Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
3 CCNP Swicth Qa Implementing Spanning Tree Guest
Încărcat de
jonjatelloDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3 CCNP Swicth Qa Implementing Spanning Tree Guest
Încărcat de
jonjatelloDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 1
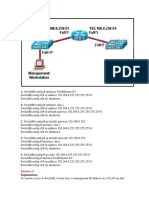
Refer to the show command above, what statement is true?
A. Will be displayed next hop address for interfaces associated with VLAN 101.
B. Will be displayed IP addresses of interfaces associated with VLAN 100.
C. Will be displayed trunk link that carries VLAN 101.
D. Will be displayed IP addresses of devices on both end of the trunk.
Answer: A
Next hop addresses for interfaces and the interfaces associated with VLAN 101 will be displayed with
Switch#show ip cef vlan 101 command, that is used to view general information about FIB (Forwarding
Information Base) entries, that are associated with the specific VLAN.
Thic command does not show information about trunk links associated with VLAN 101. To do that you
have to use command Switch#show trunk.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 2
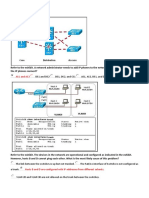
Which three effects does the interface command switchport host have when entered on a switch? (Choose
three)
A. Sets the switch port mode to access
B. Enables BPDU guard
C. Enables spanning tree PortFast
D. Enables root guard
E. Disables channel grouping
F. Enables BPDU filtering
Answer: A, C, E
Command switchport host is macro command that optimizes the port for Layer 2 host connection. This is
done by enabling some and disabling other features. It sets switch port to access mode. Enables spanning
tree PortFast and disables EtherChannel grouping.
Example of issuing switchport host command on interface gig1/0/27 is shown below.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 3
One switch in a Layer 2 switched spanning-tree domain is converted to PVRST+using the spanning-tree
mode rapid-pvst global configuration mode command. The remaining switches are running PVST+. What
is the effect on the spanning-tree operation?
A. Spanning tree is effectively disabled in the network.
B. The PVRST+switch forwards 802.1D BPDUs, but does not participate as a node in any spanning tree.
C. All switches default to one 802.1D spanning tree for all VLANs.
D. The PVSRT+reverts to PVST+to interoperate with the PVST+switches.
Answer: D
More on: Link1
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 4
Refer to the exhibit. What conclusion does the output support?
A. PortFast is enabled on interface fa0/6.
B. IEEE 802.1w is enabled on VLAN1.
C. The forward delay timer has been changed from the default value.
D. Standard IEEE 802.1D behavior is shown.
Answer: D
The STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for
any bridged Ethernet local area network. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and
the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is standardized as
to include
spare (redundant) links to provide automatic backup paths if an active link fails, without the danger of
bridge loops, or the need for manual enabling/disabling of these backup links.
IEEE 802.1D.
STP switch port states:
Blocking - A port that would cause a switching loop, no user data is sent or received but it may go
into forwarding mode if the other links in use were to fail and the spanning tree algorithm determines
the port may transition to the forwarding state. BPDU data is still received in blocking state. Prevents
the use of looped paths.
Listening - The switch processes BPDUs and awaits possible new information that would cause it to
return to the blocking state. It does not populate the MAC address table and it does not forward
frames.
Learning - While the port does not yet forward frames it does learn source addresses from frames
received and adds them to the filtering database (switching database). It populates the MAC Address
table, but does not forward frames.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 5
Forwarding - A port receiving and sending data, normal operation. STP still monitors incoming
BPDUs that would indicate it should return to the blocking state to prevent a loop.
Disabled - Not strictly part of STP, a network administrator can manually disable a port
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 6
Refer to the exhibit. What two conclusions does the output show to be true? (Choose two)
A. DLS1 is running IEEE 802.1s on instance 1.
B. DLS1 is running IEEE 802.1D on instance 1.
C. DLS1 is the Root Bridge for instance 1.
D. Interface fa0/12 will move into the err-disable state if a BPDU is received.
E. Interfaces fa0/1 through fa0/6 are trunk ports.
Answer: A, C
From show command above we can see that on DLS1 MST is configured and displayed are MST01
instance information.
From ID information, we can see priority, MAC address, that this switch is Root Bridge and values for
Hello Time, Max Age and Forward Delay.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 7
Which three parameters should match all switches within an MST region? (Choose three)
A. Port costs on trunk ports.
B. Configuration name
C. Revision number
D. Trunk encapsulation method.
E. Bridge priority
F. VLAN-to-instance mappings.
Answer: B, C, F
The default spanning tree mode on Cisco Catalyst switches is PVST+or, on newer models, Rapid
PVST+. These protocols result in a direct one-to-one mapping of spanning tree instances to VLANs. For
example, if there are eight VLANs on a switch, the switch must participate in eight independent spanning
trees. This is often undesirable, as the number of actually unique spanning tree topologies is typically less
than the number of VLANs (at worst, the two will be equal). Running only a single common spanning
tree (CST, which is not supported on Cisco Catalyst switches) would be more efficient, but it does not
allow for the design flexibility afforded by PVST.
Multiple Spanning Tree
(MST) was created to allow for multiple spanning tree topologies while
preserving scalability. MST enables an administrator to map an arbitrary number of VLANs to a single
MST instance, resulting in the minimum number of instances needed to satisfy a design. If, for example,
you have six VLANs but only two unique layer two topologies, you need only two MST instances.
MST region as a collection of switches, sharing the same view of physical topology partitioning into set
of logical topologies. For two switches to become members of the same region, the following attributes
must match: Configuration name; Configuration revision number (16 bits); The table of 4096 elements
which map the respective VLAN to STP instance number.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 8
Users complain that they lost connectivity to all resources in the network. A network administrator
suspects the presence of a bridging loop as a root cause of the problem. Which two actions will determine
the existence of the bridging loop? (Choose two)
A. Confirm MAC port security is enabled on all access switches.
B. Check the port utilization on devices and look for abnormal values.
C. Verify that the management VLAN is properly configured on all root bridges.
D. Capture the traffic on the saturated link and verify if duplicate packets are seen.
E. Ensure that the root guard and loop guard are properly configured on all distribution links.
Answer: B, D
Forwarding loops seeming can cause all sorts of wacky behavior in various Cisco switches. Forwarding
loops vary greatly both in their origin (cause) and effect. Due to the wide variety of issues that can affect
STP, we will provide general guidelines about how to troubleshoot forwarding loops. Before you start to
troubleshoot, you must obtain this information: An actual topology diagram that details all of the switches
and bridges; Their corresponding (interconnecting) port numbers; STP configuration details, such as
which switch is the root and backup root, which links have a non-default cost or priority, and the location
of blocking ports. Generally, troubleshooting involves these steps:
1. Identify the loop:
When a forwarding loop has developed in the network, these are the usual symptoms: Loss of
connectivity to, from, and through affected network regions; High CPU utilization on routers connected to
affected segments or VLANs that can lead to various symptoms, such as routing protocol neighbor
flapping or Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) active router flapping; High link utilization (often 100
percent); High switch backplane utilization (compared to the baseline utilization); Syslog messages that
indicate packet looping in the network (for example HSRP duplicate IP address messages); Syslog
messages that indicate constant address relearning or MAC address flapping messages; An increasing
number of output drops on many interfaces
Note: Any of these reasons alone may indicate different issues (or no issue at all). However, when many
of these are observed at the same time, it is highly probable that a forwarding loop has developed in the
network. If the current traffic level is well above normal or if the baseline level is not known, check
whether the peak level has been achieved recently and whether it is close to the current traffic level. For
example, if the peak traffic level is 15 percent and it was reached just two minutes ago and current traffic
level is 14 percent, then that would mean that the switch is working under an unusually high load. If the
traffic load is at a normal level, then that probably means that there is either no loop or that this device is
not involved in the loop. However, it still could be involved in a slow loop.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 9
2. Discover the topology (scope) of the loop.
Once it has been established that the reason for the network outage is a forwarding loop, the highest
priority is to stop the loop and restore the network operation. In order to stop the loop, you must know
which ports are involved in the loop: look at the ports with the highest link utilization (packets per
second). The show interface Cisco IOS software command displays the utilization for each interface. In
order to display only the utilization information and the interface name (for a quick analysis), you might
use Cisco IOS software regular expression output filtering. Issue the show interface | include line|\/sec
command to display only the packet per second statistics and the interface name. Pay particular attention
to the interfaces with the highest link utilization.
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 10
Refer to the exhibit. Switch SW1 is receiving traffic from SW2. However, SW2 is not receiving traffic
from SW1. Which STP feature should be implemented to prevent inadvertent loops in the network?
A. UDLD
B. PortFast
C. BPDU guard
D. BPDU filtering
Answer: A
The UDLD protocol allows devices connected through fiber-optic or copper Ethernet cables (for example,
Category 5 cabling) to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional
link exists. When a unidirectional link is detected, UDLD shuts down the affected port and alerts the user.
Unidirectional links can cause a variety of problems, including spanning-tree topology loops.
More on: Link1
CCNP Switch 642-813 Questions/Answers Implementing Spanning-Tree
2013 11
Which interfaces should loop guard be enabled on?
A. Root ports
B. Designated ports
C. Root port and alternate ports.
D. Ports configured with PortFast.
E. Root port and ports configured with PortFast.
Answer: C
Loop Guard feature sets the switch port to detect potential loop due to inactive UDLD. Loop Guard must
be enabled on the non-designated ports (more precisely, on root and alternate ports) for all possible
combinations of active topologies.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CCNA 2 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials PDFDocument139 paginiCCNA 2 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials PDFJuan Carlos Alvarez Rojas100% (1)
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsDe la EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Broadcast Service in Ericsson RAN P7Document36 paginiCell Broadcast Service in Ericsson RAN P7Saky KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompTIA Networkplus Rapid Review Exam N10 005Document362 paginiCompTIA Networkplus Rapid Review Exam N10 005Marcelo100% (2)
- Take Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Document14 paginiTake Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Manuel Valdés100% (2)
- CCNP Switch CH 3 AnswerDocument14 paginiCCNP Switch CH 3 AnswerNeil AchacosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco CCNA 200-105 Questions With AnswersDocument157 paginiCisco CCNA 200-105 Questions With AnswerssilviaubertiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccna 3Document53 paginiCcna 3Anonymous h87K4sTÎncă nu există evaluări
- JN0-360 V2-Oct 2016 PDFDocument258 paginiJN0-360 V2-Oct 2016 PDFwerna samÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA3 v4 Final Exam-Update 2012Document56 paginiCCNA3 v4 Final Exam-Update 2012Wozi WozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Testinises 200-125 Vce V2017-Jan-17 by Kent 329q Vce PDFDocument19 paginiCisco Testinises 200-125 Vce V2017-Jan-17 by Kent 329q Vce PDFpytersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The PVSRT+ Reverts To PVST+ To Interoperate With The PVST+ SwitchesDocument10 paginiThe PVSRT+ Reverts To PVST+ To Interoperate With The PVST+ SwitchesjwakooliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Dump JNO-360: SectionsDocument260 paginiBrain Dump JNO-360: SectionsCao Vu ThangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccna TestDocument24 paginiCcna TestArt CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Issues of Switches, Vlan, Etherchannel, HSRP, Nat and DHCPDocument62 paginiIssues of Switches, Vlan, Etherchannel, HSRP, Nat and DHCPEmerson Barros Rivas100% (1)
- CCNA Preguntas Parte 2Document10 paginiCCNA Preguntas Parte 2JeremyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Answers Full PDFDocument14 paginiCCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Answers Full PDFعائشة القرشيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 V 7 BlancDocument8 paginiChapter 4 V 7 BlancLuis Alfredo Dureaux LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP BCMSN - Module - 3 - Exam-CCNPSpanning-TreeDocument6 paginiCCNP BCMSN - Module - 3 - Exam-CCNPSpanning-TreetootootoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccnpv7 Switch - Chapter 4Document9 paginiCcnpv7 Switch - Chapter 4Maria De La O Pequeña73% (11)
- New Pass4itsure Cisco 200-155 Dumps PDFDocument9 paginiNew Pass4itsure Cisco 200-155 Dumps PDFKimberly W. AveryÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP Switch - Chapter 3Document10 paginiCCNP Switch - Chapter 3armani_delatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switch Final Exam CCNP 6Document12 paginiSwitch Final Exam CCNP 6Tuấn Linh100% (2)
- CCNP Switch Final ExamDocument47 paginiCCNP Switch Final ExamRizzo Dubz60% (5)
- CCNA LAN Switching and Wireless Final Exam-PracticeDocument21 paginiCCNA LAN Switching and Wireless Final Exam-Practicesabriel69Încă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Training New CCNA - STPDocument5 paginiCCNA Training New CCNA - STPokotete evidenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCIE 400-101 - 747 QuestionsDocument591 paginiCCIE 400-101 - 747 QuestionsDaniel Olmedo Torres100% (2)
- Correct Answer: B Explanation:: Home Previous Up NextDocument6 paginiCorrect Answer: B Explanation:: Home Previous Up NextABBASSI RABAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccie R&S 400-101 - 779 Q&aDocument604 paginiCcie R&S 400-101 - 779 Q&aSalmanShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 400 101Document457 pagini400 101Rana ShboulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 101 CCNP Route PADocument483 pagini300 101 CCNP Route PASisir KarmakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 400 101 PDFDocument508 pagini400 101 PDFMeklati Youness100% (1)
- Cisco PracticeTest 200-105 Vce V2018-Jun-25 by Borg 234q VceDocument14 paginiCisco PracticeTest 200-105 Vce V2018-Jun-25 by Borg 234q VceTung DinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Route Exam TrialDocument88 paginiCisco Route Exam TrialkofiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP SimulationsDocument261 paginiCCNP SimulationsEmmanuel Teixeira de SousaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP RouteDocument326 paginiCCNP RouteJoão MunizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Switching AnswersDocument11 paginiFinal Exam Switching AnswersAfridi AteeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Discovery 3 Chapter 3 100%Document5 paginiCCNA Discovery 3 Chapter 3 100%jugnudeep100% (2)
- RSTP ProtocolDocument5 paginiRSTP ProtocolaakashtrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1.0Document15 paginiNumber: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1.0Gabriela PopescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco CCNA 200-125 Exam Dumps Latest - New Questions & AnswersDocument136 paginiCisco CCNA 200-125 Exam Dumps Latest - New Questions & Answersergu vfuko fghuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- E SwitchingDocument44 paginiE SwitchingKhaledhosny2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Cisco - Lead2pass.642 813.v2013!06!17.by - Boomish CDocument65 paginiCisco - Lead2pass.642 813.v2013!06!17.by - Boomish CWinHtut BoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccna 3d v4 Module 3 ExamDocument7 paginiCcna 3d v4 Module 3 Exami'll_help_you100% (3)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDe la EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingDe la EverandSPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDe la EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingDe la EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolDe la EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDe la EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewDe la EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDe la EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversDe la EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1De la EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Datasheet Iscom2110ea-Ma 20120830Document5 paginiDatasheet Iscom2110ea-Ma 20120830Vu Minh TuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network - Security LAB-2Document7 paginiNetwork - Security LAB-2SRM AP armyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuring Q in Q Vlan TunnelsDocument16 paginiConfiguring Q in Q Vlan TunnelsmarcusrodasmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding DTMF Negotiation and Troubleshooting On SIP Trunks - IP Telephony - Cisco Support Community - 5961 - 144711Document30 paginiUnderstanding DTMF Negotiation and Troubleshooting On SIP Trunks - IP Telephony - Cisco Support Community - 5961 - 144711will_blixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ SettingsDocument17 paginiLab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ SettingsKasozi BakulumpagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITF11019 Fahad Mazhar Lab Task 03 (CN)Document2 paginiITF11019 Fahad Mazhar Lab Task 03 (CN)Muhammad QasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- D-Link DSL-2730U: User ManualDocument81 paginiD-Link DSL-2730U: User Manuallipi_chhayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSM Examples2 PDFDocument6 paginiVLSM Examples2 PDFАли АлжирÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC MitsubishiDocument228 paginiPLC MitsubishideeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonicwall Gen 7 Nsa SeriesDocument8 paginiSonicwall Gen 7 Nsa Seriesenigma29Încă nu există evaluări
- Device Server User Guide: Part Number 900-417 Revision G June 2015Document87 paginiDevice Server User Guide: Part Number 900-417 Revision G June 2015HAROL ALEXIS VALENCIA OSPINAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 - Cisco IOS XR MPLS Operation and Implementation - Student Learning Guide v5.0 - Word-DPDocument50 pagini16 - Cisco IOS XR MPLS Operation and Implementation - Student Learning Guide v5.0 - Word-DPDúber PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Junos Intermediate Routing PDFDocument3 paginiJunos Intermediate Routing PDFThomas ScottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gy InterfaceDocument63 paginiGy InterfacePratyush HalderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ipv6 Allocation Policy and Procedure: Global Ipv6 Summit in China 2007 April 13, 2007 Gerard Ross and Guangliang PanDocument433 paginiIpv6 Allocation Policy and Procedure: Global Ipv6 Summit in China 2007 April 13, 2007 Gerard Ross and Guangliang PanNILESH WANKHEDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nmap Cheat SheetDocument9 paginiNmap Cheat SheetDraKon GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 黃致恩、郭冠廷、許富菘Document10 paginiGroup 5 黃致恩、郭冠廷、許富菘郭冠廷Încă nu există evaluări
- Volte OverviewDocument26 paginiVolte OverviewAlan BeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technote Mme 00Document12 paginiTechnote Mme 00BudiMulya SetiadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SmartRadar FlexLine SpecificationDocument4 paginiSmartRadar FlexLine SpecificationRafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-14 MSTP ConfigurationDocument103 pagini01-14 MSTP ConfigurationaalmotaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cấu Hình Dự Phòng Với HSRPDocument28 paginiCấu Hình Dự Phòng Với HSRPHoa NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet Qnp-6230rh ViDocument5 paginiDatasheet Qnp-6230rh ViDang ThuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Camara Vivotek IP7135Document65 paginiManual Camara Vivotek IP7135cesarvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Switching: FDM and TDM: FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) 4 Users ExampleDocument46 paginiCircuit Switching: FDM and TDM: FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) 4 Users ExamplemailstonaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 01 - Implement Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMDocument10 paginiLab 01 - Implement Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMPeter AltamiranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument31 paginiTCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingHungry LadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3RD Grading Periodical TestDocument4 pagini3RD Grading Periodical TestMaricris CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări