Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
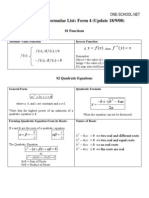
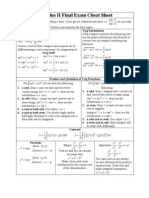
Coplex Number Formulas
Încărcat de
Mohan KhedkarDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Coplex Number Formulas
Încărcat de
Mohan KhedkarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Formulas to remember
1 Complex numbers.
Let z = x + iy be a complex number.
1. The conjugate z = x iy.
The real part Re(z) = x =
z+z
2
.
The imaginary part Im(z) = y =
zz
2i
.
The norm |z| =
zz =
x
2
+ y
2
.
2. The reciprocal
1
z
=
xiy
x
2
+y
2
.
3. The direction from 0 (for a non zero z)
z
|z|
.
4. The Euler representation. z = r exp(i) where r = |z| and = Arg(z) = arctan(y/z).
The angle can be replaced by any angle in the set arg(z) = {Arg(z) + 2n|n ZZ}.
2 Finite series formulas.
1. Arithmetic series.
a + (a + d) + + (a + (n 1)d) =
n
1
(a + (i 1)d) =
n(2a + (n 1)d)
2
.
2. Geometric series formula.
a + ar + ar
n1
=
n
1
ar
i1
= a
1 r
n
1 r
.
3. Telescoping series formula. If g(x) = f(x) f(x 1), then
n
1
g(i) = f(n) f(0).
4. Sums of powers.
(a)
n
1
1 = n.
1
(b)
n
1
i =
n(n + 1)
2
.
(c)
n
1
i
2
=
n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
6
.
(d)
n
1
i
3
=
n
2
(n + 1)
2
4
.
(e)
n
1
i
4
=
n(n + 1)(2n + 1)(3n
2
+ 3n 1)
30
.
3 Power series
1. Geometric series
0
ax
i
= a + ax + ax
2
+ =
a
1 x
where |x| < 1 .
2. Exponential series
exp(x) =
0
x
i
= 1 + x +
x
2
2!
+ +
x
n
n!
+ for all x .
3. Basic Trigonometric series
sin(x) =
0
(1)
i
x
2i+1
(2i + 1)!
= x
x
3
3!
+
x
5
5!
for all x .
cos(x) =
0
(1)
i
x
2i
(2i)!
= 1
x
2
2!
+
x
4
4!
for all x .
4. Generalized Binomial series
(1 + x)
n
=
0
n
C
i
x
i
=
0
(n)(n 1) (n i + 1)
i!
x
i
where |x| < 1 or n is a non negative integer and x is any complex number.
2
5. Log series
log(1 + x) = x
x
2
2
+
x
3
3
+ + (1)
n
x
n+1
n + 1
+ where x is real with |x| < 1.
6. Arctan series
arctan(x) = x
x
3
3
+
x
5
5
+ + (1)
n
x
2n+1
2n + 1
+
where x is real with |x| < 1.
7. Arcsine series
arcsin(x) = x +
1
2
x
3
3
+
(1)(3)
(2)(4)
x
5
5
+
(1)(3)(5)
(2)(4)(6)
x
7
7
+
where x is real with |x| < 1.
4 Geometry.
1. The determinant of a 2 2 matrix:
a b
c d
= ad bc.
2. Cramers Rule: To solve
ax + by = e and cx + dy = f
dene:
=
a b
c d
= ad bc,
x
=
e b
f d
= ed fc and
y
=
a e
c f
= af ec.
If = 0 then the answer is
x =
x
, y =
y
.
If = 0 and at least one of
x
,
y
is non zero then there is no solution.
If all ,
x
,
y
are zero, then there are innitely many solutions provided each of the
two equations has at least one solution.
3. The distance between two points A and B on the real line is d(A, B) = |AB|.
3
4. For two points P
1
(a
1
, b
1
) and P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) in the xy-plane: The distance between the
points is
d(P, Q) =
(a
2
a
1
)
2
+ (b
2
b
1
)
2
.
5. The parametric two point form of the line containing the points P
1
(a
1
, b
1
) and
P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) is
x = a
1
+ t(a
2
a
1
), y = b
1
+ t(b
2
b
1
).
6. The compact parametric two point form of the line is
(x, y) = P
1
+ t(P
2
P
1
) or (x, y) = (1 t)P
1
+ tP
2
.
7. The midpoint of two points A, B is
A+B
2
.
8. The two point form of the equation through the points P
1
(a
1
, b
1
), P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) is
(a
2
a
1
)y (b
2
b
1
)x = a
2
b
1
a
1
b
2
.
9. The slope of the line through two points P
1
(a
1
, b
1
), P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) is
b
2
b
1
a
2
a
1
where the slope is innite and the line is vertical if a
1
= a
2
.
10. The slope intercept form of the line joining P
1
(a
1
, b
1
), P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) is y = mx + c where
m =
b
2
b
1
a
2
a
1
is the slope and
c =
a
2
b
1
a
1
b
2
a
2
a
1
is the y-intercept.
11. If 0 = p is the x intercept and 0 = q is the y-intercept, then the line is:
x
p
+
y
q
= 1.
12. A line parallel to ax + by = c is ax + by = k for some k.
13. A line perpendicular to ax + by = c is bx ay = k for some k.
14. The quadratic function Q(x) = ax
2
+ bx + c has extremum value at x =
b
2a
. The
value is
4acb
2
4a
. It is a maximum if a < 0 and minimum if a > 0.
15. The equation ax
2
+ bx + c = 0 with a = 0 has solutions:
Quadratic Formula. x =
b
b
2
4ac
2a
4
16. The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is
(x h)
2
+ (y k)
2
= r
2
.
17. For the circle
x
2
+ y
2
+ ux + vy = w
the center is (u/2, v/2) and radius is
w +
u
2
4
+
v
2
4
.
18. A parametric form of the circle x
2
+ y
2
= r
2
is:
(x, y) =
r
1 m
2
1 + m
2
, r
2m
1 + m
2
where m is the parameter.
The trigonometry parameterization for the same circle is: z = r exp(i) or
(x, y) = (r cos(), r sin())
with parameter .
19. A circle with diameter P
1
(a
1
, b
1
), P
2
(a
2
, b
2
) is:
(x a
1
)(x a
2
) + (y b
1
)(y b
2
) = 0.
20. The distance from a point (p, q) to the line ax + by + c = 0 is:
|ap + bq + c|
a
2
+ b
2
.
The expression ap + bq + c = 0 if and only if the point lies on the line.
Moreover, the sign of the expression ap + bq + c changes if the point moves from one
side of the line to the other.
5 Trigonometry
1.
tan(x) =
sin(x)
cos(x)
, cot(x) =
cos(x)
sin(x)
, sec(x) =
1
cos(x)
, csc(x) =
1
sin(x)
.
2.
sin
2
(x) + cos
2
(x) = 1, sec
2
(x) = 1 + tan
2
(x), csc
2
(x) = 1 + cot
2
(x).
3.
sin(x + y) = sin(x) cos(y) + cos(x) sin(y).
5
4.
cos(x + y) = cos(x) cos(y) sin(x) sin(y).
5.
tan(x + y) =
tan(x) + tan(y)
1 tan(x) tan(y)
.
6.
cos(x) = cos(x), sin(x) = sin(x).
7.
cos(2x) = cos
2
(x) sin
2
(x) = 2 cos
2
(x) 1 = 1 2 sin
2
(x).
8.
sin(2x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x).
9.
cos(
x
2
) =
1 + cos(x)
2
.
sin(
x
2
) =
1 cos(x)
2
.
The signs need to be xed by the position of the locator point P(
t
2
).
10.
Sine Law.
sin(A)
a
=
sin(B)
b
=
sin(C)
c
11.
Cosine Law. a
2
= b
2
+ c
2
2bc cos(A)
6 Derivative Formulas
1. If c is a constant, then D
x
(c) = 0. Moreover, D
x
(cy) = cD
x
(y).
2. Sum Rule.
D
x
(y + z) = D
x
(y) + D
x
(z).
3. Power Rule. For any real n,
D
x
(y
n
) = ny
n1
D
x
(y).
As a special case:
D
x
(x
n
) = nx
n1
.
6
4. Product Rule.
D
x
(yz) = D
x
(y)z + yD
x
(z).
5. Quotient Rule.
D
x
y
z
=
D
x
(y)z yD
x
(z)
z
2
.
6. Chain Rule.
D
x
(f(g(x)) = f
(g(x))g
(x).
7. Linear approximation formula: Linear approximation to f(x) at x = a is:
L(x) = f(a) + f
(x)(x a).
8. Newtons Method for nding a root.
Start with some convenient guess x
0
. This is the current guess.
If x
n
is the current guess then the new current guess shall be
x
n+1
= x
n
f(x
n
)
f
(x
n
)
.
Stop when successive current guesses are close to each other (within the set
accuracy level) or when the value of the function is suciently close to zero
(within the set accuracy).
7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument7 paginiEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001Încă nu există evaluări
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 paginiMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFDocument16 paginiSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Application of Derivative ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEDocument15 paginiApplication of Derivative ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (1)
- Essential FormulaeDocument16 paginiEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Algebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesDocument20 paginiAlgebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesHiren Mistry100% (1)
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocument8 paginiAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFDocument15 pagini10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFSri DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument8 paginiActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulacheyenneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsDocument8 paginiIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsSayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocument16 paginiMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsDocument6 paginiIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 paginiAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 paginiExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4Încă nu există evaluări
- AIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)Document7 paginiAIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)kishangopi123Încă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To Homework Assignment #2, Math 253Document6 paginiSolutions To Homework Assignment #2, Math 253cool dudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Document13 paginiKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument11 paginiActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formulanirakaru123Încă nu există evaluări
- Math H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteDocument15 paginiMath H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteAmeena LundquistÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 paginiHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Geometry & CalculusDocument69 paginiAnalytic Geometry & CalculusanonreteeÎncă nu există evaluări
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 paginiX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Maths FormulaeDocument10 paginiBasic Maths FormulaeAns DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Document19 paginiAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Syazleen Nabilah AkmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit Jee 2004 Screening MathsDocument10 paginiIit Jee 2004 Screening MathsRahul BadwaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008 Paper 1Document53 pagini2008 Paper 1Aashray KothaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDe la EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDe la EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDe la EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsDe la EverandReal Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)De la EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Încă nu există evaluări
- Circles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandCircles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDe la EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)De la EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Încă nu există evaluări
- Tables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1De la EverandTables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesDe la EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesEvaluare: 1.5 din 5 stele1.5/5 (2)
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27De la EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Încă nu există evaluări
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDe la EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970De la EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)De la EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Încă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programme: Diploma Programme in IF / CM Course: Java Programming Course Code: 1441 Prerequisite: Nil Teaching & Examination SchemeDocument5 paginiProgramme: Diploma Programme in IF / CM Course: Java Programming Course Code: 1441 Prerequisite: Nil Teaching & Examination SchemeMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 4 Aim: Configuration of Linux As DNS Server Theory: Setup Static DNS Servers in Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise Pangolin)Document3 paginiExperiment No. 4 Aim: Configuration of Linux As DNS Server Theory: Setup Static DNS Servers in Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise Pangolin)Mohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMART HELMET USING ARDUINO B.Tech Project ReportDocument52 paginiSMART HELMET USING ARDUINO B.Tech Project ReportMohan Khedkar77% (47)
- Experiment No. 5 Aim: Configuration of Linux As A Firewall, SNAT and DNAT Theory: GUFW Graphical InterfaceDocument3 paginiExperiment No. 5 Aim: Configuration of Linux As A Firewall, SNAT and DNAT Theory: GUFW Graphical InterfaceMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributed Operating Systems: Dionicio D. Gante, Genevev G. Reyes & Vanylive T. GalimaDocument22 paginiDistributed Operating Systems: Dionicio D. Gante, Genevev G. Reyes & Vanylive T. GalimaMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toward A Cloud Operating SystemDocument8 paginiToward A Cloud Operating SystemMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- OODBMS&ORDBMSDocument43 paginiOODBMS&ORDBMSMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDocument52 paginiData Mining: Concepts and TechniquesNiladri DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20: Database System ArchitecturesDocument38 paginiChapter 20: Database System ArchitecturesMohan KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Assignment-01 SEM-II-2016-2017 PDFDocument5 paginiMatlab Assignment-01 SEM-II-2016-2017 PDFfarhanfendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.4 Notes Double-Angle and Half-Angle IdentitiesDocument6 pagini7.4 Notes Double-Angle and Half-Angle IdentitiesLuke Rodriguez100% (1)
- Technical: Nasa TNDocument36 paginiTechnical: Nasa TNMatt GrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sum and Difference FormulasDocument23 paginiSum and Difference FormulasHelpful PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry: John Ryan D. Regalario, ECEDocument51 paginiTrigonometry: John Ryan D. Regalario, ECEErnesto Ayoub Ching100% (1)
- Mathes 3 NotesDocument127 paginiMathes 3 NotesShashi Bhushan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA1505 Tutorial 1 QuestionsDocument4 paginiMA1505 Tutorial 1 QuestionsBilguun BatboldÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALEVEL Error AnalysisDocument16 paginiALEVEL Error AnalysisKizitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4MB0 02 Rms 20110824aDocument11 pagini4MB0 02 Rms 20110824aJehan Somasiri JayathungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C28X Control Law Accelerator Math Library (Clamath) : Module User'S Guide (Sprc993)Document13 paginiC28X Control Law Accelerator Math Library (Clamath) : Module User'S Guide (Sprc993)Cammy KohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0606 s16 Ms 12Document7 pagini0606 s16 Ms 12Devi Santhani Navarathanam PillayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further Applications of TrigonometryDocument70 paginiFurther Applications of TrigonometryJayson IsidroÎncă nu există evaluări
- USDA RUS Bulletin 1724E-150 2003 Unguyed Distribution Poles - Strength RequirementsDocument15 paginiUSDA RUS Bulletin 1724E-150 2003 Unguyed Distribution Poles - Strength Requirementsfabio268Încă nu există evaluări
- MT Chapter 06 PDFDocument6 paginiMT Chapter 06 PDFWilson LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab SImulink Collate 130121Document234 paginiMatlab SImulink Collate 130121Tini100% (1)
- Unit 1Document62 paginiUnit 1Reetesh DabeedeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complex Numbers NotesDocument14 paginiComplex Numbers NotesSo-JungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Series TableDocument3 paginiFourier Series TableAlshargabi MusaabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Sec 8Document4 paginiTrig Sec 8JSPAMoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emath and Amath FormulaDocument21 paginiEmath and Amath FormulaveryveryhappyfeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Inverse Trignometric FunctionDocument5 paginiMath Inverse Trignometric FunctionShaku JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Lesson No. 4 (Circular Functions On Real Numbers)Document30 paginiFinal Lesson No. 4 (Circular Functions On Real Numbers)Genaro Nocete de Mesa, Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Thin Aerofoil Theory NotesDocument42 paginiThin Aerofoil Theory NotesarravindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apple II Applesoft BASIC Programmer's Reference Manual - Volume 2Document134 paginiApple II Applesoft BASIC Programmer's Reference Manual - Volume 2remowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths 3 Compiled A.T.EshwarDocument47 paginiMaths 3 Compiled A.T.Eshwarsvc8670Încă nu există evaluări
- Inmo-2012 Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Mathematical Olympiad (INMO) With SolutionsDocument6 paginiInmo-2012 Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Mathematical Olympiad (INMO) With SolutionsAkshay PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Book Handbook For Spoken MathematicsDocument63 paginiE Book Handbook For Spoken MathematicsVishal AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMA102 Formula 14 Mid SemesterDocument3 paginiSMA102 Formula 14 Mid Semesterace_mehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Calculus Based PhysicsDocument164 paginiNotes On Calculus Based PhysicsThefairman UnkownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Xi Holiday Homework (2019-20) Somerville School, Vasundhara Enclave, Delhi-96 (Commerce Stream-XI B & C)Document5 paginiClass Xi Holiday Homework (2019-20) Somerville School, Vasundhara Enclave, Delhi-96 (Commerce Stream-XI B & C)Krishankant SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări