Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lessons Learned
Încărcat de
api-252471713Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lessons Learned
Încărcat de
api-252471713Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lessons learned session 1:
Course Main Objectives: Improving ones ability to spot and evaluate opportunities for a new business venture Acquiring the concepts and spirit necessary for business entrepreneurship Examining a business model as whole, rather than concentrating separately on its functional aspects Learning the importance of validating the idea and the team before creating a business
Before: Traditional approach business plan Problem: No business plan survives first contact with a customer Nowadays: Revolutionary approach - Business model (Alex Osterwalder); Customer development (Steve Blank); Lean Startup (Eric Ries). First of all - Creating the team: We have to combine different talents to have a good team: Visionary, Hacker, Hustler, Designer. Second step The idea (Remember the ideia is just 10%): To evaluate the idea: 1) Global 2) Scalable (more you produce, less you have to invest per unit) 3) Innovative (something different) 4) Disruptive (that defines a position and a new trend) 5) Viral 6) Bootstrapping (a business that do not require a lot of money) 7) Internet (the internet gives the opportunity to measure the impact: something that newspaper does not give) 8) Mobility (it is a mobile world, remember!) 9) Doable Third, how do we develop this idea and create something with it? We need a business model, a rational process that allows us to organize our ideas, discuss and make decisions on many topics and come up with a plan to make it work. We need to create delivery and capture value.
We must always keep in mind that this is a complex, complicated process and to overcome this we will use a new Business Model: 1) Simple but relevant; 2) A model that everyone intuitively understands; 3) A model that facilitates descriptions and discussion; 4) A model that is not overly simplified and that hides the complexity of the enterprise; 5) A shared language ; 6) A step-by-step program that shows the logic and the players in the creation and development process; And for this, we will use the following Business Model Canvas:
The 9 Blocks of the Business Model Canvas: 1. Customer Segments first we must understand what is that customers want; whats missing and what are they looking for and understanding that they are the heart of every business model. We must also define if we need to group them into segments according to their needs, behaviors and important attributes; 2. Value proposition spot and solve customers problems by providing them with a product or a service that will satisfy their needs;
3. Channels definition of how will we deliver value, what means of communication should be used, distribution and selling points. This represents a very important for the overall customer experience; 4. Customer Relationships how to create, maintain and boost customers relationships; 5. Revenue Streams how will we successfully create value; 6. Key Resources investment in the required assets to offer and delivery value to customers; reach markets and keep creating value. These resources can be physical, financial, intellectual and human; 7. Key Activities define the crucial activities a company must do to make the business model work and be successful; 8. Key Partners creating the right network of suppliers and outsourcing companies, pursuing strategic alliances that can be beneficial for our business; 9. Cost Structure what will all of the costs be to follow this business model; Remember: we have to test the model over and over again! So, testing hypothesis with our potential customers (with the customer development approach in mind): 1. Define who are our main customers; 2. Define what is the problem we wish to solve with the product we plan on developing and whats the solution; 3. Test the solution and analyze the results; 4. Validate if we are testing the right customer segment and, if not, change the business model; This way, we exclude potential failures and we are able to work on more adequate business models. After defining who our customers are, we should do at least one MVP. What Is MVP? MVP stands for minimum viable product and it allows the working team to collect the maximum amount of validated information. This will help us understand if customers are
interested in using the product we are offering and how much are they willing to pay for it. And, like we learned in class today, we are often surprised by our customers answers. Before engaging in this testing method, we should once again define what the outcome should be and compare the real results to the ones predicted. But, testing doesnt end here. In fact this is only the beginning. We had the opportunity to learn about other testing methods, as well as real life cases that were very successful. Main Testing Hypothesis: 1. Interviewing: it is crucial at this stage to listen to what others are telling us. We are not suppose to sell anything, but to understand what is that customers are looking for and what do they expect to get; this is a process that is time consuming but it is crucial for the success of the business model; 2. Survey: they should be short and straight forward, with the maximum of 10 questions. This is a faster way to get feedback from potential customer but should only be done after the interviewing process. 3. 3. A/B Testing: in our opinion, this is a very clever and effective way to test
between two hypotheses. The main idea is to offer the same service or product with one difference; either it is the price of the good, the name, or any other feature we are still not sure about. We can collect information and understand which one was more appealing to the public. After all that we have already the Problem defined the Solution in mind and the Market where our business fit.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hypothesis - Customer Relationships Channels and Revenue Sources ValidationDocument9 paginiHypothesis - Customer Relationships Channels and Revenue Sources Validationapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Panzerotti Interviews ConclusionsDocument5 paginiPanzerotti Interviews Conclusionsapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Business Model Canvas 2 0Document1 paginăBusiness Model Canvas 2 0api-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Top 5 Hypothesis ValidationDocument8 paginiTop 5 Hypothesis Validationapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Survey ResultsDocument20 paginiSurvey Resultsapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis - Key Resources Key Activities and Key Partners ResultsDocument8 paginiHypothesis - Key Resources Key Activities and Key Partners Resultsapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Briefings InesDocument1 paginăBriefings Inesapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Briefings JoaoDocument2 paginiBriefings Joaoapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Organizational ChartDocument1 paginăOrganizational Chartapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Panzerotti Interview ScriptDocument2 paginiPanzerotti Interview Scriptapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Briefings HenrDocument2 paginiBriefings Henrapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Briefings - LiatDocument2 paginiBriefings - Liatapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
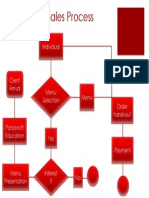
- Sales ProcessDocument1 paginăSales Processapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 6 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 6 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Session 5 - PresentationDocument18 paginiSession 5 - Presentationapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 6 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 6 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis - Key Resources Key Activities and Key PartnersDocument8 paginiHypothesis - Key Resources Key Activities and Key Partnersapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Session 6 - PresentationDocument13 paginiSession 6 - Presentationapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Panzerotti Interview ScriptDocument2 paginiPanzerotti Interview Scriptapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Business Model Canvas 1 1Document1 paginăBusiness Model Canvas 1 1api-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 5 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 5 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis - Customer Relationships Channels and Revenue SourcesDocument10 paginiHypothesis - Customer Relationships Channels and Revenue Sourcesapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Session 4 - Presentation CorrigidoDocument23 paginiSession 4 - Presentation Corrigidoapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 4 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 4 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 2 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 2 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 1 BlogDocument3 paginiLessons Learned 1 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Top 5 HypothesisDocument8 paginiTop 5 Hypothesisapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learned 3 BlogDocument4 paginiLessons Learned 3 Blogapi-252471713Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- EntrepreneurDocument19 paginiEntrepreneurKeziah CarandangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 16 QTR 2 Math 1Document7 paginiWeek 16 QTR 2 Math 1Cjezpacia VictorinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Brigada Eskwela PlanDocument3 pagini2020 Brigada Eskwela PlanEdmar De Guzman Jane92% (12)
- My AnswersDocument8 paginiMy AnswersPlatonus Doesn'texistÎncă nu există evaluări
- WPI Work Personality Index PDFDocument90 paginiWPI Work Personality Index PDFdanielitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Physical EducationDocument18 paginiLesson 1 Physical EducationJohnne Erika LarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance TaskDocument2 paginiPerformance TaskHoney Sevilla100% (1)
- Adjectives in Text ProductionDocument68 paginiAdjectives in Text ProductionclementecollingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reciprocal: TeachingDocument6 paginiReciprocal: Teachingvikas kadamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Political Philosophy English Course 2nd Semestre 2021Document31 paginiPolitical Philosophy English Course 2nd Semestre 2021marcelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Observation Guide Tool 1Document1 paginăClass Observation Guide Tool 1camilo reyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - 1 OBE, MQF and MQA Overview The BIG PictureDocument93 paginiModule 1 - 1 OBE, MQF and MQA Overview The BIG PictureMahatma Murthi100% (1)
- A Review of Colin Lankshear's and Michele Knobel's Handbook For Teacher Research: From Design To ImplementationDocument4 paginiA Review of Colin Lankshear's and Michele Knobel's Handbook For Teacher Research: From Design To ImplementationTATIANA SOFIA MECON MECONÎncă nu există evaluări
- The SAMR Model: Background and Exemplars: Ruben R. Puentedura, PH.DDocument69 paginiThe SAMR Model: Background and Exemplars: Ruben R. Puentedura, PH.DJess DjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Festival and Special Event Management - AllenDocument3 paginiFestival and Special Event Management - Allenvaleria_popa33% (6)
- Facebook Usage - Research Paper 1Document26 paginiFacebook Usage - Research Paper 1Alba, Lenard S.Încă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource Thesis SampleDocument5 paginiHuman Resource Thesis SampleAhmad H. FadliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criteria Overview CBSTDocument2 paginiCriteria Overview CBSTAgot Dowes DogomeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eugene Albert Nida - Learning A Foreign Language - A Handbook Prepared Especially For Missionaries (1957) PDFDocument224 paginiEugene Albert Nida - Learning A Foreign Language - A Handbook Prepared Especially For Missionaries (1957) PDFFernando ZemorÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLA SkriptaDocument22 paginiSLA SkriptaAnđela AračićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weisbach ResumeDocument1 paginăWeisbach Resumeapi-282302410Încă nu există evaluări
- Professional Competency Assessment 1Document19 paginiProfessional Competency Assessment 1Bruce MannÎncă nu există evaluări
- 091218-NITK Poster3Document1 pagină091218-NITK Poster3Gomatesh M. RavanavarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR&R Data Sheet GR&R Data Sheet: Variable Data Results - Total Variation Variable Data Results - Total VariationDocument4 paginiGR&R Data Sheet GR&R Data Sheet: Variable Data Results - Total Variation Variable Data Results - Total VariationRahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Course-Syllabus American-CultureDocument9 pagini2021 Course-Syllabus American-CultureMin MinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jwele AhmedDocument1 paginăJwele AhmedMa Hdi ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHLP Format 2021-2022Document1 paginăWHLP Format 2021-2022Mark Owen BaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level B1 Intensive Course: Worksheet For Week 8Document6 paginiLevel B1 Intensive Course: Worksheet For Week 8farid perez bustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Indexing and Abstracting of Document TextsDocument282 paginiAutomatic Indexing and Abstracting of Document TextsSalton GerardÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCU ExhibitionDocument18 paginiCCU ExhibitionmeitaÎncă nu există evaluări