk based decisions without these criteria, which are used to decide if the frequency of the mitigated consequence (with the IPLs in place) is low enough. CCPS (6) provides guidance and references on how to develop and use risk criteria. Consistency. When an organization implements LOPA, it is important to establish tools, including aids like look-up tables for consequence severity, initiating event frequency, and PFD for standard IPLs. The calculation tools must be documented, and users trained. All LOPA practitioners in an organization must use the same rules in the same way to ensure consistent results (6).
CONCLUSION
Process safety engineers and SIL assignment teams from many companies have concluded that LOPA is an effective tool for SIL assignment. LOPA requires fewer resources and is faster than fault tree analysis or quantitative risk assessment. If more detailed analysis is needed, the LOPA scenarios and candidate IPLs provide an excellent starting point. LOPA has the following advantages: Focuses on severe consequences Considers all the identified initiating causes, Encourages system perspective Confirms which IPLs are effective for which initiating causes Allocates risk reduction resources efficiently Provides clarity in the reasoning process, Documents everything that was considered, Improves consistency of SIL assignment Offers a rational basis for managing IPLs in an operating plant
REFERENCES
1. 2. Center for Chemical Process Safety (CCPS), Guidelines for Safe Automation of Chemical Processes, American Institute of Chemical Engineers, New York, NY, 1993. The Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society (ISA), ANSI/ISA 84.01-1996, Application of Safety Instrumented Systems to the Process Industries, The Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society, Research Triangle Park, NC, 1996.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Root Cause Analysis Handbook: A Guide to Efficient and Effective Incident InvestigationDe la EverandRoot Cause Analysis Handbook: A Guide to Efficient and Effective Incident InvestigationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft System Safety: Assessments for Initial Airworthiness CertificationDe la EverandAircraft System Safety: Assessments for Initial Airworthiness CertificationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survival Analysis Using SAS: A Practical Guide, Second EditionDe la EverandSurvival Analysis Using SAS: A Practical Guide, Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation For Apple M1 ChipDocument16 paginiPresentation For Apple M1 ChipVilayat Ali100% (1)
- Lean Six Sigma QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Lean Six SigmaDe la EverandLean Six Sigma QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Lean Six SigmaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- All Student of BuetDocument79 paginiAll Student of Buetzunaidur_rashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New CCPS Guideline BookDocument17 paginiA New CCPS Guideline BookMahmood Vahid100% (1)
- Conduct Effective Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) - StepsDocument14 paginiConduct Effective Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) - Stepsamal118Încă nu există evaluări
- How To Develop A Statement of Applicability According To ISO 27001-2013Document10 paginiHow To Develop A Statement of Applicability According To ISO 27001-2013SecureAware100% (3)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessDe la EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- The Redemption Service Membership Application PDFDocument1 paginăThe Redemption Service Membership Application PDFrrcocorey1_170011228Încă nu există evaluări
- Sms Tools& Analysis MethodDocument27 paginiSms Tools& Analysis Methodsaif ur rehman shahid hussain (aviator)Încă nu există evaluări
- Faq Layers of Protection Analysis (Lopa)Document6 paginiFaq Layers of Protection Analysis (Lopa)OSIIQPGRISÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 - HazopDocument23 pagini5 - HazopMuhammad Raditya Adjie PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snares To LOPA Action Items: GCPS 2013Document9 paginiSnares To LOPA Action Items: GCPS 2013userscribd2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Applying GAMP 5 To Validate An ERP SystemDocument8 paginiApplying GAMP 5 To Validate An ERP SystemTahir ZiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument17 paginiRoot Cause AnalysisvenkylearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Pha Methods PDFDocument10 paginiComparison of Pha Methods PDFQayyum KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Process Hazard Analysis: What Is It and How Do I Do It?Document5 paginiIndustrial Process Hazard Analysis: What Is It and How Do I Do It?Heri IsmantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFDocument16 paginiSelection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFdediodedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazop Training GuideDocument9 paginiHazop Training GuideAli RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evaluation of Safety Barriers Using The Method LopaDocument7 paginiThe Evaluation of Safety Barriers Using The Method LopaDiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layer of Protection AnalysisDocument9 paginiLayer of Protection Analysiscera211164Încă nu există evaluări
- Core Tools PDFDocument3 paginiCore Tools PDFR.BalasubramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Factors in LOPADocument26 paginiHuman Factors in LOPASaqib NazirÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAZOP Training Guide NewDocument13 paginiHAZOP Training Guide NewKhalis RiyanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improved Integration of LOPA With HAZOP Analyses: Dick Baum, Nancy Faulk, and P.E. John Pe RezDocument4 paginiImproved Integration of LOPA With HAZOP Analyses: Dick Baum, Nancy Faulk, and P.E. John Pe RezJéssica LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazard Identification Techniques in IndustryDocument4 paginiHazard Identification Techniques in IndustrylennyÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAZOP Training GuideDocument9 paginiHAZOP Training GuideOoAlquimistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazop Training GuideDocument9 paginiHazop Training GuideAdyBorsosÎncă nu există evaluări
- T12A Papierz Arkadiusz TORASDocument6 paginiT12A Papierz Arkadiusz TORASArek PapierzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Anaylsis by Hybrid Hazop and Fmea TechniqueDocument12 paginiRisk Anaylsis by Hybrid Hazop and Fmea TechniqueGiuseppe GoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layer of Protection AnalysisDocument6 paginiLayer of Protection Analysishmatora72_905124701Încă nu există evaluări
- TRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerDocument5 paginiTRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerAnonymous JyrLl3RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Operation AuditingDocument24 paginiChapter 3 Operation AuditingChristine Joy AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplified Risk Analysis (LOPA)Document8 paginiSimplified Risk Analysis (LOPA)hmatora72_905124701Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of Process Hazard Analysis in An Oil & Gas Pipeline Company: From Ad-Hoc To An Enterprise Standard PracticeDocument10 paginiEvolution of Process Hazard Analysis in An Oil & Gas Pipeline Company: From Ad-Hoc To An Enterprise Standard PracticeMarcelo Varejão CasarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 06 Risk AnalysisDocument20 paginiLecture 06 Risk Analysisrowan mamdouhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Characteristics For Security Critical DomainDocument4 paginiQuality Characteristics For Security Critical DomainGhulam Qadir MehrviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument12 paginiRoot Cause Analysisosalp internationalÎncă nu există evaluări
- XIV Paper 38Document11 paginiXIV Paper 38Zenon KociubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECADocument2 paginiBasic Concepts of FMEA and FMECAalyalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rbps Module 02 - Overview of Rbps 11-29-12Document28 paginiRbps Module 02 - Overview of Rbps 11-29-12Stephanny DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrating Hazop and Sil/Lopa Analysis: Best Practice RecommendationsDocument10 paginiIntegrating Hazop and Sil/Lopa Analysis: Best Practice Recommendationsavinash_mokashi7073100% (1)
- Implementation of A Risk-Based Process Safety Management SystemDocument22 paginiImplementation of A Risk-Based Process Safety Management SystemDeepak Dubey100% (2)
- AIAG FMEA Manual The BenchmarkDocument2 paginiAIAG FMEA Manual The BenchmarkUmer Al-FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Validation Master Plan (VMP) For Plasmapheresis. Plasmapheresis in 54 StepsDocument21 paginiValidation Master Plan (VMP) For Plasmapheresis. Plasmapheresis in 54 StepscpkakopeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Layer of Protection Analysis: KeywordsDocument6 paginiIntroduction To Layer of Protection Analysis: KeywordsAquiles_voyÎncă nu există evaluări
- GAMP 5 Quality Risk Management Approach: by Kevin C. Martin and Dr. Arthur (Randy) PerezDocument7 paginiGAMP 5 Quality Risk Management Approach: by Kevin C. Martin and Dr. Arthur (Randy) PerezSaurabh VijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management Tools PDFDocument27 paginiRisk Management Tools PDFGeorge John AmegashieÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To ISO Standard Methodology For Condition MonitoringDocument5 paginiAn Introduction To ISO Standard Methodology For Condition Monitoringralexml100% (1)
- SETLabs Briefings Software ValidationDocument75 paginiSETLabs Briefings Software ValidationaustinfruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damage Mechanism Hazard ReviewDocument17 paginiDamage Mechanism Hazard ReviewBobby VonnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 11 12 - FMECADocument21 paginiSession 11 12 - FMECASusanoo12Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisDe la EverandGas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Troubleshooting and Root Cause Failure Analysis: Equipment Problem SolvingDe la EverandTroubleshooting and Root Cause Failure Analysis: Equipment Problem SolvingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Conduct of Operations and Operational Discipline: For Improving Process Safety in IndustryDe la EverandConduct of Operations and Operational Discipline: For Improving Process Safety in IndustryEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Implementation of Anti-Money Laundering Information SystemsDe la EverandImplementation of Anti-Money Laundering Information SystemsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Operational Risk & Control (ORC) Best Practice FrameworkDe la EverandOperational Risk & Control (ORC) Best Practice FrameworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operational Risk & Control (ORC) Best Practice FrameworkDe la EverandOperational Risk & Control (ORC) Best Practice FrameworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certifiable Software Applications 2: Support ProcessesDe la EverandCertifiable Software Applications 2: Support ProcessesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Oxford 3000 Word ListDocument20 paginiThe Oxford 3000 Word ListCH1253100% (1)
- Class MinutesDocument1 paginăClass MinutesCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Crossing A Jungle To A Sea of Mermaids Dragon Ebook DraftDocument39 paginiCrossing A Jungle To A Sea of Mermaids Dragon Ebook DraftCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrochimica Acta: Shrikant S. Raut, Babasaheb R. SankapalDocument9 paginiElectrochimica Acta: Shrikant S. Raut, Babasaheb R. SankapalCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrochimica Acta: Shrikant S. Raut, Babasaheb R. SankapalDocument9 paginiElectrochimica Acta: Shrikant S. Raut, Babasaheb R. SankapalCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Highly Visible Light Responsive, Narrow Band Gap Tio Ƥ Elemental Red Phosphorus For Photocatalysis and Photoelectrochemical ApplicationsDocument1 paginăHighly Visible Light Responsive, Narrow Band Gap Tio Ƥ Elemental Red Phosphorus For Photocatalysis and Photoelectrochemical ApplicationsCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Sustainability in The Water-Energy-Food-Environment Nexus: The Role of Chemical EngineersDocument1 paginăSustainability in The Water-Energy-Food-Environment Nexus: The Role of Chemical EngineersCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Highly Visible Light Responsive Narrow Band Gap TiDocument10 paginiHighly Visible Light Responsive Narrow Band Gap TiCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Training Functional Safety 04 Risk Assessment Rev0 Part1Document1 paginăTraining Functional Safety 04 Risk Assessment Rev0 Part1CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Mi 2011Document5 paginiMi 2011CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Vaishnava Song BookDocument115 paginiVaishnava Song BookSuryasukra100% (14)
- VitaleDocument11 paginiVitaleCH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part27Document1 paginăFlash Part27CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- NFPA 704 Warning Placard RequirementsDocument1 paginăNFPA 704 Warning Placard RequirementsMirna Ghaib InsaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magoosh GRE Flashcards Advance - Part1Document1 paginăMagoosh GRE Flashcards Advance - Part1CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part38Document1 paginăFlash Part38CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Ommon - Part22Document1 paginăOmmon - Part22CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part38Document1 paginăFlash Part38CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part34Document1 paginăFlash Part34CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part31Document1 paginăFlash Part31CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part17Document1 paginăFlash Part17CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part31Document1 paginăFlash Part31CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part24Document1 paginăFlash Part24CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part26Document1 paginăFlash Part26CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part38Document1 paginăFlash Part38CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part27Document1 paginăFlash Part27CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Flash Part23Document1 paginăFlash Part23CH1253Încă nu există evaluări
- Student Results Management SystemDocument12 paginiStudent Results Management Systemamol100% (1)
- Course Overview Guide - Intro To CS MakeCode MicrobitDocument26 paginiCourse Overview Guide - Intro To CS MakeCode MicrobitUmair AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Guide For Gel Doc 2000Document2 paginiQuick Guide For Gel Doc 2000RNM1747Încă nu există evaluări
- Mercedita M. Vergara: Personal DataDocument2 paginiMercedita M. Vergara: Personal DataAtienza JohnrehÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hanging Tree - Jennifer LawrenceDocument6 paginiThe Hanging Tree - Jennifer LawrenceChan Sek Yeong100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document61 paginiLecture 2AMBELEMBIJEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation9 - Query Processing and Query Optimization in DBMSDocument36 paginiPresentation9 - Query Processing and Query Optimization in DBMSsatyam singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- NFS2-640/E: Fire Alarm Control Panel Installation ManualDocument76 paginiNFS2-640/E: Fire Alarm Control Panel Installation ManualRafa DunkelhaarigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Density 12MFDocument3 paginiUsing Density 12MFM Ahmed LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ManagementDocument13 paginiProject ManagementTushar TaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Start Guide For Colubris/HP Gateways: 2008, Wifi-Soft Solutions All Rights ReservedDocument10 paginiQuick Start Guide For Colubris/HP Gateways: 2008, Wifi-Soft Solutions All Rights ReservedTùng LâmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catel.4.2.0.documentationDocument388 paginiCatel.4.2.0.documentationfsfsfsefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hasp SecurityDocument88 paginiHasp Securitysnji kariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rover ConstructionDocument19 paginiRover ConstructionNicolas Del BuonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Integrate Google Drive With OdooDocument13 paginiHow To Integrate Google Drive With OdoorobogormanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Q2 Global Digital StatshotDocument50 pagini2018 Q2 Global Digital StatshotAlbert LuzxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Introduction New 2021-22 - OddDocument120 paginiPython Introduction New 2021-22 - OddRahul A 1si19ei049Încă nu există evaluări
- The Main Stakeholders For The Wedding Parties EverythingDocument10 paginiThe Main Stakeholders For The Wedding Parties EverythingLakpa TenzinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSE8003 Installation InstructionsDocument2 paginiDSE8003 Installation InstructionsIBRAHIM AL-SURAIHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 and 4Document31 paginiChapter 3 and 4Rey Allen TenosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PreDCR Do and DontDocument31 paginiPreDCR Do and Dontvenkata satyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing-Secure Distributed Deduplication Systems With Improved ReliabilityDocument9 paginiDesigning-Secure Distributed Deduplication Systems With Improved ReliabilityrashmithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avocado Watering Monitor With Telegram BOTDocument3 paginiAvocado Watering Monitor With Telegram BOTKARTHIK N RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acm IcpcDocument3 paginiAcm IcpcSivaramakrishna Markandeya GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recognizing The Computer NetworkDocument16 paginiRecognizing The Computer NetworkAgus Dian PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ItpDocument2 paginiItphazim gomer PangodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Station in Surveying - Operation, Uses and AdvantagesDocument6 paginiTotal Station in Surveying - Operation, Uses and AdvantagesRipzan xhtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales InvoiceDocument15 paginiSales InvoiceUn Int100% (1)