Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MEDSURG3 RD TEST
Încărcat de
DonnaCapassoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MEDSURG3 RD TEST
Încărcat de
DonnaCapassoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
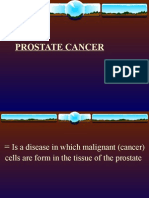
Prostate Cancer
Patho:
Commonly occurs in men age 50 and older. African Amercian men are at highest risk. It
is slow growing and spreads through the lymphatic system and bloodstream. The exact
cause is unknown but high-fat diets and exposure to certain chemical are a suspected
cause...!" is not a risk factor
Age# ethnicity# family hx are non-modifiable risk factors
Diagnostics:
!rostate-$pecific Antigen test%!$A&# !rostatic Acid !hosphatase%!A!&# 'igital (ectal
)xam%'()&# iopsy of The !rostate *land# +ale $elf )xam
,either !$A or digital rectal exam are definiti-e diagnosis...ine needle aspiration biopsy
needed for definiti-e diagnsois
DRE should begin at 50 but African Americans should begin at /5.
Male Self Exam...use both hands# after shower# warm area# roll testes between thumb%on
top& and fingers%on bottom&..any bumps or dimpling should be reported. Abnormal
prostate findings include hardness# nodular# assymetric of the testes
Digital Rectal Exam... insert lubricated finger into rectum...feeling for smoothness..any
cre-ices# bumps# dimpling should be reported..a colonoscopy may be ordered
Signs & Symptoms:
+ostly asymptomatic in the begining. If symptoms are present they are usually difficulty
urinating# hematuria# and back pain.
0ater $igns include urinary obstruction %difficulty and fre1uency of urination# retention#
decreased si2e and force of the urinary stream& # blood in urine or semen# painful
e3aculation# sexual dysnfunction# metastasis%causes backache# hip pain# perineal and
rectal discomfort# anemia# weight loss# weakness# nausea# oliguria# spontaneous
pathologic fractures&
Drug Therapy:
"ormonal meds prescribed to decrease tumor progression. 0uteini2ing hormon-releasing
hormones are often used %0upron# 4oladex&. !ain management and corticosteroids are
used in con3unction with hormonal medications. Chemotherapy is also an option.
$urgical remo-al of the tumor may be needed.
Androgen receptor blockers - .lutamide# ,ilutamide and bicalmutide
)strogen - %person will be at risk for an +I# '5T# $troke6C5A&
An ele-ated !$A le-el is a sign this therapy isnt working
Chemo:
Chemo may be done for those with hormone resistant prostate cancer....goal is palliation
Radiation
External Beam Radiation - most widely used%for /-7weeks# 5 days a week& ..skin
becomes dry - skin care is -ery important...keep dry skin moist # *I problems# $exual
dysfunction# urinary problems# bone marrow suppression # fatigue%patient really needs
rest periods&
Brachytherapy - radiocati-e seeds into prostate gland ..outpatient procedure...through
rectum ..best for stages 8 and 9. can cause urinary problems ... for those with more
ad-acnes tumors# brachytherapy is combined with external radiation or hormone therapy
Cryosurgery may be done to kill the tumor %second line treatment after radiation
fails&..treatment takes about 9 hours..patient does not need to be opened--- no surgical site
Complcations: fistula%abnormal connection..hole between two body systems& ..urethral
rectal fistual- urine can ha-e feces in it6 feces can ha-e urine in it# damage to urethra#
tissue sloughing# erectile dysfunction# urinary incontinence# prostatitis
Surgical Care:
Radical prostatectomy may be done to remo-e the entire prostate gland%entire gland#
seminal -esicles#retroperineal lymph nodes and part of bladder neck remo-ed&considered
most effecti-e for sur-i-al . A suprapubic prostatectomy can be done when the prostate
is remo-ed through an abdominal incision or a perineal incision# or a transurethral
prostatectomy %Trans;rethral(esection<fThe !rostate-TRP& is performed using a
resectoscope passed through the urethra. !erenal surgery poses higher risk for infection
during healing... urine and bowel mo-ements...meticulous care of surgical site is
necesary.
+ost men choose radiation6chemo instead of a radical prostatectomy%penis will not be
able to become erect&
After surgery# a catheter is placed and a ballon inflated to =0m0 for hemostasis. A three-
way irrigation system may be used to pre-ent clotting and clot retention.
!rchiectomy %teste remo-al& may be done alone or with prostatectomy... allows for rapid
relief of bone pain# releases shrinkage of prostate and relie-es urinary
obstructions6symptoms %will need to bank sperm& ..will ha-e less testosterone.... may
experience hot flashes# osteoporosis# loss of muscle mass# irritability# weight gain# )'#
%menopausal symptoms&
"er#e$sparing surgical procedure can be done to spare the ner-es responsible for
erection%usually done in men under 50&
"ursing Care & Complications:
+onitor 56$. +onitor urine output. There may be may be blood in the urine> this is
normal. If clotting is obser-ed or an abnormal amount of blood is expelled# call the
physician. $trict intake and output needs to be done e-ery shift. Continuous bladder
irrigation decreases bleeding and helps restore bladder function. Irrigate as ordered by the
physician. ecause there is an abdominal incision# daily dressing changes are needed.
'iet is slowly tolerated# starting with a clear li1uid diet. Ambulation is encouraged 9/
hours after surgery.
"emorrage - bright red blood# urinary retention# infection# dehisence# '5T# !ulmonary
emboli are all complications of the surgery
)rectile dysfunction after surgery is dependent on patients age and preoperati-e sexual
function..teach patient kegel exercises %-oid# hold urine# -oid# hold urine# -oid..it will
help to strengthen the pel-ic area&
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BP%
<ne of the most common disorders of older men. ,on-malignant enlargement of the
prostate. +ay block urine flow.
Treated with T;(! surgery
!" symptoms: dysuria# hesitancy# dribbling# fre1uency# urgency# hematuria# nocturia#
retention# interruption of urinary stream# inability to urinate# ;TI# renal calculi#
acute6chronic renal failure
5oiding diary# Inspect palpate bladder for distention# digital rectal exam%will re-eal a
rubbery enlargement of the prostate&
!ost$urgical Care in-ol-es care and maintenance of indwelling catheter to ensure patency
and ade1uacy of irrigation. $tool softners to pre-ent straining. +onitoring of catheter
drainage ..$urgeon should be notified if patient de-elops fran hematuria or an abrupt
change in urinary output. +ost critical complications are septic or hemorrhagic shock.
!atient should maintain s high fluid intake of at least 90 a day. ;rinary output should be
monitored for at least /-? weeks
!atient should monitor for symptoms as !" can reoccur.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
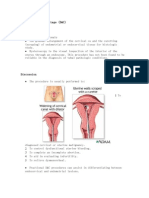
!#arian and Cer#ical Cancers:
Cer-ical cancer..occurs mostly in white women 55-?5
+ost diagnosed ha-e ad-ance disease%because regluar check-ups decrease after
menopause&
0ink between reast and Cer-ical cancer..(CA genes
"igh risk if family members ha-e6had breast# colon# nonpolyp rectal cancer
@omen ne-er pregnant at highest risk
"igh fat diet# greater A of o-ulatory cycles# hormone replacement# use of fertility drugs
increase risk
0owers (isk: birth control pill use# breast feeders# more than 8 pregnancy# ha-ing babies
at early age
B0C of o-arian cancers are from epithelial carcinomas
$pecimen taken: fine needle biopsy# -acuum biopsy
<-arian cancer can metastisi2e directly from shedding malignant cells..spreads -ia
lymphatic system
Can de-elop bowel# bladder cancers from spread
Signs & Symptoms:
Abdominal discomfort# bloating# pel-ic pain# urinary fre1uency6urgency# feel full
1uickly ...one or more of these symptoms should reported to 'r.
0ater $igns: increase in abdominal girth# unexplained weight gain or loss# menstrual
irregularities
!ost menopausal women should ,<T ha-e palpable o-aries
iannual pel-ic examination should be performed...as early stages are asymptomatic
Age 98 o-er should ha-e yearly
,o screening tests exist for o-arian cancer
5aginal ultrasound: clean glo-es# lubricate co-ered wand# full bladder and exam
performed# empty bladder and perform exam again
)xploratory laparotomy to diagnose and stage disease
<5A8 uses blood sample to test for changes related to o-arian cancer..tests for 5 proteins
that change as a result of o-arian cancer..it is not intended for screening or for a definiti-e
diagnosis
Also look for CA-895..70C of women with marker diagnosed
<opherectomy - o-ary remo-al...usually done laparascopically-reduces surgical
compliactions and reco-ery..reduces possibly..doesnt stop it from occurring
$tage8 - limited to o-aries:
Total "ysterectomy %e-erything remo-es&
ilateral $alpingo-oophorectomy %fallopian tubes and o-aries&
)-aluation of remaining tissue in abdomen and pel-is
Chemotherapy or intraperitoneal radioisotopes if poorly differentiated
$tage 9 - limited to true pel-is
)xternal radiation
Intraperitoneal radiation
$ystremic C<mbo chemo after tumor reducing surgery
Dsecond lookD procedure done after to make sure all clear
Cisplatin# Carboplatin usually used %at stage /&
"exaline - palliati-e for recurrin
Taxol - usually gi-en when there is metastasis
'ebulking may be done with surgery ...may also ha-e internal radiation
"ealth "x-
.amily "x
ladder or bowle dysfunction
!el-ic or abdominal !ain
!regnancy "x
;$e of fertility drug or "(T
"igh fat diet
"a-e they breast fedE
+enstrual irregulaties
<b3ecti-e data: pel-ic# abdominal examiantion# abnormal ultrasound# increased
abdominal girth# ascites
!atient may ha-e: anxiety# acute pain# inneffecti-e sexual patterns
,urse must ha-e patient participate in their own care... must achie-e satifactory pain
control..recogni2e and report problems promptly
)ncourage patient to return to life as normal# continue to screen# educate risk factors#
lifestyle changes
Preop - !ro-ide psychological support# 'ouche%usually some kind of -inegar..to remo-e
any bacteria&# neomycin enema%incase they nick the bowel during surgery they clean out
as much normal flora as possible - prophalactic treatment against peritonitis&# catheter %to
keep area clean from urine&%clean genital area from meatus outward with soap and
water ..clean glo-es used&
women may experience fear or secondary sex caharacteristics such as more hair growth
after remo-al of o-aries
ladder must be empty before going into operating room
&cute inter#ention after surgery:
Teach patient to mo-e fre1uently# a-oid knee pressue%no pillow under knee-may increase
'5T risk&&# leg exercises# may be wearing an abdominal binder# compression stockings
'ischarge acti-ities: no hea-y lifting for ?-7 weeks# should be up walking# clothing
should be loose# teach patient about signs and symptoms of infection%fe-er# pain#
swelling# discharge&
'eep breathing and coughing..medicate patient ade1uately# teach splinting
in patient has radiation implant: no more than =0 mins at a time near patient.. stay at foot
of bed to reduce exposure# -isitors should not -isit more than a total of = hrs per day
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
'idney Transplant & Dialysis
Transplants -- < match ha-e highest chance
Contraindications: diesseminated malignancites# untreated cardiac disease#
chronic affections# psychosocial histories
some patients with "I5 are now considered if they demonstarte similar
graft E
extensi-e blood work and health hx to find someone who is a potential
donor...
donor sources: blodd relati-es# emotionally related li-ing donors# altruistic
li-ing donor# deceased donor
0i-e donor- nephrectomy - begins 8 or 9 hours before recipient is in <(
most common approach of kidney procurement
laparoscopic can also be done... it reduces hospital stay# >ess pain# less blood
loss# less recuperation time... recipient
efore transplant: catheter placed# .......
kidney transplants with li-ing donors are more difficult because the -essels
will be shorter%E&
---------
'ialysis: is really a fistula... between -enous and arterial system ...should
hear a thrill if you ha-e a functioning dialysis system
If kidneys not working..potassium will be high# un and creatinine will be
high %patient will be on dialysis for a few hours to draw out the extra
potassium# bun# creatinin&..
monitor donorFs "CT# renal function after procedure %they will only ha-e 8
kidney&
'onor will be in hospital 9-/ days..can return to work in /-? weeks. no
hea-y lifting or weights
"CT should not fall more than =-? points
(ecipient - patient may ha-e large -olumes of urine right after transplant
!ost <p teaching should include treatment for re3ection# infection# surgery
complications%infection# d-t# hemmorhage# atalectisis&
*oal of immunosuppressi-e therapy: suppress immune response# maintain
sufficient immunity %stay away from sick&
GG<rgan (e3ection - hyperacute re3ection occurs within minutes to hours of
transplant# acute re3ection can occur days6weeks and up to = months#
Chronic re3ection is long term re3ection. (e3ection can include pain at site of
transplant# flulike symptoms# changes in heart rate# reduction of urinary
output# weight changes# agglutination ..
Acute and hyperacute is re-ersible
Chronic re3ection is irre-ersible and can occur months to years
+uromonab-C'= is the only drug on the market for organ transplant
re3ection and re-ersal
Cellcept# imuran# prograf are some prophylactic organ re3ection drugs
!ossible complications after transplant:
Infection: fungal%candida& ..-ery few things to treat..at risk of death
5iral Infections: C+5# epstein barr# "epres simplex...anti-iral meds will be
gi-en
Cardio-ascular 'isease may become a problem after transplant ... increased
incidence pf arthersclerotic -ascular disease
Malignancies are a risk after transplant ..skin cancer# lips# li-er# kidney#
-ul-a# karposi sarcoma# lymphomas# perineum
Corticosteroid related complications: asceptic necrosis of hips# knees and
other 3oints# peptic ulcer disease# glucose intolerance and diabetes# lipids
increase- can get cataracts
)-aluation: +onitor daily weight# monitor for infection# edema# albumin
le-els
!atient will need to be on meds for rest of life
'rains do not get clamped
aminoglycoside antibiotics can be nephrotoxic
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Motorcycle Troubleshooting ManualDocument15 paginiMotorcycle Troubleshooting ManualJan Warmerdam100% (1)
- Imaging of AdrenalsDocument140 paginiImaging of AdrenalsSahana RÎncă nu există evaluări
- JDM B18C Type RDocument6 paginiJDM B18C Type RSeenka CapuqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Diagnosis of Thyroid Disorders - A Self-Instructional Program - ROJoson - 1992Document20 paginiClinical Diagnosis of Thyroid Disorders - A Self-Instructional Program - ROJoson - 1992rojosonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psalm151 160Document3 paginiPsalm151 160Gina KristenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of WinesDocument91 paginiTypes of Winesrajanrld19880% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswersDocument7 paginiCSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswerscxcchemistryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oh No, It's A Big Fat Bitch SpayDocument8 paginiOh No, It's A Big Fat Bitch SpayWilliam Chandler100% (1)
- Surgtest GI Surgery NEET SS 2022 RecallDocument58 paginiSurgtest GI Surgery NEET SS 2022 RecallRajhan 410Încă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Trauma: Supervised By: Dr. Hussein Al-HeisDocument63 paginiAbdominal Trauma: Supervised By: Dr. Hussein Al-HeisRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood TransfusionDocument39 paginiBlood TransfusionGeraldine Gallaron - Casipong100% (4)
- 6 Hysterectomy/TAHBSO Nursing Care Plans: Low Self-EsteemDocument5 pagini6 Hysterectomy/TAHBSO Nursing Care Plans: Low Self-Esteemonlyone_unik50% (2)
- Malignant Ovarian TumourDocument42 paginiMalignant Ovarian TumourJones MarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent Advances in Breast DiseasesDocument39 paginiRecent Advances in Breast DiseasesmathisyncÎncă nu există evaluări
- VARICOCELEDocument65 paginiVARICOCELEParamartha KesumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Gynecologic ProceduresDocument55 paginiCommon Gynecologic ProceduresQurrataini IbanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNC 2Document6 paginiDNC 2Maria VisitacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Referat CA PancreasDocument25 paginiReferat CA PancreasPamela VasikhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancreatic CancerDocument16 paginiPancreatic CancerShelby Arellano100% (1)
- Oncologic NursingDocument16 paginiOncologic NursingDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UrethroplastyDocument9 paginiUrethroplastyBayu Mario GintingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endometrial SamplingDocument4 paginiEndometrial SamplingsalamredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rangkuman TeratomaDocument22 paginiRangkuman TeratomaFelicia Fernanda IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal System - Kristiene JoyDocument11 paginiRenal System - Kristiene JoyijayFLx64Încă nu există evaluări
- Cervical CADocument6 paginiCervical CAEdelou Alegria JumawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Adv-Nced Tr-um-Life Support (ATLS) : Prim-Ry Survey (ABCDE)Document8 paginiIntroduction To Adv-Nced Tr-um-Life Support (ATLS) : Prim-Ry Survey (ABCDE)razan.girl.2010Încă nu există evaluări
- 20.MBBS Pancreatic CancerDocument52 pagini20.MBBS Pancreatic Cancermrajah95Încă nu există evaluări
- Cervical CancerDocument53 paginiCervical Cancerthamizh555Încă nu există evaluări
- College of Nursing: Local Anaesthetic, Thin Tube Dye Tissue X-Ray Film CatheterDocument16 paginiCollege of Nursing: Local Anaesthetic, Thin Tube Dye Tissue X-Ray Film CatheterCherrie CatingubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Facts in Brief Bio Physical Concept in Nursing and Rehabilitation/laboratory TestsDocument9 paginiNursing Facts in Brief Bio Physical Concept in Nursing and Rehabilitation/laboratory TestsDhine Dhine ArguellesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Document9 paginiAdvanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Omar AlruwailiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CancerDocument10 paginiCancercitidotnetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iabp Almost Final VersionDocument7 paginiIabp Almost Final Versionapi-258141893Încă nu există evaluări
- Fertility and Sterility@Document4 paginiFertility and Sterility@Robertus HajaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solitary Thyroid Nodule Done by Dr. Dana Al-Zarraq Supervised y Dr. Saleh HammadDocument50 paginiSolitary Thyroid Nodule Done by Dr. Dana Al-Zarraq Supervised y Dr. Saleh HammadMohammad BanisalmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor Markers Some Laboratory Aspects of Pregnancy Cerebrospinal Fluid AnalysisDocument40 paginiTumor Markers Some Laboratory Aspects of Pregnancy Cerebrospinal Fluid AnalysisMans FansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder CancerDocument18 paginiBladder CancerjackbayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Branch Ere AuDocument226 paginiBranch Ere Auامين امينÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benign Ovarian Tumors - Unilateral, 99% Cystic, MobileDocument9 paginiBenign Ovarian Tumors - Unilateral, 99% Cystic, MobileSolomon Seth SallforsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian MalignancyDocument51 paginiOvarian MalignancydeepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery E: MD Najmus Sakir K-75Document14 paginiSurgery E: MD Najmus Sakir K-75Kitty GraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debulking (Cytoreductive) SurgeryDocument23 paginiDebulking (Cytoreductive) Surgerytsega tilahunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Mass Removal: Hugh H. Allen, M.DDocument6 paginiAbdominal Mass Removal: Hugh H. Allen, M.DAbbyKristekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Margaret Xaira R. Mercado RNDocument38 paginiMargaret Xaira R. Mercado RNxaira_rnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder CancerDocument3 paginiBladder CancerGhea Jovita SinagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prostate FinalDocument6 paginiProstate FinalivanaldrichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast CancerDocument9 paginiBreast CancerIrfan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Must Know Breast Anatomy & Pathology MCQsDocument23 paginiMust Know Breast Anatomy & Pathology MCQssb medexÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAH and BSO (TAH-BSO) Is Still Considered The Standard Operative Procedure For Patients With Endometrial CancerDocument3 paginiTAH and BSO (TAH-BSO) Is Still Considered The Standard Operative Procedure For Patients With Endometrial CancerVanessa VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian CancerDocument8 paginiOvarian Cancerthabetamal63Încă nu există evaluări
- Tumor MarkerDocument47 paginiTumor MarkerUsmle GuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prostate CancerDocument34 paginiProstate CancerKoRnflakes100% (1)
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy - Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy and OmentectomyDocument36 paginiTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy - Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy and OmentectomyVignesh JayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Operations: Several Surgical Options For The Thyroid Gland Depending On The ProblemDocument3 paginiThyroid Operations: Several Surgical Options For The Thyroid Gland Depending On The ProblemIwan InteristiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment, Diagnosis and Treatment For CancerDocument70 paginiAssessment, Diagnosis and Treatment For CancerJojo JustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Case Title Hard Acrylic Anterior Repositioning ApplianceDocument3 paginiClinical Case Title Hard Acrylic Anterior Repositioning ApplianceDrAla MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transurethral Resection of ProstateDocument10 paginiTransurethral Resection of ProstateMa. Ydela MeradoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- TotalAbdomHysterBilateralSalpingoOophorectPelvicNodeDissection EndometrialCancer TH PD9300Document36 paginiTotalAbdomHysterBilateralSalpingoOophorectPelvicNodeDissection EndometrialCancer TH PD9300Red StohlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Site Screening, Laboratory Test Diagnostic Test and Tumor Markers Nursing Responsibility in Preparing The Client and Significant OtherDocument9 paginiCancer Site Screening, Laboratory Test Diagnostic Test and Tumor Markers Nursing Responsibility in Preparing The Client and Significant OtherKei CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testicular Tumors The EndDocument67 paginiTesticular Tumors The EndRamesh ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otto Van Delden and Robin SmithuisDocument11 paginiOtto Van Delden and Robin SmithuisSheila AnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preoperative Details For Simple ProstatectomyDocument3 paginiPreoperative Details For Simple ProstatectomyWyethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gynecology: Three Minimally Invasive Procedures You Need to Know About For: Permanent Birth Control, Heavy Menstrual Periods, Accidental Loss of Urine Plus: Modern Hormone Therapy for the Post Menopausal WomenDe la EverandGynecology: Three Minimally Invasive Procedures You Need to Know About For: Permanent Birth Control, Heavy Menstrual Periods, Accidental Loss of Urine Plus: Modern Hormone Therapy for the Post Menopausal WomenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazel Rhs Horticulture Level 2 Essay 1Document24 paginiHazel Rhs Horticulture Level 2 Essay 1hazeldwyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Pile Driving Equipment Equipment CatalogDocument25 paginiAmerican Pile Driving Equipment Equipment CatalogW Morales100% (1)
- Scalextric Arc One GuideDocument46 paginiScalextric Arc One GuidenotifyatpriÎncă nu există evaluări
- ForewordDocument96 paginiForewordkkcmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenDocument2 paginiVeg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenmusicalcarpetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etl 213-1208.10 enDocument1 paginăEtl 213-1208.10 enhossamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joseph Conrad - Heart of DarknessDocument86 paginiJoseph Conrad - Heart of DarknessCaztor SscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge /28 Application / 22 Thinking / 12 Communication / 9Document8 paginiKnowledge /28 Application / 22 Thinking / 12 Communication / 9NmÎncă nu există evaluări
- PANCREATITISDocument38 paginiPANCREATITISVEDHIKAVIJAYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)Document13 paginiNotice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)FyBerri InkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Material ChangesDocument6 paginiChapter 9 Material ChangesFitria Istikomah DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Kalman FilterDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Kalman FilterArghya MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionDocument18 paginiPlaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionFranck BertrandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital ElectronicsDocument18 paginiDigital ElectronicsHarry BeggyÎncă nu există evaluări
- WD 02Document1 paginăWD 02Elezer BatchoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoDocument3 paginiSVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoChejarla Naveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFDocument2 paginiAnchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFdellindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ah 1000Document1 paginăAh 1000Zafir SihabuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- WPCE Wireline Lubricator With Threaded Unions PDFDocument1 paginăWPCE Wireline Lubricator With Threaded Unions PDFDidik safdaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Installation ProcedureDocument5 paginiBattery Installation ProceduresantoshkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spina 2002Document10 paginiSpina 2002hasantapÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02-09-18 SR - IZ Jee-Adv 2011-P1 PTA-03 Q PDFDocument31 pagini02-09-18 SR - IZ Jee-Adv 2011-P1 PTA-03 Q PDFswarupÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3592 Operator GuideDocument103 pagini3592 Operator GuideNaim GhattasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Document26 paginiScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PositioningDocument2 paginiPositioningKishan AndureÎncă nu există evaluări