Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
29 - Kim PD Measure and Monitoring On HV Cables PDF
Încărcat de
bcqbaoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
29 - Kim PD Measure and Monitoring On HV Cables PDF
Încărcat de
bcqbaoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Presentation 29.
1
OMICRON electronics Asia Limited 2013 Conference on Electrical Power Equipment Diagnostics
PD Simultaneous Measurement duri ng HVAC Test
Dong Hoon Lim (KESCO), Won Nyon Kim (KESCO)
1. Introducti on
With the recent increase in diagnosis of extra-high
voltage cable, partial discharge (PD) tests are
widely used. Taihan Electric Wire and LS cable
that are manufacturer introduced the PD test while
they laid the underground line of 345kV XLPE
cable in 2003. In the recent years, PD test is widely
expanded at the 154kV cable.
In 2005, Taihan obtained the turn-key project of
Transpower in New Zealand. KESCO cooperated
with Taihan, who performed the test after
installation of the 220kV underground line. We
used the MPD 600 PD system according to the
request of the customer. In addition, we installed
the foil sensor at the outside of the cable to
perform the PD test.
The MPD600 could cover the configuration of
North Island Upgrade project, because maximum
distance between joints was less than 800[m].
The optical fiber cable was installed in the 32mm
HDPE pipe along the power cable route and used
to connect MPD600s with each other.
The 220kV underground cable connection between
Brownhill and Pakuranga was 10.874km XLPE
three-phase cable system in Auckland, New
Zealand. PD measurements (Off-line PD test) were
carried out by Taihan personnel on 22nd-29th
J une, 2012 on the 220kV underground cable.
PD measurements were carried out on the site by
means of the MPD600 system which is designed
and manufactured by OMICRON.
The drawing relevant to the entire circuit from
Brownhill to Pakuranga is depicted below Figure 1.
Figure 1.Circuit Diagram from Brownhill to Pakuranga
Customer Transpower
Location & Country Auckland, New Zealand
Cable Circuit Brownhill to Pakuranga
Installer Taihan / LS
Cable Type 220kV 1C * 2500SQ XLPE
Circuit length 10.874km
Test voltage
and frequency
180kV(Ph-Grd) =1.4Uo
23Hz (off-line)
Cable length[km]
Circuit#1 : 32,622
Circuit#2 : 32,793
Total : 65,415
Outdoor Sealing End
Circuit#1 : 6
Circuit#2 : 6
Total : 12
Premolded Insulating J oint
Circuit#1 : 51
Circuit#2 : 48
Total : 99
2. PD Measuring System
2.1 PD Anal yzing System
The Synchronous Multi-Channel PD Measuring
System MPD600 of OMICRON electronics is
developed and optimized for on-site PD cable
testing.
Due to its modular design it can easily be adapted
to the required number of measurement channels
depending on the cable length. This allows a
synchronous PD measurement for all joins and
cable terminations at one time. Therefore a fiber
optic connection is required from one acquisition
unit to the next (BUS-system) and finally to the PC.
Figure 2.Connection between MPD600s
Presentation 29.2
OMICRON electronics Asia Limited 2013 Conference on Electrical Power Equipment Diagnostics
2.2 PD Sensor
The copper foil sensors were installed on the
cable PVC or PE jacket around an insulated joint
(I.J ) and they had capacitive characteristics
electrically. The foil sensors did not affect electrical
and mechanical characteristics of the cable or the
joint. Four sensors should be attached on the cable
and two of them were for calibration, and the rest
of them were connected to impedance box for
measurement as shown in figure 3. An adhesive-
lined heat shrinkable tube shall be used as
waterproof covers for the foil sensors.
Figure 3.Capacitive Foil Sensor Installation at the
Insulation J oint
RG213 cable was used to connect the foil sensor
with measurement device. As shown in figure 3, in
the case of the foil sensor equivalent circuit, there
were capacitances (C3, C4) between the foil
sensor and the Power cable, and these were
connected to measurement impedance Z. It was
desirable for impedance of C3 and C4 to be small
enough compared with Z. Effects of C3 and C4
were negligible if the size of foil sensors were big
enough. Cg was the defect at figure 10 when a PD
happens at the left side of the insulated joint box or
the cable. Then C2 of the right side worked as a
Capacitor Divider Ck, and PD signal could be
detected through the measurement impedance Z
which was connected to foil sensors attached on
the joint divided by the insulator.
Figure 4.Equivalent Circuit of the Sensor and J oint
Figure 5.Capacitive Foil Sensor Installation at
Outdoor Sealing End
Two capacitive copper foil sensors are attached
on the cable of an Outdoor sealing end as shown
in figure 5. One is connected to impedance box
and used for PD measurement, and the other one
is used for calibration.
2.3 AC Phase Synchronization
For AC phase synchronization around the 22Hz
frequency range component was accepted from
the voltage divider of HVAC.
Figure 6.Connection between HVAC voltage
divider and MPD600.
2.4 Conceptual Diagram of AC Test and PD
Measurement
The AC voltage generator was connected to
PAKURANGA S/S considering site condition.
Capacitive foil sensors, their coaxial cables, and
optical cables were installed permanently, and
coaxial cables reach at the IP level box which
located at a space near the link box.
Presentation 29.3
OMICRON electronics Asia Limited 2013 Conference on Electrical Power Equipment Diagnostics
Shown in figure 7, impedance boxes, coaxial
cables, MPD600, and MCU502 will be installed at
the site temporarily for simultaneous
measurement. Sensitivity will be measured at each
joint bay before AC high voltage test, and MPD600
which is connected to fully charged battery pack
under AC test.
Figure 7.During HVAC test, PD measurement data is
acquired from each MPD600 unit
2.5 Test Equipment List
Item Description
22 x MPD 600 Partial Discharge Acquisition Units
22 x MPP 600 Battery packs for MPD 600 units
21 x CPL 542 impedance boxes
MCU 502 Fiber optic bus controller
CAL 542 Charge calibrator
Software For partial discharge analysis
2.6 Calibration
Prior to testing, the inner pair of PD sensors at
each joint had been calibrated by applying a
calibration signal on the outer pair of foil sensors
with a Z box and MPD 600 connected across the
inner pair. The calibration was done at each joint
and termination at a measurement frequency that
gave the best signal to noise ratio at that position.
This resulted in the signal divider (gain) of the MPD
600 varying between 9 and 212 between individual
joints. Part of the variation was explained by the
different measurement frequency used (2.4 to 6
MHz) as a higher gain was required at a higher
frequency. However as the PD sensor foils and
220 kV joint and cable arrangements at each joint
were identical there should be only small
differences in gain required between joints.
The test procedure given in NIGUP-TZ-ENG-173
Section 2.12 Procedure of ACHV Test and PD
Measurement required common settings including
frequency tuning and divider factors to be applied
to all joint MPD 600s factors a significant difference
in calibration pulse amplitudes to be investigated
before testing commences.
The calibration carried out prior to testing was
therefore not considered acceptable and it was
decided to select a common measurement
frequency of 3 MHz with a bandwidth of 300 kHz
as being the best compromise of signal to noise
ratio and gain required.
The BHL termination was then calibrated for PD
measurements by connecting a Z box and MPD
600 to the test sets capacitor divider and applying
a calibration pulse between the HV connection to
the cable termination and earth
3. Concl usi ons
220kV underground cable partial discharge
diagnosis at 111 points has been carried out and
concluded that PD signal was not detected.
Partial discharge measurements were
successfully carried out during the high voltage
withstand test on BHL-PAK Circuit 1 and 2 and no
partial discharges could be detected from the cable
circuits.
Background noise levels varied being highest at
the terminations (20 to 30 pC) and lowest at joints
(5 to 10 pC). Reinstatement and earthworks were
still being carried out on some long sections of the
cable route when the tests were being done out
and this resulted in higher noise levels.
Weather conditions were marginal with several
rain showers that interrupted testing.
Consequently the capacitor voltage dividers
although protected by tarpaulins during rain were
subjected to a damp environment from the 19 to 29
J une 2010.
There was a high level of noise generated by the
test set which was removed by dynamic gating.
The test set noise significantly increased during the
tests with apparent misfiring of the IGBTs and the
cause of this requires investigation.
References
[1] Takesi Endoh : Development of PD Decection
Method for Long-Distance Transmission
Cable Lines : T,IEE J apan. Vol.121-B, No.4,
2001
[2] J . Kaumanns and E. Plieth : On-Site AC
Testing and PD Measurement of 345 kV/2500
mm : XLPE Cable Systems for Bulk Power
Transmission : J ICABLE 03 - International
Conference on Insulated Power Cables
[3] Test Report : North Island Upgrade Project
Brownhill RD to Pakurnaga Design, Supply
and Install -220kV Under Gruoud Cables : PD
Simultaneous Measurement during HVAC
Test
Presentation 29.4
OMICRON electronics Asia Limited 2013 Conference on Electrical Power Equipment Diagnostics
Lim Dong Hoon
Lim is now head of Engineering Service of
KESCO. Lim has worked for 27 years at KESCO.
He studied electrical engineering at the University
of Kwangwoon and received the Masters degree.
He has more than 20 years of experience and
taken responsibilities in analysis of electrical power
system, commissioning of petrochemical plant and
diagnosis of electric power facilities. He is an
evaluation member of Korea Environment
Corporation and Energy team of Seoul City. He
also is an active member of subcommittee at the
Korea Electric Association.
Kim Won Nyon
Kim is now worked for Engineering Service of
KESCO. Prior to joining the KESCO team, he
worked at the company that manufacture and
construct the cable. He has lots of experience in
the commissioning and maintenance of the extra-
high voltage cable. Since 2006, he has worked for
the diagnosis of electric power system at the
KESCO. His main responsibility is in PD testing of
different type of electrical systems.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Test Procedure of Surge ArresterDocument6 paginiTest Procedure of Surge Arrestersmi1989100% (3)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Hide and DrinkDocument562 paginiHide and DrinkMao Lee100% (1)
- 2015-D1-1 Partial Discharge Measurements in The Sub-VLF-RangeDocument6 pagini2015-D1-1 Partial Discharge Measurements in The Sub-VLF-RangeSantanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Transformer FRA Responses - Part II: Influence of Transformer StructureDocument8 paginiInterpretation of Transformer FRA Responses - Part II: Influence of Transformer StructureErfan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13-Mike Engelbrecht - Methods of Maintenance On High Voltage Fluid FilledDocument5 pagini13-Mike Engelbrecht - Methods of Maintenance On High Voltage Fluid FilledRomany AllamÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP - Virtual Magnetic Field Assessment - v2Document10 paginiWP - Virtual Magnetic Field Assessment - v2jmmendesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PD 6 Online PD Monitoring Power CablesDocument21 paginiPD 6 Online PD Monitoring Power CablesAbhishek GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodsDocument2 paginiPartial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodskashifÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS RC Voltage DividerDocument6 paginiGIS RC Voltage DividerEldin EnggÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cigre Tf21-05id44ver24Document10 paginiCigre Tf21-05id44ver24salekojic5332Încă nu există evaluări
- CigreDocument11 paginiCigreAlfan Farizki HarahapÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Jicable - Risk On Failure Based On PD Measurements in Actual MV PILC and XLPE Cables.Document3 pagini2015 Jicable - Risk On Failure Based On PD Measurements in Actual MV PILC and XLPE Cables.des1982Încă nu există evaluări
- PD Measurement For HV Cable SystemDocument7 paginiPD Measurement For HV Cable SystemMichael Parohinog GregasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Discharges in Humid Environments Generators, Effects, ApplicationDocument142 paginiElectrical Discharges in Humid Environments Generators, Effects, ApplicationAnonymous 6tg80e6BqAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 CIGRE A2 - 211 TrafoDocument9 pagini2010 CIGRE A2 - 211 TrafoDante FilhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HV Cables: Techimp Case StudiesDocument66 paginiHV Cables: Techimp Case StudiesJuanes CevallosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 International Conference On Insulated Power CablesDocument6 pagini8 International Conference On Insulated Power CablesHafiziAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omicron - Synchronous Multi-Channel PD Measurements and The Benefits For PD AnalysesDocument8 paginiOmicron - Synchronous Multi-Channel PD Measurements and The Benefits For PD AnalysesNguyen Vu Nhat HaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens Surge Arrester Technical DatasheetDocument2 paginiSiemens Surge Arrester Technical DatasheetWilliam CheungÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Tutorials & Colloquium On Latest Trends and Innovations OnDocument12 paginiInternational Tutorials & Colloquium On Latest Trends and Innovations OnAradhana RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ausgrid Utiltiy Cable Test Plan 2017Document31 paginiAusgrid Utiltiy Cable Test Plan 2017Ali NaderianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goodwin Cable DiagnosticsDocument19 paginiGoodwin Cable DiagnosticsMohammadasif ThakorÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDCheck User Manual - Rev08Document59 paginiPDCheck User Manual - Rev08anurag_jay12464100% (1)
- HVDC Voltage DividerDocument4 paginiHVDC Voltage DividerelengineerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urn100511 PDFDocument148 paginiUrn100511 PDFbabakfazelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009Document21 paginiDoble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009reza515heiÎncă nu există evaluări
- máy cắt sf6 abbDocument7 paginimáy cắt sf6 abbQuảng Thành NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFRA Method - Frequency Analysis of TransformersDocument4 paginiSFRA Method - Frequency Analysis of TransformersNirmal mehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOR-WG+B1 38+After+laying+tests+on+AC+and+DC+cable+systems+with+new+technologiesDocument2 paginiTOR-WG+B1 38+After+laying+tests+on+AC+and+DC+cable+systems+with+new+technologiesWalter CataldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 10 - High Voltage TestingDocument29 paginiCHAPTER 10 - High Voltage TestingDeepan0507Încă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Dielectric Spectroscopy Results in Time and Frequency Domains For Power CablesDocument7 paginiInterpretation of Dielectric Spectroscopy Results in Time and Frequency Domains For Power CablesOrlandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide For Transformer Maintenance: Echnical RochureDocument5 paginiGuide For Transformer Maintenance: Echnical RochureHoracio BerniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of Phase Resolved Partial Discharge Waveforms From Instrument Transformer Using Statistical Signal Processing TechniqueDocument6 paginiCharacterization of Phase Resolved Partial Discharge Waveforms From Instrument Transformer Using Statistical Signal Processing TechniqueDebojyoti MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Substation Case StudyDocument10 paginiSubstation Case StudyMaribel C. MagbanuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Ed Gulski PraesentationDocument45 pagini13 Ed Gulski Praesentationcarlos vidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB MWK Surge Arrester DatasheetDocument2 paginiABB MWK Surge Arrester DatasheetMatt ChecksfieldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of VLF / Tan Delta & Partial Discharge Acceptance Testing of New 23kV CablesDocument38 paginiCase Study of VLF / Tan Delta & Partial Discharge Acceptance Testing of New 23kV CablesAshwin SevariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCA Shunt ReactorDocument11 paginiLCA Shunt ReactorTalo RKÎncă nu există evaluări
- LA Condition MonitoringDocument20 paginiLA Condition MonitoringPET MADAKKATHARAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction BAUR Products VLF TD PD MWT IEEE 2018Document77 paginiIntroduction BAUR Products VLF TD PD MWT IEEE 2018Lucho RufoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009Document21 paginiDoble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009taufiqishak09Încă nu există evaluări
- Chap 6 - High Voltage Testing of EquipmentDocument16 paginiChap 6 - High Voltage Testing of Equipmenthadrien100% (1)
- 674 Benefits of PD Diagnosis On GIS Condition AssessmentDocument56 pagini674 Benefits of PD Diagnosis On GIS Condition Assessmentasi midobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Testing of High Voltage Circuit Breaker-2Document23 paginiDigital Testing of High Voltage Circuit Breaker-2Sreevidya GopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanding The Diagnostic Impact of Power Factor Testing: Interpretation of Narrow Band Dielectric Frequency ResponseDocument5 paginiExpanding The Diagnostic Impact of Power Factor Testing: Interpretation of Narrow Band Dielectric Frequency ResponseMosa Elnaid Elnaid100% (1)
- Partial Discharge Patterns in High Voltage InsulationDocument7 paginiPartial Discharge Patterns in High Voltage Insulationfery zenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB Kabeldon Cable Joints Terminations Separable Connectors LV HVDocument132 paginiABB Kabeldon Cable Joints Terminations Separable Connectors LV HVrocketvtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Response Analysis of Power Transformers: TransmissionDocument4 paginiFrequency Response Analysis of Power Transformers: Transmissionrcarrasco07Încă nu există evaluări
- IEEE Guide C5712200-2022Document84 paginiIEEE Guide C5712200-2022Sontri ChiggumÎncă nu există evaluări
- HV TestDocument6 paginiHV Testvjvijay88Încă nu există evaluări
- Cigre 2010 - On-Site Commissioning Test and Diagnostics ofDocument7 paginiCigre 2010 - On-Site Commissioning Test and Diagnostics ofAnonymous F71F47EnKÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA 821-070 BAUR Manual Cable Fault Location enDocument60 paginiMA 821-070 BAUR Manual Cable Fault Location enOsman Altun100% (2)
- CB Monitor: On Line Circuit Breaker Monitoring SystemDocument4 paginiCB Monitor: On Line Circuit Breaker Monitoring Systemashu_2787Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersDocument22 paginiSample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersedgardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Type Tests and Documentation For Arrester Type PEXLIM Q-Y LAK 7963 Rev 3 Pphc/AkbDocument1 paginăSummary of Type Tests and Documentation For Arrester Type PEXLIM Q-Y LAK 7963 Rev 3 Pphc/AkbLuis AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PowerPD Case Studies Rev 2.6Document64 paginiPowerPD Case Studies Rev 2.6vtechelectricÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0515 PartialDischarge EmersonDocument44 pagini0515 PartialDischarge EmersonAll4UyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Ish Pattern Recognition of Partial Discharge in Gis Based On Improved BP NetworkDocument6 pagini2015 Ish Pattern Recognition of Partial Discharge in Gis Based On Improved BP NetworkHartanto KartojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Different Techniques of Partial Discharge (PD) Detection in Power Transformers Winding: Simulation Between Paper and EPOXY Resin Using UHF MethodDocument5 paginiStudy On Different Techniques of Partial Discharge (PD) Detection in Power Transformers Winding: Simulation Between Paper and EPOXY Resin Using UHF MethodashwiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDe la EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDe la EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condition Monitoring of Instrument Transformers - POWERGRID ExperienceDocument36 paginiCondition Monitoring of Instrument Transformers - POWERGRID ExperiencebcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zero Lead Length Configuration PDFDocument2 paginiZero Lead Length Configuration PDFfourwheelerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arrester Disconnector PDFDocument7 paginiArrester Disconnector PDFipraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCAR10Document5 paginiSCAR10Joshi DhvanitÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead LengthDocument11 paginiArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead Lengthnshj196Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Factoring Surge ArrestersDocument2 paginiPower Factoring Surge Arrestersdacow22Încă nu există evaluări
- Application Note: Determining Harmonic DirectionDocument5 paginiApplication Note: Determining Harmonic DirectionAnton MatzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Voltages For CablesDocument3 paginiTest Voltages For CablesMahmoud EidÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE Guide For Fault Locating Techniques On Shielded Power Cable SystemsDocument37 paginiIEEE Guide For Fault Locating Techniques On Shielded Power Cable SystemsbcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - 14 Experiences EuroDoble MeetingsDocument22 pagini2 - 14 Experiences EuroDoble Meetingsbcqbao100% (1)
- Testing of High Voltage CablesDocument7 paginiTesting of High Voltage CablesYogi Rungi100% (2)
- DOE Diagnostic Testing of Underground Cable Systems CDFI - Phase - 1 - Final-ReportDocument323 paginiDOE Diagnostic Testing of Underground Cable Systems CDFI - Phase - 1 - Final-ReportGustavo AguayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Voltages For CablesDocument3 paginiTest Voltages For CablesMahmoud EidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be On Guard For Effective Testing: 5 KV and 10 K Insulation TestingDocument8 paginiBe On Guard For Effective Testing: 5 KV and 10 K Insulation TestingKarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic AG en US1Document5 paginiDiagnostic AG en US1bcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic AG en US1Document5 paginiDiagnostic AG en US1bcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mineral Insulating OilDocument96 paginiMineral Insulating OilnbhawyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Above1kV UG en V04Document36 paginiAbove1kV UG en V04Amal MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM-1 Doble Case Studies LewandDocument21 paginiIM-1 Doble Case Studies LewandbcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5kV DiagnosticTestingDocument41 pagini5kV DiagnosticTestingkl_tsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Oil Testing - SD Myers - Jun 08Document51 paginiTransformer Oil Testing - SD Myers - Jun 08Prabhu Koppal100% (1)
- SF6 Technical PaperDocument2 paginiSF6 Technical PaperbcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Low Resistance Booklet-CROPICODocument39 paginiGuide To Low Resistance Booklet-CROPICObcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM-1 Doble Case Studies LewandDocument21 paginiIM-1 Doble Case Studies LewandbcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Revised)Document78 paginiOil Revised)shhansikaÎncă nu există evaluări
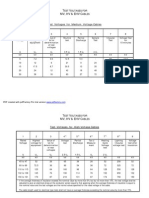
- Efficient Method To Accelerate Resistance Measurement of Transformer LV WindingDocument8 paginiEfficient Method To Accelerate Resistance Measurement of Transformer LV WindingbcqbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Issues Tracker - DAFDocument28 paginiHSE Issues Tracker - DAFMohd Abdul MujeebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Installation - AfbcDocument2 paginiBoiler Installation - AfbcSarah FrazierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Habits & Dance Culture Faridkot (Punjab) : Presented By: Kendriya Vidyalaya FaridkotDocument17 paginiFood Habits & Dance Culture Faridkot (Punjab) : Presented By: Kendriya Vidyalaya FaridkotJagdeep KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Composting Brochure - Connecticut USADocument2 paginiHome Composting Brochure - Connecticut USAPennsylvania Association for Sustainable AgricultureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Psychology (2022)Document642 paginiIntroduction To Psychology (2022)hongnhung.tgdd2018Încă nu există evaluări
- Chest and Triceps ExercisesDocument6 paginiChest and Triceps ExercisesTess WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating ProceduresDocument1 paginăScaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating Proceduresmohammed muzammilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Left Side View: Electrical System G3516A and G3516B EngineDocument2 paginiLeft Side View: Electrical System G3516A and G3516B EngineAM76100% (1)
- Introduction To Mine SurveyingDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Mine SurveyingJoshua Miguel MejiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relationship Between Date of Birth and IndividDocument13 paginiThe Relationship Between Date of Birth and IndividAnonymous ktNyZTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pin ContentDocument20 paginiPin ContentSwetha100% (2)
- Electron Configurations of The Elements (Data Page) - WikipediaDocument25 paginiElectron Configurations of The Elements (Data Page) - WikipediaAlex OmungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EP-HQ-GDL-008-00 Safety - Critical - Elements - Integrity - Management - GuidelineDocument57 paginiEP-HQ-GDL-008-00 Safety - Critical - Elements - Integrity - Management - GuidelineAHMED AMIRA100% (5)
- The Company - MicroDocument2 paginiThe Company - MicroMai Hương QuỳnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSE8620 MKII Operator ManualDocument224 paginiDSE8620 MKII Operator Manualhenrygrados44Încă nu există evaluări
- BCRSPDocument2 paginiBCRSPDastan YermegaliyevÎncă nu există evaluări
- HC-33 Maximum Moisture Hair Styling Gel PDFDocument2 paginiHC-33 Maximum Moisture Hair Styling Gel PDFdianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predrag Mladenovic CVDocument3 paginiPredrag Mladenovic CVStefan Markovic JagodinacÎncă nu există evaluări
- EO MNC 10 June 2022Document4 paginiEO MNC 10 June 2022LeulaDianneCantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 MAPEH Baler - Grade 6Document6 pagini2019 MAPEH Baler - Grade 6Maria Rosario VelicariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conut Shell: A Substitute For Aggregate in Mix Proportioning of CementDocument17 paginiConut Shell: A Substitute For Aggregate in Mix Proportioning of CementStephanie SilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALDocument200 pagini1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALRuan BritsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Marina Structures and FacilitiesDocument23 paginiDesign of Marina Structures and FacilitiesAhmed Balah0% (1)
- Issues Pertaining To Maintenance of WifeDocument2 paginiIssues Pertaining To Maintenance of WifeVaishnavi YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrialisation by InvitationDocument10 paginiIndustrialisation by InvitationkimberlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium Cyanide: Hydrogen Cyanide. CONSULT THE NEW JERSEYDocument6 paginiCalcium Cyanide: Hydrogen Cyanide. CONSULT THE NEW JERSEYbacabacabacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steady State & Dynamic Wind Turbine ModelDocument4 paginiSteady State & Dynamic Wind Turbine ModeldarshanraghuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoasteeringDocument1 paginăCoasteeringIrishwavesÎncă nu există evaluări
- E4 - Review Unit 11 To Unit 20Document16 paginiE4 - Review Unit 11 To Unit 20Tuyen NgoÎncă nu există evaluări