Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Modul 3 Form 5
Încărcat de
Nurul Afida TahirDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Modul 3 Form 5
Încărcat de
Nurul Afida TahirDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ESTETIKA SDN BHD
TEACHERS COPY
MODUL 3 FORM 5 Chapter 2 (Force & Motion) 1. To test the knowledge of physics in Chapter 2 by using completing the sentences below What is meant by Statement 1. Linear motion Motion along a . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Scalar quantity Vector quantity Velocity Speed Acceleration Distance Displacement Inertia A physical quantity which has only . A physical quantity which has both ..and . The rate of change of . The rate of change of . The rate of change of .. The total .. of the path travelled
Displacement is the .. distance from one point to another point along a specific . The tendency of an object to ..changes to its state of motion whether the object is at or ...with constant velocity An object will at rest or motion with . velocity along a straight line unless it is acted upon by an external force. The .. of an object is directly proportional to the . acting on the object and inversely proportional to the. of the object To every . there is an equal and opposite .. . The product of and .. of an object The total momentum of a system before and after the collision is . if no external forces acted on the system. A push or a pull that can change the , or . of an object. Change of .. Rate of change of ..
10. Newtons First law
11. Newtons Second law
12. Newtons Third law 13. Momentum 14. Principle of conservation of momentum 15. Force 16. Impulse 17. Impulsive force
ESTETIKA SDN BHD 18. Weight Gravitational .. acting on an .
TEACHERS COPY
19. Mass 20. Free fall
The measurement of .. in the object. Free fall occurs when an object falling under the . of only without being affected by any other .forces and accelerates with a . acceleration regardless their The product of and the along the direction of the ..that cause the displacement The to do work. The region in which an object experiences a due to attraction. The energy . in the object because of its ..
21. Work
22. Energy 23. Gravitational field
24. Gravitational potential energy 25. Elastic potential energy
The energy of an object when it is .or .
26. Kinetic energy
The energy of an object due to its
27. The principle of conservation Energy cannot be .or . . It can be transformed from one form to another, but the total energy in a closed of energy system is constant. 28. Power The rate at which is done or energy is transferred.
29. Elasticity
The property of an object that enables it to return to its .. and dimensions (size) after an applied external force is removed. The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the . provided the elastic limit is not exceeded. The elastic limit of a spring is the force which can be applied to the spring before it loses its elasticity. The force constant of a spring is the .. per unit . or . distance
30. Hookes law 31. Elastic limit 32. Force constant (spring constant)
ESTETIKA SDN BHD 2 A car traveling with a velocity of 10 m s-1 accelerates uniformly at a rate of 3 m s-2 for 20 s. Calculate the displacement of the car while it is accelerating.
TEACHERS COPY
3 A van that is traveling with velocity 16 m s-1 decelerates until it comes to rest. If the distance traveled is 8 m, calculate the deceleration of the van.
4.
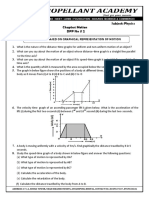
Figure 2.1 shows a tape chart consisting of 5-tick strip. Describe the motion represented by AB and BC. In each case, determine the ; (a) displacement (b) (c) average velocity acceleration
Length / cm 16 12 8 4 Figure 2.1
0A
B C Time/s Figure 2.1
5. Diagram 1 shows a ticker tape produced when a trolley move along an inclined runway.
(a)
Diagram 1 Complete the sentence below by ticking () the correct box. The type of current used for ticker timer alternating current. direct current. On Diagram 1 mark X to show one tick . Based on Diagram 1 determines the velocity of the trolley?
(b) (c)
ESTETIKA SDN BHD ANSWERS 1. What is meant by 1. Linear motion 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Scalar quantity Vector quantity Velocity Speed Acceleration Distance Displacement Inertia
TEACHERS COPY
Statement Motion along a straight line A physical quantity which has only magnitude A physical quantity which has both magnitude and direction The rate of change of displacement The rate of change of distance The rate of change of velocity The total length of the path travelled Displacement is the total distance from one point to another point along a specific direction The tendency of an object to resist changes to its state of motion whether the object is at rest or moving with constant velocity An object will remain at rest or motion with constant velocity along a straight line unless it is acted upon by an external force. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The product of mass and velocity of an object The total momentum of a system before and after the collision is equal if no external forces acted on the system. A push or a pull that can change the size, shape or direction of an object. Change of momentum Rate of change of momentum
10. Newtons First law
11. Newtons Second law
12. Newtons Third law 13. Momentum 14. Principle of conservation of momentum 15. Force 16. Impulse 17. Impulsive force
ESTETIKA SDN BHD 18. Weight Gravitational force acting on an object
TEACHERS COPY
19. Mass 20. Free fall
The measurement of matter in the object. Free fall occurs when an object falling under the effect of gravity only without being affected by any other external forces and accelerates with a constant acceleration regardless their mass The product of force and the displacement along the direction of the force that cause the displacement The ability to do work. The region in which an object experiences a force due to gravitational attraction. The energy stored in the object because of its position
21. Work
22. Energy 23. Gravitational field
24. Gravitational potential energy 25. Elastic potential energy
The energy of an object when it is compressed or extended
26. Kinetic energy
The energy of an object due to its motion
27. The principle of conservation Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can be transformed from one form to another, but the total energy in a closed of energy system is constant. 28. Power The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
29. Elasticity
The property of an object that enables it to return to its original shape and dimensions (size) after an applied external force is removed. The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force provided the elastic limit is not exceeded. The elastic limit of a spring is the maximum force which can be applied to the spring before it loses its elasticity. The force constant of a spring is the force per unit compression or extension distance.
30. Hookes law 31. Elastic limit 32. Force constant (spring constant)
ESTETIKA SDN BHD 2. s = ut + at2 s = (10)(20) + (3)(20)2 s = 800 m v2 = u2 + 2 as 02 = 162 + 2 a(8) a = -16 ms-2
TEACHERS COPY
3.
4. (a) s = 4 + 8 + 12 + 16 + 16 + 16 = 72.0 cm (b)
vaverage =
72 .0 6(0.1)
= 120.0 cm s-1
(c) v =
16.0 = 1.6 cm s-1 0.1 v u 1.6 0.4 = t 0.5
u=
a=
4 .0 = 0.4 cm s-1 0 .1
= 2.4 cm s-2
t = 5 (0.1) = 0.5 s
5. (a) alternating current (b) X is anywhere between 2 consecutive dots (c) 50 cm s-1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- MODUL 1 FORM 5 (Fizik)Document5 paginiMODUL 1 FORM 5 (Fizik)Nurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion: Unit 6Document20 paginiCircular Motion: Unit 6Nurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- MagnetismDocument42 paginiMagnetismNurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors and DielectricsDocument26 paginiCapacitors and DielectricsNurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul 1 Form 5Document5 paginiModul 1 Form 5Nurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Halal Overseas List PDFDocument23 paginiHalal Overseas List PDFFatihah Fatin SallehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiation TechniquesDocument9 paginiDifferentiation TechniquesNurul Afida TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- PHYSICS Review Guide 2D Motion: M - L B NDocument4 paginiPHYSICS Review Guide 2D Motion: M - L B Npotatoman51325Încă nu există evaluări
- Stefan Marinov Classicalphysicspart3maririchDocument284 paginiStefan Marinov Classicalphysicspart3maririchpalmi90100% (1)
- Class: 9 Subject: Physics Chapter: Motion DPP No # 2: Questions Based On Graphical Representation of MotionDocument3 paginiClass: 9 Subject: Physics Chapter: Motion DPP No # 2: Questions Based On Graphical Representation of MotionshashwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Class KinematicsDocument12 pagini2 Class KinematicsEva García DasíÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numericals On Equations of MotionDocument8 paginiNumericals On Equations of MotionAnjal GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 paginiRelative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics of A Rigid Body: DM D D DM DFDocument3 paginiDynamics of A Rigid Body: DM D D DM DFAlessio ScarabelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rectilinear Motion, Motion Graphs, Projectile and Curvilinear Motion, and Tangential and Normal Motion Sample ProblemsDocument16 paginiRectilinear Motion, Motion Graphs, Projectile and Curvilinear Motion, and Tangential and Normal Motion Sample ProblemsJohn AngeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent TasksDocument5 paginiNewtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent Tasksapi-372548146Încă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Notes (Xiii) : Constraint MotionDocument4 paginiTeaching Notes (Xiii) : Constraint MotionSankar KumarasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Uitm Sabah: Marks (10%)Document6 paginiUniversiti Teknologi Mara Uitm Sabah: Marks (10%)Nur AimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mean TimeDocument12 paginiMean TimeEikichi OniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysRevLett 130 221502Document6 paginiPhysRevLett 130 221502Edwin QuirogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate GeometryDocument34 paginiCoordinate GeometryNorhapidah Mohd SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- g484 Module 2 4 2 1circular MotionDocument8 paginig484 Module 2 4 2 1circular Motionapi-236179294Încă nu există evaluări
- Transcripción VsauceDocument4 paginiTranscripción VsauceFrancisco PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Assignment (Kinematics) Class-XII (Question)Document2 pagini1 Assignment (Kinematics) Class-XII (Question)Rahul SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment of A Force About A Point: Problem Set 3Document5 paginiMoment of A Force About A Point: Problem Set 3HeliosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 12-105Document53 paginiProblem 12-105adam johnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mth-382 Analytical Dynamics: MSC MathematicsDocument51 paginiMth-382 Analytical Dynamics: MSC MathematicsediealiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time TravelDocument28 paginiTime Travelkelvin vieira100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Motion in 1 - D II PracticeDocument8 paginiUnit 3 - Motion in 1 - D II PracticejoshvasilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yousef Maklad Gizmo Term 3 1Document6 paginiYousef Maklad Gizmo Term 3 1api-551575177Încă nu există evaluări
- Integral Calculus: John Rey M. Pacturanan, CE, MPDocument2 paginiIntegral Calculus: John Rey M. Pacturanan, CE, MPNathanielle AndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics 2: Effects of Forces Turning EffectDocument1 paginăMechanics 2: Effects of Forces Turning EffectGeanelle BonilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Physics 11se Ua EndDocument6 pagini03 Physics 11se Ua Endpecan_lisa38Încă nu există evaluări
- Speed Distance and TimeDocument7 paginiSpeed Distance and TimeNamaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter10 - Rotational MotionDocument80 paginiChapter10 - Rotational MotionHan VuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion 0625 - w01 - QP - 3-2Document2 paginiCircular Motion 0625 - w01 - QP - 3-2Nicole NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări