Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
F 1261041405446
Încărcat de
Tariq BezinjoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
F 1261041405446
Încărcat de
Tariq BezinjoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction
Though the prevalence and quality of telecommunication networking has undergone leaps and bounds since the telephone was first invented in 1847, yet the adaptation of large-capacity networking in developed countries remain rather limited and in certain fixed areas, which has turned the majority of the developing countries to continue searching for solutions through VPN and remote area high-quality communications applications. The VSAT technology that begun in the 90s not only serves to provide regional services through intangible wiring routes but also provides comparable competitiveness in functionality, service types, accessibility, transmission cost, expansion cost and so forth when compared with tangible wiring routes.
1.Introduction of the VSAT technology
VSAT,the acronym of very small aperture terminal, signifies a small-diameter ground terminal in straight interpretation, deriving from the fact that the wiring diameter of a VSAT systems ground tends to be smaller, usually between 0.3m and 2.4m. A new satellite communications system developed in the mid 90s utilizing the modern technology, VSAT systems come with characteristics of a dynamic flexibility, dependability, low cost, easy to use, and a direct linkup to the user through a local station. Whereby a VSAT user terminal can link up directly to a remote server through satellite channel to complete data transmission, document exchange or even remote processing to resolve the problem of ground station signal interruptions. In light of which, in remote spots where the ground networking-infrastructure may be less than perfected, the quality of communications wiring may be poor, or in the absence of a high-speed transmission networking, the adaptation of the VSAT system would poise to improve the foresaid problems.
2.Characteristics of the VSAT system
A VSAT networking framework comprises of several small VSAT substations and a main hub working together to constitute a wide-area networked (of a multi-station configuration of smaller substation workload) satellite communications network. Compared with a ground s t a t i o n c o m m u n i c a t i o n s n e t w o r k , a V S AT communications network offers the following nine characteristics: (1)Its signals cover a far-flung area; (2)It is able to provide to all ground stations the identical service types and broadband service quality, including error bit rate, transmission delay, etc.; (3)Offering fine expandability with low expansion cost and a relative short time for installing new communication stations of smaller diameter antenna, and easy system launching and maintenance; (4)Offering fine flexibility, where a multiple of services can be combined in a single network and provide varied service types, with adjustable feature for bandwidth allocation and quality grade; (5)Offering fine communication capability of point to point, one point to multiple points, multiple points to multiple points, whereby the user can communicate with other users without routed through the ground station; (6)As a user designated communications network, it is not confined by the telecommunications provider, hence warranting an outstanding independent operability, and besides fixed equipment, there are choices of mobile equipment; (7)Offering fine inter-working capability for users on varied communications protocols can communicate through the same VSAT network using different ground stations; (8)Offering fine communications quality, with lower error bit rate and shorter networking response timing; (9)A VSAT system offers intelligent functions, i.e. intelligent operations, interface, IT supportive operations and frequency management) to allow man-less operations to conserve operating manpower.
(2) Intermediary phase (first generation):Of equipment developed during 1983 and 1988, which cover not only newly developed multi address linkup but characterized by a Ku band and satellite-configured networking framework in digital transmission. (3) Near phase (second generation):Second generation VSAT is now being transformed from a simple digital transmission mode to an integrated digital/voice/ graphic service orientation, together with a networking communication framework, which covers the timeline of roughly from 1988 to the mid 1990s. Since mid 90s, VSAT has begun broaching towards third generation function development, which is characterized by a stepped-up management and control capability, meaning using software to control a VSAT system operations. At present, the VSAT systems are broaching towards the direction of standardized hardware and software, allowing VSAT equipment to provide a rudimentary operating platform function in essential networking, and that the addition of module configured hardware equipment and operating software, made to the user requirements, can further enhance a VSAT system networking exchange and transmission functions.
4.The VSAT system applications
Besides designated broadband operations, a VSAT satellite communications network also supports the existing operational services, such as voice, digital, fax, LAN linkup, Audiovisual teleconferencing system, low-speed graphic transmission, FR interface-based interactive graphic prompting, television and digital music services; some of its tangible operational categories and typical applications are as charted below,
F a x
T V R O ( B T V (
3.The VSAT system development is divided into the following three phases
(1) Initial phase: This phase pertains to that around 1980, when C band is used as the primarily communication channel, and is limited to digital services of one-way reception and low-speed transmission.
) (
C A D / C A M L A N
C P U - C P U D T E - C P U
5.The VSAT networking framework
(1)Main hub The main hub serves as the central nerve of a VSAT network, and operates on large-scale antenna same as the general ground stations with a diameter measuring approx. 3.5m to 8m (on Ku band) or 7m to 13m (on C band). When applied in digital services, a VSAT main hub serves as the processing center and also the networking control center, where at the same time the main hub is equipped with a networking control center (NCC), which is responsible for monitoring, managing, controlling and maintaining various facilities. When applied in voice services, a VSAT systems control center can be placed in the same station as the services center or in a separate station. In addition, to facilitate equipment mounting, dismounting and assembly, the main hub is usually in a modulated structured, and links up to various substations using the high-speed regional network configuration. (2)VSAT substations A VSAT substation is comprised of three elements the small diameter antenna, outdoor unit (ODU) and indoor unit (IDU). Under identical setting, i.e. identical bandwidth, frequency projector, etc., a voice VSAT networks substations serve to provide direct linkup between the substations, and whose antenna design would ominously be larger than that of the digital SVAT substations that only communicate with the main hub. (3)Satellite attenuator First generation VSAT network operates on C band attenuator, and second generation VSAT and onward are largely operating on the Ku band. As to the operating bandwidth, it has not been tied to the oquipment but rather whether the satellite itself comes with the resources of frequency conversion equipment.
6.VSATs LAN applications
Given that the adaptation of a VSAT system in regional networking (LAN) helps to enhance the dependability between networks, since mid 90s, the VSAT systems are able to support serially connected interfaces to a LAN/ MAN network knot interfaces. Communications between a VSAT network and LAN can either be in a direct mode or an intermediary mode. When communicating directly with LAN using a VSAT system, there are three options of using a bridge device, router or streamliner, and varied linkup methods would produce varied effects in VSAT system communications protocols, bandwidth utilization and flexibility. Some of the prevailing LAN protocols include TCP/IP, SNA, DECnet, IPX and the like.
7.Concept for the Coast Guard Administrations adapting the VSAT system
A predominant poor quality of communications at the administrations remote areas, namely at offshore and coastal islands, has stemmed from Chung Hwa Telecommunications Companys insufficient broadband networking infrastructure for remote regions, such as the Coast Guards ADSL linkup. In search of resolving and improving remote regions broadcast communications issue, the VSAT system emerges as an optimal solution. In the case of the Dong Sha and Nan Sha regions that fall under the administrations jurisdiction that are in dire need of improvement, a conceptual drawing is hereby presented depicting the adaptation of a VSAT system in the Dong Sha and Nan Sha regions as showed below, Adopting the VSAT system for integrating voice, data and video multimedia signals is not only a current trend but best support the administrations communication needs, as it serves more than receiving and accommodating signals of various defense units on the island, and signals transmitted back to the Taiwan main island would allow Southern Regional Patrol bureau, General Coastal Patrol Agency, or even the Coast Guard Administration to contact the superior units at the Defense Department on islands that are manned by defense troops through the administrations external linkup circuits, offering the islands a comprehensive and multimedia communication quality. It is highly anticipated that the VSAT system can be prompted as a shared regional network for all outpost personnel stationing at offshore and coastal islands under various government departments that would poise to improve the current phases poor communication problem. (The author is a specialist in communications and logistics section at the General Coastal Patrol Agency of the Coast Guard Administration)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 54 PDFDocument104 pagini54 PDFTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH07 PDFDocument30 paginiCH07 PDFTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Pay Scale 2011Document1 paginăRevised Pay Scale 2011Tariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication:: Major Components of DCDocument11 paginiData Communication:: Major Components of DCTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personnel Policy: Mir Shai Mazar BalochDocument27 paginiPersonnel Policy: Mir Shai Mazar BalochTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument32 paginiProject Management Tools and TechniquesTariq Bezinjo100% (1)
- Roots: Latin Root Basic Meaning Example Words Example WordsDocument6 paginiRoots: Latin Root Basic Meaning Example Words Example WordsTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managementhistory 140114101232 Phpapp01Document16 paginiManagementhistory 140114101232 Phpapp01Tariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of Capital Budgeting.13-14stDocument36 paginiThe Basics of Capital Budgeting.13-14stHamza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training & DevelopmentDocument9 paginiTraining & DevelopmentTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Development Life Cycle ExplainedDocument16 paginiSystem Development Life Cycle ExplainedTariq Bezinjo100% (1)
- Agenda 11Document12 paginiAgenda 11Tariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Strategic ManagementDocument56 paginiOverview of Strategic ManagementTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Strategic ManagementDocument56 paginiOverview of Strategic ManagementTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abraham MaslowDocument7 paginiAbraham MaslowTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decision MakingDocument63 paginiDecision MakingTariq BezinjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Mean, Median, Mode and RangeDocument19 paginiCalculating Mean, Median, Mode and RangeJency SerishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Ids-2cd7a46g0p-Izhsy Datasheet v5.5.130 20200727Document8 paginiIds-2cd7a46g0p-Izhsy Datasheet v5.5.130 20200727Jose PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obsolete - TEMS Discovery - Events and Metrics Including Mapping For TEMSDocument177 paginiObsolete - TEMS Discovery - Events and Metrics Including Mapping For TEMSPakcik KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Xpert Ethernet Switches Technical Data Sheet PDFDocument2 paginiPower Xpert Ethernet Switches Technical Data Sheet PDFAODVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Take Assessment - Enetwork Skill Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Document9 paginiTake Assessment - Enetwork Skill Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Nandha PatrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCI Placement Rules For IBM System IDocument52 paginiPCI Placement Rules For IBM System IchengabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arris BGW210 To BGW700 Internet Phone 3Document3 paginiArris BGW210 To BGW700 Internet Phone 3hunter don0% (1)
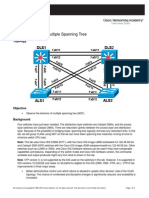
- Lab 3-3, PVSTDocument9 paginiLab 3-3, PVSTmario_angelic6381Încă nu există evaluări
- Web Port DiagramDocument1 paginăWeb Port DiagramFernando DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- OperManual LATAM ST600 Total Rev103Document106 paginiOperManual LATAM ST600 Total Rev103Camaras y GPS Emtrafesa TrujilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- A10 Networks WAF GuideDocument176 paginiA10 Networks WAF Guide1991gabolopez100% (2)
- Test Project: IT Network Systems Administration Module A - Linux EnvironmentDocument11 paginiTest Project: IT Network Systems Administration Module A - Linux EnvironmentIT CompÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual - CSE 324 - Computer Networks Lab v2.1Document42 paginiLab Manual - CSE 324 - Computer Networks Lab v2.1A. R. ParthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN LabDocument13 paginiCN Lablokesh_045Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual SpeedportW724VType Ci OTE enDocument152 paginiManual SpeedportW724VType Ci OTE enaetos999Încă nu există evaluări
- Wifi Smart: Thank You For Choosing Our Product. For Proper Operation, Please Read and Keep This Manual CarefullyDocument24 paginiWifi Smart: Thank You For Choosing Our Product. For Proper Operation, Please Read and Keep This Manual Carefullykari.junttilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teltonika Model ComparisonDocument2 paginiTeltonika Model ComparisonDaniel SherwoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Grow Fast and Increase Your Network Size: Fitel Network Case Study - SpainDocument3 paginiHow To Grow Fast and Increase Your Network Size: Fitel Network Case Study - SpainSai Kyaw HtikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avaya Aura MBT 521 Product DefinitionDocument35 paginiAvaya Aura MBT 521 Product DefinitionOscar ValleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lan Design 1 NotesDocument2 paginiLan Design 1 Noteshht7879Încă nu există evaluări
- NIC Teaming in Windows Server 2012 Brings Simple, Affordable Traffic Reliability and Load Balancing To Your Cloud Workloads - Building Clouds Blog - Site Home - TechNet BlogsDocument8 paginiNIC Teaming in Windows Server 2012 Brings Simple, Affordable Traffic Reliability and Load Balancing To Your Cloud Workloads - Building Clouds Blog - Site Home - TechNet BlogsIsraiser IsroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thiyagarajan S A&DDocument3 paginiThiyagarajan S A&DAziz Ahammed AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Command Reference 4.1Document336 paginiCommand Reference 4.1schneiderfileÎncă nu există evaluări
- EX en Cheat Sheet JunOSDocument1 paginăEX en Cheat Sheet JunOSLuis MurteiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPT Atp Document r3Document19 paginiNPT Atp Document r3satyvan2003Încă nu există evaluări
- Se License Manager GuideDocument93 paginiSe License Manager GuideRoberto Gutierrez SaezÎncă nu există evaluări
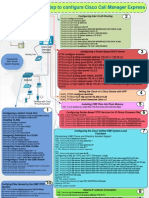
- Configure Cisco Voice Gateway and Call Manager ExpressDocument1 paginăConfigure Cisco Voice Gateway and Call Manager ExpressSudhir Vats100% (2)
- 1500 ProjectsDocument73 pagini1500 ProjectsJugalKSewagÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIBPDocument5 paginiLIBPWebert CunhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN Datasheet TEG-25GECTX (v1.0R)Document3 paginiEN Datasheet TEG-25GECTX (v1.0R)JerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Plan Microsoft MCSA Windows Server 2016-70-742Document10 paginiStudy Plan Microsoft MCSA Windows Server 2016-70-742LLumÎncă nu există evaluări