Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
6 - Design of Solar Charge Controller
Încărcat de
Nyanphyo Aung0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
95 vizualizări6 paginidesign
Titlu original
6_Design of Solar Charge Controller
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdesign
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
95 vizualizări6 pagini6 - Design of Solar Charge Controller
Încărcat de
Nyanphyo Aungdesign
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 6
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 256
Design of Solar Charge Controller by the use of
MPPT Tracking system
Ms. Arjyadhara Pradhan
1
, Dr S.M Ali
2
, Mr. Sthita Prajna Mishra
3
Mr. Subhranga Mishra
4
Asst. Professor
1
, Associate Professor
2
, Lecturer
3
, Research Scholar
4
School of Electrical Engineering, KIIT University, Patia , Bhubaneshwar-751024,Odisha,India
Abstract: When a solar PV system is deployed for practical applications, the IV Charateristics keeps on changing with insolation and
temperature. In order to receive maximum power the load must adjust itself and accordingly to track maximum power point. The voltage
at which PV module can produce maximum power is called maximum power point (or peak power voltage). Maximum power varies
with solar radiation, ambient temperature and solar cell temperature. Typical PV module produces power with maximum power voltage of
around 17 V when measured at a cell temperature of 25C, it can drop to around 15 V on a very hot day and it can also rise to 18 V on a
very cold day. Solar charge controllers are having wide range applications like in street lighting, water pumping system and many other
industrial purposes. This paper mainly gives idea about designing of solar charge controller using maximum power point tracking system.
Keywords: MPPT, PSoC, Leonics, LED
I. INTRODUCTION
The major principle of MPPT is to extract the maximum available power from PV module by making them operate at the most efficient
voltage (maximum power point). MPPT checks output of PV module, compares it to battery voltage then fixes what is the best power that
PV module can produce to charge the battery and converts it to the best voltage to get maximum current into battery. It can also supply
power to a DC load, which is connected directly to the battery. MPPT is most effective under these conditions:
1. Cold weather, cloudy or hazy days: Normally, PV module works better at cold temperatures and MPPT is utilized to extract
maximum power available from them.
2. When battery is deeply discharged: MPPT can extract more current and charge the battery if the state of charge in the battery is
lowers
II. MPPT SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER
A MPPT solar charge controller is the charge controller embedded with MPPT algorithm to maximize the amount of current going into
the battery from PV module. MPPT is DC to DC converter which operates by taking DC input from PV module, changing it to AC and
converting it back to a different DC voltage and current to exactly match the PV module to the battery.
Examples of DC to DC converter are
Boost converter is power converter which DC input voltage is less than DC output voltage. That means PV input voltage is less than the
battery voltage in system.
Buck converter is power converter which DC input voltage is greater than DC output voltage. That means PV input voltage is greater
than the battery voltage in system.
MPPT algorithm can be applied to both of them depending on system design. Normally, for battery system voltage is equal or less than 48
V, buck converter is useful. On the other hand, if battery system voltage is greater than 48 V, boost converter should be chosen.
MPPT solar charge controllers are useful for off-grid solar power systems such as stand-alone solar power system, solar home
system and solar water pump system, etc.
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 257
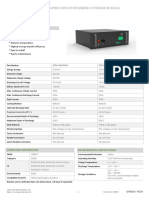
Fig 1 shows MPPT Solar Charge Controller
III. MAIN FEATURES OF MPPT SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER
Main features of MPPT solar charge controller
In any applications which PV module is energy source, MPPT solar charge controller is used to correct for detecting the
variations in the current-voltage characteristics of solar cell and shown by I-V curve.
MPPT solar charge controller is necessary for any solar power systems need to extract maximum power from PV module; it
forces PV module to operate at voltage close to maximum power point to draw maximum available power.
MPPT solar charge controller allows users to use PV module with a higher voltage output than operating voltage of battery
system.
For example, if PV module has to be placed far away from charge controller and battery, its wire size must be very large to
reduce voltage drop. With a MPPT solar charge controller, users can wire PV module for 24 or 48 V (depending on charge
controller and PV modules) and bring power into 12 or 24 V battery system. This means it reduces the wire size needed while
retaining full output of PV module.
MPPT solar charge controller reduces complexity of system while output of system is high efficiency. Additionally, it can be
applied to use with more energy sources. Since PV output power is used to control DC-DC converter directly.
MPPT solar charge controller can be applied to other renewable energy sources such as small water turbines, wind-power
turbines, etc.
IV. HOW TO CHOOSE MPPT SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER FOR PV MODULE
PV Manufactures Model Wp Vpm Ipm Isc Voc
SHARP
NE-78T1 78 17.1 4.57 5.08 21.4
ND-130T1 130 17.4 7.48 8.09 22
Kaneka
GPA 64 68 0.94 1.17 92
SANYO HIP-180B2 190 54 3.33 3.15 66.4
Bangkok Solar BS 40 40 44.8 0.9 1.16 62.2
Table 1: Specifications of PV modules separated by manufacturers
Standard Test Condition: Irradiance = 1000 W/m2, Cell temperature = 25C, Air mass = 1.5
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 258
V. SETTING OF SYSTEM CONFIGURATION OF MPPT SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER
Fig 2: Shows system configuration of MPPT solar Charge Controller
VI. USE OF SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER IN LIGHTING APPLICATIONS
Solar panels are being increasingly used in street lighting applications to make for environment friendly designs by reducing the
dependency on conventional energy. The use of High Brightness LEDs (HB-LEDs) for illumination in streetlights further increases their
energy efficiency. These systems employ lead acid batteries that get charged by solar panels during the day. The energy from the batteries
is then used to drive the LEDs in the night. Solar panels consist of photovoltaic cells that use light energy from the sun to generate
electricity through photovoltaic effect. Maximum Power Point Tracking, referred to as MPPT, is an electronic system that operates the
photovoltaic modules in solar panels to produce maximum power. MPPT varies the electrical operating point of the modules and enables
them to deliver maximum available power. MPPT can be used in conjunction with a mechanical tracking system, but the two systems are
completely different. MPPT Solar Charge Controller is a battery charger and load controller with integrated LED driver, which features a
smart tracking algorithm that maximizes energy harvest from solar panels. It is designed using Power PSOC and uses the devices
integrated hysteretic controllers, its dedicated modulators, and PSOC core to implement the MPPT smart tracking algorithm, as well as the
constant current LED driver circuit
Figure 3 shows a picture of a solar panel powered street light with high brightness LEDs.
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 259
Cypress Solution CY8CLED04D01 Power PSoC
Features MPPT Algorithm for optimized battery charging,
Buck and boost driver for LED applications
Input Solar panel open circuit voltage 21 V
Short circuit current 7 A
Battery Rating 12 V Lead acid
Maximum charging current 9.5 A
Boost Driver Rating Voltage 40 V,
Current 1 A
Floating Load Buck
Driver Rating
Voltage 8 V,
Current 1 A
Table 2 below shows the specifications of the MPPT Solar Charge Controller Reference Design
The block diagram of the integrated solar charger and LED driver is shown in Figure 4. Power delivered by the solar panel is converted to
a voltage level that can drive charging current into the battery. Power PSoC generates the necessary control signal to drive a synchronous
buck converter that converts the solar panel power to charge the battery. The MPPT algorithm embedded in the Power PSoC takes voltage
and current feedback from the panel and adjusts the control signals to operate the panel at its peak power. The Power PSoC also monitors
the battery charging process and provides status information based on battery the application described below also integrates two channels
of LED drivers. The first channel is configured in a floating load buck topology rated at 8V, 1A. The second channel is confi gured in a
boost topology rated at 40V, 1A. The user can select between these two LED driver channels to drive LEDs with power from the batteries.
The firmware in the attached code example is designed to operate one LED driver channel at a time. The solar charge controller also has
board-level protection features that protect the board from battery short circuits, battery open, and battery/panel reverse connections.
Figure 4. MPPT Solar Charge Controller Block Diagram
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 260
VII. CONCLUSION
Different MPPT techniques discussed earlier will suit different applications. For example, in space satellites and orbital stations that
involve large amount of money, the costs and complexity of the MPP tracker are not as important as its performance and reliability. The
tracker should be able to continuously track the true MPP in minimum amount of time and should not require periodic tuning. In this
paper we have seen how solar charge controller is designed by the use of MPPT System and how the charge controller is used in street
lighting system.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to thank School of Electrical Engineering, KIIT University for providing necessary experimental platform for research and analysis for the completion of the
paper.
References:
[1] "Invert your thinking: Squeezing more power out of your solar panels". scientificamerican.com. Retrieved 2011-06-09.
[2] "MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING". qwiki.com. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
[3] "Maximum Power Point Tracking". zone.ni.com. Retrieved 2011-06-18.
[4] "ADVANCED ALGORITHM FOR MPPT CONTROL OF PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM". Solar buildings.ca. Retrieved 2011-06-18.
[5] Comparative Study of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms. doi:10.1002/pip.459.
[6] "Performances Improvement of Maximum Power Point Tracking Perturb and Observe Method". Actapress.com. Retrieved 2011-06-18.
[7] "Evaluation of Micro Controller Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods Using dSPACE Platform". itee.uq.edu.au. Retrieved 2011-06-18.
[8] "MPPT ALGORITHMS". powerelectronics.com. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
[9] "Energy comparison of MPPT techniques for PV Systems". wseas.us. Retrieved 2011-06-18.
[10] Khan, M.I. Dept. of Electr. & Electron. Eng., Bangladesh Univ. of Eng. & Technol., Dhaka, Bangladesh Islam, M.R. ; Mozumder, M.Z. ; Rahman,
K.M. Photovoltaic maximum power point tracking battery charge controller E-ISBN : 978-984-33-0616-6 Print ISBN: 978-1-4244-6012-0
Biography
,
Ms Arjyadhara Pradhan is working as Assistant Professor, in school of Electrical Engineering KIIT University; Bhubaneswar .She has
done B.TECH from KIIT University in 2009. Presently She is continuing her Master degree in Power and Energy System under same
University .Her area of Research and development is Renewable Energy mainly in solar energy. She has published about 10 papers in
National and international conference and 10 International journals. She is the life member of Solar Energy Society of India , Indian
science Congress Association and life member of Indian Society of Technical Education.
ISSN: 2278 - 8875
International J ournal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, October 2012
Copyright to IJAREEIE www.ijareeie.com 261
Dr S M Ali is Associate Professor in Electrical Engineering of KIIT University Bhubaneswar. He received his DSc & Ph.D. in Electrical
Engineering from International university, California, USA in 2008 & 2006 respectively. He had done M.Tech from Calcutta University.
His area of research in the field of Renewable Energy both Solar & Wind Energy. He had also guided five nos. of Ph. D students in his
research area. He has also presented more than 50 papers in different National & International conferences in the field of Renewable
Energy apart from around 20 nos of paper also published in National and International journals. He has conducted several nos. of
Seminar, Workshop and short term training program for the Faculty members Engineering College, Polytechnic in collaboration with
AICTE, ISTE, MHRD DST, & Ministry of Industries, Govt. of India. He is Vice President of Solar Energy Society of India and Secretary
of Institution of Engineers (India) , Odisha state centre.
Mr.Sthita Prajna Mishra is working as Lecturer in Electrical Engineering, KIIT University, and Bhubaneswar. He has done B.Tech
from KIIT University in 2010.He is continuing his Master degree in Power and Energy System from KIIT University .His area of
Research and development is Renewable Energy mainly in solar and wind hybrid system. He has published 10 papers in national and
international conference He is a life member of SESI and Institute of Engineers in India. He is also the life member of ISTE.
Mr.Subhranga Mishra is working as Research Scholar in Electrical Engineering, KIIT University, and Bhubaneswar. He has done
B.Tech from KIIT University in 2010.He is continuing his Master degree in Power and Energy System from KIIT University .His area of
Research and development is Renewable Energy mainly in solar and wind hybrid system. He is a life member of SESI and Institute of
Engineers in India.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Micro Mechatronics and Micro ActuatorsDocument12 paginiMicro Mechatronics and Micro ActuatorsAlioune Badara DioufÎncă nu există evaluări
- EG Actuator Tester Models 8909-041 and 8909-059: Product Manual 55021 (Revision F, 10/2021)Document28 paginiEG Actuator Tester Models 8909-041 and 8909-059: Product Manual 55021 (Revision F, 10/2021)MussardÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Efficient Regenerative Braking System Based On Battery Supercapacitor For Electric Hybrid and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles With BLDC MotorDocument15 paginiAn Efficient Regenerative Braking System Based On Battery Supercapacitor For Electric Hybrid and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles With BLDC MotorsathishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photovoltaic Agricultural Internet of Things TowarDocument14 paginiPhotovoltaic Agricultural Internet of Things TowarvvipmembersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab01 - Routing Concepts and Static RoutingDocument8 paginiLab01 - Routing Concepts and Static RoutingPham Van XuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date: 11 March 2021 MR Rahul Sharma Rze2 Mahavi Enclave New Delhi New Delhi 110045 Delhi Policy No.: 16811926 Mobile No.: Xxxxxx3693Document6 paginiDate: 11 March 2021 MR Rahul Sharma Rze2 Mahavi Enclave New Delhi New Delhi 110045 Delhi Policy No.: 16811926 Mobile No.: Xxxxxx3693Rahul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS/Consolidated Premium Statement /ver 2.1/jan 2021: A Reliance Capital CompanyDocument1 paginăPS/Consolidated Premium Statement /ver 2.1/jan 2021: A Reliance Capital CompanyJhansi RokatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Udemy - Test 1Document41 paginiUdemy - Test 1vladyslava antosiukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unesco-Eolss Sample Chapters: Introduction To Quantum ChaosDocument10 paginiUnesco-Eolss Sample Chapters: Introduction To Quantum ChaosJohan David GarzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AccuraCap PMSDocument35 paginiAccuraCap PMSAnkur100% (1)
- Receipt SummaryDocument1 paginăReceipt SummaryKamna VaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12420/gomti Express Second Sitting (2S) : WL WLDocument2 pagini12420/gomti Express Second Sitting (2S) : WL WLMohd HashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- AR CyberDocument6 paginiAR Cyberchernet kebedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANUEL RIDE 62s ALL LANGUAGESDocument76 paginiMANUEL RIDE 62s ALL LANGUAGESJoão GonçalvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1229DUSM0100 G Speak Installation Manual 07042015 NG WebDocument42 pagini1229DUSM0100 G Speak Installation Manual 07042015 NG WebKyle Sean YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz Practice 1 - AnswersDocument5 paginiQuiz Practice 1 - AnswersJawad KaramatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gamma GroupDocument10 paginiGamma GroupYaromirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Namma Kalvi 6th Tamil Sura Sample Guide Term 3 218558Document23 paginiNamma Kalvi 6th Tamil Sura Sample Guide Term 3 218558Radhanagarathinam NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ugb 252Document7 paginiUgb 252Abdumalik KakhkhorovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget 224: PremiumDocument25 paginiBudget 224: PremiumHiralal patilÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGNOU Common Prospectus - July 2023 v.L.1.1 - Common-Prospectus-EnglishDocument365 paginiIGNOU Common Prospectus - July 2023 v.L.1.1 - Common-Prospectus-EnglishMohd KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMLR Eoi PDFDocument6 paginiGMLR Eoi PDFdheeraj sehgalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 52402dep-Notice 11032020Document222 pagini52402dep-Notice 11032020Monglafru MogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxiinc PDFDocument2 paginiOxiinc PDFChandan kumar singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- PO 4600062173 SDBiosensorHealthcarePvtLtdDocument7 paginiPO 4600062173 SDBiosensorHealthcarePvtLtdChinna ThambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Diffence MicromouseDocument51 paginiMid Diffence Micromouseshankar bhandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- BREB Supplementary 4th EditionDocument140 paginiBREB Supplementary 4th Editionkazi ahadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini ProjectDocument27 paginiMini ProjectAnju MuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Strategy (Archive of Openstrate - Gy)Document46 paginiOpen Strategy (Archive of Openstrate - Gy)Santosh mudaliarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kwiatkowski 2016Document15 paginiKwiatkowski 2016Fadwa MeguenniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Implementation of A PI-MPPT Based Buck-Boost ConverterDocument6 paginiDesign and Implementation of A PI-MPPT Based Buck-Boost ConverterWesley de PaulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Instructions: CD Stereo System SC-MAX370Document20 paginiOperating Instructions: CD Stereo System SC-MAX370Percy Mamani SucasacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dividend Policy VeddantaDocument14 paginiDividend Policy VeddantaVivek rathodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reg 114339Document35 paginiReg 114339Western CPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultraconductor ReportDocument25 paginiUltraconductor Reportamit patilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Engineering For Design of Liquid (001-122)Document122 paginiModern Engineering For Design of Liquid (001-122)Misha's Kitchen And OtherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry Summary NotesDocument98 paginiBiochemistry Summary NotesPatricia EspirituÎncă nu există evaluări
- LRZ050, Kit PSK3 - 7 C-SJ12-15, Experts Solidaires 06 2022 PDFDocument3 paginiLRZ050, Kit PSK3 - 7 C-SJ12-15, Experts Solidaires 06 2022 PDFMamadou Traore100% (1)
- As 129959 Iv3-G500ca Iv3-G500ma Iv3-G600ca Im 96M17460 WW GB 2102 1Document2 paginiAs 129959 Iv3-G500ca Iv3-G500ma Iv3-G600ca Im 96M17460 WW GB 2102 1AfifNasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer Internship Training Report: For The MBA Degree (2020-2022)Document50 paginiSummer Internship Training Report: For The MBA Degree (2020-2022)Soham DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Work: Indian Financial System (Ifs)Document20 paginiProject Work: Indian Financial System (Ifs)Vijetha MadhavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- STT - Group 9Document7 paginiSTT - Group 9ganeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sean White CV 10-2012Document2 paginiSean White CV 10-2012DangQuangTrungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pavithra DDocument53 paginiPavithra Dshubham singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Development of Robot Arm With Smartphone Control Using ArduinoDocument8 paginiThe Development of Robot Arm With Smartphone Control Using Arduinodavid frybergÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factsheet GSDocument18 paginiFactsheet GSbshriÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUN2000-50KTL-M3 EN50549-1 Cert - Intertek - 20221018Document2 paginiSUN2000-50KTL-M3 EN50549-1 Cert - Intertek - 20221018Stefan BusoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rahul R Nair - CV CMEDocument4 paginiRahul R Nair - CV CMERahul NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- SunFields Specification NAF121-128-135GK ENGDocument2 paginiSunFields Specification NAF121-128-135GK ENGkhemrajmahadewÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMM 72-00-00, STORAGE 001 PreservationDocument45 paginiLMM 72-00-00, STORAGE 001 PreservationKarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edit 430Document101 paginiEdit 430nisp cokeovensÎncă nu există evaluări
- DTDC Courier Cargo LTDDocument3 paginiDTDC Courier Cargo LTDDeepakkmrgupta786Încă nu există evaluări
- IP Unit 5Document24 paginiIP Unit 5PRATHAM RUHELAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 PB PDFDocument15 pagini2 PB PDFMusnaini UlikÎncă nu există evaluări
- OD126164812918973000Document1 paginăOD126164812918973000Manoj SirsatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bmi - Unit1Document65 paginiBmi - Unit1SanathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy106.1 RotationDocument3 paginiPhy106.1 RotationFlorence Arielle SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cooled Mini Chiller AMAC-C-2009Document180 paginiAir Cooled Mini Chiller AMAC-C-2009ADV C&L Venture S/BÎncă nu există evaluări
- 54 KkksDocument3 pagini54 KkksAndi YassaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Electric Powered Hybrid VehicleDocument4 paginiSolar Electric Powered Hybrid VehicleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title: Instructions For UseDocument14 paginiTitle: Instructions For UseNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Water Distribution System Using PLC: Abstract - The Increasing Population and Thus The WideDocument4 paginiAutomatic Water Distribution System Using PLC: Abstract - The Increasing Population and Thus The WideNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Harmonic Reduction by Using Passive Harmonic FiltersDocument6 paginiAnalysis of Harmonic Reduction by Using Passive Harmonic FiltersNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Filter Installation For Harmonic Mitigation in Residential Distribution SystemsDocument6 paginiPassive Filter Installation For Harmonic Mitigation in Residential Distribution SystemsNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arduino Micro Controller Processing For Everyone Part 1Document114 paginiArduino Micro Controller Processing For Everyone Part 1fashazee6750100% (1)
- 3044 Manuscript 10459 1 10 20150819 PDFDocument6 pagini3044 Manuscript 10459 1 10 20150819 PDFNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Boiler Automation Using Programmable Logic ControllerDocument6 paginiSteam Boiler Automation Using Programmable Logic ControllerNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using PWM Output As A Digital-To-Analog Converter On A TMS320F280x Digital Signal ControllerDocument32 paginiUsing PWM Output As A Digital-To-Analog Converter On A TMS320F280x Digital Signal ControllerAtakan OzturKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 002Document13 pagini002ajith.ganesh2420Încă nu există evaluări
- LAB 10 Introduction To Ladder Logic ProgrammingDocument10 paginiLAB 10 Introduction To Ladder Logic ProgrammingNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- AllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideDocument310 paginiAllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideNguyen Chien100% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Water Quality Control System Turku Nov 2015Document42 paginiWater Quality Control System Turku Nov 2015Nyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6658 ImportanceCoordinated KH 20140729 Web2Document12 pagini6658 ImportanceCoordinated KH 20140729 Web2Nyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ueb5 Sol PDFDocument5 paginiUeb5 Sol PDFNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- SolarDocument6 paginiSolarNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijetae 0413 102 PDFDocument5 paginiIjetae 0413 102 PDFNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- AllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideDocument310 paginiAllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideNguyen Chien100% (1)
- 105 Icpgae58 NCDocument7 pagini105 Icpgae58 NCNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 075366r02ZB AFG-ZigBee Cluster Library Public Download Version PDFDocument442 pagini075366r02ZB AFG-ZigBee Cluster Library Public Download Version PDFadryano85Încă nu există evaluări
- 42 Finalreport PDFDocument8 pagini42 Finalreport PDFNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 DigitalFiltersDocument8 pagini12 DigitalFilterstienledhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iir PZDocument13 paginiIir PZNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 42 Finalreport PDFDocument8 pagini42 Finalreport PDFNyanphyo AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIC For BeginnersDocument147 paginiPIC For Beginnersapi-3695801100% (45)
- Nissan Cefiro Wiring Ecu AirflowDocument60 paginiNissan Cefiro Wiring Ecu AirflowKen Eng100% (5)
- Viva-Voce:: Scott Connection of TransformersDocument6 paginiViva-Voce:: Scott Connection of TransformersSheri Abhishek ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Locomotive System PDFDocument2 paginiDC Locomotive System PDFRizki Fajar NovantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epcos Reactors CatDocument6 paginiEpcos Reactors Catceplmum_146137904100% (1)
- RS485 - MODBUS Communication Protocol - Solis InvertersDocument47 paginiRS485 - MODBUS Communication Protocol - Solis InvertersAnh Đinh VươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Meter GS-35B Amplifier ConstructionDocument3 pagini6 Meter GS-35B Amplifier Constructiontheodorakis017781Încă nu există evaluări
- ICC Yard - Rathmalana-Model PDFDocument1 paginăICC Yard - Rathmalana-Model PDFsajeevi piumikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C250 D5Document2 paginiC250 D5ahmedalgaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17pepe09 Distributed Generation and Microgrid SyllabusDocument1 pagină17pepe09 Distributed Generation and Microgrid SyllabusArivumani100% (1)
- CAVSP ChecklistDocument11 paginiCAVSP ChecklistJPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bussmann DFJ Fuse DatasheetDocument4 paginiBussmann DFJ Fuse DatasheetlarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signal ConditioningDocument7 paginiSignal ConditioningWild BotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Multimeter Fluke 101 - User MAnualDocument28 paginiDigital Multimeter Fluke 101 - User MAnualjaymuscatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 41 +Rectifier+Unit (FDR-Series) +Manual (영문)Document14 pagini41 +Rectifier+Unit (FDR-Series) +Manual (영문)nguyenbauhuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supercap EM Series 7.5KWhDocument2 paginiSupercap EM Series 7.5KWhRamon CuevasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asc LB Ds 3040Document2 paginiAsc LB Ds 3040Francisco MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMV-SERIES - Cabinet Filter FansDocument3 paginiPMV-SERIES - Cabinet Filter Fansluat1983Încă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Data Symbol Units Value: Lo-Cog DC Servo GearmotorDocument2 paginiAssembly Data Symbol Units Value: Lo-Cog DC Servo GearmotorJuan De los PalotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nomi CVDocument2 paginiNomi CVFozia AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accenture Electric Vehicle Market AttractivenessDocument8 paginiAccenture Electric Vehicle Market AttractivenessXiaoming HuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRUITENDocument3 paginiBRUITENGeopas GreeceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee Objective ReeDocument37 paginiEe Objective ReeErven Martinez100% (7)
- User Manual: DIN Rail Smart Energy Meter For Single and Three Phase Electrical SystemsDocument2 paginiUser Manual: DIN Rail Smart Energy Meter For Single and Three Phase Electrical SystemsAnggara KusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerostar Maintenance Manual ATA-74-IgnitionDocument30 paginiAerostar Maintenance Manual ATA-74-IgnitionNsafetyalwaysoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Brushless DC Motor Design For An Aircraft Electro-Hydraulic Actuation SystemDocument6 paginiA Brushless DC Motor Design For An Aircraft Electro-Hydraulic Actuation Systemrenyo1Încă nu există evaluări
- Elec Wiring Regs 2007 Rev 01Document240 paginiElec Wiring Regs 2007 Rev 01Akhtar Abbas Syed100% (2)
- Product Datasheet Product Datasheet DP VAL 1200 20 W 4000 K IP65Document5 paginiProduct Datasheet Product Datasheet DP VAL 1200 20 W 4000 K IP65Catalin DulceataÎncă nu există evaluări
- PQ MVF Cutsheet-Secovi 2019 PQGlobalDocument2 paginiPQ MVF Cutsheet-Secovi 2019 PQGlobalangelpadronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Result and Plotting of Graph:: Measuring Capacitor Voltage V/s Gap SpacingDocument4 paginiResult and Plotting of Graph:: Measuring Capacitor Voltage V/s Gap SpacingSumit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study of Challenges For Fuse Link Protection in The New Generations of Environmentally Friendly VehiclesDocument9 paginiA Study of Challenges For Fuse Link Protection in The New Generations of Environmentally Friendly Vehiclesjk KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Protn Philosophy&settingsDocument52 paginiGen Protn Philosophy&settingsRK KÎncă nu există evaluări