Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
GEN201 Pset 3 Q Only
Încărcat de
hkcitygirl87Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GEN201 Pset 3 Q Only
Încărcat de
hkcitygirl87Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1. You are starting a new rotation in a Drosophila lab.
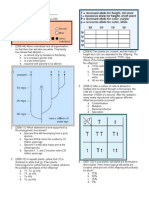
While looking at some of the lab stocks to familiarize yourself with flies, you notice a female with a spotted body phenotype in a vial of wildtype flies. You decide you want to characterize this mutation further. First, you cross the fly to a male wildtype fly to see if the mutation is dominant or recessive. alf of the progeny flies from this cross are spotted, and half have wildtype pigmentation, so you conclude that the mutation is dominant, and the spotted flies are heterozygous at the mutant locus. 1a. Your ne!t step is to map the mutation to a chromosome. "iven the following strains, what crosses would you perform to show that the spotted body mutation maps to the # chromosome$ %nclude your e!pected results if the mutation does or does not map to the # chromosome. &train genotype Sp ' ( F)*'Y +',yDescription )utant strain heterozygous for the spotted body mutation )ales containing an # chromosome balancer with a dominant bar eye phenotype +. chromosome / marker that causes a dominant lobe0shaped eye phenotype, recessive lethal ,y-. chromosome / balancer that has a dominant curly0winged phenotype, recessive lethal )ale and female wildtype flies
('(, ('Y
1b. You do this cross and confirm that the mutation maps to the # chromosome. owever, you also notice something strange. During the crosses, you never found a spotted body male, only females. What are two possible e!planations for this$ 1c. You decide you want to map e!actly where the mutation lies on the # chromosome. 1o do so, you cross spotted body females with a true breeding strain containing recessive mutations b and c 2note. these are 3ust placeholders, % don4t know many # chromosome markers5. You take the spotted body females from this cross and cross them to b and c males. 1he phenotypes of the F/ progeny are listed in the table below. F/ 6henotype Wildtype &potted b mutant phenotype c mutant phenotype &potted b mutant &potted c mutant 7umber 898 //:; ;8 1;1 *< //
b mutant c mutant &potted b mutant c mutant 1otal
::=> 1;/ *;99
Draw a map of the 8 genes that includes the gene order and the distances between ad3acent genes. 1d. ?sing mosaic analysis, you would like to determine whether being homozygous mutant would be lethal for females. "iven the following reagents and strains, briefly e!plain how you would do this. What would you e!pect if the mutations were lethal$ %f they weren4t lethal$ "iven. 0 &train 1. heterozygous for spotted body and for a recessive marker on the # chromosome @white eyes$A. Blso contains an FC1 site on the # chromosome. 0 F+6 recombinase 1e. From part d, you find out that sp is recessive lethal, so females with two copies of the mutation also die. You would like to identify a temperature0sensitive allele of this gene in order to e!amine its effect in males at different stages of development. D!plain the crosses you would perform in order to do so given the following strains and a mutagen. &train genotype F)*'F)*, F)*'Y ('(, ('Y &p1 D' ( D Description )ale and female flies with chromosome 1 balancer @see 1a for descriptionA Wildtype male and female flies Female flies with original spotted body mutation and dominant EDF marker
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 6:1 Beta-Gal AssayDocument2 pagini6:1 Beta-Gal Assayhkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- Job NotesDocument1 paginăJob Noteshkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- 3:22 Beta-Gal AssayDocument3 pagini3:22 Beta-Gal Assayhkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- GEN201 Yeast Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 paginiGEN201 Yeast Extra Practice Problemshkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- GEN201 Pset 3 QDocument4 paginiGEN201 Pset 3 Qhkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Problem Set 2 SolutionsDocument8 pagini2010 Problem Set 2 Solutionshkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- GEN201 Yeast Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 paginiGEN201 Yeast Extra Practice Problemshkcitygirl87Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Cell CycleMitosis - ElisaDocument40 paginiCell CycleMitosis - ElisabenjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reality of LifeDocument2 paginiReality of LifeDjela117Încă nu există evaluări
- Algal Biorefineries Volume 2 Products and Refinery DesignDocument555 paginiAlgal Biorefineries Volume 2 Products and Refinery DesignHernan AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Physiology of The Pancreas PDFDocument66 pagini04 Physiology of The Pancreas PDFMonesa Christy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Qualifications Courses Taken in University: Disediakan OlehDocument1 paginăAcademic Qualifications Courses Taken in University: Disediakan OlehKhairina GmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcqs On Natural Selection Neo Darwinism Mechanism of EvolutionDocument41 paginiMcqs On Natural Selection Neo Darwinism Mechanism of EvolutionAhsan Arshad BSIT-F16-LC-008100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Companies in BangladeshDocument6 paginiPharmaceutical Companies in BangladeshMd Raju Mia50% (2)
- Case 4 Novartis Gilenya (Pain)Document19 paginiCase 4 Novartis Gilenya (Pain)phaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - IB Biology (2016) - 1.3 - Membrane Structure PPT Part BDocument10 pagini3 - IB Biology (2016) - 1.3 - Membrane Structure PPT Part BUlises DeyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument130 paginiPDFShiv PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Sol Review 15 - Genetics EvolutionDocument4 paginiBio Sol Review 15 - Genetics Evolutionapi-2424050090% (1)
- HR Mail Id'sDocument15 paginiHR Mail Id'sDr-Shubhaneel NeogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMAT Biology Practice Questions Set 3Document7 paginiNMAT Biology Practice Questions Set 3Nurshayma JalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCSF Graduate School Statement of PurposeDocument2 paginiUCSF Graduate School Statement of PurposeKevin AllenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Drug Candidates by Design - A Focus On Physicochemical Properties As A Means of Improving Compound Disposition and Safety PDFDocument37 paginiImproving Drug Candidates by Design - A Focus On Physicochemical Properties As A Means of Improving Compound Disposition and Safety PDFBen ZoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Microbiology 1Document8 paginiPractical Microbiology 1Adlina TajuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem Cell ReportsDocument24 paginiStem Cell ReportsNguyen Dac Hanh HieuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intracellular Compartments and Vesicular Traffic - 2016Document32 paginiIntracellular Compartments and Vesicular Traffic - 2016Muhammad Akip PoapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.I Sec 4.Document18 paginiB.I Sec 4.dark SpizroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Pharmacy Internship Major Pharmacy Internship: University of San Agustin University of San AgustinDocument3 paginiMajor Pharmacy Internship Major Pharmacy Internship: University of San Agustin University of San AgustinJohney DoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pandemic - On The Brink (Manual)Document8 paginiPandemic - On The Brink (Manual)Friedslick6Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of cAMP Dependent Protein Kinase PKA CATALYTIC UNIT ISOFORMS Pone.0181091Document17 paginiEvolution of cAMP Dependent Protein Kinase PKA CATALYTIC UNIT ISOFORMS Pone.0181091Sudhir RavindranÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Advances in Parasitology 35) J.R. Baker, R. Muller and D. Rollinson (Eds.) - Academic Press (1995)Document347 pagini(Advances in Parasitology 35) J.R. Baker, R. Muller and D. Rollinson (Eds.) - Academic Press (1995)Stoian GoranovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fun FactsDocument1 paginăFun FactsAndrey_gpÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Handbook of Bioanalysis and Drug Metabolism 2004 0415275199 PDFDocument397 paginiA Handbook of Bioanalysis and Drug Metabolism 2004 0415275199 PDFanjum_niaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cell Biology PDFDocument41 paginiIntroduction To Cell Biology PDFediaz_956003100% (2)
- 10 1161@jaha 120 016910Document3 pagini10 1161@jaha 120 016910Isabella-Diana ChelbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment For TutorialDocument3 paginiAssessment For TutorialAngelica RocamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 7.3 and 7.4 WS KEYDocument6 paginiBiology 7.3 and 7.4 WS KEYWhaleGod82% (11)
- Mod2 PDFDocument30 paginiMod2 PDFمحمود عامرÎncă nu există evaluări