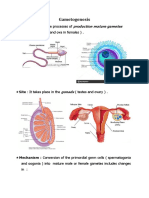
Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bio7 ch47
Încărcat de
freezo1994Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bio7 ch47
Încărcat de
freezo1994Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Biology, 7e (Campbell)
Chapter 47: Animal Development
Chapter Questions
1) Russian nesting dolls, which are a set of smaller dolls packed inside larger dolls, most resemble which one of the
following developmental theories?
A) epigenesis
B) preformation
C) cell differentiation
D) morphogenesis
E) cell theory
Answer: B
Topic: Overview
Skill: Application
2) You buy a pie that contains a mixture of cherries and blueberries. When you cut the pie up, you notice that some
slices have more blueberries than cherries and other slices have more cherries than blueberries. This uneven
distribution of cherries and blueberries is most like the uneven distribution of
A) nuclei in a zygote.
B) nuclei in an early embryo.
C) nuclei in an egg.
D) cytoplasmic determinants in a zygote.
E) cytoplasmic determinants in an early embryo.
Answer: D
Topic: Overview
Skill: Application
3) A puppy is born with a malformed right leg. A veterinarian studies the animal and determines that all of the
correct types of cells are present, but that the leg simply took on the wrong shape. This is most likely a problem of
A) morphogenesis.
B) cell differentiation.
C) histogenesis.
D) preformation.
E) fertilization.
Answer: A
Topic: Overview
Skill: Application
4) As an embryo develops, new cells are formed and different types of cells develop by the process of
A) differentiation and morphogenesis.
B) preformation and cell differentiation.
C) cell division and differentiation.
D) preformation and morphogenesis.
E) preformation and epigenesis.
Answer: C
Topic: Overview
Skill: Knowledge
2
5) Fertilization of an egg without activation is most like
A) placing the key in the ignition of a car but not starting the engine.
B) resting during halftime of a basketball game.
C) preparing a pie from scratch and baking it in the oven.
D) walking to a store and buying some groceries.
E) boarding a train in Chicago and riding it to Philadelphia.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Application
6) In some rare all-female salamander species, the females require the sperm from males of another species.
However, the developing embryos show no signs of a genetic contribution from the sperm. In this case, the sperm
appear to be used only for
A) morphogenesis.
B) epigenesis.
C) egg activation.
D) cell differentiation.
E) the creation of a diploid cell.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Application
7) Which of the following is a function of the acrosome contents during fertilization?
A) block polyspermy
B) help propel the sperm toward the egg
C) digest the exterior coats of the egg
D) nourish the mitochondria of the sperm
E) trigger the completion of meiosis by the sperm cell
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
8) Which of the following statements is (are) true concerning the vitelline layer of the sea urchin egg?
A) It is outside the fertilization membrane.
B) It releases calcium, which initiates the cortical reaction.
C) It has receptor molecules that are specific for binding acrosomal proteins.
D) A and B are true.
E) A, B, and C are true.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
9) The cortical reaction functions directly in the
A) formation of a fertilization envelope.
B) production of a fast block to polyspermy.
C) release of hydrolytic enzymes from the sperm cell.
D) generation of a nervelike impulse by the egg cell.
E) fusion of egg and sperm nuclei.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
3
10) What causes the "slow block" to polyspermy?
A) a transient voltage change across the membrane
B) the consumption of yolk protein
C) the jelly coat blocking sperm penetration
D) formation of the fertilization envelope
E) inactivation of the sperm acrosome
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
11) Which of the following is least related to the others?
A) slow block to polyspermy
B) cortical granules
C) cortical reaction
D) depolarization
E) fertilization envelope
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
12) If an egg cell contained EDTA, a chemical that binds calcium and magnesium, what effect would this have on
reproduction?
A) The acrosomal reaction would be blocked.
B) The fusion of sperm and egg nuclei would be blocked.
C) The fast block to polyspermy would not occur.
D) The fertilization envelope would not be formed.
E) The zygote would not contain maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
13) Which statement about egg development is true?
A) Eggs without a nucleus cannot initiate division.
B) A second messenger system is activated following fertilization.
C) The sperm and egg micronuclei have fused by the end of the cortical reaction.
D) The contents of the cortical granules contribute to the fast block to polyspermy.
E) The mRNA involved with early activation of the egg arises from the sperm nucleus.
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
14) Arrange the following stages of fertilization and early development into a proper sequence.
I. onset of new DNA synthesis
II. cortical reaction
III. first cell division
IV. acrosomal reaction; plasma membrane depolarization
V. fusion of egg and sperm nuclei complete
A) III, V, I, IV, II
B) V, I, IV, II, III
C) I, III, II, IV, V
D) V, III, I, II, IV
E) IV, II, V, I, III
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
4
15) Which of the following statements about fertilization is false?
A) Fertilization reinstates diploidy.
B) Fertilization invaginates the blastula to form the gastrula.
C) During fertilization, egg cell depolarization initiates the cortical reaction.
D) During fertilization, gamete fusion depolarizes the egg cell membrane and sets up a fast block to polyspermy.
E) During fertilization, a slow block to polyspermy occurs when cortical granules erect a fertilization envelope.
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
16) What part of the sperm first contacts the egg plasma membrane?
A) the vitelline membrane
B) the cortical granules
C) the acrosomal membrane
D) the actin proteins
E) the fertilization membrane
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
17) Which one of the following occurs in sea urchin but not mammalian fertilization?
A) the binding of a sperm cell to the egg
B) a fast block to polyspermy
C) hydrolytic enzymes are spilled from the acrosome
D) a slow block to polyspermy
E) a fusion of the egg and sperm membranes
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
18) As cleavage continues during frog development, the number of blastomeres
A) increases as the size of the blastomeres decreases.
B) increases as the size of the blastomeres increases.
C) decreases as the size of the blastomeres increases.
D) decreases as the size of the blastomeres decreases.
E) increases as the size of the blastomeres stays the same.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
19) Which of the following does not occur during early cleavage of a frog zygote?
A) The developing cell undergoes mitosis.
B) The nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio of the two resulting cells increases.
C) The ratio of surface area to volume of the two resulting cells increases.
D) The embryo grows significantly in mass.
E) The developing cell undergoes cytokinesis.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
5
20) How does the vegetal pole differ from the animal pole of a zygote?
A) The vegetal pole has a higher concentration of yolk.
B) The blastomeres originate only in the vegetal pole.
C) The posterior end of the embryo forms at the vegetal pole.
D) The vegetal pole cells undergo mitosis but not cytokinesis.
E) The polar bodies bud from this region.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
21) Which region of the frog blastula corresponds to the future dorsal side of the embryo?
A) morula
B) primitive streak
C) archenteron
D) gray crescent
E) blastocoel
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
22) The yolk of the frog egg
A) prevents gastrulation.
B) is concentrated at the animal pole.
C) is homogeneously arranged in the egg.
D) impedes the formation of a primitive streak.
E) leads to unequal rates of cleavage for the animal pole compared to the vegetal pole.
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
23) You observe an embryo with meroblastic cleavage, extraembryonic membranes, and a primitive streak. How
would you identify this organism, based on the information given?
A) insect
B) fish
C) amphibian
D) bird
E) sea urchin
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Application
24) Meroblastic cleavage occurs in which of the following?
I. sea urchins
II. humans
III. birds
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III only
E) II and III only
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
6
25) Which developmental sequence is correct?
A) cleavage, blastula, gastrula, morula
B) cleavage, gastrula, morula, blastula
C) cleavage, morula, blastula, gastrula
D) gastrula, morula, blastula, cleavage
E) morula, cleavage, gastrula, blastula
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
26) What is the process called that involves the movement of cells into new relative positions in an embryo and
results in the establishment of three germ tissue layers?
A) determination
B) cleavage
C) fertilization
D) induction
E) gastrulation
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
27) After gastrulation, the outer-to-inner sequence of tissue layers in a vertebrate is
A) endoderm, ectoderm, mesoderm.
B) mesoderm, endoderm, ectoderm.
C) ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm.
D) ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm.
E) endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
28) What would be the consequence if gastrulation did not occur?
A) Cleavage would not occur in the zygote.
B) Embryonic germ layers would not form.
C) Fertilization would be blocked.
D) The blastula would not be formed.
E) The blastopore would form above the gray crescent in the animal pole.
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
29) The archenteron of the developing frog eventually develops into which structure?
A) reproductive organs
B) the blastocoel
C) heart and lungs
D) digestive tract
E) brain and spinal cord
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
7
30) Without the formulation of an ectoderm, vertebrates would not form
A) a nervous system.
B) a liver.
C) a pancreas.
D) a heart.
E) kidneys.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
The following questions refer to the diagram of the embryo in Figure 47.1.
Figure 47.1
31) What type of embryo is most likely depicted here?
A) dog
B) frog
C) chick
D) snake
E) human
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
32) The next stage of development for the embryo depicted in Figure 47.1 is
A) gastrulation.
B) organogenesis.
C) blastula formation.
D) morula formation.
E) morphogenesis.
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
8
33) In Figure 47.1, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm are, respectively,
A) 1, 2, and 6.
B) 3, 4, and 5.
C) 2, 3, and 4.
D) 5, 6, and 3.
E) 1, 3, and 6.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Application
34) Which of the following will form the lumen of the digestive tract?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
35) The blastopore in this organism will become the
A) anus.
B) ears.
C) eyes.
D) nose.
E) mouth.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
36) In a frog embryo, gastrulation
A) produces a blastocoel displaced into the animal hemisphere.
B) occurs along the primitive streak in the animal hemisphere.
C) is impossible because of the large amount of yolk in the ovum.
D) proceeds by involution as cells roll over the lip of the blastopore.
E) occurs within the inner cell mass that is embedded in the large amount of yolk.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
9
The following questions refer to the diagram of an embryo in Figure 47.2. Match the word or statement to the
lettered structures.
Figure 47.2
37) coelom
Answer: a
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
38) somite
Answer: b
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
39) notochord
Answer: e
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
40) gives rise to the muscles
Answer: b
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
41) gives rise to the brain and spinal cord
Answer: d
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
10
Figure 47.3
42) The drawing in Figure 47.3 is from what stage of amphibian development?
A) blastula
B) neural stage
C) early gastrula
D) late gastrula
E) gray crescent stage
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
43) Which of the following is least related to the others?
A) germ layers
B) morula
C) blastopore
D) gastrulation
E) invagination
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
44) Which of the following is mismatched?
A) mesoderm-notochord
B) endoderm-lungs
C) ectoderm-liver
D) mesoderm-somites
E) ectoderm-eye
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
45) Which of the following is least related to the others?
A) ectoderm
B) mesoderm
C) archenteron
D) endoderm
E) germ layers
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
11
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
In a study of the development of frog embryos, several early gastrulas were stained with vital dyes. The locations of
the dyes after gastrulation were noted. The results are shown in the following table.
+)4] e4C)
`C) ]-
E4E]E- E]E
)+] _]]
] E 4] ]E] p4]
))_ E 4] -)_]4)+] 4C]4 O4O]
46) Ectoderm would give rise to tissues containing which of the following colors?
A) yellow and purple
B) purple and green
C) green and red
D) red and blue
E) red and yellow
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
47) The mesoderm was probably stained with which color?
A) blue
B) yellow
C) red
D) purple
E) green
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
48) The endoderm was probably stained with which color?
A) red and yellow
B) yellow and green
C) green and purple
D) blue and yellow
E) purple and red
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
49) Which of the following helps direct the formation of the primitive streak but contributes no cells to the embryo?
A) endoderm
B) mesoderm
C) ectoderm
D) neural crest
E) hypoblast
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
12
50) The primitive streak in a bird is the functional equivalent of
A) the lip of the blastopore in the frog.
B) the archenteron in a frog.
C) polar bodies in a sea urchin.
D) the notochord in a mammal.
E) neural crest cells in a mammal.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
51) What does the development of all vertebrates require?
A) a large supply of yolk
B) an aqueous environment
C) extraembryonic membranes
D) an amnion
E) a primitive streak
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
52) Which of the following is not an extraembryonic membrane that develops from the embryos of reptiles, birds,
and mammals?
A) chorion
B) yolk sac
C) egg shell
D) amnion
E) allantois
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
53) Which of the following is least related to the others?
A) zona pellucida
B) amnion
C) chorion
D) allantois
E) yolk sac
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
54) The least amount of yolk would be found in the egg of a
A) bird.
B) fish.
C) frog.
D) eutherian (placental) mammal.
E) reptile.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
13
55) A primitive streak forms during the early embryonic development of which of the following?
I. birds
II. frogs
III. humans
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III only
E) II and III only
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
56) Which structure in bird and mammalian embryos functions like the blastopore of frog embryos?
A) primitive streak
B) neural plate
C) archenteron
D) notochord
E) somites
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Comprehension
57) Extraembryonic membranes develop in which of the following?
I. mammals
II. birds
III. lizards
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II, and III
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
58) At the time of implantation, what is the human embryo called?
A) blastocyst
B) gastrula
C) fetus
D) somite
E) zygote
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
59) Which one of the following initiates implantation by secreting enzymes that break down the endometrium?
A) inner cell mass
B) endoderm
C) chorion
D) mesoderm
E) trophoblast
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
14
60) In placental mammals, what is the major function of the yolk sac during development?
A) It transfers nutrients from the yolk to the embryo.
B) It differentiates into the placenta.
C) It becomes a fluid-filled sac that surrounds and protects the embryo.
D) It produces blood cells that then migrate into the embryo.
E) It stores waste products from the embryo until the placenta develops.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
61) Which one of the following plays a major role in gas exchange in a mammalian embryo?
A) amnion
B) hypoblast
C) chorion
D) trophoblast
E) yolk sac
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Knowledge
62) Thalidomide is a chemical that was prescribed as a sedative in the early 1960s. Many women who took the drug
during their first trimester gave birth to children with arm and leg deformities. What developmental process did this
drug affect?
A) early cleavage divisions
B) determination of the polarity of the zygote
C) differentiation of bone tissue
D) morphogenesis
E) organogenesis
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.1
Skill: Application
63) Changes in both cell shape and cell position are involved with which process(es)?
A) gastrulation
B) organogenesis
C) cleavage
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.2
Skill: Knowledge
64) Changes in the shape of a cell usually involve a reorganization of the
A) nucleus.
B) cytoskeleton.
C) extracellular matrix.
D) transport proteins.
E) none of the above
Answer: B
Topic: Concept 47.2
Skill: Knowledge
15
65) The term applied to a morphogenetic process whereby cells extend themselves, making the mass of cells
narrower and longer, is
A) convergent extension.
B) induction.
C) elongational streaming.
D) bi-axial elongation.
E) blastomere formation.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.2
Skill: Knowledge
66) Which of the following would probably have the greatest effect on convergent extension?
A) stopping DNA synthesis
B) stopping mRNA synthesis
C) releasing an enzyme that digests glycoproteins
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.2
Skill: Comprehension
67) Which statement about cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) is false?
A) They are glycoproteins.
B) They bind to CAMs on other cells.
C) They are all produced by the same gene.
D) They contribute to cell migration.
E) They contribute to stable tissue structure.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.2
Skill: Knowledge
68) If an amphibian zygote is manipulated so that the first cleavage plane does not divide the gray crescent, what is
the expected fate of the two daughter cells?
A) The daughter cell with the entire gray crescent will die.
B) Both daughter cells will develop normally because amphibians are totipotent at this stage.
C) Only the daughter cell with the gray crescent will develop normally.
D) Both daughter cells will develop abnormally.
E) Both daughter cells will die immediately.
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Comprehension
69) In humans, identical twins are possible because
A) of the heterogeneous distribution of cytoplasmic determinants in unfertilized eggs.
B) of interactions between extraembryonic cells and the zygote nucleus.
C) of convergent extension.
D) early blastomeres can form a complete embryo if isolated.
E) the gray crescent divides the dorsal-ventral axis into new cells.
Answer: D
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Comprehension
16
70) Hans Spemann has referred to which of the following structures as the primary organizer in the early
development of amphibian embryos?
A) optic cup
B) notochord
C) neural tube
D) dorsal ectoderm
E) dorsal lip of the blastopore
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Knowledge
71) In frogs, formation of the eye lens is induced by chemical signals from
A) cells that will become the neural plate.
B) cells that are forming the inner ear.
C) an outgrowth of the developing brain.
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
Answer: E
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Comprehension
72) The arrangement of organs and tissues in their characteristic places in three-dimensional space defines
A) pattern formation.
B) induction.
C) differentiation.
D) determination.
E) organogenesis.
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Knowledge
73) Which mathematical situation has a parallel in embryonic limb development?
A) using X, Y, and Z coordinates to plot a graph
B) plotting a graph of an exponential growth curve
C) plotting a graph of a linear growth curve
D) using parallel lines to construct a parallelogram
E) E = mc
2
Answer: A
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Comprehension
74) Which of the following is not involved in positional information for pattern formation?
A) apical ectodermal ridge
B) zone of polarizing activity
C) cadherins
D) fibroblast growth factors
E) Sonic hedgehog
Answer: C
Topic: Concept 47.3
Skill: Knowledge
17
Media Activity Questions
75) As cleavage continues, a zygote forms into a solid multicellular ball called a(n)
A) endometrium.
B) morula.
C) trophoblast.
D) gastrula.
E) blastula.
Answer: B
Topic: Web/CD Activity: Sea Urchin Development
76) During gastrulation, invagination occurs at the
A) archenteron.
B) blastocoel.
C) endometrium.
D) blastopore.
E) trophoblast.
Answer: D
Topic: Web/CD Activity: Sea Urchin Development
77) During gastrulation in frogs, a rod of mesoderm under the dorsal surface forms the
A) notochord.
B) ectoderm.
C) endoderm.
D) archenteron.
E) blastopore.
Answer: A
Topic: Web/CD Activity: Frog Development
78) During gastrulation in frogs, cells from the animal pole spread over the embryo and form the
A) endoderm.
B) ectoderm.
C) archenteron.
D) blastopore.
E) blastula
Answer: B
Topic: Web/CD Activity: Frog Development
79) The posterior portion of the neural tube will develop into the frog's
A) spinal cord.
B) brain.
C) blastocoel.
D) digestive tract.
E) anus.
Answer: A
Topic: Web/CD Activity: Frog Development
18
Self-Quiz Questions
80) The cortical reaction of sea urchin eggs functions directly in the
A) formation of a fertilization envelope.
B) production of a fast block to polyspermy.
C) release of hydrolytic enzymes from the sperm cell.
D) generation of an electrical impulse by the egg cell.
E) fusion of egg and sperm nuclei.
Answer: A
81) Which of the following is common to both avian and mammalian development?
A) holoblastic cleavage
B) epiblast and hypoblast
C) trophoblast
D) yolk plug
E) gray crescent
Answer: B
82) The archenteron develops into
A) the mesoderm.
B) the blastocoel.
C) the endoderm.
D) the placenta.
E) the lumen of the digestive tract.
Answer: E
83) In a frog embryo, the blastocoel is
A) completely obliterated by yolk platelets.
B) lined with endoderm during gastrulation.
C) located primarily in the animal hemisphere.
D) the cavity that becomes the coelom.
E) the cavity that later forms the archenteron.
Answer: C
84) What structural adaptation in chickens allows them to lay their eggs in arid environments, rather than in water?
A) extraembryonic membranes
B) yolk
C) cleavage
D) gastrulation
E) development of the brain from ectoderm
Answer: A
85) In an amphibian embryo, a band of cells called the neural crest
A) rolls up to form the neural tube.
B) develops into the main sections of the brain.
C) produces cells that migrate to form teeth, skull bones, and other structures in the embryo.
D) has been shown by experiments to be the organizer region of the developing embryo.
E) induces the formation of the notochord.
Answer: C
19
86) Differences in the development of different cells in the early frog embryo (zygote to blastula) are due to
A) the differences between meroblastic and holoblastic cleavage.
B) the heterogeneous distribution of cytoplasmic determinants, such as proteins and mRNA.
C) inductive interactions occurring between the developing cells.
D) concentration gradients for regulatory molecules such as BMP-4.
E) the position of the cells relative to the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA).
Answer: B
87) During convergent extension,
A) cells on the opposite side of the embryo follow converging developmental pathways leading to bilateral
symmetry.
B) the cells of the neural folds adhere to one another to complete the neural tube.
C) the cells of a tissue layer reorganize, forming a narrowed, elongated sheet.
D) the dorsal-ventral axis is established.
E) cell adhesion molecules are expressed, causing the eight blastomeres to adhere tightly to one another.
Answer: C
88) In the early development of an amphibian embryo, an important "organizer" is located in the
A) neural tube.
B) notochord.
C) archenteron roof.
D) dorsal ectoderm.
E) dorsal lip of the blastopore.
Answer: E
89) Any blastomere removed from an eight-cell mammalian embryo can develop into a normal late-stage embryo.
This finding supports the idea that
A) only the zygote is totipotent.
B) the progressive restriction of potency hypothesis applies.
C) the first cleavage event must be transverse to the animal-vegetal axis of the zygote.
D) cell divisions producing the earliest blastomeres do not result in an asymmetrical distribution of cytoplasmic
determinants.
E) there is no organizer in mammals.
Answer: D
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionDocument69 paginiHUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionAyan Sarkar100% (1)
- Embryology Questions and AnswersDocument29 paginiEmbryology Questions and AnswersFlower83% (6)
- Quiz EmbryologyDocument41 paginiQuiz EmbryologyMedShare90% (67)
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDocument8 pagini24-Hr Chick EmbryopauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology BCQ Review: Meiosis, Gametogenesis and Early Embryonic DevelopmentDocument58 paginiEmbryology BCQ Review: Meiosis, Gametogenesis and Early Embryonic DevelopmentAriba Asif100% (1)
- Exam Emberyology and HistologyDocument10 paginiExam Emberyology and Histologymohaz100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (2)
- Comparative Placentation - Structures Functions Evolution PDFDocument304 paginiComparative Placentation - Structures Functions Evolution PDFFábio Amoroso100% (1)
- Embryo ExamDocument28 paginiEmbryo Exammoha100% (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- C8e 13 Test BankDocument19 paginiC8e 13 Test Bankkiden30100% (2)
- 10 - PlacentaDocument21 pagini10 - Placentaalejosshht100% (1)
- Arun PPT - PPTX ..HUMAN REPRODUCTION FOR HSC Board Maharashtra State..Document65 paginiArun PPT - PPTX ..HUMAN REPRODUCTION FOR HSC Board Maharashtra State..arunmishra1986100% (1)
- Development of the Placenta: A Comprehensive GuideDocument74 paginiDevelopment of the Placenta: A Comprehensive GuideEllagEsz33% (3)
- Veterinary Embryology (Class Notes) PDFDocument77 paginiVeterinary Embryology (Class Notes) PDFluis feo0% (3)
- Ebook Campbell Essential Biology 5Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiEbook Campbell Essential Biology 5Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (14)
- Chick Serial SectionsDocument74 paginiChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankDocument20 paginiHuman Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankKerriAdamsdwroi100% (14)
- Bio7 ch48Document20 paginiBio7 ch48freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Brain and Behavior 5th Edition Kolb Test BankDocument20 paginiIntroduction To Brain and Behavior 5th Edition Kolb Test Bankericsimmonspasmcokyge100% (21)
- Placental ExaminationDocument12 paginiPlacental ExaminationNidhi Sharma100% (7)
- Zoology MCQsDocument26 paginiZoology MCQsUmair KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1661181380biology Sample PaperDocument29 pagini1661181380biology Sample PaperTabinda IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOLOGY, PT1 QuestionsDocument8 paginiBIOLOGY, PT1 QuestionsAbhishek ratnooÎncă nu există evaluări
- REEC7295 09 TB Chapter46Document25 paginiREEC7295 09 TB Chapter46Tony PhillipsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC6_08_Test_BankDocument16 paginiCC6_08_Test_Bankhunmin4083Încă nu există evaluări
- Cuestionario2 TestBank - Basics - Bio10a - Chapter9 División Celular (Kelly Merchán)Document8 paginiCuestionario2 TestBank - Basics - Bio10a - Chapter9 División Celular (Kelly Merchán)Kelly MerchánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print Chapter 47 flashcardsDocument16 paginiPrint Chapter 47 flashcardsnfnf otupyooorefnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanisms of Morphogenesis and Pattern FormationDocument37 paginiMechanisms of Morphogenesis and Pattern Formationstoic_2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Nand Foundation Academy, Shegaon. 9834274427: Xii - A DivDocument14 paginiNand Foundation Academy, Shegaon. 9834274427: Xii - A DivSanket PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUMAN REPRUCTION NCERT BASED HAND PICKED MCQsDocument3 paginiHUMAN REPRUCTION NCERT BASED HAND PICKED MCQstashukumar33Încă nu există evaluări
- Test-15 ReproductionDocument4 paginiTest-15 Reproductionarehmanmalik619Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQs On "Human Reproduction & Embryonic Development".Document27 paginiMCQs On "Human Reproduction & Embryonic Development".Pukazhvanthen ParamanandhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 43 Reproductive Systems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 paginiChapter 43 Reproductive Systems: Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Life On Earth 10Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiBiology Life On Earth 10Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbridget.price734100% (12)
- Instant Download Biopsychology Pinel 9th Edition Test Bank PDF ScribdDocument30 paginiInstant Download Biopsychology Pinel 9th Edition Test Bank PDF ScribdChristian RandleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReproductionDocument17 paginiReproductionkaran79Încă nu există evaluări
- Practice Sheet How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument3 paginiPractice Sheet How Do Organisms ReproduceKanishka ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SND Public School: BiologyDocument4 paginiSND Public School: BiologyD2b x8Încă nu există evaluări
- Developmental BiologyDocument43 paginiDevelopmental BiologyChala KelbessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebook Campbell Essential Biology With Physiology 4Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiEbook Campbell Essential Biology With Physiology 4Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMichaelCarrollmnzq100% (12)
- Assignment Class-12 Subject:Bio - Zoology Unit 1: Chapter 2. Human ReproductionDocument6 paginiAssignment Class-12 Subject:Bio - Zoology Unit 1: Chapter 2. Human ReproductionjohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQS Human Reproduction Class 12Document13 paginiMCQS Human Reproduction Class 12Shaashwati TandonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12th Sample Questions Autumn BreakDocument6 pagini12th Sample Questions Autumn BreakMᴀïᴢᴍɛɛŋ AŋꜱᴀʀïÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReproductionDocument8 paginiReproductionmalak abd el hameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Chapt 4Document19 paginiMicrobiology Chapt 4Adejumo ChampionÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScienceDocument52 paginiScienceVannyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts of Genetics 12th Edition Klug Test BanDwnload Full Concepts of Genetics 12th Edition Klug Test Bank PDFDocument35 paginiConcepts of Genetics 12th Edition Klug Test BanDwnload Full Concepts of Genetics 12th Edition Klug Test Bank PDFmaryjomacklemus100% (13)
- Mitosis Meiosis TestDocument4 paginiMitosis Meiosis TestCarla MinghettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotech - Plant Cell StructureDocument7 paginiBiotech - Plant Cell StructureMarla Grace Estanda AbdulganiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio cuetDocument13 paginiBio cuetGaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQS Developmental Biology QuestionsDocument4 paginiMCQS Developmental Biology QuestionsAima Iram BatoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- XII Biology MCQDocument33 paginiXII Biology MCQsairishiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromosome Transmission and ReproductionDocument14 paginiChromosome Transmission and ReproductionDiego Garcia100% (1)
- Science 8 ReviewerDocument14 paginiScience 8 Reviewerlucel baganoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Document23 pagini620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Jiya PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in AnimalsDocument11 paginiNCERT Exemplar For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in AnimalsVivek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure Gizmo - ExploreLearningDocument3 paginiCell Structure Gizmo - ExploreLearningJigisha SanyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 9th MCQs - BioDocument11 paginiClass 9th MCQs - BioAmit PratapÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 BiologyDocument9 pagini12 BiologysohiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 3rd Edition Bauman Test BankDocument18 paginiMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 3rd Edition Bauman Test BankPaulMartinagbze100% (11)
- Chapter 3Document17 paginiChapter 3Anna CortiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Cell Fundamental Unit of Life YTDocument50 paginiMCQ Cell Fundamental Unit of Life YTAaryan PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer:a Explanation: Chorion Is One of The Membranes That Surround The Fetus While It Is Still Being FormDocument7 paginiAnswer:a Explanation: Chorion Is One of The Membranes That Surround The Fetus While It Is Still Being FormDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prenatal Development, Birth, and The Newborn Baby: Multiple ChoiceDocument28 paginiPrenatal Development, Birth, and The Newborn Baby: Multiple ChoiceTamarix76Încă nu există evaluări
- International Indian School, Riyadh: General InstructionsDocument22 paginiInternational Indian School, Riyadh: General InstructionsAltaf Hussain KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch54Document16 paginiBio7 ch54freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch52Document18 paginiBio7 ch52freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch51Document16 paginiBio7 ch51freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch49Document15 paginiBio7 ch49freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch12Document18 paginiBio7 ch12Neil KoshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch13Document17 paginiBio7 ch13freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch11Document14 paginiBio7 ch11freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch07Document18 paginiBio7 ch07freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch08Document21 paginiBio7 ch08freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio7 ch05Document22 paginiBio7 ch05freezo1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Islam and ScienceDocument10 paginiIslam and ScienceAhmed ZaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank for Before We Are Born 8th EditionDocument13 paginiTest Bank for Before We Are Born 8th EditionTofik MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Face &it's Applied AspectsDocument95 paginiDevelopment of Face &it's Applied AspectsHansa KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Third Week of DevelopmentDocument57 paginiThe Third Week of DevelopmentStanley OdiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickDocument21 paginiDevelopmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickHoney krishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Embryology 2022Document130 paginiGeneral Embryology 2022KAMAL ALSOFIANYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocument20 paginiStages of Prenatal DevelopmentKimay DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Muscular System AtfDocument3 paginiDevelopment of Muscular System AtfKim Sa-buÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology Summary NotesDocument6 paginiEmbryology Summary Notessayeda.raza24Încă nu există evaluări
- Intra Embryonic MesodermDocument26 paginiIntra Embryonic MesodermEniola DaramolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extraembryonic MembraneDocument41 paginiExtraembryonic MembraneDangkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology ObgDocument36 paginiEmbryology ObgsamrusangaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Embryology Lecture GuideDocument23 paginiIntroduction to Embryology Lecture GuideAldrin Hardy PabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Pelvis and MeasurementsDocument21 paginiFemale Pelvis and MeasurementsBia KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Enhancement Biology Basics Part 1Document6 paginiPerformance Enhancement Biology Basics Part 1Tera Bap50% (2)
- Wilberding, James - Forms, Souls, and Embryos (2016, Routledge)Document243 paginiWilberding, James - Forms, Souls, and Embryos (2016, Routledge)Cuca BeludoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Three Villus TypesDocument12 paginiThe Three Villus TypesMarhina Asarabi MukimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care, 4th Edition, by Whitaker, ISBN-10: 1439059438, ISBN-13: 9781439059432Document36 paginiTest Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care, 4th Edition, by Whitaker, ISBN-10: 1439059438, ISBN-13: 9781439059432meghantaylorxzfyijkotm100% (12)
- Jurnal GemelliDocument7 paginiJurnal GemelliIka SeptianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL108L-YA Ex6 PDFDocument7 paginiBIOL108L-YA Ex6 PDFIsabille MusongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 38 Animal DevelopmentDocument77 paginiChapter 38 Animal Developmentmaria banunaekÎncă nu există evaluări