Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Trigno Metry Fundas
Încărcat de
Amit ChaturvediDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Trigno Metry Fundas
Încărcat de
Amit ChaturvediDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
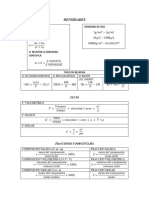
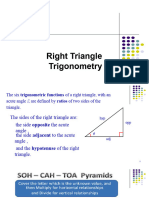
In a right-angled triangle, Sin= Opposite Side/Hypotenuse Cos= Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse Tan= Sin/Cos = Opposite Side/Adjacent Side Cosec = 1/Sin=
Hypotenuse/Opposite Side Sec = 1/Cos = Hypotenuse/Adjacent Side Cot = 1/tan = Cos/Sin = Adjacent Side/Opposite Side SinCosec = CosSec = TanCot = 1 Sin !"-# = Cos, Cos !"-# = Sin Sin$ % Cos$ = 1 Tan$ % 1 = Sec$ Cot$ % 1 = Cosec$ Addition and su&traction 'or(ula)Sin A%*# = SinACos* % CosASin* Sin A-*# = SinACos& - CosASin* Cos A%*# = CosACos* - SinASin*
Cos A-*# = CosACos* % SinASin* Tan A%*# = TanA%Tan*#/ 1-TanATan*# Tan A-*# = TanA - Tan*#/ 1%TanATan*# Cot A%*# = CotACot*-1#/ CotA % Cot*# Cot A-*# = CotACot*%1#/ Cot*-CotA# Sin A%*#%Sin A-*# = +SinACos* Sin A%*#-Sin A-*# = +CosASin* Cos A%*#%Cos A-*# = +CosACos* Cos A-*# - Cos A-*# = +SinASin* SinC % Sin, = +Sin- C%,#/+.Cos- C-,#/+. SinC - Sin, = +Cos- C%,#/+.Sin- C-,#/+. CosC % Cos, = +Cos- C%,#/+.Cos- C-,#/+. CosC - Cos, = +Sin- C%,#/+.Sin- ,-C#/+. Sin+ = +SinCos = +tan#/ 1%tan$# Cos+ = Cos$ - Sin$ = +Cos$ - 1= 1 - +Sin$ =
1-tan$#/ 1%tan$# Tan+ = +tan$/ 1-tan#
Angles are gi/en in degrees, !" degrees, 10" degrees etc1# I1 Sin -#=-Sin Cos -# = Cos tan -# = -tan cot -# = -cot sec -# = sec cosec -#= - cosec II1 sin !"-# = cos cos !"-# = sin tan !"-# = cot cot !"-# = tan sec !"-# = cosec cosec !"-# = sec III1 sin !"%# = cos cos !"%# = -sin tan !"%# = -cot cot !"%# = -tan
sec !"%# = -cosec cosec !"%# = sec I21 sin 10"-# = sin cos 10"-# = -cos tan 10"-# = -tan cot 10"-# = cot sec 10"-# = -sec cosec 10"-# = cosec 21 sin 10"%# = -sin cos 10"%# = -cos tan 10"%# = tan cot 10"%# = cot sec 10"%# = -sec cosec 10"%# = -cosec
Formulas which express the sum or difference in product
Formulae which express products as sums or difference of Sines and Cosines
Trignometric ratios of Multiple Angles
Trignometric ratios of 3
Trignometric ratios of sub-multiple angles
Properties of n!erse Trignometric Functions
Properties of Triangles Sine Formula "or #aw of Sines$ In any 3A*C,
Cosine Formula "or #aw of Cosines$ In any 3A*C,
These 'or(ulas are also 4ritten as
Pro%ection formulas In any 3A*C,
&alf-Angles and Sides
In any 3A*C,
Area of a Triangle
Hero5s 'ro(ula
ncircle and Circumcircle A circle 4hich touches the three sides o' a traingle internally is called the incircle1The center o' the circle is called the incentre and the raidus is called the inradius1 I' r is the inradius, then
The circle 4hich passes through the /ertices o' a triangle is called the circu(circle o' a triangle or circu(scri&ing circle1 The centre o' this circle is the circu(centre and the radius o' the circu(circle is the circu(radius1 I' 6 is the circu(radius, then
I' 3 is the area o' the triangle,
&'perbolic Functions
(elation between circular and h'perbolic functions
Addition formulas for &'perbolic functions
Periods of h'perbolic functions
n!erse &'perbolic functions
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- An Introduction to Elementary Algebra Part 1De la EverandAn Introduction to Elementary Algebra Part 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths 101 TrigonometryDocument7 paginiMaths 101 TrigonometryPrince Rocker SaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsDocument8 paginiQuiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsRaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Formula SheetDocument1 paginăTrig Formula SheetNeil BreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratio and ProprtionDocument17 paginiRatio and ProprtionNikita SangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric FunctionDocument4 paginiTrigonometric FunctionAna May BanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre Calculus Chapter 12 - TrigonometryDocument43 paginiPre Calculus Chapter 12 - TrigonometryJordan PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorDocument4 paginiDouble Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorErin PhillipsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stewart's Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiStewart's Cheat Sheetcgo1114Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.5 Circular FunctionsDocument12 pagini3.5 Circular FunctionsRowly Pearl NedicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 paginiTrigonometric IdentitiesnedcordovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocument6 paginiTrigonometric FunctionsnathanalocilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hexagon For Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument11 paginiThe Hexagon For Trigonometric IdentitiesDeno Jay PialaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)Document6 paginiTrigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)ambresh.09Încă nu există evaluări
- 5.5 - Trig. Identity PracticeDocument2 pagini5.5 - Trig. Identity PracticeAmarveer BathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Practice Questions: Introduction To Risk, Return, and The Opportunity Cost of CapitalDocument10 paginiAnswers To Practice Questions: Introduction To Risk, Return, and The Opportunity Cost of CapitalJose TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 TrigonometryDocument4 pagini1.3 TrigonometryWaruni JayasundaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument38 paginiTrigonometric Identitiesetamil87Încă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsDocument6 paginiTrigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsJulie Ailene AsuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFDocument3 paginiLecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFSahaj ChhetriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Formulas - Handy Summary Sheet: 1 0 0 0 Cos SinDocument2 paginiTrigonometric Formulas - Handy Summary Sheet: 1 0 0 0 Cos SindeenawantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometryDocument19 paginiTrigonometryshwpna1979Încă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometryDocument13 paginiTrigonometryjobmajuneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pythagorean Identities Half Angle FormulaeDocument1 paginăPythagorean Identities Half Angle FormulaeKun ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 2 Third Sum-DiffDocument2 paginiHW 2 Third Sum-DiffGuadalupe Meza MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Aptitude Cheat Sheet: Formulae and FundasDocument11 paginiQuantitative Aptitude Cheat Sheet: Formulae and FundasSyed Monsoor AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Introducing Transword.: Commercial Words - Vocabulario Comercial - Unidad 1Document2 paginiUnit 1 Introducing Transword.: Commercial Words - Vocabulario Comercial - Unidad 1Raquel SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identitas Trigonometri Kelas XDocument11 paginiIdentitas Trigonometri Kelas XGerald Ryan TriyonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Algebraic ExpressionDocument23 pagini3 - Algebraic ExpressionCeledonio, Joanah Mae B.Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 7 Transformation by Trigonometric FormulasDocument14 paginiLesson 7 Transformation by Trigonometric FormulasMarvin James JaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- !angent (Ines - ClassworkDocument53 pagini!angent (Ines - ClassworkjazzmathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.1 Template Super ElevationDocument1 pagină7.1 Template Super ElevationJohn Joseph SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xi 7aug2012 Trigo & M InducDocument3 paginiXi 7aug2012 Trigo & M InducYuxdar ContellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationsDocument22 paginiTrigonometric Identities and Equationsmihlemgoduka22Încă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometri Booklet - 5 - Part - 1Document23 paginiTrigonometri Booklet - 5 - Part - 1Aat JuhatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions 2Document3 paginiSolutions 2hiyaxem683Încă nu există evaluări
- Triangle Trigonometry: Cha PterDocument44 paginiTriangle Trigonometry: Cha PterMathew Beckhouse100% (1)
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument17 paginiTrigonometric Identitiesmaligaya evelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 Lecture Slides PDFDocument49 paginiWeek 4 Lecture Slides PDFTanapat LapanunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulario IntroduccionDocument2 paginiFormulario Introduccionrtipas4445Încă nu există evaluări
- Elt Teo-32Document1 paginăElt Teo-32Kevin YanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hhong@princeton - Edu Mdbaron@princeton - Edu Jk@princeton - EDU Jiangmin@princeton - EDUDocument5 paginiHhong@princeton - Edu Mdbaron@princeton - Edu Jk@princeton - EDU Jiangmin@princeton - EDUurbanadudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 7Document3 paginiModule 7BawbityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faiz Ul HassanDocument5 paginiFaiz Ul HassanFaiz Ul HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAC 1147 Final Exam SP 21Document7 paginiMAC 1147 Final Exam SP 21Neil BreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index: Key To TrignometryDocument15 paginiIndex: Key To TrignometryQasim TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coning Angle Forward FlightDocument3 paginiConing Angle Forward FlightmanitheaerialfighterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivation of The Model of A ThreeDocument6 paginiDerivation of The Model of A ThreeEmanuel Morales RergisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0xip21 MATHMATICS THE Languge of PHYSICSDocument12 pagini0xip21 MATHMATICS THE Languge of PHYSICSsolitudesherniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Breathing Gym Trombon PDFDocument16 paginiThe Breathing Gym Trombon PDFMikko100% (2)
- Mathematics TrigonometryDocument4 paginiMathematics TrigonometryVara Prasad VemulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAT Math TrigonometryDocument5 paginiSAT Math TrigonometryΜάριος Α. ΠαππάςÎncă nu există evaluări
- Right Triangle TrigonometryDocument39 paginiRight Triangle TrigonometryErjohn OcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clipping Against Three Dimensional ParallelpipedDocument1 paginăClipping Against Three Dimensional ParallelpipedRenu Bharat KewalramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cochrane J. H. Asset Pricing Solution 2010Document34 paginiCochrane J. H. Asset Pricing Solution 2010ire04100% (3)
- Mixture Final 94 Math PDFDocument55 paginiMixture Final 94 Math PDFEraj MaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gases: Short Range, Important at Longer Range, Important atDocument10 paginiGases: Short Range, Important at Longer Range, Important atSaad AnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- NuisanceDocument5 paginiNuisanceAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doli Capax Is A Latin Term That MeansDocument1 paginăDoli Capax Is A Latin Term That MeansAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-29 10 18Document14 paginiAssignment-29 10 18Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPC AssignmentDocument21 paginiIPC AssignmentAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admin Law Assignment 14Document1 paginăAdmin Law Assignment 14Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admin Law Assignment 13Document1 paginăAdmin Law Assignment 13Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admin Law Assignment 16Document1 paginăAdmin Law Assignment 16Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document For Global Venture ABCDDocument1 paginăDocument For Global Venture ABCDAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter of Credit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 paginiLetter of Credit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Doctrine of Necessity and CompulsionDocument4 paginiThe Doctrine of Necessity and CompulsionAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wrongful Restrain & Wrongful ConfinementDocument1 paginăWrongful Restrain & Wrongful ConfinementAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- GP 1Document5 paginiGP 1neepubrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admin Law Assignment 14Document1 paginăAdmin Law Assignment 14Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document For Global Venture ABCDDocument1 paginăDocument For Global Venture ABCDAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doctrine of Mens ReaDocument1 paginăDoctrine of Mens ReaAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airborne Particle Size Chart - Engineering Design Micron ChartDocument3 paginiAirborne Particle Size Chart - Engineering Design Micron ChartAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Capital ConceptsDocument42 paginiWorking Capital Conceptsdabloo_3sep86% (7)
- GST Concept Status Ason01052017Document15 paginiGST Concept Status Ason01052017Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jeevan Saral: Golden Peacock Award Winner PlanDocument6 paginiJeevan Saral: Golden Peacock Award Winner PlanAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSRF 1 FormDocument4 paginiCSRF 1 FormAbhishek KrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade/Industry:: (I) Reduction in Multiplicity of TaxesDocument1 paginăTrade/Industry:: (I) Reduction in Multiplicity of TaxesAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myth Booklet English Compressed PDFDocument28 paginiMyth Booklet English Compressed PDFAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sal Sheet MetroDocument3 paginiSal Sheet MetroAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 18Document7 paginiCH 18Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Payment of Gratuity Act 1972Document13 paginiThe Payment of Gratuity Act 1972KijanjooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chauhans Need To Streamline Investments, Increase Equity Exposure - The Economic TimesDocument4 paginiChauhans Need To Streamline Investments, Increase Equity Exposure - The Economic TimesAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- What NPS Changes Mean For You - The Economic Times PDFDocument2 paginiWhat NPS Changes Mean For You - The Economic Times PDFAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- 33118ipcc Idtc Rev Nov14 Pm1Document77 pagini33118ipcc Idtc Rev Nov14 Pm1Rocker FarmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test DocumentDocument1 paginăTest DocumentAmit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 1Document2 paginiBook 1Amit ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listing Agreement: This Is A Legally Binding Contract. If You Do Not Understand It, Seek Legal AdviceDocument3 paginiListing Agreement: This Is A Legally Binding Contract. If You Do Not Understand It, Seek Legal AdviceLou100% (1)
- Types of HousesDocument13 paginiTypes of HousesAdrian Devey FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- H Vs Feasibility StudyDocument170 paginiH Vs Feasibility StudyBagus Deddy AndriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aec10 - Business Taxation Solution Tabag CH4Document8 paginiAec10 - Business Taxation Solution Tabag CH4EdeksupligÎncă nu există evaluări
- G.R. No. 193453 Spouses Hojas v. Philippine Amanah BankDocument6 paginiG.R. No. 193453 Spouses Hojas v. Philippine Amanah BankmehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventura Mall Profile 2024Document14 paginiVentura Mall Profile 2024Joefil FlorÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIAG - Test Book 2.6 Real Estate Taxation RDL40q 8p 2014Document8 paginiDIAG - Test Book 2.6 Real Estate Taxation RDL40q 8p 2014Noel Remolacio100% (1)
- Land and BuildingDocument23 paginiLand and BuildingblahblahblueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Communication Building Critical Skills Canadian 6Th Edition Braun Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 paginiBusiness Communication Building Critical Skills Canadian 6Th Edition Braun Test Bank Full Chapter PDFAdamPerezDVMabtc100% (12)
- Joint Circular No. 1Document1 paginăJoint Circular No. 1Jasper Dela PenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Housing Project Alternatives in Santiago de ChileDocument14 paginiHousing Project Alternatives in Santiago de Chiletaylorwade09Încă nu există evaluări
- Points To Be Added For Goa Land Due DiligenceDocument5 paginiPoints To Be Added For Goa Land Due Diligenceparasshah.kljÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rulings About Partition SuitDocument4 paginiRulings About Partition SuitadvsalahuddinahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freemium Data 43-Los Pinos Condos Owners Data ScrapeDocument3 paginiFreemium Data 43-Los Pinos Condos Owners Data ScrapePersepsiku Persepsimu100% (1)
- WILLS Bar Exam OutlineDocument26 paginiWILLS Bar Exam OutlineJenna Alia100% (2)
- Berke NK OtterDocument2 paginiBerke NK OtterJade Francis Caberte TanggaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rule 131-133Document20 paginiRule 131-133Natasha MilitarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suarez V Spouses Emboy JRDocument8 paginiSuarez V Spouses Emboy JRaudreyracelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slum-Free India: Operationalising Rajiv Awas YojanaDocument12 paginiSlum-Free India: Operationalising Rajiv Awas YojanaDevrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Litam Vs EspirituDocument4 paginiLitam Vs EspirituJay Kent RoilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Register of Deeds Vs China Banking CorporationDocument1 paginăRegister of Deeds Vs China Banking Corporationcmv mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- USPAP - Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal PracticeDocument70 paginiUSPAP - Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal PracticeIván Ferreira Rodríguez100% (2)
- Republic of The Philippines, Petitioner, vs. Jeremias and David HERBIETO, RespondentsDocument8 paginiRepublic of The Philippines, Petitioner, vs. Jeremias and David HERBIETO, RespondentsPatÎncă nu există evaluări
- G.R. No. 12908 - Carmelita Leano vs. Court of AppealsDocument6 paginiG.R. No. 12908 - Carmelita Leano vs. Court of AppealsPrimabelle Sanchez DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credai BrochureDocument4 paginiCredai BrochureMohammad ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wills Part 2Document18 paginiWills Part 2Raf RufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Niranjan Developers ProfileDocument11 paginiNiranjan Developers ProfileashrithgowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warranty DeedDocument3 paginiWarranty DeedacetresleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faas Building MachineDocument2 paginiFaas Building Machinenaomi melayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hulst Vs PR BuildersDocument1 paginăHulst Vs PR BuildersDi ko alamÎncă nu există evaluări