Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
2 1 32
Încărcat de
Sergey MovchanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2 1 32
Încărcat de
Sergey MovchanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SECTION 2 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Group 1 Pump Device - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-1
Group 2 Main Control Valve - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-21
Group 3 Swing Device - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-51
Group 4 Travel Device - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-60
Group 5 RCV Lever - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-67
Group 6 RCV Pedal - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2-74
2-1
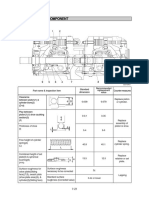
1. STRUCTURE
The pump device consists of main pump, regulator and gear pump.
SECTION 2 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
GROUP 1 PUMP DEVICE
Pi1 Pm1
Dr
Pi1
Pm1
Psv
Psv
Pm2
Pi2
Pm2 Pi2
a4
a4
A3
B3
Dr
B3
B1
a3
a1
a1
A1
A2
A3 B3 B1
Dr
Pi1
Pm1
Psv
a2
a4
a3
Qmin adjusting screw
Regulator Regulator
Gear pump Rear pump Front pump
Port block
Qmax adjusting screw
Qmin adjusting screw
a2
Port
A1,2
B1
Dr
Pi1,i2
Pm1,m2
Psv
a1,2,4
a3
A3
B3
Port name
Delivery port
Suction port
Drain port
Pilot port
Qmax cut port
Servo assist port
Gauge port
Gauge port
Gear pump delivery port
Gear pump suction port
Port size
SAE6000psi 3/4"
SAE2500psi 2 1/2"
PF 3/4 - 20
PF 1/4 - 15
PF 1/4 - 15
PF 1/4 - 15
PF 1/4 - 15
PF 1/4-14
PF 1/2 - 19
PF 3/4 - 20
Pm2
Pi2
2-2
MAIN PUMP(1/2)
The main pump consists of two piston pumps(front & rear) and valve block.
1)
04 Gear pump
111 Drive shaft(F)
113 Drive shaft(R)
114 Spline coupling
123 Roller bearing
124 Needle bearing
127 Bearing spacer
141 Cylinder block
151 Piston
152 Shoe
153 Set plate
156 Bushing
157 Cylinder spring
211 Shoe plate
212 Swash plate
214 Bushing
251 Support
789, 732 532 214 548 531 724
702
792 901 808 954 717 151 152 534 211 113
04
401 271 141 314 885 466
725
114 312 124 313 468
728
157 156 153 490
212
251
123
710
127
824
111
774
261
406
886
953
717
806
535
261 Seal cover(F)
271 Pump casing
312 Valve block
313 Valve plate(R)
314 Valve plate(L)
401 Hexagon socket bolt
406 Hexagon socket bolt
466 VP Plug
468 VP Plug
490 Plug
531 Tilting pin
532 Servo piston
534 Stopper(L)
535 Stopper(S)
548 Pin
702 O-ring
710 O-ring
717 O-ring
724 O-ring
725 O-ring
728 O-ring
732 O-ring
774 Oil seal
789 Back up ring
792 Back up ring
806 Hexagon head nut
808 Hexagon head nut
824 Snap ring
885 Pin
886 Spring pin
901 Eye bolt
953 Set screw
954 Set screw
22007C2MP02
2-3
MAIN PUMP(2/2)
079 Proportional reducing valve
541 Seat
543 Stopper 1
544 Stopper 2
545 Steel ball
544
543
545
541
079
VIEW A
2-3
2-4
REGULATOR(1/2) 2)
A
A
A
B
B
B
SECTION B-B
VIEW C
P2
Pf
Pm
Pi
KR3G-9C32
755
858
614
615
613
611
438
801
924
647
648
723
642
801
656
438
735
722
897
612
875 874 412
641 730 643 708 644 645 646 728
413 438
496 724 725 436
Port
A
B
Pi
Pm
Port name
Delivery port
Suction port
Pilot port
Qmax cut port
port size
3/4"
2 1/2"
PF 1/4-15
PF 1/4-15
2-4
2-4
2-5
REGULATOR(2/2)
412 Hexagon socket screw
413 Hexagon socket screw
436 Hexagon socket screw
438 Hexagon socket screw
496 Plug
601 Casing
611 Feed back lever
612 Lever(1)
613 Lever(2)
614 Fulcrum plug
615 Adjust plug
621 Compensator piston
622 Piston case
623 Compensator rod
624 Spring seat(C)
625 Outer spring
626 Inner spring
627 Adjust stem(C)
628 Adjust screw(C)
629 Cover(C)
630 Lock nut
631 Sleeve, pf
641 Pilot cover
642 Pilot cover(QMC)
643 Pilot piston
644 Spring seat(Q)
645 Adjust stem(Q)
646 Pilot spring
647 Stopper
648 Piston(QMC)
651 Sleeve
652 Spool
653 Spring seat
654 Return spring
655 Set spring
656 Block cover
708 O-ring
722 O-ring
723 O-ring
724 O-ring
725 O-ring
728 O-ring
730 O-ring
732 O-ring
733 O-ring
734 O-ring
735 O-ring
755 O-ring
756 O-ring
763 O-ring
801 Nut
814 Snap ring
836 Snap ring
858 Snap ring
874 Pin
875 Pin
887 Pin
897 Pin
898 Pin
924 Set screw
925 Adjust screw(QI)
734 653 654 836 651 652 601 624 629 630 628
655
641
814
898
631
732
733
622
C
801
925
627
732
621 623 625 626 887 763 756
SECTION A-A
2-5
2-6
GEAR PUMP 3)
307 Poppet
308 Seat
309 Spring seat
310 Spring
311 Screw
312 Nut
351 Gear case
353 Drive gear
354 Driven gear
355 Filter
361 Front case
433 Flange socket
434 Flange socket
435 Flange socket
466 Plug
700 Ring
710 O-ring
725 O-ring
732 O-ring
850 Snap ring
700 354 351 433
434
311
312
850
355
a3
A3
B3
710 435 361 353 732 309 307 310 308 434 466, 725
2-6
2-7
Rotary group
The rotary group consists of drive shaft
(F)(111), cylinder block(141), piston
shoes(151,152), set plate(153), spherical
bush(156), spacer(158) and cylinder
spring(157). The drive shaft is supported
by bearing(123,124) at its both ends.
The shoe is caulked to the piston to from
a spherical coupling. It has a pocket to
relieve thrust force generated by loading
pressure and the take hydraulic balance
so that it slides lightly over the shoe
plate(211). The sub group composed by
a piston and a shoe is pressed against the
shoe plate by the action of the cylinder
spring via a retainer and a spherical bush.
Similarly, the cylinder block is pressed
against valve plate(313) by the action of
the cylinder spring.
Swash plate group
The swash plate group consists of swash
plate(212), shoe plate(211), swash plate
support(251), tilting bush(214), tilting
pin(531) and servo piston(532).
The swash plate is a cylindrical part
formed on the opposite side of the sliding
surface of the shoe and is supported by
the swash support.
If the servo piston moves to the right and
left as hydraulic force controlled by the
regulator is admitted to hydraulic chamber
located on both sides of the servo piston,
the swash plate slides over the swash
plate support via the spherical part of the
tilting pin to change the tilting angle()
2. FUNCTION
MAIN PUMP
The pumps may classified roughly into the rotary group performing a rotary motion and working as
the major part of the whole pump function: the swash plate group that varies the delivery rates: and
the valve cover group that changes over oil suction and discharge.
1)
(1)
(2)
157
211
211
123
111
212
251
532
151
152
531
548
214
124
313
141
158
156
153
2-7(1)
2-7
2-8
Valve block group
The valve block group consists of valve
block(312), valve plate(313) and valve
plate pin(885).
The valve plate having two melon-shaped
ports is fixed to the valve block and feeds
and collects oil to and from the cylinder
block.
The oil changed over by the valve plate is
connected to an external pipeline by way
of the valve block.
Now, if the drive shaft is driven by a prime
mover(electric motor, engine, etc), it
rotates the cylinder block via a spline
linkage at the same time. If the swash
plate is tilted as in Fig(previous page) the
pistons arranged in the cylinder block
make a reciprocating motion with respect
to the cylinder block, while they revolve
with the cylinder block.
If you pay attention to a single piston, it
performs a motion away from the valve
plate(oil sucking process) within 180
degrees, and makes a motion towards the
valve plate(or oil discharging process) in
the rest of 180 degrees. When the swash
plate has a tilting angle of zero, the piston
makes no stroke and discharges no oil.
(3)
313
885
312
2-8
2-9
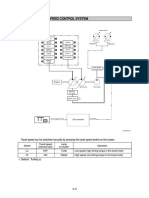
Negative flow control
By changing the pilot pressure Pi, the
pump tilting angle(delivery flow) is
regulated arbitrarily, as shown in the
figure.
This regulator is of the negative flow
control in which the delivery flow Q
decreases as the pilot pressure Pi rises.
With this mechanism, when the pilot
pressure corresponding to the flow
required for the work is commanded, the
pump discharges the required flow only,
and so it does not consume the power
uselessly.
REGULATOR
Regulator consists of the negative flow control, total horse power control and power shift control
function.
2)
(1)
Pilot pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
2-10
Flow reducing function _
As the pilot pressure Pi rises, the pilot piston(643) moves to the right to a position where the force
of the pilot spring(646) balances with the hydraulic force.
The groove(A) in the pilot piston is fitted with the pin(875) that is fixed to lever 2(613). Therefore,
when the pilot piston moves, lever 2 rotates around the fulcrum of point B [fixed by the fulcrum
plug(614) and pin(875)]. Since the large hole section(C) of lever 2 contains a protruding pin(897)
fixed to the feedback lever(611), the pin(897) moves to the right as lever 2 rotates. Since the
opposing-flat section(D) of the feedback lever is fitted with the pin(548) fixed by the tilting pin(531)
that swings the swash plate, the feedback lever rotates around the fulcrum of point D, as the
pin(897) moves.
Since the feedback lever is connected with the spool(652) via the pin(874), the spool moves to
the right.
The movement of the spool causes the delivery pressure P1 to connect to port CL through the
spool and to be admitted to the large diameter section of the servo piston. The delivery pressure
P1 that is constantly admitted to the small diameter section of the servo piston moves the servo
piston to the right due to the area difference, resulting in decrease of the tilting angle.
When the servo piston moves to the right, point D also moves to the right. The spool is fitted
with the return spring(654) and is tensioned to the left at all times, and so the pin(897) is pressed
against the large hole section(C) of lever 2.
Therefore, as point D moves, the feedback lever rotates around the fulcrum of point C, and the
spool is shifted to the left. This causes the opening between the sleeve(651) and spool(652) to
close slowly, and the servo piston comes to a complete stop when it closes completely.
643 654 651 652 613 646
B(E)
874
897
875
C
A
611
CL P1
531
548
D
Small diameter
chamber
Servo piston
Large diameter
chamber
2-10
2-11
Flow increasing function _
As the pilot pressure Pi decreases, the pilot piston(643) moves to the left by the action of the pilot
spring(646) and causes lever 2(613) to rotate around the fulcrum of point B. Since the pin(897)
is pressed against the large hole section(C) of lever 2 by the action of the return spring(654) via
the spool(652), pin(874), and feedback lever(611), the feedback lever rotates around the fulcrum
of point D as lever 2 rotates, and shifts the spool to the left. Port CL opens a way to the tank port
as the spool moves. This deprives the large diameter section of the servo piston of pressure,
and shifts the servo piston to the left by the discharge pressure P1 in the small diameter section,
resulting in an increase in the flow rate.
As the servo piston moves, point D also moves to the left, the feedback lever rotates around the
fulcrum of point C, and the spool moves to the right till the opening between the spool and sleeve
is closed.
643 654 651 652 613 646
B(E)
874
897
875
C
611
CL P1
531
548
D
Small diameter
chamber
Servo piston
Large diameter
chamber
2-11
2-12
The flow control characteristic can be
adjusted with the adjusting screw.
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon
nut(801) and by tightening(or loosening)
the hexagonal socket head screw(924).
Tightening the screw shifts the control
chart to the right as shown in the figure.
Adjusting values are shown in table.
Adjustment of flow control characteristic
Pilot pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
Adjustment of flow control
characteristic
Speed
Tightening Flow control Flow change
amount of starting amount
adjusting pressure
screw(924) change
amount
(min
-1
) (Turn) (kgf/cm
2
) (/min)
1950 +1/4 +1.5 +12.6
801
924
_
2-13
Total horsepower control
The regulator decreases the pump tilting
angle(delivery flow) automatically to limit
the input torque within a certain value with
a rise in the delivery pressure P1 of the
self pump and the delivery pressure P2 of
the companion pump.
(The input horsepower is constant when
the speed is constant.)
Since the regulator is of the simultaneous
total horsepower type that operates by the
sum of load pressures of the two pumps
in the tandem double-pump system, the
prime mover is automatically prevented
from being overloaded, irrespective of the
load condition of the two pumps, when
horsepower control is under way.
Since this regulator is of the simultaneous
total horsepower type, it controls the tilting
angles(displacement volumes) of the two
pumps to the same value as represented
by the following equation :
Tin = P1q/2+ P2q/2
= (P1+P2)q/2
The horsepower control function is the
same as the flow control function and is
summarized in the following.(For detailed
behaviors of respective parts, refer to the
section of flow control).
(2)
Delivery pressure, (P1+P2)
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
2-14
Overload preventive function _
When the self pump delivery pressure P1 or the companion pump delivery pressure P2 rises, it
acts on the stepped part of the compensating piston(621). It presses the compensating rod(623)
to the right till the force of the outer spring(625) and inner spring(626) balances with the hydraulic
force. The movement of the compensating rod is transmitted to lever 1(612) via pin(875).
Lever 1 rotates around the pin(875) (E) fixed to the casing(601).
Since the large hole section(F) of lever 1 contains a protruding pin(897) fixed to the feedback
lever(611), the feedback lever rotates around the fulcrum of point D as lever 1 rotates, and then
the spool(652) is shifted to the right. As the spool moves, the delivery pressure P1 is admitted to
the large diameter section of the servo piston via port CL, causes the servo piston move to the
right, reduces the pump delivery, flow rate, and prevents the prime mover from being overloaded.
The movement of the servo piston is transmitted to the feedback lever via point D. Then the
feedback lever rotates around the fulcrum of point F and the spool is shifted to the left. The
spool moves till the opening between the spool(652) and sleeve(651) is closed.
621 651 652 623 612 601 625 626
B(E)
897
875
F
611
CL P1
P2 P1
D
Small diameter
chamber
Servo piston
Large diameter
chamber
2-14
2-15
Flow reset function _
As the self pump delivery pressure P1 or the companion pump delivery pressure P2 decreases,
the compensating rod(623) is pushed back by the action of the springs(625 & 626) to rotate lever
1(612) around point E. Rotating of lever 1 causes the feedback lever(611) to rotate around the
fulcrum of point D and then the spool(652) to move to the left. As a result, port CL opens a way
to the tank port.
This causes the servo piston to move to the left and the pump's delivery rate to increase.
The movement of the servo piston is transmitted to the spool by the action of the feedback
mechanism to move it till the opening between the spool and sleeve is closed.
621 651 652 623 612 601 625 626
B(E)
897
875
F
CL P1
P2 P1
D
Small diameter
chamber Servo piston
Large diameter
chamber
2-15
2-16
Adjustment of outer spring
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon
nut(630) and by tightening(or loosening)
the adjusting screw C(628). Tightening
the screw shifts the control chart to the
right and increases the input
horsepower as shown in the figure.
Since turning the adjusting screw C by
N turns changes the setting of the inner
spring(626), return the adjusting screw
QI(925) by NA turns at first.(A=2.2)
Adjusting values are shown in table
Low tilting angle(Low flow) command preferential function
As mentioned above, flow control and horsepower control tilting angle commands are
transmitted to the feedback lever and spool via the large-hole sections(C & F) of levers 1 and 2.
However, since sections C and F have the pins(+4) protruding from the large hole(+8), only the
lever lessening the tilting angle contacts the pin(897) ; the hole(+8) in the lever of a larger tilting
angle command is freed without contacting the pin(897). Such a mechanical selection method
permits preference of the lower tilting angle command of the flow control and horsepower control.
Adjustment of input horsepower
Since the regulator is of total cumulative horsepower type, adjust the adjusting screws of both the
front and rear pumps, when changing the horsepower set values. The pressure change values
by adjustment are based on two pumps pressurized at the same time, and the values will be
doubled when only one pump is loaded.
_
_
a.
Delivery pressure, (P1+P2)
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
625 626 630 628
801
925
2-16
Adjustment of flow control
characteristic
Speed
Tightening Flow control Flow change
amount of starting amount
adjusting pressure
screw(924) change
amount
(min
-1
) (Turn) (kgf/cm
2
) (/min)
1950 +1/4 +15.9 +4.3
2-17
Adjustment of inner spring
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon nut
(801) and by tightening(or loosening)
the adjusting screw QI(925).
Tightening the screw increases the flow
and then the input horsepower as
shown in the figure.
Adjusting valves are shown in table
b.
Delivery pressure, (P1+P2)
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
626
801
925
2-17
Adjustment of flow control
characteristic
Speed
Tightening Compensa Input torque
amount of ting control change
adjusting starting amount
screw(QI) pressure
(925) change
amount
(min
-1
) (Turn) (kgf/cm
2
) (kgfm)
1950 +1/4 +9.7 +4.2
2-18
Power shift control
The set horsepower valve is shifted by
varying the command current level of the
proportional pressure reducing valve
attached to the pump.
Only one proportional pressure reducing
valve is provided.
However, the secondary pressure Pf
(power shift pressure) is admitted to the
horsepower control section of each pump
regulator through the pump's internal path
to shift it to the same set horsepower level.
This function permits arbitrary setting of the pump output power, thereby providing the optimum
power level according to the operating condition.
The power shift pressure Pf controls the set horsepower of the pump to a desired level, as shown
in the figure.
As the power shift pressure Pf rises, the compensating rod(623) moves to the right via the
pin(898) and compensating piston(621).
This decreases the pump tilting angle and then the set horsepower in the same way as explained
in the overload preventive function of the horsepower control. On the contrary, the set
horsepower rises as the power shift pressure Pf falls.
(3)
Delivery pressure, (P1+P2)
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
P
f
=
M
A
X
.
P
f
=
M
I
N
.
621 651 652 623 612 625 626
B(E)
897
875
898
611
F
CL P1
P2
Pf
P1
D
Small diameter
chamber Servo piston
Large diameter
chamber
2-18
2-19
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon
nut(808) and by tightening(or loosening)
the set screw(954).
The maximum flow only is adjusted
without changing other control
characteristics.
Adjustment of minimum flow
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon
nut(808) and by tightening(or loosening)
the hexagonal socket head set screw
(953). Similarly to the adjustment of the
maximum flow, other characteristics are
not changed.
However, remember that, if tightened too
much, the required horsepower during
the maximum delivery pressure(or during
relieving) may increase.
Adjustment of maximum and minimum flows (4)
Delivery pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
808
954
806
953
Adjustment of max flow
Speed
(min
-1
)
1950
Tightening
amount of
adjusting screw
(954)
(Turn)
+1/4
Flow change
amount
(/min)
-5.6
Delivery pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
2-19(1)
2-19(2)
Adjustment of min flow
Speed
(min
-1
)
1950
Tightening
amount of
adjusting screw
(953)
(Turn)
+1/4
Flow change
amount
(/min)
+4.5
2-20
Qmax cut control
The regulator regulates the
maximum delivery flow by
inputting the pilot pressure
Pm. Since this is a 2-position
control method, the maximum
delivery flow may be
switched in two steps by
turning on/off the pilot
pressure Pm. (The maximum
control flow cannot be
controlled in intermediate
level.)
Functional explanation
As shown in the figure, the pilot pressure
Pm switches the maximum flow in two
steps.
When the pilot pressure Pm is given, it is
admitted to the lefthand side of the piston
QMC(648). The piston QMC moves the
stopper(647) and pilot piston(643) to the
right, overcoming the force of the pilot
spring(646), thereby reducing the
delivery flow of the pump.
Since the adjusting screw QMC(642) is
provided with a flange, the piston QMC
stops upon contact with the flange, and
the position of the pilot piston at this time
determines the maximum flow of the
pump.
Adjustment of Qmax cut flow
Adjust it by loosening the hexagon
nut(801) and by tightening(or loosening)
the adjusting screw QMC(642).
Tightening the screw decreases the
Qmax cut flow as shown in the figure.
_
_
Pilot pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
Pilot pressure, Pi
D
e
l
i
v
e
r
y
f
l
o
w
,
Q
647
648
723
642
801
438
801
924
641 730 643 708 644 645 646 728
Pm
(5)
2-4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Group 4 Disassembly and Assembly: 1. Electro-Hydraulic Control UnitDocument210 paginiGroup 4 Disassembly and Assembly: 1. Electro-Hydraulic Control UnitSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Section 7 Disassembly and AssemblyDocument4 paginiSection 7 Disassembly and AssemblySergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Group 2 Major ComponentDocument11 paginiGroup 2 Major ComponentSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 2 Tightening Torque: 1. Major ComponentsDocument3 paginiGroup 2 Tightening Torque: 1. Major ComponentsSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Group 2 Tightening Torque: 1. Major ComponentsDocument3 paginiGroup 2 Tightening Torque: 1. Major ComponentsSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Group 2 Major ComponentDocument11 paginiGroup 2 Major ComponentSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Group 2 Tightening TorqueDocument3 paginiGroup 2 Tightening TorqueSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Group 3 Tests and Adjustments: 1. Parking Brake PerformanceDocument2 paginiGroup 3 Tests and Adjustments: 1. Parking Brake PerformanceSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Group 2 Major Component: 1. Main PumpDocument11 paginiGroup 2 Major Component: 1. Main PumpSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Group 5 Travel Speed Control SystemDocument1 paginăGroup 5 Travel Speed Control SystemSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- G Group 3 Tests and Adjustments: 1. Parking Brake PerformanceDocument2 paginiG Group 3 Tests and Adjustments: 1. Parking Brake PerformanceSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Group 2 Operational Checks and TroubleshootingDocument11 paginiGroup 2 Operational Checks and TroubleshootingSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Group 4 Main Control Valve Group 4 Main Control Valve: 1. Removal and Install of MotorDocument14 paginiGroup 4 Main Control Valve Group 4 Main Control Valve: 1. Removal and Install of MotorSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Group 3 Pump Device: 1. Removal and InstallDocument22 paginiGroup 3 Pump Device: 1. Removal and InstallSergey MovchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat Forklift Nr3500 36v Schematic Operation Maintenance ManualDocument27 paginiCat Forklift Nr3500 36v Schematic Operation Maintenance Manualmichellemacias080283gfz100% (53)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Electro-Hydraulic Actuators For Valves SKB32.. SKB82.. SKB62.. SKB60Document22 paginiElectro-Hydraulic Actuators For Valves SKB32.. SKB82.. SKB62.. SKB60Anand MunkhbatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2000 Nissan Frontier KA24DE LCDocument16 pagini2000 Nissan Frontier KA24DE LCDavid CervantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportDocument301 paginiNM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportNM Transparency InitiativeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- PSS 1.1-300 - Operating Manual - Vol. 2 - 2019Document41 paginiPSS 1.1-300 - Operating Manual - Vol. 2 - 2019Centrifugal SeparatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Types of PumpsDocument45 paginiChapter 11 Types of Pumpssuraj7266Încă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Hydraulic EnergyDocument10 paginiHydraulic EnergySameer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro ConeDocument11 paginiHydro ConeJubert Angelo Ramos ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Heater Plastic: Item No. 141600 (-02) - 141605 (-02)Document2 paginiElectric Heater Plastic: Item No. 141600 (-02) - 141605 (-02)Ala AlasdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Front Shovel enDocument15 paginiFront Shovel enAlejandro RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Price List 50-2017 - EN Low Res ItaliaDocument84 paginiPrice List 50-2017 - EN Low Res ItaliaivoniciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hole Cleaning DynamicsDocument38 paginiHole Cleaning DynamicsSAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Online QuestDocument80 paginiGeneral Online QuestPankaj PooniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Oilwell: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For Baylor Eddy Current Brake, Model 7838Document51 paginiNational Oilwell: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For Baylor Eddy Current Brake, Model 7838sorangel_123100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- SPE 68747 Clean Up and Well Testing Operations in High-Rate Gas-Condensate Field Result in Improved Sand Management SystemDocument14 paginiSPE 68747 Clean Up and Well Testing Operations in High-Rate Gas-Condensate Field Result in Improved Sand Management SystemTheNourEldenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vol IE Tender DrawingsDocument53 paginiVol IE Tender DrawingsAnnisa Nabilah Mohd HashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Liquefied Gases: Cryogenic Transfer PumpsDocument13 paginiFor Liquefied Gases: Cryogenic Transfer PumpsSud Haldar100% (1)
- Baviera Steam System 11Document17 paginiBaviera Steam System 11Mustafa Mert SAMLIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Visit Report NoboDocument17 paginiIndustrial Visit Report Noboaemon05Încă nu există evaluări
- Group 3 Disassembly and AssemblyDocument99 paginiGroup 3 Disassembly and AssemblyBaciu NicolaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batch Pasteurizer For MilkDocument8 paginiBatch Pasteurizer For MilkMustafa AmroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nene II. V.H. Aust. Operational InstructionsDocument10 paginiNene II. V.H. Aust. Operational InstructionsLeft VentricleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Hydraulic System DesignDocument33 pagini3 - Hydraulic System DesignAbere GetachewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Seal AramcoDocument18 paginiMechanical Seal AramcoMohamed AbdelsalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- TOO Catalog File 2022 - 30.10.22Document6 paginiTOO Catalog File 2022 - 30.10.22Hen BenjaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specification of CAT 330D CaterpillarDocument24 paginiSpecification of CAT 330D CaterpillarBassel AmmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 EuxtnziktmzuvnaDocument7 pagini2 Euxtnziktmzuvnaسام سپه پورÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pump Element Type MPE and PE For Radial Piston Pumps Pump Element Type MPE and PE For Radial Piston PumpsDocument14 paginiPump Element Type MPE and PE For Radial Piston Pumps Pump Element Type MPE and PE For Radial Piston PumpsHasan DEPECİKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 - MANUAL ORIGINAL DE USUARIO - Operación y Servicio BásicoDocument74 pagini21 - MANUAL ORIGINAL DE USUARIO - Operación y Servicio BásicoNorbey Marin MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAXIMATOR High Pressure Pumps 09 2015Document40 paginiMAXIMATOR High Pressure Pumps 09 2015Anonymous 8rb48tZSÎncă nu există evaluări