Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Panel Edificio Con Amortiguadores
Încărcat de
Daniel QuirogaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Panel Edificio Con Amortiguadores
Încărcat de
Daniel QuirogaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
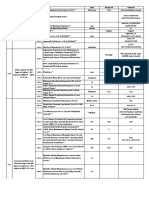
Response Controlled Building and Device Datasheet - EXAMPLE
Building name Shinagawa Tower Completion date May, 2000 Building owner Tokyo Electric Corp. Architect Kantou Sekkei Corp. Structural designer Saitama Engineering Contractor Gunma Co.,LTD. Building site Shinagawa,Tokyo,Japan Maximum eaves height 120m Principal use Office Classification of structure Steel structure Number of Stories 20 stories Structural type Moment frame Total floor area 1800 m2 Foundation Pile foundation 2 30 Building area 900 m Number of control device Purpose of employing response control system a. To reduce building response under moderately big earthquake and big earthquake for seismic safety b. To reduce building acceleration under typhoon or strong wind for habitability Pictures, diagrams, tables, figures (no format)
9m
6.5m 37.5m 6.5m 6.5m
9m
Features of structure a. Using Concrete Filled steel Tubes for columns b. Using steel hysteretic dampers as studs for each floor Target performance of building Earthquake Wind Excitation *1 *2 Input level Maximum velocity 25 cm/s Maximum velocity 50 cm/s Maximum velocity 28 m/s Maximum stress Short-term allowable stress Elastic limit Maximum story shear coefficient Maximum story drift 1/200 1/100 1/1000 Residual story drift *3 1/1000 Maximum acceleration 5 cm/s2 Maximum ductility factor Check of control devices *4 No check Check No check Verification of performance Excitation *1 Earthquake Wind Modeling Discrete mass model Discrete mass model Analysis method Dynamic response analysis Dynamic response analysis Seismic wave El Centro NS 1940, Taft EW 1952, Hachinohe NS 1968 Input level *2 Maximum velocity 25 cm/s Maximum velocity 50 cm/s Maximum velocity 28 m/s Maximum stress 90% of S.T. allowable stress 75% of Elastic limit 0.16 Maximum story shear coefficient 0.09 Maximum story drift 1/230 1/125 1/1865 *3 Residual story drift 1/1650 Maximum acceleration 322 cm/s2 589 cm/s2 3.8 cm/s2 0.84 1.39 Maximum ductility factor Response control system and device Classification P-E-V Type of Device Steel hysteretic damper Mechanism Energy Dissipation Name of Device Unbond Brace for Seismic Control Type of control Hysteretic damping Applications *5 10 buildings for height over 60m Features a. Hysteretic damper of axially yielding type with low yield point steel and concrete filled steel tube b. Energy dissipation by axial deformation of low yield point steel c. Installed as brace in a frame d. Adequet stiffness and strength by adjusting thickness and width of steel plates e. Down sizing of connectors by high-friction steel plates Notes *1 Fill in kinds of excitation, such as Earthquake, Wind, Machinery vibration, etc. *2 Fill in according to the practice in each country. For example, maximum velocity 25 cm/s and 50 cm/s are employed for rare (once in several decades) and extremely rare (once in 50 decades) earthquake, respectively in Japan.
3.25m 5.75m 6.5m
6.5m 37.5m
6.5m
5.75
3.25m
Photo of building
location of device
Framing plan
story
Story shaer force
story
Figure of device
Photo of device
Framing elevation and analytical model
Story drift
*3 Fill in if prescribed for target performance *4 Special inspection for disorder of control devices
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 3.01 - Steel Silo 3200 MTDocument3 pagini3.01 - Steel Silo 3200 MTCelltron SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Retaining Reinforced Concrete Section To BS 8007& BS 8110Document15 paginiLiquid Retaining Reinforced Concrete Section To BS 8007& BS 8110tttmm100% (1)
- ITP of Admin Building NEW AutosavedDocument14 paginiITP of Admin Building NEW Autosavedomda4wady0% (1)
- 4 Inch Ips (GTP)Document1 pagină4 Inch Ips (GTP)S ManoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel Chimney and RCC Foundation As Per Indian Code 22052014Document12 paginiDesign of Steel Chimney and RCC Foundation As Per Indian Code 22052014Ahmad Badsha Quadri58% (19)
- Long Span and High-Rise Steel ConstructionDocument89 paginiLong Span and High-Rise Steel Constructionကိုနေဝင်း100% (1)
- Complete Design Report of Bridge Using CSiBridgeDocument60 paginiComplete Design Report of Bridge Using CSiBridgeKS Lee75% (4)
- Aluminum Flexible Duct Machine - AFT1Document1 paginăAluminum Flexible Duct Machine - AFT1tubeformerÎncă nu există evaluări
- REU Course - Tower and Foundation - June 2011Document46 paginiREU Course - Tower and Foundation - June 2011Elena DamocÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - AC Equipment ScheduleDocument8 pagini02 - AC Equipment ScheduleductienssjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix: Data Sheets of Applications 383Document6 paginiAppendix: Data Sheets of Applications 383Luis Gil MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design of Warehouse Using Structural SteelDocument154 paginiStructural Design of Warehouse Using Structural Steelnirez14100% (3)
- BOQ - Canteen ExtentionDocument5 paginiBOQ - Canteen ExtentionHantu TuahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACCC® Helsinki Spec SheetsDocument31 paginiACCC® Helsinki Spec SheetsRamzes47Încă nu există evaluări
- Information - Roofing SheetDocument5 paginiInformation - Roofing SheetRajeev RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Carrying Steel Truss BridgeDocument50 paginiPipe Carrying Steel Truss BridgeMesfin Derbew91% (11)
- General Functions: Home Canadian American Log-OutDocument6 paginiGeneral Functions: Home Canadian American Log-OutanithaamarnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS3 HVAC Duct Metal Work Specifications FINALDocument8 paginiCVS3 HVAC Duct Metal Work Specifications FINALMohammed MohieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 132kV May 2016-1 DemirerDocument2 pagini132kV May 2016-1 DemirerKonsultio Dario KrausseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design DataDocument1 paginăStructural Design DatawanjohimuiyuroÎncă nu există evaluări
- GF - Kangkung Lampung - Slim Tower 30M - 18 Maret 2022 - Rev00Document113 paginiGF - Kangkung Lampung - Slim Tower 30M - 18 Maret 2022 - Rev00galang setiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of 220kv Transmission Line Tower in Different Zones I & V With Different Base Widths A Comparative StudyDocument9 paginiAnalysis and Design of 220kv Transmission Line Tower in Different Zones I & V With Different Base Widths A Comparative StudyVaibhav JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- DESIGN CALCULATIONS - GL-03 2509 - 4.0mDocument17 paginiDESIGN CALCULATIONS - GL-03 2509 - 4.0mmsiddiq1Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural Glass Design-CP3Document5 paginiStructural Glass Design-CP3msiddiq1Încă nu există evaluări
- SECTION 15815 Sheet Metal Duct Work Part 1 - General 1.1 Related DocumentsDocument14 paginiSECTION 15815 Sheet Metal Duct Work Part 1 - General 1.1 Related DocumentsMunir RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Considerations: Types of Busbar Choice of Busbar MaterialDocument96 paginiDesign Considerations: Types of Busbar Choice of Busbar MaterialNikhilesh BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- HV TransformerDocument11 paginiHV Transformermavericksailor100% (1)
- Statical Calculation of 50m TowerDocument25 paginiStatical Calculation of 50m TowerAntenasmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slab Design CombinedDocument28 paginiSlab Design CombinedEr. Rajendra Acharaya0% (1)
- SL - No Item Units 11Kv VCB Panel 1.0 Data SheetDocument4 paginiSL - No Item Units 11Kv VCB Panel 1.0 Data SheetAntra ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penstocks: Figure: Typical Installaion of PenstocksDocument6 paginiPenstocks: Figure: Typical Installaion of PenstocksTharindu Nuwan JayakodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design ConsiderationsDocument5 paginiDesign ConsiderationsKhalith MansoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITCC in Riyadh Residential Complex J10-13300 08920-1 Glazed Aluminum Curtain WallsDocument9 paginiITCC in Riyadh Residential Complex J10-13300 08920-1 Glazed Aluminum Curtain WallsuddinnadeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- IC-20 Commercial Flatwork IronerDocument2 paginiIC-20 Commercial Flatwork IronerAl AdcockÎncă nu există evaluări
- SB Series: Specification SheetDocument18 paginiSB Series: Specification Sheet'X-fuera' Orchid PhiencÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Wall ExampleDocument3 paginiRC Wall Examplendoan_44Încă nu există evaluări
- Glass PanelDocument2 paginiGlass PanelEIWAA50% (2)
- Sediver Composite Gapless Line Surge Arresters: FeaturesDocument2 paginiSediver Composite Gapless Line Surge Arresters: FeaturesAnonymous rAFSAGDAEJ100% (1)
- U Type Retaining WallDocument12 paginiU Type Retaining Wallharnishtanna212100% (2)
- PRC National Standard: ICS 83 .120 Q23Document27 paginiPRC National Standard: ICS 83 .120 Q23邢焕震Încă nu există evaluări
- New Zealand Soakage Design Manual - Auckland CityDocument11 paginiNew Zealand Soakage Design Manual - Auckland CityFree Rain Garden ManualsÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinalDocument12 paginiFinalchompink6900Încă nu există evaluări
- Tower Design ReportDocument91 paginiTower Design Reportkbkshanaka86% (7)
- Vibration Standards For Different Countries PDFDocument7 paginiVibration Standards For Different Countries PDFokt_lyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro PileDocument8 paginiMicro PileJennifer Pearson100% (3)
- Final Acoustic Enclosure PresentationDocument48 paginiFinal Acoustic Enclosure PresentationsartajyadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Cable Trench Section 1-1: Soil ParametersDocument23 paginiDesign of Cable Trench Section 1-1: Soil Parametersg4goharÎncă nu există evaluări
- 51 PDFDocument8 pagini51 PDFhutuguoÎncă nu există evaluări
- StaircaseDocument74 paginiStaircaseakhlaq_hssainkotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus Bar Insulating ShroudsDocument3 paginiBus Bar Insulating ShroudsRohit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminum Flexible Duct Machine - AFT2Document1 paginăAluminum Flexible Duct Machine - AFT2tubeformerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convention Center Structural CalculationsDocument2.776 paginiConvention Center Structural CalculationsGiho Kim0% (1)
- Structural Handrail DesignDocument3 paginiStructural Handrail Designmsiddiq1100% (1)
- Amrita Vishwavidyapeetham Amrita School of Engineering, Bangalore Ansys - Lab ExamDocument2 paginiAmrita Vishwavidyapeetham Amrita School of Engineering, Bangalore Ansys - Lab ExamPramod GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Str. Design Calc of Boundary WallDocument7 paginiStr. Design Calc of Boundary WallAnonymous NBGW6fj8Yl100% (2)
- MD Structure Hap Eoc PiuraDocument12 paginiMD Structure Hap Eoc PiuraazegarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignDe la EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsDe la EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesDe la EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- R5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process DataDocument24 paginiR5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process Datanico123456789Încă nu există evaluări
- (BS EN 1148 - 1999) - Heat Exchangers. Water-To-Water Heat Exchangers For District Heating. Test Procedures For Establishing The Performance Data.Document12 pagini(BS EN 1148 - 1999) - Heat Exchangers. Water-To-Water Heat Exchangers For District Heating. Test Procedures For Establishing The Performance Data.sfar yassineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2Document2 paginiReview Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2John Andre MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HGV Gas Fuel Throttle ValveDocument41 paginiHGV Gas Fuel Throttle ValveSayayinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEF University Math 115 Calculus Fall 2018-19 Midterm Exam 1 2 3 4 PDocument4 paginiMEF University Math 115 Calculus Fall 2018-19 Midterm Exam 1 2 3 4 PMELİHA KOÇÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yoga in Daily LifeDocument9 paginiYoga in Daily LifeLaerteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hardness Test BlocksDocument2 paginiHardness Test BlocksAvijit DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biophy-Lec (Mod1 - The-Basics) PDFDocument18 paginiBiophy-Lec (Mod1 - The-Basics) PDFShekinah LeynesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speech About Go GreenDocument4 paginiSpeech About Go GreenMuhammadArifAzw100% (1)
- SETTLING VELOCITY 2.1 - Calculations of Sedimentation Velocity and Hindered Settling Rate of ParticlesDocument74 paginiSETTLING VELOCITY 2.1 - Calculations of Sedimentation Velocity and Hindered Settling Rate of ParticlesSonu Singh100% (4)
- Frac To GraphyDocument639 paginiFrac To GraphyBHARANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Behaviour of Stainless Steel Bolted ConnectionsDocument11 paginiAnalysis of The Behaviour of Stainless Steel Bolted ConnectionsSam SamouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Report - EvaporationDocument14 paginiLaboratory Report - EvaporationWayne Tandingan0% (1)
- 1 Introduction of EOR LecturesDocument19 pagini1 Introduction of EOR LecturessereptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate: Well Test Analysis For Gas Condensate ReservoirDocument19 paginiCertificate: Well Test Analysis For Gas Condensate Reservoiryash chavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exemplo 9.5, Tipler e MoscaDocument1 paginăExemplo 9.5, Tipler e MoscaLaís VelameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Motor Problems & Diagnostic TechniquesDocument12 paginiElectric Motor Problems & Diagnostic Techniquesjuanca249Încă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Movie SummaryDocument2 pagini2012 Movie SummaryRenée NinteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edo Arte ExoskeletonDocument54 paginiEdo Arte ExoskeletonBlanca RiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- At N.p.c.i.l., RawatbhataDocument30 paginiAt N.p.c.i.l., RawatbhataDevendra SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparison of IEC 479-1 and IEEE STD 80 On Grounding Safety CriteriaDocument10 paginiA Comparison of IEC 479-1 and IEEE STD 80 On Grounding Safety Criteriaperijoy100% (1)
- Workshop 3-3: Rectangular Patch Antenna: Introduction To ANSYS Electronics DesktopDocument21 paginiWorkshop 3-3: Rectangular Patch Antenna: Introduction To ANSYS Electronics DesktopRodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Analysis of Properties of Ready Mix Concrete With Site Mix Concrete of Smart Road ProjectDocument6 paginiCritical Analysis of Properties of Ready Mix Concrete With Site Mix Concrete of Smart Road ProjectGolam Shahriar SakibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norwegian Maritime-Equipment 2016Document568 paginiNorwegian Maritime-Equipment 2016budiazis100% (1)
- ENGINEERING - MATHEMATICS - 2 VTU Syllabus PDFDocument167 paginiENGINEERING - MATHEMATICS - 2 VTU Syllabus PDFAdarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causality Bernhard SchölkopfDocument169 paginiCausality Bernhard SchölkopfQingsong GuoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Mechanical Properties of Concrete On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Copper Slag and Granite PowderDocument4 paginiStudy On Mechanical Properties of Concrete On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Copper Slag and Granite PowderIJIRST100% (1)
- Framo Cargo Pumps MaintenanceDocument6 paginiFramo Cargo Pumps MaintenanceOsman ŞenerÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAIC-A-2015 Rev 7Document8 paginiSAIC-A-2015 Rev 7Bebin Mathew0% (1)