Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Thermal Conditions (Loading/Overloading Cycles, - The Dynamic Stresses Due To System Short Circuit Stresses
Încărcat de
Luciano EncisoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The Thermal Conditions (Loading/Overloading Cycles, - The Dynamic Stresses Due To System Short Circuit Stresses
Încărcat de
Luciano EncisoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Dielectric conditions (continuous and over voltages/system
inherent and transient/atmospheric over voltages, frequency of occurrence and amplitude) The thermal conditions (Loading/Overloading cycles, ambient temperatures) The dynamic stresses due to system short circuit stresses (shrinkage of insulation (normal ageing) and increase of dynamic stresses) Chemical changes due to the effect of agents Figure 1: Operational stresses
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Condition Normal Definition No obvious problems. No actions justified. No evidence of degradation Acceptable, but does not imply defect-free
Aged? Normal in service? Defective
No significant impact on short-term reliability but asset life may be affected in long terms, unless remedial action is carried out
Faulty
Can remain in service, but short-term reliability may be reduced. Remedial actions may or may not be successful
Failed
Has lost its functionality, cannot remain in service. Remedial action required before being returned to service (may be inexpensive repair or requiring replacement).
Figure 2: Definition of condition classification, acc. to CIGRE A2 WG 12.18
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 2
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
The main insulation ageing factors are: Air/Oxygen Moisture Temperature Mechanical/Electrical Stress Insulation Contamination These factors are strongly interlinked and act together Figure 3: Main Ageing Factors
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 3
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Impact of Air
Air/oxygen ingress causes: Ageing of the oil already at service temperatures (<7590C) and Ageing of the solid insulation Figure 4: Impact of Air
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 4
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Impact of Moisture Water/Moisture in a transformer is developed from: Ageing of cellulose To some extent from oil ageing and Mainly through diffusion/ingress external moisture Once water has penetrated and distributed in oil and solid insulation it causes: Accelerated ageing of cellulose Reduction of dielectric strength of oil and solid insulation Risk of bubble formation causing partial discharges
Figure 5: Impact of Moisture
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 5
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
1% moisture
1,2 1 0,8 0,6 0,4 0,2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10
4% moisture
Ti me ( mont hs)
10% moisture
Additional moisture ingress
Figure 6: Degree of polymerization of pressboard under different moisture contents at 95C
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 6
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Figure 7: Ageing of pressboard under moisture temp. Under the ingren of moisture DP-Values of < 200 are reached even at operating temperatures < 90 C
ARWtr 2004
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 7
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Air Humidity Temperatu re Contamina tion Electrical and Mechanica
Ageing of oil and Paper
Acids Sludge Humidity Conductive Particles
l
Overstress
Figure 8: Interaction between the various ageing factors
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 8
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
A transformer is defined by the following subsystems [5] - Electromagnetic circuit - Current carrying circuit - Dielectric system - Mechanical structure - Cooling system - Bushings - OLTC - Oil preservation and expansion system - Protection and Controls / Monitoring
Figure 9: Definition of functional Subsystems
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 9
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Electro-magnetic ability and integrity to transfer energy under specified conditions Integrity of current carrying circuits Dielectric withstand strength under specified stresses and normal ageing Mechanical withstand strength (short circuit fault current conditions). The Diagnostics must consider: What defects / faults can be expected in the transformer core and coil assembly What is the possible defect evolution into a failure
Figure 10: Service-Ability Requirements
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 10
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Summary of Functional related Diagnostics Generally applicable diagnostics (6.3.1) for Dielectric failure recognition in magnetic circuits (6.3.2) for Dielectric failure recognition in windings / main insulation (6.3.3) for Thermal failure recognition (6.3.4) for Critical ageing of oil and celluloses (6.3.5) for mechanical failure recognition (6.3.6) for Dielectric / thermal / mechanical failure in OLTC (6.3.7) for Dielectric / thermal failure in bushings (6.3.8)
Figure 11: Overview of diagnostic procedures
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 11
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Dielectric failure Recognition in Windings / main insulation DGA Oil analysis (BDV, dissipation, neutralization, etc.) Interfacial tension Humidity in oil Dielectric response (PDC / FDS) measurement for moisture / ageing Karl Fischer for moisture Degree of Depolymerisation (DP) Power factor and capacitance Winding resistance Dew-point measurement Partial discharge measurement and localization Transfer function analysis Frequency response Analysis Humidity in oil by sampling / On-line Monitoring
ARWtr 2004 Figure 12: Diagnostics of Dielectric failures in windings and main insulation
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 12
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Thermal Failures detection DGA Oil Analysis Interfacial tension FURAN Derivate Analysis Control of winding temperatures / oil temperatures Dielectric Response measurements (PDC, FDS) - for excess moisture control Hotspot controls by Thermo-Vision Magnetizing current control for core and/or winding thermal defect (depending DGA in Oil Analysis results
Figure 13: Thermal Ageing / defect recognition
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 13
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
DGA Oil Analysis Interfacial tension Moisture in oil Moisture in solid insulation by - Karl Fischer Titration - Dielectric Response Measurement (PDC / FDS) Power factor and capacitance Degree of depolymerisation (DP) FURAN DERIVAT-Analysis Thermo vision of hotspots in tanks or magnetic shields Winding hotspot measurement On-Line Monitoring of operational conditions PD-Measurement and localization
Critical Ageing due to thermal and / or dielectric problems
Figure 14: Some of the most important diagnostic procedures for critical ageing ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 14
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
For mechanical defect recognition
3-dimensional Shock recorder monitoring for excess dynamic impacts during transport Impedance measurement with low voltage (LV) precision instrumentation Low voltage impulse injection (LVI) response measurements DC-resistance measurements / solder joint control on multi-strand conductors FRA comparison with fingerprint and phase wise Transfer function analysis Clamping force control Noise and vibration measurement Visual inspection Repeat of dielectric test at 80 100 % U test
Figure 15: Mechanical defect recognition
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 15
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany Principles of Condition Assessment:
One of the most demanding engineering tasks is to derive from the symptoms of deficits the nature of the fault, the location of the faulty / defective component. But even more important is the validation of continued service-ability or of the involved risks. Is it normal Is it serious or or is there a fault is it fit for service
what is the reliability or the risk? These are the key questions for Condition Assessment. One quite successful way of condition assessment is: Definition of characteristics of defective conditions By fingerprinting from the factory By trend analysis.
With all the diagnostic procedures given in 6.3 above we now need good identification of defective symptoms - but more important we need to develop guidelines in limitations of diagnostic signatures. Examples see 10, Annex 1. Figure 16: Condition Assessment
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 16
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
DGA-Analysis Guidelines
100 Cellulose
Electrical Fault Normal Ageing
Discharge Discharge PD PD with with with high en. with low high energy low energy density en. density lower than 300C
Thermal Fault
from 300C higher than to 1000C 1000C
El. + Therm. Fault
overheating overheatinga and nd discharge PD
Concentration ratios
10
0,1 C2H2/C2H6 H2/CH4 C2H4 /C2H6 C2H4/C3H6 CO2/CO
Figure 17: MSS / VDE DGA Interpretation Scheme
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 17
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
3 2,5 2 2-FAL 1,5 1 0,5 0 0
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
1% Humidity
4% Humidity
10% Humidity
200
400 DP
600
800
1000
Figure 18: 2 FAL/DP Development at 95 C for different starting moisture content
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 18
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Case Nr. 10.3: 234 MVA-, 345 kV - ST, make in 1991. Defective winding Fault Symptom: Elevated DC-Resistance Detected by: DGA, DC-Resistance Measurement History: After 11 years of service, rising amounts of fault gases from thermal oil decomposition with small amounts of acetylene have been detected by DGA (Table IV). Furthermore the ratio carbon monoxide/carbon dioxide was < 3, which suggested an electrical degradation of cellulose. The transformer was inspected on site. A resistance measurement was carried out. There was a remarkable increase in the DC-resistance. The transformer was sent for repair to the factory.
Figure 19: Example 1, page 1: Defective Windings
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 19
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany One broken twin conductor of two twins with burnt out insulation paper was detected. The damage was a defective solder joint at the outmost turn of the ground end disc.
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
Figure 20: Examlple 1, page 2 - A broken twin conductor as a consequence of a defective solder joint
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 20
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Table IV: Last DGA before taking out of service Type of gas Hydrogen Methane Ethane Ethylene Acetylene Carbon monoxide Carbon dioxide ppm (v/v) 1060 2481 703 2187 4 450 995
Diagnosis: Defective solder joint Action taken: The winding was repaired and the transformer was taken in service again and is working trouble free. Figure 21: Example 1, page 3
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 21
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
Case Nr. 10.4: 60 MVA-, 123 kV- Compensating Reactor, make 1979. Defective insulation system Fault Symptom: Sludge in oil Detected by: DP, furanes, oil analysis History: After 20 years of successful operation, time-based maintenance (DGA, oil and furane analysis) indicated severe ageing of oil and insulation. The reactor was brought back in the factory for refurbishment of the cooling system. DGA showed no failure indications (MSS Code 01002), but suggested a severe ageing of the solid insulation. The oil analysis revealed also a strongly aged oil (Colour 5,5, Neutralisation value 0,18 mg KOH/g oil) with sludge formation. The oil sludge has plugged the cooling ducts of the radiators and led to overheating. The paper samples of the winding were covered heavily with sludge and the DP-value was only 200. The measured furanes showed values of 2-FAL of 11,5 mg/kg oil. The solid insulation has reached the end of life. Diagnosis: accelerated ageing of the insulating system as a consequence of inadequate cooling. Action taken: A complete refurbishment was carried out winding, oil, cooling system. Figure 22; Example 2, Aged Compensator Reactor
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 22
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
1) The most powerful diagnostic tool is the DGA. It may be used to identify dielectric, thermal and chemical ageing problems. 2) Oil analysis as established in all facts is the second most powerful diagnostic tool. 3) It normally takes 2 or more different diagnostic approaches to really identify the nature of the defect. 4) The existing diagnostic procedures are mature and can also be used to identify defects in peripheral components (cooling plant, bushings etc.) 5) Both off-line and on-line diagnostics can be extremely successful to avoid catastrophic and costly outages, if applied consequently.
Figure 23: Conclusions page 1
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 23
Transformers
ARWtr 04, VIGO, Spain, Oct. 28 - 30, 2004 - FUNCTIONAL and COMPONENT RELATED DIAGNOSTICS for POWER TRANSFORMERS, a Basis for successful Transformer Life Management Key Note Speech by Dr. A. J. Kachler, Siemens, Germany
6) Consequent maintenance, with fingerprinting, trend analysis and ad hoc on site diagnostic testing as well as life extension measures are indispensable for transformer life management 7) Chapter 8 suggests the future research. 8) The state of the art in Transformer diagnostics allows to identify dielectric, thermal and chemical ageing and defective problems. 9) For the impact of air, moisture and temperature closed system transformers are less susceptible to ageing than open breathers.
Figure 24: Conclusions page 2
ARWtr 2004
Modern Transformers
28 -30 October. Vigo Spain
http://webs.uvigo.es/arwtr04
PTD T - Consult - ARWtr 4, VIGO, Spain - 24
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Transformer Design PresentationDocument75 paginiTransformer Design Presentationkrmurali2000Încă nu există evaluări
- A3 Discussion 2006 Meeting SummaryDocument7 paginiA3 Discussion 2006 Meeting SummaryAmbadas DevkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation Design for Electrical Equipment RoomsDocument79 paginiVentilation Design for Electrical Equipment RoomsCarlos Herrera100% (1)
- Ariola-Pironti2016 Book MagneticControlOfTokamakPlasmaDocument208 paginiAriola-Pironti2016 Book MagneticControlOfTokamakPlasmaVICENTE VILLAVERDE MUÑOZÎncă nu există evaluări
- SF6 Properties and Use in MV and HV SwitchgearDocument26 paginiSF6 Properties and Use in MV and HV SwitchgearPradeep_Vashist100% (1)
- Ecodesign Study Lot2 Transformers 2011Document428 paginiEcodesign Study Lot2 Transformers 2011Isagani MadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMiRT-23 Paper 617 ContainementTests CourtoisJohnston-SMIRTversionv2Document11 paginiSMiRT-23 Paper 617 ContainementTests CourtoisJohnston-SMIRTversionv2CourtoisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Turbine O&M Survey and Research NeedsDocument44 paginiWind Turbine O&M Survey and Research NeedsVladimir PîrvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 Conference VSokolov4Document9 pagini2006 Conference VSokolov4juanete29Încă nu există evaluări
- Full TextDocument18 paginiFull TextFabián AcevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Paper - CIGREDocument12 paginiTechnical Paper - CIGREGobinath BalasubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single & Three Phase TransformersDocument8 paginiSingle & Three Phase TransformersMunawar Sher MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27Document7 pagini27Loka VyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proceedings of the 2006 IASME/WSEAS Conference on Energy & Environmental SystemsDocument8 paginiProceedings of the 2006 IASME/WSEAS Conference on Energy & Environmental SystemsSueja MalligwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hv. en HV MV Oil TransformerDocument11 paginiHv. en HV MV Oil TransformerDheeraj YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development and Application of New Condition Assessment Methods For Power TransformersDocument10 paginiDevelopment and Application of New Condition Assessment Methods For Power TransformersRoy Dz HutapeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 198 Vacuum SwitchingDocument36 pagini198 Vacuum Switchingleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Study and Analysis of Systems For Monitoring in Power SubstationsDocument3 paginiStudy and Analysis of Systems For Monitoring in Power SubstationsIsrael DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation and Protection of Power TransformersDocument65 paginiOperation and Protection of Power TransformersSrinath Chary KajanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Turbine Standards and TestingDocument4 paginiHydraulic Turbine Standards and Testingraghu_mnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trends enDocument0 paginiTrends enmaxi_1987Încă nu există evaluări
- WEG Three Phase Flameproof Motors w22x and Bfgc4 Series Technical European Market 125.71 Brochure EnglishDocument202 paginiWEG Three Phase Flameproof Motors w22x and Bfgc4 Series Technical European Market 125.71 Brochure EnglishVishal NarkhedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onlinepotentiometerhandbook PDFDocument227 paginiOnlinepotentiometerhandbook PDFDozer122Încă nu există evaluări
- Extending The Life of Transformer Units Through Maintenance Based On Insulation RevitalizationDocument7 paginiExtending The Life of Transformer Units Through Maintenance Based On Insulation RevitalizationbenlahnecheÎncă nu există evaluări
- NXT4 Bia e 1 50Document20 paginiNXT4 Bia e 1 50Miguel Hernández LeónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenges and Strategies in Transformer DesignDocument75 paginiChallenges and Strategies in Transformer DesignaocalayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utr - PLN Suar PDFDocument86 paginiUtr - PLN Suar PDFJaka Sembung Golok100% (1)
- Standards PDFDocument74 paginiStandards PDFbdaminda6701100% (1)
- Electric Fuses 0863413994Document262 paginiElectric Fuses 0863413994Lidija Preljvukić100% (1)
- DFR Measurement On CT PDFDocument26 paginiDFR Measurement On CT PDFdkymq100% (1)
- Commissioning Circuit BreakersDocument77 paginiCommissioning Circuit Breakershuji_osirisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System IngDocument522 paginiPower System IngMohd Mounir50% (4)
- Guide To Transformer SpecificationDocument95 paginiGuide To Transformer SpecificationMurat BozkurtÎncă nu există evaluări
- OE CORP ENG TN 0002 Pre Commissioning Overview Umbilicals Rev C1Document16 paginiOE CORP ENG TN 0002 Pre Commissioning Overview Umbilicals Rev C1hatakerobot100% (1)
- Power QualityDocument36 paginiPower QualityIppiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressor Surge and Rotating Stall PDFDocument233 paginiCompressor Surge and Rotating Stall PDFQuân Chu Hoàng100% (1)
- Ect211 PDFDocument38 paginiEct211 PDFmersium0% (1)
- Transformers (Book Review) : IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine December 2005Document2 paginiTransformers (Book Review) : IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine December 2005Kanav MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eda Test To Perform Predictive Maintenance in Relevant Rotating MachinesDocument32 paginiEda Test To Perform Predictive Maintenance in Relevant Rotating MachinesR0B0T2013Încă nu există evaluări
- Xiros N Robust Control of Diesel Ship PropulsionDocument221 paginiXiros N Robust Control of Diesel Ship PropulsionNicolás SadmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEG Technological Advancements in The Development of Ex Rated MotorsDocument13 paginiWEG Technological Advancements in The Development of Ex Rated MotorsdhoomketuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 05 Total Pressure MeasurementDocument43 paginiChapter 05 Total Pressure MeasurementUsama PerwezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of A Switched Reluctance MotorDocument4 paginiEnvironmental and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of A Switched Reluctance MotorAmgad_A_Salama_239Încă nu există evaluări
- New Techniques To Detect The Suitable Time To Close The Tap Hole of A Blast FurnaceDocument9 paginiNew Techniques To Detect The Suitable Time To Close The Tap Hole of A Blast FurnacerivrsideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestra Condensate ManualDocument172 paginiGestra Condensate ManualGeorge ClaessenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active magnetic bearing design and characterization for high temperature applicationsDocument147 paginiActive magnetic bearing design and characterization for high temperature applicationsVijayTijareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitor and assess power transformersDocument6 paginiMonitor and assess power transformerssureshnfclÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Aging of The Insulation of Low Voltage Machines: Model Definition and Test With The Design of ExperimentsDocument11 paginiElectrical Aging of The Insulation of Low Voltage Machines: Model Definition and Test With The Design of ExperimentsBinh TaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesDe la EverandMarine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (8)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyDe la EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Risks of Nuclear Energy Technology: Safety Concepts of Light Water ReactorsDe la EverandThe Risks of Nuclear Energy Technology: Safety Concepts of Light Water ReactorsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water (R718) Turbo Compressor and Ejector Refrigeration / Heat Pump TechnologyDe la EverandWater (R718) Turbo Compressor and Ejector Refrigeration / Heat Pump TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Assessment in Light Water Reactors for Long Term Operation: Good Practices and Lessons LearnedDe la EverandFatigue Assessment in Light Water Reactors for Long Term Operation: Good Practices and Lessons LearnedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded Mechatronic Systems 2: Analysis of Failures, Modeling, Simulation and OptimizationDe la EverandEmbedded Mechatronic Systems 2: Analysis of Failures, Modeling, Simulation and OptimizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reliability of High-Power Mechatronic Systems 1: Aerospace and Automotive Applications: Simulation, Modeling and OptimizationDe la EverandReliability of High-Power Mechatronic Systems 1: Aerospace and Automotive Applications: Simulation, Modeling and OptimizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationDe la EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsDe la EverandFinite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mit PDFDocument143 paginiMit PDFLuciano EncisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Experimental Evaluation - CDocument8 pagini4-Experimental Evaluation - Colag_dracoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Experimental Evaluation - CDocument8 pagini4-Experimental Evaluation - Colag_dracoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Temperatura On Time-Domain Dielectric Diagnostics of Transformers PDFDocument6 paginiEffect of Temperatura On Time-Domain Dielectric Diagnostics of Transformers PDFLuciano EncisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FALHAS - Bushings Unlocked by WWW Freemypdf ComDocument29 paginiFALHAS - Bushings Unlocked by WWW Freemypdf ComFeigin LeonidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1 1 25Document6 pagini10 1 1 25Luciano EncisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DELTA 4000: Reference Manual Applications GuideDocument48 paginiDELTA 4000: Reference Manual Applications GuidepetarlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miniature FusesDocument88 paginiMiniature FusesEliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 53200A ManualDocument303 pagini53200A ManualHazem ElabedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3S MTDocument9 pagini3S MTThomas GarzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Digital Design FundamentalsDocument78 paginiBipolar Digital Design FundamentalsViktor GardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bang Gia SelecDocument7 paginiBang Gia Selecking0deuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wharfedale Pro r-1604 324Document6 paginiWharfedale Pro r-1604 324GwsazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Door Interlocking SystemDocument10 pagini2 Door Interlocking SystemrajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certa-Flow DATA SHEET OkDocument4 paginiCerta-Flow DATA SHEET OkJAIME HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underground Electrical Cable Bury DepthsDocument2 paginiUnderground Electrical Cable Bury DepthsTesfahun GirmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baran Energy Ecosystem Project - Baran EnergyDocument12 paginiBaran Energy Ecosystem Project - Baran EnergyAgungSetya100% (2)
- 2VAA002134 - en S Control NTDI02 Digital IO Termination UnitDocument47 pagini2VAA002134 - en S Control NTDI02 Digital IO Termination UnitanbarasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line Reactance, Zero Sequence Reactance and Mutual Zero Sequence ReactanceDocument39 paginiLine Reactance, Zero Sequence Reactance and Mutual Zero Sequence ReactanceHanh-Trang DangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventative Maintenance Report UPSDocument4 paginiPreventative Maintenance Report UPSĐạt Xuân LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- DECS 200 ManualDocument177 paginiDECS 200 ManualMohan RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Power ElectronicsDocument12 paginiFundamentals of Power ElectronicsYT ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec Syllabus 2003 Scheme Kerala UniversityDocument46 paginiEc Syllabus 2003 Scheme Kerala Universityajesh5130123Încă nu există evaluări
- BFA902 As BuiltDocument37 paginiBFA902 As Builtbenjamin paulinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- H058en 200606 jbz-02Document8 paginiH058en 200606 jbz-02Pedro FernandesÎncă nu există evaluări
- M 2 - Data Centre RequirementsDocument20 paginiM 2 - Data Centre Requirementsalan sibyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of Photocatalysis - Current Understandingand PerspectivesDocument6 paginiDefinition of Photocatalysis - Current Understandingand PerspectivesNuman AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENADocument9 paginiBalanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENAA. VillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSK2 15 C SJ75 3 PDFDocument2 paginiPSK2 15 C SJ75 3 PDFDWIGHT GERONIMOÎncă nu există evaluări
- VD-H2X2-CPUSEW-43 Product SpecificationsDocument2 paginiVD-H2X2-CPUSEW-43 Product SpecificationsWitto PereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System ComponentsDocument29 paginiControl System Componentsshreemanti0% (1)
- Section 12 Metal Inert-Active Gas Welding (MIG MAG GMAW)Document12 paginiSection 12 Metal Inert-Active Gas Welding (MIG MAG GMAW)S GoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 Eng NaderDocument8 paginiExperiment 2 Eng Naderياسر العويطيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lead Times Rockwell Automation 2023-03-29Document3 paginiLead Times Rockwell Automation 2023-03-29Omar Alfredo Del Castillo QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled DiagramDocument1 paginăUntitled DiagramirfanÎncă nu există evaluări
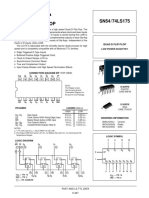
- Quad D Flip-Flop SN54/74LS175: Low Power SchottkyDocument5 paginiQuad D Flip-Flop SN54/74LS175: Low Power SchottkyNicolasÎncă nu există evaluări
- H - 408x - BM - TI Service Manual Four MieleDocument84 paginiH - 408x - BM - TI Service Manual Four Mielecuistots80% (5)