Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Y A X B: 2 Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks)
Încărcat de
jimmytanlimlongTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Y A X B: 2 Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks)
Încărcat de
jimmytanlimlongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2
DHS 2011 2011 DHS Year 6 H2 Math Preliminary Examination Paper 2 [Turn over
Section A: Pure Mathematics [40 marks]
1 (a) A family of curves is given by e 2sin ,
x
y A x B = + + where A and B are arbitrary
constants. Show that
2
2
d d
2(sin cos ).
d
d
y y
x x
x
x
= + [3]
(b) Use the substitution y ux = to find the particular solution of the differential
equation
2 2
d
4 2 ,
d
y
x x y y
x
= + + given that 0 y = when .
8
x
t
= Express your
answer in the form f ( ). y x = [5]
2 (a) Given that the complex numbers w and z satisfy the equations
* 2 i and (1 2i) 3 3i, w z w z + = + = +
find w and z in the form i a b + , where a and b are real. [4]
(b) Solve the equation
3
i 2 2i z = . [3]
Hence deduce the roots of the equation
3
i 2 2i w = + . [2]
[Give all answers exactly in the form
i
e r
u
, where r >0 and . t u t < s ]
3 A curve C has parametric equations
1 1
, , 0. x at y bt t
t t
= = + >
For 1 and 2, a b = =
(i) without finding the cartesian equation of C, find the area enclosed by C, the line
5 x = , the y-axis and the x-axis, giving your answer correct to 2 decimal places,
[4]
(ii) find the value(s) of t for which both x and y have the same rate of change with
respect to t. [3]
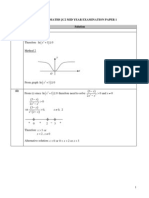
For 1 and 1, a b = = the curve C has two oblique asymptotes y x = and y x = .
(iii) By considering the curve of C, sketch the graph of f '( ). y x = [3]
3
DHS 2011 2011 DHS Year 6 H2 Math Preliminary Examination Paper 2 [Turn over
4 (a) Express
3
( 3) r r +
in partial fractions. [1]
Hence find the sum of the series
1 1 1 1
...
4 10 18 ( 3) n n
+ + + +
+
. [3]
Give a reason why the series
1 1 1
...
2 5 9
+ + + is convergent and state its exact value.
[2]
(b) A sequence
1 2 3
, , , ... u u u is such that
1
3
2
u = and
1
1
, for all .
( 1)( 2)
n n
u u n
n n
+
+
= + e
+ +
(i) Find the values of
2 3 4
, and . u u u [2]
(ii) Form a conjecture for
n
u in terms of n. [1]
(iii) Prove your conjecture for
n
u using mathematical induction. [4]
Section B: Statistics [60 marks]
5 In a binomial probability distribution X, there are n trials and the probability of success
for each trial is p. If n =20 and P( 1) 0.8, X s =
determine the value of p. Hence find the
least value of a such that P( ) 0.999 X a < > . [5]
6 Find the number of ways 4 boys and 3 girls can be seated
(i) in a row such that no two girls are next to each other, [2]
(ii) at a round table with 10 identical seats, such that the 4 boys must sit together. [3]
7 [In this question give all answers correct to 3 places of decimals.]
A computer game consists of at most 3 stages. The probability that a player clears the
first stage (i.e. successful) is 0.7. For each subsequent stage,
- the conditional probability that a player clears that stage, given that he cleared the
preceding stage, is half the probability of success at the preceding stage,
- the conditional probability that a player clears that stage, given that he failed at
the preceding stage, is the same as the probability of success at the preceding
stage.
The game ends prematurely if a player fails to clear 2 consecutive stages.
Draw a probability tree diagram to represent the above information. [2]
Find the probability that
(i) the game ends prematurely, [1]
(ii) a player clears exactly 2 stages, [3]
(iii) a player clears the third stage given that he cleared exactly 2 stages. [2]
4
DHS 2011 2011 DHS Year 6 H2 Math Preliminary Examination Paper 2 [Turn over
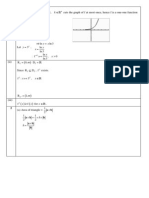
8 (a) Give a reason why it is advisable to plot a scatter diagram before interpreting a
correlation coefficient calculated for a sample drawn from a bivariate distribution.
[1]
(b) Due to urbanisation in a country, the average density of birds (per km
2
) found in
the city, x, and those in the forest, y, have changed over the years from 2000 to
2007. The findings are given in the table.
Year 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
City bird
density (x)
75 79 86 97 110 125 131 136
Forest bird
density (y)
400 398 395 392 380 351 331 303
According to experts, counting birds in the city is easier than counting those in
the forest. It is desired to determine only the density of birds in the city and use it
to estimate the density of birds in the forest.
(i) Calculate the product moment correlation coefficient between x and y.
Comment on whether a linear model is appropriate. [2]
(ii) Draw a scatter diagram for the data, labelling the axes clearly. [2]
(iii) Another suggested model takes the form
2
y a bx = + where a and b are
constants. Explain whether this model provides a better fit than a linear
model between x and y. [2]
(iv) Given that the city bird density for a particular year is 150, use an
appropriate model to find the forest bird density for that year. Comment on
the reliability of your prediction. [2]
If birds migrate from the forest to the city due to urbanisation, state a reason
why the total bird density in the city and forest for each year from 2000 to
2007, is not a constant number. [1]
5
DHS 2011 2011 DHS Year 6 H2 Math Preliminary Examination Paper 2 [Turn over
9 In a certain junior college, the marks (out of 100) scored by a J C 1 student in a Class
Test, Common Test and Promotional Examination are denoted by C, T and S
respectively. C, T and S may be modelled by normal distributions with means and
standard deviations as shown in the table below.
Type of assessment Mean Standard deviation
Class Test, C 68 o
Common Test, T 65 8
Promotional
Examination, S
70 10
(i) Given that P( 85) 0.05, C > =
determine the value of . o [2]
In a particular year, a student sits for five Class Tests, a Common Test and a
Promotional Examination. The average mark of the five Class Tests constitutes 20% of
the overall assessment mark for the year. The Common Test and Promotional
Examination constitute 20% and 60% of the overall assessment mark for the year
respectively.
For the following parts, assume 10 o = .
(ii) Find the probability that the average mark scored by a student in the five Class
Tests is more than 75. [3]
(iii) Find the probability that a student scores an overall mark of more than 80 for the
year. [4]
(iv) State an assumption used in your calculations for (iii). [1]
10 Based on past data, the mean number of dengue cases per day was reported as 30. The
authorities suspect that the recent hot and wet weather has increased the mean number
of dengue cases per day. A random sample of 60 days is taken and the number of
dengue cases per day, X, is summarised by
( ) ( )
2
8 1400, 8 34800. x x = =
(i) Calculate unbiased estimates of the mean and variance of X. [2]
(ii) Test, at the 5% significance level, whether the mean number of dengue cases per
day has increased. [4]
Explain, in the context of the question, the meaning of the p-value. [1]
6
DHS 2011 2011 DHS Year 6 H2 Math Preliminary Examination Paper 2
(iii) After the authorities have increased surveillance to eliminate mosquito breeding
and stepped up public education, they claimed that the mean number of dengue
cases per day has dropped below 30. The number of dengue cases occurring over
7 randomly selected days are recorded and the unbiased estimate of the
population variance can be assumed to be the same as that obtained in (i).
State suitable null and alternative hypotheses, and also the assumption required
for an appropriate significance test. [2]
Find the range of values for the sample mean x such that there is evidence to
support the authorities claim at the 5% significance level. [2]
11 The number of traffic offences occurring at a particular stretch of road between 7:30am
to 9:30am on any day follows a Poisson distribution with mean . Given that the
probability of at least one traffic offence occurring between 7:30am to 9:30am on any
day is 0.95, show that 3 = , correct to the nearest integer. [2]
For the subsequent parts, use 3. =
(i) Find the probability that there are at least 17 traffic offences occurring between
7:30am to 9:30am during weekdays (i.e. Monday to Friday) in a given week. [2]
(ii) Find the probability that the mean number (taken over a year i.e. 52 weeks) of
traffic offences occurring between 7:30am to 9:30am during weekdays in a week
is at least 13 but not more than 16. [2]
(iii) Find, using a suitable approximation, the probability that there are between 30
and 42 weeks in a year where there are at most 16 traffic offences occurring
between 7:30am to 9:30am during weekdays in a week. [4]
(iv) Explain why it is not appropriate to use a Poisson distribution with mean 36 to
model the number of traffic offences occurring in any one full day. [1]
END OF PAPER
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nyjc H2 Math P2Document6 paginiNyjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document10 paginiMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 A LevelsDocument8 pagini2007 A LevelsKok Chee KeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hci H2 Math P2Document6 paginiHci H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document8 paginiIJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 paginiJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acjc h2 Maths p2 QN PaperDocument8 paginiAcjc h2 Maths p2 QN Papervincesee85Încă nu există evaluări
- TPJC Prelim H2 Paper2Document7 paginiTPJC Prelim H2 Paper2Wei Qin Ashleigh Lim0% (1)
- RI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1Document4 paginiRI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1nej200695Încă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Mathematics HCI Prelim Paper 2Document5 pagini2011 Mathematics HCI Prelim Paper 2ShaphynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument5 paginiCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 paginiPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijc H2 Math P2Document5 paginiIjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 DHS Paper 1Document5 pagini2010 DHS Paper 1Pooja KapurÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks) 1 Given: y y y X y y yDocument4 paginiSection A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks) 1 Given: y y y X y y yjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yjc H2 Math P1Document6 paginiYjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P2Document6 paginiAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P2nej200695Încă nu există evaluări
- Ajc H2 Math P2Document8 paginiAjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Business Mathematics For CmaDocument5 paginiFundamentals of Business Mathematics For CmaSujay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACJC 2014 H2 Math JC2 Supp QP PaperDocument7 paginiACJC 2014 H2 Math JC2 Supp QP PaperRaymondZhang100% (1)
- Mathematics 9740/01 Higher 2 Paper 1: Meridian Junior CollegeDocument6 paginiMathematics 9740/01 Higher 2 Paper 1: Meridian Junior CollegekarpeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 paginiMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 2Document6 paginiACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 2DKFBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationDocument9 paginiPan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationMarc MarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 paginiAnswer All Questions in This SectionSTPMmaths100% (1)
- P2 SMK Ampuan Durah SerembanDocument5 paginiP2 SMK Ampuan Durah SerembanmasyatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC/2011 JC2 Preliminary Exam Paper 2/9740Document4 paginiMJC/2011 JC2 Preliminary Exam Paper 2/9740jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 paginiACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Mary Sabah 2013 M2 (Q)Document3 paginiSt. Mary Sabah 2013 M2 (Q)STPMmathsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijc H2 Math P1Document6 paginiIjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 paginiRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ajc H2 Math P1Document6 paginiAjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsDocument7 paginiMJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsAlxÎncă nu există evaluări
- h2 Mathematics Practice Paper 1 For Prelim Exam 2011Document4 paginih2 Mathematics Practice Paper 1 For Prelim Exam 2011Augustine NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Maths Weekend Assignment For JC2: 2009 JJC Prelim Exam P 1Document4 paginiH2 Maths Weekend Assignment For JC2: 2009 JJC Prelim Exam P 1ManFang NeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Document9 paginiIGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Kothakonda Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 M Second Term March 2017 DSEDocument5 pagini9 M Second Term March 2017 DSEJaison D'CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catholic Junior College: MathematicsDocument4 paginiCatholic Junior College: MathematicskarpeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 9740/01: Higher 2Document7 paginiMathematics 9740/01: Higher 2Alex SoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC - H1 Math 2014Document8 paginiAC - H1 Math 2014ofji4oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanyang Junior College 2008 Jc2 Preliminary ExaminationDocument5 paginiNanyang Junior College 2008 Jc2 Preliminary ExaminationkarpeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 2Document6 paginiACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 2ofji4oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acs I Y4 Prelim Em2 2010Document10 paginiAcs I Y4 Prelim Em2 2010math3matics3Încă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel November 1999 Paper 6Document4 paginiEdexcel November 1999 Paper 6Varun PanickerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 4016/02: School BDocument10 paginiMathematics 4016/02: School BJoanne ErÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acjc h2 Maths p1 QN PaperDocument6 paginiAcjc h2 Maths p1 QN Papervincesee85Încă nu există evaluări
- 2012 H2 Other JC Prelim (Selected)Document9 pagini2012 H2 Other JC Prelim (Selected)csanjeevan0% (1)
- 2010 TJC Prelim Paper 2 Qns Final)Document8 pagini2010 TJC Prelim Paper 2 Qns Final)cjcsucksÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (KEDAH) SMK KhirJohariDocument9 paginiTRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (KEDAH) SMK KhirJohariSKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Hci Prelim p2Document6 pagini2014 Hci Prelim p2Chia Pei XianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Entrance Examination January 2020Document4 paginiMathematics: Entrance Examination January 2020CorneliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 1Document5 paginiACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 1DKFBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section B AnsDocument7 paginiSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- J1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2aDocument8 paginiJ1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2ajimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 paginiVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)Document34 pagini2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Which of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sDocument1 paginăWhich of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument4 paginiVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 paginiTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 paginiRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 paginiRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 paginiSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 paginiMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 paginiTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 paginiTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document10 paginiPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 paginiSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document7 paginiPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlong0% (1)
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 paginiRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 paginiPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 paginiNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document7 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 paginiJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document11 paginiMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 paginiNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 paginiJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 paginiMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 paginiCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 7 Classroom Observation Lesson Plan 1 FinalDocument9 paginiMath 7 Classroom Observation Lesson Plan 1 Finaldxoxnxg100% (1)
- Seminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFDocument18 paginiSeminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFAnonymous bwVxI8Y8WÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper ADocument5 pagini2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper Avincesee85Încă nu există evaluări
- Factoring Quadratics HomeworkDocument4 paginiFactoring Quadratics Homeworkafmsubdww100% (1)
- Mit Matlab CourseDocument205 paginiMit Matlab CoursewistonjrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 430: Lecture 2 Newton's 2 Law in Cartesian and Polar CoordinatesDocument17 paginiPhysics 430: Lecture 2 Newton's 2 Law in Cartesian and Polar CoordinatesDapperÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Pure1 Oct2021 Mark SchemeDocument27 paginiA Level Pure1 Oct2021 Mark Schememzino100406Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of ODEsDocument40 paginiIntroduction of ODEsMuhammad Aminnur Hasmin B. HasminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math HLSL Calculator Instructions PDFDocument75 paginiMath HLSL Calculator Instructions PDFapdpjpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Series SRM SyllabusDocument3 paginiFourier Series SRM SyllabusAmrita SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHS SyllabusDocument39 paginiMATHS SyllabusAndrew NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 41 Years MathsDocument625 pagini41 Years MathsSanat KauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematic-1 MA100 (Pre Calculus)Document3 paginiMathematic-1 MA100 (Pre Calculus)Noman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Pharmacy IY - R17 - Remedial MathsDocument2 paginiB.Pharmacy IY - R17 - Remedial MathsrajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan Matematika Bab 6Document7 paginiLatihan Matematika Bab 6Risma fÎncă nu există evaluări
- 40 Items First Quarter Exam in Gen Math With Tos Quarter 1Document7 pagini40 Items First Quarter Exam in Gen Math With Tos Quarter 1shabsappari24Încă nu există evaluări
- JUMP Math CC AP Book 7-2 Sample RP7-31 To 35-0-0Document12 paginiJUMP Math CC AP Book 7-2 Sample RP7-31 To 35-0-0Sónia RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibration of Continuous SystemsDocument14 paginiVibration of Continuous SystemsRidwan OlatunjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentials Textbook (Diffy Q'S)Document315 paginiDifferentials Textbook (Diffy Q'S)James DeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.E in Basic Science Engineer and Maths PDFDocument2 paginiB.E in Basic Science Engineer and Maths PDFvrsafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 10 Computer Application Marking Scheme 2019-20Document30 paginiCBSE Class 10 Computer Application Marking Scheme 2019-20suneet kuma meenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Material 12th Maths 2023-24Document79 paginiStudy Material 12th Maths 2023-24Gunish GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adiabatic InvariantsDocument4 paginiAdiabatic InvariantsVINICIUS DA SILVAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11th Maths ArihantDocument161 pagini11th Maths ArihantSankar Ranjan100% (7)
- W 00Document18 paginiW 00iwouldwishforyouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Marks QuestionsDocument12 paginiTwo Marks QuestionsSsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaussian Elimination Method PDFDocument14 paginiGaussian Elimination Method PDFUmer farooq100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Algebra WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 6 Algebra WorksheetAnsuman Mahanty100% (5)
- Chapter 5: Thermal Effects and Energy Balances 5.1 Temperature Dependence 0f Reaction RatesDocument13 paginiChapter 5: Thermal Effects and Energy Balances 5.1 Temperature Dependence 0f Reaction RatesChristina Joana GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra 3Document37 paginiAlgebra 3Michael Damian100% (1)