Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
GMAT Algebra Note
Încărcat de
suvra12Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GMAT Algebra Note
Încărcat de
suvra12Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Algebra ======== Chapter - 1 (PEMDAS) ========================= PEMDAS - parenthesis/absolote value - exponent- multiplication - addition - subt raction A group of multiplication
and division operation must be performed from left to right. A group of addition and subtraction operations must be performed from left to ri ght. Chapter - 2 (Linear Equation) ============================= Linear equation solved by substitution and combination. 3x- 5 = 9 - Example of linear equation Absolute value equation will have 2 answer 1 positive and 1 negative |-5| = 5 |5| = 5
Chapter3 (Exponent) ===================== 0 raised to any power equals 0 1 raised to any power equals 1 A base raised to the 0 power equals 1 (x to the power 0 = 1) 0 to the power 0 - undefined Notes in pad. Chapter4 (Root) ================ Notes in pad. Print out book Page 48 and 49 Chapter 5(Quadratic equation) ============================= x(x + 3)(x 1) = 0 answer -> x = 0/x = 1/x = -3 If you have a quadratic expression equal to 0, and you can factor an * out of th e expression, then x = 0 is a solution of the equation. Math convention does not allow division by 0. When 0 appears in the denominator of an expression, then that expression is undefined. (x-3)(x+4)/x = 0 then x = 3 or x = -4 Special Formula----------------(a +b)2 / (a - b)2 / a2- b2
Chapter 7 (inequality) ======================== When you multiply or divide an inequality by a negative number, the inequality s ign flips! 4-3x < 10 -3x < 6 -x < 2 x > -2 Adding inequalities together is a powerful technique on the GMAT. However, note that you should never subtract or divide two inequalities. Only multiply inequalities together if both sides of both inequalities are posit ive. Absolute Value --------------|x-2|<5 Case 1: x-2 < 5 x < 5 +2 x < 7 Case2: -(x - 2) < 5 -x + 2 < 5 -X < 5 - 2 -X < 3 X > -3 Exponents, inequality problems involving even exponents require you to consider two scenarios (+ and -). Chapter 8 (Algebra Strategy) ============================ When a Data Sufficiency question asks for a combination of variables, don t try to solve for the value of each variable. Manipulate the statements to solve directly for the combinatio n. Example - What is the value of x/Y 1) X + Y/Y = 3 2) Y = 4 with option 1 ---------------x/y + y/y = 3 x/y + 1 = 3 x/y = 2 do not need to plug Y to 1st formula and solve for X. Directly manipulate the st
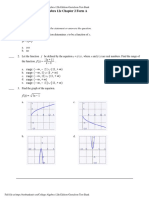
atement to solve for combination x/y. In this case 1st formula is sufficient to answer the question. **As is often the case with Combo problems, one statement by itself was sufficie nt to answer the question. **When a Data Sufficiency question contains an equation in the question stem, is olate the wanted variable and create the simplest combo you can. **Most Data Sufficiency questions that include inequalities are Yes/No questions . Whenever inequalities appear on Data Sufficiency,try to find values in a range t hat will give you different answers to a Yes/No question. Remember --------xy > 0 - x and y are both positive OR both negative xy < 0 - x and y have different signs (one positive, one negative) x2 (x square)- x < 0 - x2( x square ) < x so 0 < x < 1 Chapter 9 (Extra equation strategy) =================================== Note in pad. Chapter 10 (Functions) =========== The domain of a function indicates the possible inputs. The range of a function indi cates the possible outputs. For instance, the function f(x ) = x2 [x square] can take any input but never produces a negative number. So the domain is all numbers, but the range isf(x) > 0. Function problem ---------------**Direct proportion Write y1/x1 = y2/x2 **Inversly proportion write y1x1 = y2x2 **Linear Growth When growth in at a constant rate y = mx + b (Y is quantity, m is the constant rate of growth, x is time and Y int ercept b is the value of the quantity at time zero) **Exponential growth In exponential growth, a quantity is multiplied by the same constant each period of time (rather than adding the same constant, as in linear growth). Any expone ntial growth can be written as y(t) =y(0) kt in which y represents the quantity as a function of time t,y0 is t he value of the quantity at time t = 0, and k represents the constant multiplier for one period. Commonly, exponential growth multipliers take the form of percentage multipliers. For instance, for a quantit
y that increases by 7% each period, k = 1.07. **Symmetry Some difficult GMAT function questions revolve around symmetry, or the property th at two seemingly different inputs to the function always yield the same output. Always pick numbe rs to solve this. Chapter 11 (Extra Inequalities Strategies) =========================================== Note in notepad Print out page - 149, 150 - 151
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- MUHAMMAD ADRIAN KOSAKATA POLA BILANGAN, KOORDINAT KARTESIUS, DAN RELASI DAN FUNGSI-dikonversiDocument3 paginiMUHAMMAD ADRIAN KOSAKATA POLA BILANGAN, KOORDINAT KARTESIUS, DAN RELASI DAN FUNGSI-dikonversimuhammad adrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eicher School Faridabad Math Test Analyzes Note-Book SalesDocument3 paginiEicher School Faridabad Math Test Analyzes Note-Book SalesAnmol SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Equation - DPP 01 - Saakaar Batch For IIT JAM MathematicsDocument3 paginiDifferential Equation - DPP 01 - Saakaar Batch For IIT JAM MathematicsSadhana YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- CU-2021 B.sc. (Honours) Mathematics Semester-1 Paper-CC-1 QPDocument4 paginiCU-2021 B.sc. (Honours) Mathematics Semester-1 Paper-CC-1 QPMy MathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 5 Mixed Numbers To Decimals FDocument2 paginiGrade 5 Mixed Numbers To Decimals FTanja LazovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Here are the answers to the MCQ worksheet-II on Knowing Our Numbers:1. a2. c 3. d4. d5. b6. b7. d 8. a9. 99,985,10210. d11. cDocument64 paginiHere are the answers to the MCQ worksheet-II on Knowing Our Numbers:1. a2. c 3. d4. d5. b6. b7. d 8. a9. 99,985,10210. d11. cAditya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Digital Systems and Binary NumbersDocument100 paginiChapter 1 Digital Systems and Binary NumbersVandana JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chanukah MathDocument2 paginiChanukah MathRabbi Benyomin HoffmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divisibility Rules Guide for NumbersDocument5 paginiDivisibility Rules Guide for NumbersshubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample 50436Document16 paginiSample 50436Kunal SumukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cahigam Es Grade 5 Q1 Data-Bank-In-Math-5Document4 paginiCahigam Es Grade 5 Q1 Data-Bank-In-Math-5Jingky Petallo RayosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pentagon in The Projective PlaneDocument5 paginiPentagon in The Projective Planebison jadisÎncă nu există evaluări
- College Algebra 12th Edition Gustafson Test BankDocument58 paginiCollege Algebra 12th Edition Gustafson Test Banka190513728Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 9Document95 paginiModule 9Kush JuvekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9 Instructional Support Material 4th QDocument17 paginiGrade 9 Instructional Support Material 4th QJay ar SagmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus Tutorial 1 - Differential CalculusDocument25 paginiCalculus Tutorial 1 - Differential CalculusDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -K100% (9)
- tm111 PDFDocument22 paginitm111 PDFAmit ParmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2015Document24 paginiICSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2015Faisal GheyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- DepEd Order No. 42, s. 2016 Annex 1B Mathematics 9 Lesson PlanDocument11 paginiDepEd Order No. 42, s. 2016 Annex 1B Mathematics 9 Lesson PlandapitomaryjoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FractionDocument3 paginiFractionDoo RaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unang Panahunang Pagsusulit Sa Araling Panlipunan 5: Talaan NG IspesipikasyonDocument2 paginiUnang Panahunang Pagsusulit Sa Araling Panlipunan 5: Talaan NG IspesipikasyonEleonor Viola Enricoso BalilingÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSEFM Sequences WorksheetDocument1 paginăIGCSEFM Sequences WorksheetSwati 06Încă nu există evaluări
- Section 8.1: Using Basic Integration FormulasDocument3 paginiSection 8.1: Using Basic Integration Formulasgebran sarkisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4.5.1 Volumes by SlicingDocument6 paginiLecture 4.5.1 Volumes by SlicingMohd Haffiszul Bin Mohd SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsDocument5 pagini2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsHarris Lee50% (2)
- GED Math Lessons Practice Problems Workbook (PDFDrive)Document357 paginiGED Math Lessons Practice Problems Workbook (PDFDrive)Guo QiangÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 3 The DiscriminantDocument10 pagini10 3 The Discriminantapi-233527181Încă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Quarter 3 Week 7 and 8Document2 paginiWeekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Quarter 3 Week 7 and 8zaldy mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Maths and All Sciences NotesDocument117 paginiCombined Maths and All Sciences NotesAkshay AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Rmo NBHM 2012Document2 paginiPre-Rmo NBHM 2012Himansu Mookherjee0% (1)