Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Strategizing at Monarchia Matt Iinternational
Încărcat de
michalis72Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Strategizing at Monarchia Matt Iinternational
Încărcat de
michalis72Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1.
The PESTEL Framework
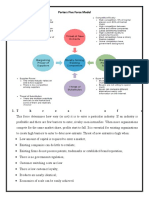
Political: (a) Soviet system and Communism (supply and distribution only in other Eastern bloc countries, destroy winemaking). (b) Privatization of hectare state-owned winery from Hungarian government. (c) International winemakers invested in Hungarian vineyards. (d) European Union gives Hungary a great access to other member countries. (e) Hungarian government did not support the nation's wineries Economic: (a) Trade-off between quality and quantity, wine making -> capital intensive. (b) Economic value limit capital commitment, create price premium with high quality Socio-cultural: (a) Eating habits changes (multimedia promotion and years). (b) Consumers criteria for choosing wine. (c) Wine history - Hungary (p.6) Environmental: Hungary's weather conditions yearly(warmer sunnier summer and less cloud cover and autumnal rain) led to more consistent growing conditions allowing slow ripening that maximizes flavor and aromas. (Success factor in the strategy quality) Legal: (a) Alcohol distribution system: complex and highly fragmented. (b) Internet-based alcohol sales between states. (c) Wine wholesale license: complicated, costly, took over 5 years 2. Porter's five forces framework
The threat of entry & Barriers to entry: (Low threat of entry - High barriers to entry) Threat of entry can consider as Low because barriers to entry are high. High barriers because (a) import and distribution licenses is a lengthy procedure, (b) Economies of scale in the specific industry is not the key issue, of course it is important to produce as much as possible in a premium cost but in that case the important thing is the quality of the final product. So the experience could be considered as an advantage for new entrants since they have already know how to do things more efficiently in terms of choosing quality wines instead of huge quantities. (c) Supply and distribution could be through direct ownership or through customer or supplier loyalty. (d) Differentiation means providing a product/service with higher perceived value than the competition. Wines are differentiated regarding quality, taste, region, cost etc. Threat of substitutes (substitutes are products/services that offer similar benefit to an industrys products/services, but by a different process). Threat of substitutes is high. According to exhibit 3 and exhibit 5 of the case study the per capita consumption by beverage type shows that per capita the consumption of wine is less than other beverage like beer (extra industry effects). Additionally there are multiple choices/alternatives inside the wine industry that the consumer could prefer because of their lower prices (price/performance ratio). The bargaining power of buyers: High. Low switching costs, since the buyer can easily switch between one supplier and another in order to pressure the suppliers for better prices. Additionally in some cases the buyer could supply himself and that makes him powerful, since he can do the suppliers job himself. Where the amount of customers is high the power
of the buyer is also high since they are more likely to search for the best price and therefore squeeze suppliers for more trivial purchases. The bargaining power of suppliers: Medium to Low. Regarding wine industry there are so many suppliers for a buyer that the power of the supplier is minimized. If a buyer decides to switch between suppliers, the cost it may not a large issue but the quality is. Of course in this case it is depend of the needs and requirements of the buyer. Rivalry between competitors: Equal size, Aggressive leadership, Mature or declining market, High fixed costs, High exit barriers, Differentiation level 3. Industry structure/Lifecycle
According to five force analysis we conclude that the barriers o entry tends to be high and experience benefits are important. Products seems to standardize in terms of taste and quality, even there are differentiation on price and region. Buyers become powerful since they can easily switch between suppliers and they can also do the suppliers job. Regarding market share in the industry, there is a providing leverage against buyers, since they offer differentiated wines in terms of taste, kind, region, quality, price etc. The cost key is not there for the industry. Even there is the trade-off between quality and quantity in the case of MMI the key is the quality in a premium price. In my opinion the industry seems to be at the maturity stage. 4. Market Segmentation Age, Income, Location, Lifestyle Choice criteria Product similarity, price, quality Industry, Profitability Choice criteria, Distribution channel Quality
Characteristics of people/organization Purchase/ use situation Users need and preferences for product characteristics
5.
Stakeholders
(a)All in exhibit 6: High power High interest. (b) Customers: High power Low interest. (c) Political: Medium to High power (legislation) Low interest. (d) Suppliers: Medium power Medium interest. (e) Competitors: High power Medium interest. 6. Competitor/Strategic group analysis
Strategic groups are organizations within an industry or sector with similar strategic characteristics, following similar strategies or competing on similar bases. MMIs competitors are other companies larger or equal size than MMI and single market distributors. MMIs similarities with its competitors are the offering products. The differences are focused on the quality and the variety of the products.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- MUFCDocument3 paginiMUFCmichalis7250% (2)
- MUFCDocument3 paginiMUFCmichalis7250% (2)
- Porter 5 Forces I.EDocument4 paginiPorter 5 Forces I.Eazza_j50% (2)
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionDe la EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- The Pricing Journey: The Organizational Transformation Toward Pricing ExcellenceDe la EverandThe Pricing Journey: The Organizational Transformation Toward Pricing ExcellenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Case AnalysisDocument4 paginiGroup Case AnalysisHannah Jean86% (7)
- Case 2 - Competition in Energy DrinksDocument3 paginiCase 2 - Competition in Energy DrinksSheena GabrielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brewing Industry Case Study Part AnsDocument9 paginiBrewing Industry Case Study Part AnsNyenti DelphineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Five Forces of Dairy IndustryDocument4 paginiPorter's Five Forces of Dairy IndustrySowmya KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamDe la EverandQuality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Business in Social and Economic DevelopmentDocument26 paginiThe Role of Business in Social and Economic Developmentmichelle80% (5)
- Policies Toward Monopolies and Oligopolies Privatization and DeregulationDocument10 paginiPolicies Toward Monopolies and Oligopolies Privatization and DeregulationJamaica RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 2 Tanner - The Sales Function & Multi Sales Channels 280516Document17 paginiChap 2 Tanner - The Sales Function & Multi Sales Channels 280516Shahzain RafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mide TermDocument2 paginiMide Termmichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Performing A Competitor Analysis For Wine in DenmarkDocument5 pagini2011 Performing A Competitor Analysis For Wine in DenmarkNovia LieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of The Analysis: - Porter's 5 Forces - PEST AnalysisDocument15 paginiOverview of The Analysis: - Porter's 5 Forces - PEST AnalysisTaraRajagopalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEST Soft Drinks IndustryDocument16 paginiPEST Soft Drinks Industryannekaren23Încă nu există evaluări
- HavmorDocument7 paginiHavmorKunal Jana0% (1)
- ENTP CIA 3 - Feasability AnalysisDocument20 paginiENTP CIA 3 - Feasability AnalysisSujith VichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cola Wars Continue: Coke and Pepsi in 2010: 1.barriers To EntryDocument5 paginiCola Wars Continue: Coke and Pepsi in 2010: 1.barriers To EntryPradIpta Kaphle100% (2)
- Monolpoly CompetitionDocument4 paginiMonolpoly CompetitionAdnanDemirovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Structures Pricing StrategyDocument73 paginiMarket Structures Pricing StrategyKumar Gaurab JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poters Five ForcesDocument4 paginiPoters Five ForcesSanam AdvaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter Five ForcesDocument5 paginiPorter Five ForcesSumaiyaLimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Want To Keep Growing Profitably? Consider Managing Your Prices StrategicallyDocument4 paginiWant To Keep Growing Profitably? Consider Managing Your Prices Strategicallytim_wells2Încă nu există evaluări
- Soft Drinks Industry: ResearchDocument11 paginiSoft Drinks Industry: ResearchDemoxtraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The European Brewery IndustryDocument3 paginiThe European Brewery IndustryAditya MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Michael Porter Analysis (Five Forces Model)Document18 paginiMichael Porter Analysis (Five Forces Model)popat vishalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porters 5 ForcesDocument3 paginiPorters 5 Forcesjabbimuhammed50Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Competitors and CompetitionDocument58 paginiChapter 5 - Competitors and CompetitionMia SentosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poters Five ForcesDocument27 paginiPoters Five ForcesRachana ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The External EnvironmentDocument12 paginiThe External EnvironmentAnggah KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cola Wars Continue - StrategyDocument3 paginiCola Wars Continue - StrategyAnvi ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Is Soft Drink Industry So Profitable? Low Threat of EntryDocument2 paginiWhy Is Soft Drink Industry So Profitable? Low Threat of EntryRobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porters Five Force ModelDocument13 paginiPorters Five Force ModelyuvarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 5 Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument36 paginiThe 5 Competitive Forces That Shape StrategydanilynfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifying and Analyzing CompetitorsDocument13 paginiIdentifying and Analyzing CompetitorsThenmozhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stratejik 2Document3 paginiStratejik 2Popy DefriantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product DifferentiationDocument28 paginiProduct DifferentiationAbhishek JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- External Environment Analysis: BY Prasad KulkarniDocument15 paginiExternal Environment Analysis: BY Prasad KulkarniPreeti ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approaches To Competitor AnalysisDocument32 paginiApproaches To Competitor AnalysisIsrar Raja100% (1)
- Karen Diane Rivera - Course Learning OutcomesDocument17 paginiKaren Diane Rivera - Course Learning OutcomesKaren Diane Chua RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Five TheoryDocument6 paginiPorter's Five TheoryPrity chhetryÎncă nu există evaluări
- International PricingDocument22 paginiInternational PricingManish Sabharwal0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document13 paginiChapter 6GemechuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Purpose of Five-Forces AnalysisDocument9 paginiThe Purpose of Five-Forces AnalysisRahul KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cola WarsDocument2 paginiCola WarsAbhi100% (1)
- Session 2 - ClassDocument54 paginiSession 2 - ClassSrijan SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsDocument32 paginiCustomers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsanashussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Influences On Pricing DecisionsDocument3 paginiMajor Influences On Pricing DecisionsMuhammad BasitÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Strategy Assg - 1Document3 paginiGeneral Strategy Assg - 1Sunny M.Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study BREWERYDocument4 paginiCase Study BREWERYCharlotte Lemaire0% (1)
- BUS 444 Cheat Sheet1Document4 paginiBUS 444 Cheat Sheet1LisaManucciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Task EnvironmentDocument8 paginiThe Task EnvironmentStoryKingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Model of Industry Rivalry (Five Forces)Document6 paginiPorter's Model of Industry Rivalry (Five Forces)Anupamaa SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Marketing Porters 5 Forces HeadingsDocument3 paginiStrategic Marketing Porters 5 Forces Headingsdt0035620Încă nu există evaluări
- 404 AssiDocument9 pagini404 AssiYasmina A. Badr El-deenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Competitors and CompetitionDocument58 paginiChapter 5 Competitors and CompetitionRidho AnjikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics GR Assign't. 2Document9 paginiEconomics GR Assign't. 2Assefa FikaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Competitive EnvironmentDocument46 paginiAnalysis of The Competitive Environmentshivbab1Încă nu există evaluări
- Economics Analysis of Demand & SupplyDocument8 paginiEconomics Analysis of Demand & Supply0302038Încă nu există evaluări
- Porters Five Force ModelDocument5 paginiPorters Five Force ModelHimanshu DarganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Five Force ModelDocument32 paginiPorter's Five Force Modelkregson04Încă nu există evaluări
- Adolph Coors (1) Group 1Document8 paginiAdolph Coors (1) Group 1HaroonNasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pricing Types: Signalling Market Positioning IntentDe la EverandPricing Types: Signalling Market Positioning IntentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Description Summary:: IT ManagerDocument3 paginiJob Description Summary:: IT Managermichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Strategy NotesDocument2 paginiCorporate Strategy Notesmichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- SWOT Analysis TemplatesDocument11 paginiSWOT Analysis Templateszapspaz100% (1)
- Transcript of Strategy CaseDocument15 paginiTranscript of Strategy Casemichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- PESTEL ModelPharmaceutical IndustryDocument4 paginiPESTEL ModelPharmaceutical Industrymichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- Break It Like Beckham Manchester United Football Club Has A Number of StakDocument7 paginiBreak It Like Beckham Manchester United Football Club Has A Number of Stakmichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- VirginDocument2 paginiVirginmichalis72100% (1)
- Break It Like Beckham Manchester United Football Club Has A Number of StakDocument7 paginiBreak It Like Beckham Manchester United Football Club Has A Number of Stakmichalis72Încă nu există evaluări
- The Second Oracle at DelphiDocument14 paginiThe Second Oracle at Delphiapi-302698865Încă nu există evaluări
- Crossen For Sale On Market - 05.23.2019Document26 paginiCrossen For Sale On Market - 05.23.2019Article LinksÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Built - X-Section - 160+700 To 1660+825Document5 paginiAs Built - X-Section - 160+700 To 1660+825Md Mukul MiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emerging and Reemerginginfectious Diseases PDFDocument98 paginiEmerging and Reemerginginfectious Diseases PDFRakesh100% (1)
- Learning CompetenciesDocument44 paginiLearning CompetenciesJeson GalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type Certificate Data Sheet: No. EASA.R.100Document9 paginiType Certificate Data Sheet: No. EASA.R.100SauliusÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA 9072 (National Cave Act)Document4 paginiRA 9072 (National Cave Act)Lorelain ImperialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Studies in Entrepreneurship-3MDocument3 paginiCase Studies in Entrepreneurship-3MAshish ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramesh and GargiDocument14 paginiRamesh and GargiAlok AhirwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015.74013.essentials of Spanish With Readings Volume I TextDocument459 pagini2015.74013.essentials of Spanish With Readings Volume I TextmuytradingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 5Document5 paginiQuiz 5asaad5299Încă nu există evaluări
- Gps DVR FlierDocument2 paginiGps DVR FlierShankar PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (FINA1303) (2014) (F) Midterm Yq5j8 42714Document19 pagini(FINA1303) (2014) (F) Midterm Yq5j8 42714sarah shanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neste Annual Report 2019Document213 paginiNeste Annual Report 2019Xianchi ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmulDocument24 paginiAmulmaskeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper General Principle in The Construction of StatutesDocument8 paginiTerm Paper General Principle in The Construction of StatutesRonald DalidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Change Your Life PDF FreeDocument51 paginiChange Your Life PDF FreeJochebed MukandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acts and Key EventsDocument25 paginiActs and Key Eventsemilyjaneboyle100% (1)
- Application To Visit Australia For Tourism: or Other Recreational ActivitiesDocument13 paginiApplication To Visit Australia For Tourism: or Other Recreational ActivitiesZoran H. VukchichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis On Renaissance and 20th Century Modern ArchitectureDocument2 paginiComparative Analysis On Renaissance and 20th Century Modern ArchitectureJeriel CandidatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- G.R. No. 113899. October 13, 1999. Great Pacific Life Assurance Corp., Petitioner, vs. Court of Appeals and Medarda V. Leuterio, RespondentsDocument12 paginiG.R. No. 113899. October 13, 1999. Great Pacific Life Assurance Corp., Petitioner, vs. Court of Appeals and Medarda V. Leuterio, RespondentsdanexrainierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhonda Taube - Sexuality Meso FigurinesDocument5 paginiRhonda Taube - Sexuality Meso FigurinesSneshko SnegicÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Chapter 1Document9 paginiMCQ Chapter 1K57 TRAN THI MINH NGOCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Reptiles and Amphibians????Document2 paginiDifference Between Reptiles and Amphibians????vijaybansalfetÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - JM Influencer MarketingDocument19 pagini1 - JM Influencer MarketingMochamad RochmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Joselle A. Gaco Btled-He3A: THE 303-School Foodservice ManagementDocument3 paginiName: Joselle A. Gaco Btled-He3A: THE 303-School Foodservice ManagementJoselle GacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quizlet - SOM 122 Chapter 5 - ManagementDocument3 paginiQuizlet - SOM 122 Chapter 5 - ManagementBob KaneÎncă nu există evaluări