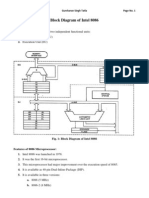
Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Oracle Interview Question
Încărcat de
Atul GalandeDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Oracle Interview Question
Încărcat de
Atul GalandeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Difference between char, varchar, nchar and nvarchar data type in SQL
Server database
What is difference between char and varchar in SQL, followed by nchar and nvarchar, is one of the
popular SQL interview question, and surprisingly not every programmer knows this basic difference. If you go
with name, which you should, than you can figure out that char is a fixed length data type
while varchar should be variable length data type. Though all char, varchar, nchar,
and nvarchar are used to store text or String datathere are subtle differences between them. As I said
char is fixed length, which means a variable or a column e.g.Zipcode char(10) will take only 10 bytes to
store data, including space. On the other hand a varchar variable or column will take variable space,
depending upon data you store + 2 additional bytes for storing length. For example a varchar column
name varchar name(20) will take 6 bytes if you store "Jack" (4 + 2) and 7 bytes if you store "Jones"
(5 + 2). In order to get better performance, you should use char for fixed length columns e.g.zipcode,
where every row are under certain length e.g. 6 for India, and 5 + 4 digits postal codes for USA. On
the other hand, for a variable length column it's better to use varchar data type to save the space, which is
lost in case of char type, if actual data is always way less than capacity. In particular this question is next in
series of couple of popular SQL interview question, e.g. difference between WHERE and HAVING
clause and writing SQL query to join three tables. If you come across any other interesting SQL queries than
you can also share with us, if you don't know answer, we will try to find out together.
NCHAR vs NVARCHAR in SQL
Now let's see difference between nchar and nvarchar data types in
SQL. nchar(n) andnvarchar(n) are similar to there counterpart char and varchar, but they take twice
space than them, to support multilingual languages. Additional space is used to store Unicode character for
eachcharacter, which means 2 bytes for each character, 1 for character + 1 for Unicode. Apart from this
fundamental question, you often see couple of follow-up questions like when to use char and varchar in
database? or more frequently what is difference between char(20) and varchar(20) variables, as they can
only store 20 bytes to store data. Well, main difference is that varchar might take less bytes, depending
upon length of data you store on it. For example if we store "USA" in a variable of
type char(20) and varchar(20) than first will take 20 bytes, while second will take only 5 bytes (3 +2 ),
but performance of char columns are better inSELECT query than varchar columns. Similarly if we
use nchar(20) and nvarchar(20) for storing "SQL" string than first will take 40 bytes (2*20) and
second variable will take 8 bytes (3*2 +2).
Here is a summary of how much space
a char(10), varchar(10), nchar(10) and nvarchar(10) variable takes for storing same data :
declare @cData char(10)
set @cData = 'SQL' -- 10 bytes
set @cData = 'Java' -- 10 bytes
declare @vcData varchar(10)
set @vcData = 'SQL' -- 3 + 2 = 5 bytes
set @vcData = 'Java' -- 4 + 2 = 6 bytes
declare @ncData nchar(10)
set @ncData = 'SQL' -- 10*2 = 20 bytes
set @ncData = 'Java' -- 10*2 = 20 bytes
declare @nvcData varchar(10)
set @nvcData = 'SQL' -- 3*2+2 = 8 bytes
set @nvcData = 'Java' -- 4*2+2 = 10 bytes
Thanks guys, that's all on difference between char and varchar data types in SQL and nchar vs nvarchar. I
hope this knowledge of basic, not only helps in SQL interviews but also choosing right type for your columns
in tables and variables in your stored procedures. Let me know if you have any doubt or question on char or
varchar variables.
T H U R S D A Y , A U G U S T 1 , 2 0 1 3
Difference between WHERE vs HAVING clause in SQL - GROUP BY
Comparison with Example
What is difference between WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL is one of the most popular question asked on SQL
and database interviews, especially to beginners. Since programming jobs, required more than one skill, its quite
common to see couple of SQL Interview questions in Java and .NET interviews. By the way unlike any other
question, not many Java programmers or dot net developers, who is supposed to have knowledge of basic SQL, fail
to answer this question. Though almost half of the programmer says that WHERE is used in any SELECT query,
while HAVING clause is only used in SELECT queries, which contains aggregate function or group by clause, which is
correct. Though both WHERE and HAVING clause is used to specify filtering condition in SQL, there is subtle
difference between them. Real twist comes into interview, when they are asked to explain result of a SELECT query,
which contains both WHERE and HAVING clause, I have seen many people getting confused there. Key point, which is
also main difference between WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL is that, condition specified in WHERE clause is used
while fetching data (rows) from table, and data which doesn't pass the condition will not be fetched into result set, on
the other hand HAVING clause is later used to filter summarized data or grouped data. In short if
both WHERE and HAVING clause is used in a SELECT query with aggregate function or GROUP BY clause, it will
execute before HAVING clause. This will be more clear, when we will see an example
of WHERE, HAVING, JOIN and GROUP BYclause together.
WHERE vs HAVING Clause Example in SQL
In this example of WHERE and HAVING clause, we have two
tables Employee and Department. Employeecontains details of employees e.g. id, name, age, salary and
department id, while Department contains id and department name. In order to show, which employee works for
which department we need to join two tables onDEPT_ID to get the the department name. Our requirement is to find
how many employees are working in each department and average salary of department. In order to
use WHERE clause, we will only include employees who are earning more than 5000. Before executing our query
which contains WHERE, HAVING, and GROUP BY clause, let see data fromEmployee and Department table:
SELECT * FROM Employee;
EMP_ID EMP_NAME EMP_AGE EMP_SALARY DEPT_ID
1 Virat 23 10000 1
2 Rohit 24 7000 2
3 Suresh 25 8000 3
4 Shikhar 27 6000 1
5 Vijay 28 5000 2
SELECT * FROM Department;
DEPT_ID DEPT_NAME
1 Accounting
2 Marketing
3 Sales
SELECT d.DEPT_NAME, count(e.EMP_NAME) as NUM_EMPLOYEE, avg(e.EMP_SALARY) asAV
G_SALARY FROM Employee e,
Department d WHERE e.DEPT_ID=d.DEPT_ID AND EMP_SALARY
> 5000 GROUP BYd.DEPT_NAME;
DEPT_NAME NUM_EMPLOYEE AVG_SALARY
Accounting 1 8000
Marketing 1 7000
Sales 2 8000
From the number of employee (NUM_EMPLOYEE) column you can see that only Vijay who work
for Marketing department is not included in result set because his earning 5000. This example shows that,
condition in WHERE clause is used to filter rows before you aggregate them and then HAVING clause comes in picture
for final filtering, which is clear from following query, now Marketing department is excluded because it doesn't pass
condition in HAVING clause i..e AVG_SALARY > 7000
SELECT d.DEPT_NAME, count(e.EMP_NAME) as NUM_EMPLOYEE, avg(e.EMP_SALARY) asAV
G_SALARY FROM Employee e,
Department d WHERE e.DEPT_ID=d.DEPT_ID AND EMP_SALARY
> 5000 GROUP BYd.DEPT_NAME HAVING AVG_SALARY > 7000;
DEPT_NAME NUM_EMPLOYEE AVG_SALARY
Accounting 1 8000
Sales 2 8000
Difference between WHERE and HAVING in SQL
Apart from this key difference we have seen in this article, here are few more differences
between WHERE and HAVING clause, which is worth remembering and can be used to compare both of them :
1) Apart from SELECT queries, you can use WHERE clause with UPDATE and DELETE clause but HAVING clause can
only be used with SELECT query. For example following query, which involve WHERE clause will work but other which
uses HAVINGclause will not work :
update DEPARTMENT set DEPT_NAME="NewSales" WHERE DEPT_ID=1 ; // works fine
update DEPARTMENT set DEPT_NAME="NewSales" HAVING DEPT_ID=1 ; // error
Incorrect syntax near the
keyword 'HAVING'.: update DEPARTMENT setDEPT_NAME='NewSales' HAVING DEPT_ID=1
2) WHERE clause is used for filtering rows and it applies on each and every row, while HAVING clause is used to filter
groups in SQL.
3) One syntax level difference between WHERE and HAVING clause is that, former is used before GROUP BY clause,
while later is used after GROUP BY clause.
4) When WHERE and HAVING clause are used together in a SELECT query with aggregate function, WHERE clause is
applied first on individual rows and only rows which pass the condition is included for creating groups. Once group is
created, HAVINGclause is used to filter groups based upon condition specified.
That's all on difference between WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL. As I said this is very popular question and you
can't afford not to prepare it. Always remember key difference between WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL,
if WHERE and HAVING clause is used together, first WHERE clause is applied to filter rows and only after
grouping HAVING clause is applied.
Difference between Clustered Index and Non Clustered Index in SQL Server
- Database Interview Question
In SQL Server database there are mainly two types of indexes, Clustered index and Non Clustered index, and
difference between Clustered and Non Clustered index is very important from SQL performance perspective. It is also
one of the most common SQL Interview question, similar to difference between truncate and delete, primary key or
unique key or correlated vs non correlated subquery. For those, who are not aware of benefits of Index or why we
use index in database, they help in making your SELECT query faster. A query with index is sometime 100 times
faster than a query without index, of course depending upon how big your table is, but, you must index on columns
which are frequently used in WHERE clause of SELECT query, or which forms major criterion for searching in
database. For example in Employee database, EmployeeId or EmployeeName are common conditions to find an
Employee in database. As I said, there can be either clustered index or non clustered index in database, former is
used to decide how data is physically stored in disk and that's why there can be only one clustered index in any table.
In this article, we will explore more about both of this indexes and learn some keydifference between clustered and
non clustered index from interview and performance perspective.
2 words on Indexes in SQL
Continuing from first paragraph, Index are used to make search faster in SQL. They are mostly maintained as
balanced tree (BST), where tree traversal gives you performance in order of log(N). In case of clustered index, data
is present in leaf node, so when we run a particular query, which uses clustered index, we can directly find the data
by tree traversal. Query optimizer is a component of database, which decides whether to use an index or not to
execute a SELECT query, or if use index then which one. You can even see, which index is used for executing your
query by looking at query plan, a FULL TABLE SCAN means no index is used and every row of table is scanned by
database to find data, on the other hand INDEX UNIQUE SCAN or INDEX RANGE SCAN suggest use of Index for
finding data. By the Index also has there own disadvantage as they make INSERT and UPDATE query slower and
they also need space. A careful use of index is the best way to go.
Clustered vs Non Clustered Index in SQL
Now we have some idea about what is Index in database and how they work, it's time to look some key differences
between clustered and non clustered index in SQL Server, which is mostly true for other database as well e.g. Oracle
or MySQL.
1) One of the main difference between clustered and non clustered index in SQL Server is that, one table can only
have one clustered Index but It can have many non clustered index, approximately 250. This limitation comes from
the fact clustered index is used to determines how data is stored physically in table. You should be very careful while
choosing clustered index and should use columns which can be queried in range e.g. select * from Employee
where EMP_ID > 20 and EMP_ID < 50. Since clustered index stores data in cluster, related data are stored
together and it's easy for database to retrieve all data in one shot. This further reduces lots of disk IO which is very
expensive operation. Clustered Index is also very good on finding unique values in a table e.g. queries like select
* from Employee where EMP_ID=40; can be very fast if EMP_ID has clustered index on it.
2) Another key difference between Clustered Index and Non Clustered Index in database is that many relational
database including SQL Server by default creates clustered index on PRIMARY KEY constraint, if there is no
clustered index exists in database and a nonclustered index is not specified while declaring PRIMARY
KEY constraint.
3) One more difference between them is that, clustered index contains data i..e rows in there leaf node, as Index
is represented as BST, while nonclustered index contains pointer to data (address or rows) in there leaf node, which
means one more extra step to get the data.
4) By the way there is a misconception that we can only define clustered index with one column, which is not true.
You can create clustered index with multiple columns, known as composite index. For example in Employee table,
a composite index on firstname and lastname can be a good clustered index, because most of the query uses
this as criterion. Though you should try to minimize number of columns in clustered index for better performance in
SQL Server. On related not, while declaring composite index, pay some attention to the order of columns in index,
that can decide which statement will use index and which will not. In fact this is one of the mostly asked question as,
does order of columns in composite index matters.
Last but not the least, pay some attention while creating clustered and non clustered index in database. Create
clustered index for columns which contains unique values, are accessed sequentially, used in range queries and
return large result set. Avoid creating clustered index on columns, which are update frequently because that would
lead rearrangement of rows on disk level, a potentially slow operation.
That's all on difference between clustered and nonclustered index in SQL Server database. Remember that, it's
possible to create clustered index on non PRIMARY KEY column and PRIMARY KEY constraint only creates a
clustered index, if there is not already in database and a nonclustered index is not provided. Key difference is that,
clustered index decides physical sorting or order of data in disk.
F R I D A Y , M A Y 1 0 , 2 0 1 3
Difference between LEFT and RIGHT OUTER Joins in SQL - MySQL Join
example
There are two kinds of OUTER joins in SQL, LEFT OUTER join and RIGHT OUTER join. Main difference
between RIGHT OUTERjoin and LEFT OUTER join, as there name suggest, is inclusion of non matched rows.
Sine INNER join only include matching rows, where value of joining column is same, in final result set, but OUTER join
extends that functionality and also include unmatched rows in final result. LEFT outer join includes unmatched rows
from table written on left of join predicate. On the other hand RIGHT OUTER join, along with all matching rows,
includes unmatched rows from right side of table. In short result of LEFT outer join is INNER JOIN + unmatched rows
from LEFT table and RIGHT OUTER join is INNER JOIN + unmatched rows from right hand side table. Similar to
difference between INNER join and OUTER join, difference between LEFT andRIGHT OUTER JOIN can be better
understand by a simple example, which we will see in next section. By the way joins are very popular in SQL
interviews, and along with classic questions like finding second highest salary of employee, Inner join vs outer join or
left outer join vs right outer join is commonly asked.
LEFT and RIGHT OUTER Join Example in SQL
In order to understand difference between LEFT and RIGHT outer join, we will use once again use
classicalEmployee and Department relationship. In this example, both of these table are connected
using dept_id, which means both have same set of data in that column, let's see data on these two table.
mysql> select * from employee;
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_id | salary |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
| 103 | Jack | 1 | 1400 |
| 104 | John | 2 | 1450 |
| 108 | Alan | 3 | 1150 |
| 107 | Ram | NULL | 600 |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from department;
+---------+-----------+
| dept_id | dept_name |
+---------+-----------+
| 1 | Sales |
| 2 | Finance |
| 3 | Accounts |
| 4 | Marketing |
+---------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
If you look closely, there is one row in employee table which contains NULL, for which there is no entry
in department table. Similarly department table contains a department (row) Marketing ,for which there is no
employee in employee table. When we do a LEFT or RIGHT outer join it includes unmatched rows from left or right
table. In this case LEFT OUTER JOINshould include employee with NULL as department and RIGHT OUTER
JOIN should include Marketing department. Here is example of LEFT and RIGHT OUTER Join in MySQL database :
mysql> select e.emp_id, e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employee e LEFT JOIN department d
on e.dept_id=d.dept_id;
+--------+----------+-----------+
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_name |
+--------+----------+-----------+
| 103 | Jack | Sales |
| 104 | John | Finance |
| 108 | Alan | Accounts |
| 107 | Ram | NULL |
+--------+----------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
As I said unmatched rows, i.e. row with dept_id as NULL has included in final result and dept_name for that row
is NULL, as there is no corresponding row for NULL dept_id in department table. But note
that Marketing department is not included in this result. Now, let's see example of RIGHT OUTER JOIN in MySQL,
this should include Marketingdepartment but leave out employee with NULL dept_id.
mysql> select e.emp_id, e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employee e RIGHT JOIN department
d on e.dept_id=d.dept_id;
+--------+----------+-----------+
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_name |
+--------+----------+-----------+
| 103 | Jack | Sales |
| 104 | John | Finance |
| 108 | Alan | Accounts |
| NULL | NULL | Marketing |
+--------+----------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
As I said, final result set has Marketing department and emp_id, emp_name is NULL in that row because there is
no employee with dept_id=4 in employee table.
Difference between LEFT and RIGHT OUTER JOIN in SQL
In short, following are some notable difference between LEFT and RIGHT outer join in SQL :
1) LEFT OUTER join includes unmatched rows from left table while RIGHT OUTER join includes unmatched rows
from right side of table.
2) Result of LEFT OUTER join can be seen as INNER JOIN + unmatched rows of left able while result of RIGHT
OUTER join is equal to INNER JOIN + unmatched rows from right side table.
3) In ANSI SQL, left outer join is written as LEFT JOIN while right outer join is written as RIGHT JOIN in select sql
statements.
4) In Transact-SQL syntax left outer join is written as *= and right outer join is written as =*, Sybase database
supports both syntax and you can write join queries in both ANSI and T-SQL syntax.
That's all on difference between LEFT and RIGHT OUTER JOIN in SQL. We have seen example of RIGHT and
LEFT join in MySQL database but since we have used ANSI syntax of OUTER joins, it's for other databases e.g.
Oracle, Sybase, SQL Server and PostgreSQL as well. JOIN is a one of the most important and common concept in
SQL and you should be good enough to figure out which rows will be included as a result of JOIN statement before
actually running that SELECT queryagainst any table. Some time erroneous JOIN query can bring loads of data and
potentially may hang your database so beware of it.
Question 1: Oracle version 9.2.0.4.0 what does each number refers to?
Answer : oracle version number refers
9-Major database release number
2-Database Maintenance release number
0-Application server release number
4-Component Specific release number
0-Platform specific release number
Question 2: How do you find current date and time in oracle?
Answer: This is one of the frequently asked Oracle Interview questions. I have seen this question every now and
then. By the waySYSDATE function is used in oracle to find current date and time of operating system on which the
database is running return type of function is DATE
Syntax: SELECT TO_CHAR (SYSDATE, 'MM-DD-YYYY HH24:MI:SS') "Current_Date" FROM DUAL.
Question 3: Write the syntax to find current date and time in format YYYY-MM-DD.
Answer: SELECT TO_CHAR (SYSDATE, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') "Current_Date" FROM DUAL
Question 4: How will you convert a date to char in Oracle give one example
Answer : Similar to previous Oracle Interview question, this is also one of the popular question in various Oracle
Interviews.to_char() function is used to convert date to character we can specify format also in which we want the
output.
SELECT to_char( to_date('11-01-2012', 'DD-MM-YYYY') , 'YYYY-MM-DD') FROM dual;
or
SELECT to_char( to_date('11-01-2012, 'DD-MM-YYYY') , 'DD-MM-YYYY') FROM dual;
Question 5: What is bulk copy or BCP in oracle?
Answer: BCP or bulk copy tool is one type of command line tool for unload data from database came into existence
after oracle 8 .it is used to import or export data from tables and views but it will not copy structure of data same.
Main advantage is fast mechanism for copying data and we can take backup of important data easily.
Question 6: What are the extensions used by oracle reports
Answer : Oracle reports are used to make business enable to provide information of all level within or outside in
secure way.REP file and RDF file extensions are used by oracle report.
Question 7: What is Save Points in Oracle database?
Answer : SAVE POINTS are used to divide a transaction into smaller parts. It enables rolling back part of a
transaction. Maximum of five save points are allowed. Whenever we encounter error we can rollback from the point
where we set our SAVEPOINT.This is useful for multistage transaction and conditional transaction where commit and
rollback depend on certain condition. This is another commonly asked Oracle Interview Question and since save
points are also available in other database e.g. SQL Server, some time Interviewer follow up with differences with
other database as well.
Question 8: How will you convert string to a date in oracle database?
Answer : This Oracle Interview questions is some time asked as follow up of previous Oracle Interview questions
related to converting date to char in Oracle. By the way to_ date function is used to convert string to a date function.
Syntax : to_date(string, format)
Example: to_date('2012/06/12', 'yyyy/mm/dd') It will return June 12, 2012
Question 9: What is hash cluster in Oracle?
Answer : This is one of my favorite Oracle Interview question. Hash cluster is one of the techniques to store the table
in a hash cluster to improve the performance of data retrieval .we apply hash function on the table rows cluster key
value and store in the hash cluster. All rows with the same hash key value are stores together on disk.key value is
same like key of index cluster ,for data retrieval Oracle applies the hash function to the row's cluster key value.
Question 10: What is Snap shot in Oracle database?
Answer : Snapshots are read-only copies of a master table located on a remote node which is periodically refreshed
to reflect changes made to the master table.
Thats all on this list of Oracle Interview questions and answers. This can be a good recap before appearing to any
programming job interview, where questions from Oracle database is expected. You may want to prepare some SQL
Interview question as well along with these Oracle questions, as questions related to SQL query e.g. How to find
second highest salary in SQL or How to find duplicate records in table is quite popular on various Oracle Interviews.
T H U R S D A Y , N O V E M B E R 2 2 , 2 0 1 2
How to join three tables in SQL query MySQL Example
Three table JOIN Example SQL
Joining three tables in single SQL query can be very tricky if you are not good with concept of SQL Join. SQL Joins
have always been tricky not only for new programmers but for many others, who are in programming and SQL for
more than 2 to 3 years. There are enough to confuse someone on SQL JOIN ranging from various types of SQL
JOIN like INNER and OUTER join, LEFT and RIGHT outer join, CROSS join etc. Between all of these fundamentals,
What is most important about Join is, combining multiple tables. If you need data from multiple tables in one SELECT
query you need to use either subquery or JOIN . Most of times we only join two tables
like Employee and Department but some time you may require to join more than two tables and a popular case is
joining three tables in SQL. In case of joining three tables table 1 relates to table 2 and than table 2 relates to table 3.
If you look at closely you find that table 2 is a joining table which contains primary key from both table 1 and table 2.
As I said it can be extremely confusing to understand join of three or more tables. I have found that understanding
table relationship as primary key and foreign key helps to alleviate confusion than the classical matching row
paradigm. SQL Join is also a very popular topic in SQL interviews and there is always been some questions from
Join like Difference between INNER and OUTER JOIN, SQL query with JOIN
e.g.Employee Department relationship and Difference between LEFT and RIGHT OUTER JOIN etc. In short this
is one of the most important topic in SQL both from experience and interview point of view.
Three table JOIN syntax in SQL
Here is a general SQL query syntax to join three or more table. This SQL query should work in all major relation
database e.g. MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQLServer, Sybase and PostgreSQL :
SELECT t1.col, t3.col FROM table1 join table2 ON table1.primarykey = table2.foreignkey
join table3 ON table2.primarykey = table3.foreignkey
We first join table 1 and table 2 which produce a temporary table with combined data from table1 and
table2, which is then joined to table3. This formula can be extended for more than 3 tables to N tables, You just need
to make sure that SQL query should have N-1 join statement in order to join N tables. like for joining two tables we
require 1 join statement and for joining 3 tables we need 2 join statement.
SQL Query to JOIN three tables in MySQL
In order to better understand joining of 3 tables in SQL query let's see an example. Consider popular
example of Employee and Department schema. I our case we have used a link table called Registerwhich
link or relate both Employee to Department. Primary key of Employee table (emp_id) is foriegn key
inRegister and similarly primary key of Department table (dept_id) is foreign key in Register table.
In order to write an SQL query to print employee name and department name along side we need to join 3 tables.
First JOIN statement will join Employee and Register and create a temporary table which will have dept_id as
another column. Now second JOIN statement will join this temp table with Department table on dept_id to get
desired result. Here is the complete SELECT SQL query example to join 3 tables and it can be extended to join more
than 3 or N tables.
mysql> SELECT * FROM Employee;
+--------+----------+--------+
| emp_id | emp_name | salary |
+--------+----------+--------+
| 1 | James | 2000 |
| 2 | Jack | 4000 |
| 3 | Henry | 6000 |
| 4 | Tom | 8000 |
+--------+----------+--------+
4 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM Department;
+---------+-----------+
| dept_id | dept_name |
+---------+-----------+
| 101 | Sales |
| 102 | Marketing |
| 103 | Finance |
+---------+-----------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM Register;
+--------+---------+
| emp_id | dept_id |
+--------+---------+
| 1 | 101 |
| 2 | 102 |
| 3 | 103 |
| 4 | 102 |
+--------+---------+
4 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT emp_name, dept_name FROM Employee e JOIN Register
r ON e.emp_id=r.emp_id JOINDepartment d ON r.dept_id=d.dept_id;
+----------+-----------+
| emp_name | dept_name |
+----------+-----------+
| James | Sales |
| Jack | Marketing |
| Henry | Finance |
| Tom | Marketing |
+----------+-----------+
4 rows IN SET (0.01 sec)
If you want to understand it even more better than try joining tables step by step. So instead of joining 3 tables in one
go, first join 2 tables and see how the result table will look like. Thats all on How to join three tables in one SQL query
in relational database. By the way in this SQL JOIN Example we have used ANSI SQL and it will work in other
relational database as well e.g. Oracle , SQL Server, Sybase, PostgreSQL etc. Let us know if you face any issue
while running this 3 table JOIN query in any other database.
10 Example Queries of SQL Select Command
Select command in SQL is one of the most powerful and heavily used commands. This is I guess the
first command any one learn in SQL even before CREATE which is used to create table in SQL. SELECT
is used in SQL to fetch records from database tables and you can do a lot many things using Select.
For example you can select all records, you can select few records based on condition specified in
WHERE clause, select all columns using wild card (*) or only selecting few columns by explicitly
declaring them in query.
In this SELECT SQL command tutorial we will see some examples of select command or Select
Statement and will write sql queries to demonstrate the result. We will use following table and data for
our SQL query examples, one table represent Stocks listed in various market and other table contains
Details of market e.g. Country. MySQL is my favorite RDBMS and great for learning purpose you can
download MySQL and start working on it. My suggestion is to use command line interface for writing
queries instead of using GUI e.g. SQL Developer or MySQL query tool. Command line is best for
learning and real fun of writing SQL query is only on command prompt.
mysql> select * from STOCK;
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from MARKET;
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
| RIC | NAME | COUNTRY |
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
| T | Tokyo Stock Exchange | Japan |
| O | NASDAQ | United States |
| N | New York Stock Exchange | United States |
| BO | Bombay Stock Exchange | India |
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
SQL SELECT command query examples
here are some of my favorite select clause examples which explores different ways one can use select
command for reporting purpose and display results.
1) Finding how many rows in tables
mysql> select count(*) from STOCK;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
2) Finding all records from tables; we are using wildcard start * for getting all columns.
mysql> select * from STOCK;
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3. Selecting few records based on some condition from tables in SQL
mysql> select * from STOCK where RIC='GOOG.O';
+--------+------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+--------+------------+--------------------+
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
+--------+------------+--------------------+
4. How to select few columns instead of all columns?
Instead of using start wild-card just give name of interested columns to SELECT clause.
mysql> select COMPANY from STOCK where RIC='GOOG.O';
+------------+
| COMPANY |
+------------+
| Google Inc |
+------------+
5. Select distinct (unique) records from Columns
Distinct keyword is used to show only unique records it will not show any duplicate values.
mysql> select distinct LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE from Stock;
+--------------------+
| LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+--------------------+
| T |
| O |
| N |
| BO |
| L |
+--------------------+
6. Selecting value with condition based on less than, greater than (>, <, >=, <=) etc.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC > 'I';
+---------+--------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+--------------------+--------------------+
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+--------------------+--------------------+
7. Combining condition using logical operator AND & OR
AND and OR Can be effectively used to combine two conditions on WHERE clause and gives you lot of
flexibility to write SQL query.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC <'I' AND RIC > 'G';
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
You can put any number of AND, OR conditions on WHERE Clause, some time things become quite
easy when you combine AND, OR in SQL.
8. How to find records which is not null using keyword NULL and IS NULL
NULL is very tricky in SQL; NULL means anything which doesn't have value. NULL is not "null" which
will be treated as text.To demonstrate this we will insert a Stock which is not listed on any Market yet.
mysql> select * from STOCK;
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INDIGO | INDIGO Airlines | NULL |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
You See there is only one row who has LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE null, we will now see count using NULL
and IS NULL which will verify this result.
mysql> select count(*) from STOCK where LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE IS NULL;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 1 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from STOCK where LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE IS NOT NULL;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from STOCK;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 6 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
9. SELECT Statement using BETWEEN and NOT BETWEEN
As name suggest BETWEEN is used to get data between a ranges.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC BETWEEN 'G' AND 'I';
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
10. Pattern matching in SQL queries using LIKE and NOT LIKE
LIKE is a pattern matching operator and used to find records which are not exact match but probable
match.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC LIKE 'V%';
+-------+--------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+-------+--------------------+--------------------+
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+-------+--------------------+--------------------+
NOT LIKE is opposit of LIKE and display records which are not probable match.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC NOT LIKE 'V%';
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INDIGO | INDIGO Airlines | NULL |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
11. IN and NOT IN
IN is another useful SQL operator we can use alongside SELECT. it provides set of values which can be
used in WHERE cluase.
mysql> select * from Stock where RIC in ('GS.N' , 'INFY.BO');
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
12. Sorting ResultSet in SQL using ORDER BY, ASC, DESC
Order by is used to sort records in result set returned by SELECT clause. By default it list in Ascending
order but we can use either ascending or descending using specifier ASC and DESC.
mysql> select * from Stock order by COMPANY;
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| INDIGO | INDIGO Airlines | NULL |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
14. Selecting data from multiple tables by using JOIN in SQL
Join in SQL is powerful concept which allows you to select data from multiple tables. You can generate
report where data is accumulated from different tables based on conditions specified in Join
statement.
Suppose you need to display list of Records and Name of Market where they are listed. Here name of
Stock in STOCK table while name of exchange in MARKET table. We need to join both of them to
display this report.
mysql> select s.RIC, m.NAME from Stock s, Market m where s.LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE=m.RIC;
+---------+-------------------------+
| RIC | NAME |
+---------+-------------------------+
| 6758.T | Tokyo Stock Exchange |
| GOOG.O | NASDAQ |
| GS.N | New York Stock Exchange |
| INFY.BO | Bombay Stock Exchange |
+---------+-------------------------+
Above method is called implicit Join an d This query can also be written by using explicit join style
which uses ON clause to join tables.
mysql> select s.RIC, m.NAME from Stock s INNER JOIN Market ON m I s.LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE=m.RIC;
15. Calling function on SELECT clause e.g. displaying current date
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2011-10-13 10:25:47 |
+---------------------+
16. Doing calculation using SELECT CLAUSE
You can perform some basic calculation using SELECT clause e.g addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division etc.
mysql> select 1+2;
+-----+
| 1+2 |
+-----+
| 3 |
+-----+
17. SELECT data from one row till another row like Paging
If you are thinking to implement paging and getting data from specified row you can do this easily in
Mysql by using LIMIT clause.
mysql> select * from Stock order by COMPANY LIMIT 0,2;
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
+--------+-------------------------+--------------------+
Here first parameter '0' says start from first record and '2' says get 2 record only.
18. Selecting data from result of another query by using derived table.
Sometime information needed to produce final SELCT result comes from another query and act as
table for outer SELECT statement. This table also called Derived table
mysql> select RIC from (select s.RIC, m.NAME from Stock s, Market m where
s.LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE=m.RIC) t where RIC > 'G'
+---------+
| RIC |
+---------+
| GOOG.O |
| GS.N |
| INFY.BO |
+---------+
Some Important point about SELECT command in SQL:
So Far we have seen different examples of SELECT clause in SQL which will enable you to take full
advantage of SELECT while writing SQL queries. Here I have listed some important points which you
should consider while writing SQL query not just SELECT but with any other keyword also.
1) Most often we use SELECT Operator with WHERE Clause, try to use column which has index on
WHERE clause. Using a non index column on WHERE clause can slow your query
drastically and effect would be more visible when your table data increases. a example with 1 Million
records query without index was taking 80 second while after index it just took .3 second, whopping
260% increase in speed.
2) If you don't need all columns, dont use * wild card. SELECT query with few columns are slightly
faster than all columns.
3) If you are retrieving data from large table, do a count (*) check before firing actual select
query, this will give you en estimate of how many records you are about to get and how much time it
could take.
4) You can introduce new columns in result set of SELECT Query by using keyword "AS" as
shown in below example. Very useful for displaying calculated value e.g. average or percentage.
5) Always use IS NULL or NULL for including or excluding values which could be null. Dont use
'null' that will be treated as text.
6) While writing SQL query not just SELECT, its good practice to write keyword in small
case and TABLES and COLUMNS in capital. So that they will stand out from whole query and
makes query more readable.
That's all on SQL Select command examples, I tried to cover good number of select command example to
provide an overview what SELECT statement can do. If you know any good select example in sql please
share.
W E D N E S D A Y , O C T O B E R 1 9 , 2 0 1 1
Difference between Truncate and Delete command in SQL - Interview
Questions with Example
Delete and truncate command in SQL
Truncate and delete in SQL are two commands which is used to remove or delete data from table.
Though quite basic in nature both sql commands can create lot of trouble until you are familiar with
details before using it. Difference between Truncate and delete are not just important to understand
perspective but also a very popular SQL interview topic which in my opinion a definite worthy topic.
What makes them tricky is amount of data. Since most of Electronic trading system stores large
amount of transactional data and some even maintain historical data, good understanding of delete
and truncate command is required to effectively work on those environment.I have still seen people
firing delete command just to empty a table with millions of records which eventually lock the whole
table for doing anything and take ages to complete or Simply blew log segment or hang the machine.
Most of enterprise stock trading systemmaintains two kind of database one transactional and other
static. Transactional data is for day by day records which need to be purge at end of data or moved to
historical data so that application can make a fresh start another day. If you need to work on such
large set of data, my advice is to get clear and complete knowledge of delete and truncate command,
along with there differences and when to use which command to remove data or purge tables.
In this article we will see where to use truncate in SQL and where to use delete in SQL, How to use
truncate or delete and what danger or harm they can create if not used carefully along with difference
between truncate and delete in SQL.
What is Truncate command in SQL
Use truncate table if you need to delete all rows, since truncate doesn't allow you to specify WHERE
clause. truncate removes data by deallocating space used by table which removes lot of overhead in
terms of logging and locking and that's why truncate is faster than delete.What you need to take care
is rollback, data deleted by truncate can not be rolled back until data server specifically supports it
e.g. MSSQL Server which allows to commit or rollback truncate table statement transactional. Another
caveat with truncate table statement is that it doesn't fire a trigger and you can not truncate a table
when a foreign key references any column to the table to be truncated. Only situation I see which is
perfect for using truncate is purging tables with huge data, though there is another solution exists to
drop table and recreated it if that make sense.
Example of truncate command in SQL
truncate table Orders; //Order table shouldn't have a column which is foreign key on other table
What is Delete command in SQL
Delete is another sql command available for removing records from table. Delete is even more flexible
than truncate like it provides support to WHERE Clause which can be use to remove selective data. It
logs each row which allows operation to be rolled back and it also fires triggers. One disadvantage of
using delete is speed and locking. Delete acquires lock on table and its also very slow operation
because of logging, which makes it unsuitable for removing records from large tables. One
workaround for this is batch-delete in which you remove batch of records instead on one record at a
time. Delete is most suitable fore removing selective data and use it where you want to rollback
transaction in database. Its not useful to purge large amount of data from tables and should not be
used, otherwise it could lock the table for very long time, blew log segment and can take ages to
complete.
Example of delete command in SQL
delete * from Orders; //delete all row from Orders, should not be used if Orders is large
delete * from Orders where Symbol="MSFT.NQ" //delete all orders where symbol is MSFT.NQ
Difference between truncate and delete command in SQL
This is an important point to understand before using truncate or delete on production environment,
or writing any script which purges data from tables.
1. truncate is fast delete is slow.
2. truncate doesn't do logging delete logs on per row basis.
3. rollback is possible with delete not with truncate until specifically supported by vendor.
4. truncate doesn't fire trigger, delete does.
5. Don't delete, truncate it when it comes to purge tables.
6. truncate reset identity column in table if any, delete doesn't.
7. truncate is DDL while delete is DML (use this when you are writing exam)
8. truncate doesn't support where clause, delete does.
So finally if you have table with huge data and want to empty it dont Delete, truncate it
Interview questions on truncate and delete in SQL
Truncate and delete both are popular interview topics and there is always some question on these
commands in SQL interview. Here I am listing some of SQL interview questions based on delete and
truncate command in SQL, you can find answer in this article itself or by google.
1) If you have table which contains large amount of data which command will you use for removing
data, truncate or delete?
2) What are differences between truncate and delete?
3) Which one is fast truncate or delete?
4) What is disadvantage of using truncate in sql?
5) How will you delete data if truncate is not supported and log segment is also not big
enough to support complete delete?
6) Is there any way to remove data other than truncate and delete in SQL?
How to find second highest or maximum salary of Employee in SQL -
Interview question
How to find second highest or second maximum salary of an Employee is one of the most frequently asked SQL
interview question similar to finding duplicate records in table and when to use truncate vs delete. There are many
ways to find second highest salary based upon which database you are using as different database provides different
feature which can be used to find second maximum or Nth maximum salary of employee. Well this question can
also be generalized with other scenario like finding second maximum age etc. In this SQL tutorial we will see different
example of SELECT SQL query to find second highest salary independent of databases or you may call in ANSI SQL
and other SQL queries which uses database specific feature to find second maximum salary.
SQL query to find second maximum salary of Employee
In this section we will write SQL query to get second highest salary of Employee. Before writing query its
good to be familiar with schema as well as data in table. Here is the Employee table we will be using this SQL
example:
mysql> SELECT * FROM Employee;
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_id | salary |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
| 1 | James | 10 | 2000 |
| 2 | Jack | 10 | 4000 |
| 3 | Henry | 11 | 6000 |
| 4 | Tom | 11 | 8000 |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+
4 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
If you look data, you will find that second maximum salary in this case is 6000 and employee name is Henry. Now
lets see some SQL example to find out this second maximum salary.
Second maximum salary using sub query and IN clause
Sub queries in SQL are great tool for this kind of scenario, here we first select maximum salary and then another
maximum excluding result of subquery. To learn more about Subquery see correlate and non-correlate subquery in
SQL
mysql> SELECT max(salary) FROM Employee WHERE salary NOT IN (SELECT max(salary) FROMEm
ployee);
+-------------+
| max(salary) |
+-------------+
| 6000 |
+-------------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
Here is another SQL query to find second highest salary using subquery and < operator instead of IN clause:
mysql> SELECT max(salary) FROM Employee WHERE salary < (SELECT max(salary) FROMEmploye
e);
+-------------+
| max(salary) |
+-------------+
| 6000 |
+-------------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
Both of above SQL example will work on all database including Oracle, MySQL, Sybase and SQL Server as they are
written using standard SQL keywords. But sometime you can also use database specific features like TOP keyword
of SQL Server or Sybase database to find out second highest salary of Employee.
Second highest salary using TOP keyword of Sybase or SQL Server database
TOP keyword of Sybase and SQL Server database is used to select top record or row of any result set, by carefully
using TOP keyword you can find out second maximum or Nth maximum salary as shown below.
SELECT TOP 1 salary FROM ( SELECT TOP 2 salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC) AS
emp ORDER BY salary ASC
Here is what this SQL query is doing : First find out top 2 salary from Employee table and list them in descending
order, Now second highest salary of employee is at top so just take that value. Though you need to keep in mind of
usingdistinct keyword if there are more than one employee with top salary, because in that case same salary will
be repeated and TOP 2 may list same salary twice.
Second maximum salary using LIMIT keyword of MYSQL database
LIMIT keyword of MySQL database is little bit similar with TOP keyword of SQL Server database and allows to take
only certain rows from result set. If you look at below SQL example, its very much similar to SQL Server TOP
keyword example.
mysql> SELECT salary FROM (SELECT salary FROM Employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 2)
ASemp ORDER BY salary LIMIT 1;
+--------+
| salary |
+--------+
| 6000 |
+--------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
Thats on How to find second highest salary of Employee using SQL query. This is good question which really test
your SQL knowledge, its not tough but definitely tricky for beginners. As follow up question you can ask him to find
third maximum salary or Nth maximum salary as well.
F R I D A Y , N O V E M B E R 2 5 , 2 0 1 1
Database Transaction Tutorial in SQL with Example for Beginners
Database transaction is an important concept to understand while working in database and SQL.
Transaction in database is required to protect data and keep it consistent when multiple users access
the database at same time. In this database transaction tutorial we will learn what is transaction
in database, why do you need transaction in database, ACID properties of database transaction and an
example of database transaction along with commit and rollback. Almost all vendors like Oracle,
MySQL, SQL Server or Sybase provide transaction facility though MySQL only provide it for certain
storage engine like InnoDB and BDB and not for MyISAM.
What is transaction in database?
Database transaction is collection of SQL queries which forms a logical one task. For transaction
to be completed successfully all SQL queries has to run successfully. Database transaction executes
either all or none, so for example if your database transaction contains 4 SQL queries and one of them
fails then change made by other 3 queries will be rolled back. This way your database always remain
consistent whether transaction succeeded or failed. Transaction is implemented in database using SQL
keyword transaction, commit and rollback. Commit writes the changes made by transaction into
database and rollback removes temporary changes logged in transaction log by database transaction.
Database Transaction tutorial
Why transaction is required in database
Database is used to store data required by real life application e.g. Banking, Healthcare, Finance etc.
All your money stored in banks is stored in database, all your shares of DMAT account is stored in
database and many application constantly work on these data. In order to protect data and keep it
consistent any changes in this data needs to be done in transaction so that even in case of failure data
remain in previous state before start of transaction. Consider a Classical example of ATM (Automated
Tailor Machine); we all use to withdraw and transfer money by using ATM. If you break withdrawal
operation into individual steps you will find:
1) Verify account details.
2) Accept withdrawal request
3) Check balance
4) Update balance
4) Dispense money
Suppose your account balance is 1000$ and you make a withdrawal request of 900$. At fourth step
your balance is updated to 900$ and ATM machine stops working due to power outage
Once power comes back and you again tried to withdraw money you surprised by seeing your balance
just 100$ instead of 1000$. This is not acceptable by any person in the world :) so we need
transaction to perform such task. If SQL statements would have been executed inside transaction in
database balance would be either 100$ until money has been dispensed or 1000$ if money has not
been dispensed.
ACID Properties of database transaction
There are four important properties of database transactions these are represented by acronym
ACID and also called ACID properties or database transaction where:
A stands for Atomicity, Atom is considered to be smallest particle which can not be broken into
further pieces.database transaction has to be atomic means either all steps of transaction completes
or none of them.
C stands for Consistency, transaction must leave database in consistent state even if it succeed or
rollback.
I is for Isolation
Two database transactions happening at same time should not affect each other and has consistent
view of database. This is achieved by using isolation levels in database.
D stands for Durability
Data has to be persisted successfully in database once transaction completed successfully and it has
to be saved from power outage or other threats. This is achieved by saving data related to transaction
in more than one places along with database.
When to use database transaction
Whenever any operation falls under ACID criteria you should use transactions. Many real world
scenarios require transaction mostly in banking, finance and trading domain.
How to implement transaction in SQL
Database transaction is implemented in SQL using three keywords start transaction, commit and
rollback.once you type start transaction, database starts a transaction and execute all subsequent SQL
statements in transaction and keep track of all of them to either commit or rollback
changes. Commitkeywords saves then changes made by transaction into database and after commit
change is normally visible to other transaction though is subject to isolation level. In case you
encountered any error while executing individual sql statements inside database transaction, you can
rollback all your changes by executing "rollback" command.
Database Transaction Example
To understand database transaction better let's see a real life example of transaction in database. For
this example we will assume we have an Account table which represent a Bank Account and we will
transfer money from one account to another account
Request: transfer 900$ from Account 9001 to 9002
start transaction
select balance from Account where Account_Number='9001';
select balance from Account where Account_Number='9002';
update Account set balance=balance-900 here Account_Number='9001' ;
update Account set balance=balance+900 here Account_Number='9002' ;
commit; //if all sql queries succed
rollback; //if any of Sql queries failed or error
Database transaction in MySQL
In my previous mysql command tutorials I have talked aobut different databse storage engines
available in mysql e.g. myISAM or InnoDB. Not all mysql engines supports transaction in order to
make transaction works in mysql you either need to use InnoDB or BDB Engine. You can specify
engige while creating table in mysql or you can also change your engine in mysql by using ALTER
keyword. For example"ALTER TABLE tablename TYPE=InnoDB;
Important point about database transaction
1. Database transaction is nothing but a set of SQL statement.
2. Transaction in database is either all or none means either all SQL statement success or none.
3. Its good practice to execute sql query inside transaction and commit or rollback based on result but
you need to be little careful with transaction log. To faciliate rollback and commit every sql query
which executed inside database transaction is written into transaction log and size of transaction log
can grow significantly if don't commit or rollback for longtime.
4. Effect of two simulteneous database transaction into data is controlled by using Isolation level.
Isolation level is used to separate one database transaction with other and currently there are four
databse isolation levels:
1) Read Uncommited
This is lowest level of databse isolation level in this one database transaction can see changes made
by other databse transaction which is not yet commited. This can allow you dirty read so quite
dangerous.
2) Read Commited
This is sligltly better where one database transaction only sees commited changes by other database
transaction. But this is also not safe and can lead you to non-repeatable reads problem.
3) Repeatable Reads
4) Serializable
Highest level of database isolation level. In this all database transactions are totally isolated with
other database transaction.though this is safe but this safety can cause significant performance hit.
5. MyISAM storage engine in MySQL doesn't support transaction. In order to make transaction works
in MySQL use InnoDB.
6. Databse transaction should follow ACID properties.
Thats all for now on database transaction tutorial, I will add more useful points about transaction in
databse as I come across or recall, you can also provide your input and issues face during transaction
in database on different RDBMS e.g. Oracle, MySQL, MSSQL Server or Sybase etc.
F R I D A Y , D E C E M B E R 1 4 , 2 0 1 2
How to find duplicate records in a table on database - SQL tips
How to find duplicate records in table is a popular SQL interview question which has been asked as many times
asdifference between truncate and delete in SQL or finding second highest salary of employee. Both of these SQL
queries are must know for any one who is appearing on any programming interview where some questions on
database and SQL are expected. In order to find duplicate records in database table you need to confirm definition of
duplicates, for example in below contact table which is suppose to store name and phone number of contact, a
record is considered to be duplicate if both name and phone number is same but unique if either of them varies.
Problem of duplicates in database arise when you don't have a primary key or unique key on database and that's why
its recommended to have a key column in table. Anyway its easy to find duplicate records in table by using group by
clause of ANSI SQL. Group by clause is used to group data based upon any column or a number of columns. Here
in order to locate duplicate records we need to use group by clause on both name and phone as shown in
second SQL SELECT query example. You can see in first query that it listed Ruby as duplicate record even though
both Ruby have different phone number because we only performed group by on name. Once you have grouped data
you can filter out duplicates by using having clause. Having clause is counter part of where clause for aggregation
queries. Just remember to provide temporary name tocount() data in order to use them in having clause.
SQL Query to find duplicate records in a table in MySQL
In this section we will see SQL query which can be used to locate duplicate records in table. As explained in
previous section, definition of duplicate depends upon business rules which must be used in group by clause. In
following query we have used SELECT query to select all records from Contacts table. Here James, Johnny, Harry
and Ron are duplicated four times.
mysql> select * from Contacts;
+-------+----------+
| name | phone |
+-------+----------+
| James | 80983243 |
| Johnny | 67543212 |
| Harry | 12341234 |
| Ron | 44446666 |
| James | 80983243 |
| Johnny | 67543212 |
| Harry | 12341234 |
| Ron | 44446666 |
| James | 80983243 |
| Johnny | 67543212 |
| Harry | 12341234 |
| Ron | 44446666 |
| James | 80983243 |
| Johnny | 67543212 |
| Harry | 12341234 |
| Ron | 44446666 |
| Ruby | 8965342 |
| Ruby | 6888342 |
+-------+----------+
18 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Following SELECT query will only find duplicates records based on name which might not be correct if two
contact of same but different numbers are stored, as in following result set Ruby is shown as duplicate which is
incorrect.
mysql> select name, count(name) from contacts group by name;
+-------+-------------+
| name | count(name) |
+-------+-------------+
| Harry | 4 |
| James | 4 |
| Johnny | 4 |
| Ron | 4 |
| Ruby | 2 |
+-------+-------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
This is the correct way of finding duplicate contacts at it look both name and phone number and only print duplicate
if both name and phone is same.
mysql> select name, count(name) from contacts group by name, phone;
+-------+-------------+
| name | count(name) |
+-------+-------------+
| Harry | 4 |
| James | 4 |
| Johnny | 4 |
| Ron | 4 |
| Ruby | 1 |
| Ruby | 1 |
+-------+-------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
having clause in SQL query will filter duplicate records from non duplicate records. As in following query it print all
duplicate records and how many times they are duplicated in table.
mysql> select name, count(name) as times from contacts group by name, phone having
times>1;
+-------+-------+
| name | times |
+-------+-------+
| Harry | 4 |
| James | 4 |
| Johnny | 4 |
| Ron | 4 |
+-------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
That's all on how to find duplicate records in table, These SQL queries will work on all database like MySQL, Oracle,
SQL Server and Sybase as it only uses ANSI SQL and doesn't use any database specific feature. Another interesting
SQL query interview question is "How to delete duplicate records from table" which we will see in another post.
What is difference between primary key and unique key in table
- SQL database
primary key vs unique key in SQL
primary key and unique key are two important concept in relational database, and used to uniquely
identify a row in a table. Both primary key and unique key can identify a row uniquely but there are some
subtle difference between them which we will see in this article. In fact primary key vs unique is a popular
SQL interview questions along with classics like truncate vs delete and How to manage transaction in
database, mostly asked to fresher and 2 to 3 years experience guys in any programming language. SQL
is not just limited to any DBA or PLSQL developer but its an important skill even for Java programmer and
you can expect SQL interview question even in many Java interviews. Some time programmer also
confuse between foreign key and unique key, which is primary key of other table in relation.
Difference between primary key and unique key in SQL
As I said both primary and unique key uniquely identifies each row in table but there are some
subtle difference between them. here are some of them :
1) Unique key in a table can be null, at-least one but primary key can not be null in any table in relation
database like MySQL , Oracle etc.
2) Primary key can be combination of more than one unique keys in same table.
3) There can be only one primary key per table in relation database e.g. MySQL, Oracle or Sybase but
there can be more than one unique key per table.
4) Unique key is represented using unique constraint while primary key is created using primary key
constraint in any table and it's automatically gets unique constraint.
5) Many database engine automatically puts clustered index on primary key and since you can only have
one clustered index per table, its not available to any other unique key at same time.
These were some of the difference between primary key and unique key in SQL or any table. Its's one
of those SQL interview questions which you don't like to miss before going for any programming
interview or any database, SQL interview.
S A T U R D A Y , J U L Y 7 , 2 0 1 2
SubQuery Example in SQL Correlated vs Noncorrelated
SubQuery in SQL is a query inside another query. Some time to get a particular information from database you may
need to fire two separate sql queries, subQuery is a way to combine or join them in single query. SQL query which is
on inner part of main query is called inner query while outer part of main query is called outer query. for example in
below sql query
SELECT name FROM City WHERE pincode IN (SELECT pincode FROM pin WHERE zone='west')
section not highlighted is OUTER query while section highlighted with grey is INNER query. In this SQL tutorial we
will see both Correlated and non correlated sub-query and there examples, some differences between correlated and
noncorrelated subqueries and finally subquery vs join which is classic debatable topic in SQL. By the way this SQL
tutorial is next in series of SQL and database articles in Javarevisited like truncate vs delete and 10 examples
of SELECT queries. If you are new here then you may find those examples interesting.
SubQuery Rules in SQL
Like any other concept in SQL, subquery also has some rules and you can only embed one query inside another by
following rules :
1. subquery can be used in insert statement.
2. subquery can be used in select statement as column.
3. subquery should always return either a scaler value if used with where clause or value from a column if used
with IN orNOT IN clause.
Before going to understand non-correlated and correlated subquery, lets see the table and data which we are
going to use in this example. Until you have an understanding of how table look like and what kind of data it stores its
little difficult to understand queries. In this subquery example we will use two table Stock and Market. Stock holds
different stocks and Market holds all stock exchanges in the world.
mysql> select * from stock;
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| RIC | COMPANY | LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
| 6758.T | Sony | T |
| GOOG.O | Google Inc | O |
| GS.N | Goldman Sachs Group Inc | N |
| INDIGO | INDIGO Airlines | NULL |
| INFY.BO | InfoSys | BO |
| VOD.L | Vodafone Group PLC | L |
+---------+-------------------------+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select from Market;
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
| RIC | NAME | COUNTRY |
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
| T | Tokyo Stock Exchange | Japan |
| O | NASDAQ | United States |
| N | New York Stock Exchange | United States |
| BO | Bombay Stock Exchange | India |
+------+-------------------------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Noncorrelated subquery in SQL
There are two kind of subquery in SQL one is called non-correlated and other is called correlated subquery. In non
correlated subquery, inner query doesn't depend on outer query and can run as stand alone query.Subquery used
along-with IN or NOT IN sql clause is good examples of Noncorrelated subquery in SQL. Let's a noncorrelated
subquery example to understand it better.
NonCorrelated Subquery Example:
Lets see the query Find all stocks from Japan, If we analyze this query we know that stock names are stored
in Stock table while Country name is stored in Market table, so we need to fire two query first to get RIC for
Japanese market and than all stocks which is listed on that Market. we can combine these two queries into one sql
query by using subquery as shown in below example:
mysql> SELECT COMPANY FROM Stock WHERE LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE =(SELECT RIC FROM Market WHE
RE COUNTRY='Japan');
+---------+
| COMPANY |
+---------+
| Sony |
+---------+
1 row IN SET (0.02 sec)
Here part which is inside bracket is called inner query or subquery. As you see in this example of subquery, inner
query can run alone and its not depended on outer query and that's why its called NonCorrelated query.
NonCorrelated Subquery Example with IN Clause SQL
NonCorrelated subquery are used along-with IN and NOT IN clause. here is an example of subquery with IN clause
in SQL.
SQL query: Find all stocks from United States and India
mysql> SELECT COMPANY FROM Stock WHERE LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE IN (SELECT RIC FROM Market W
HERECOUNTRY='United States' OR COUNTRY= 'INDIA');
+-------------------------+
| COMPANY |
+-------------------------+
| Google Inc |
| Goldman Sachs GROUP Inc |
| InfoSys |
+-------------------------+
When Subquery is used along-with IN or NOT IN Clause it returns result from one column instead of Scaler value.
Correlated SubQuery in SQL
Correlated subqueries are the one in which inner query or subquery reference outer query. Outer query needs
to be executed before inner query. One of the most common example of correlated subquery is using
keywords exits and not exits. An important point to note is that correlated subqueries are slower queries and
one should avoid it as much as possible.
Example of Correlated Subquery in SQL
Here is an example of Correlated subquery Return all markets which has at least one stock listed on it.
mysql> SELECT m.NAME FROM Market
m WHERE m.RIC = (SELECT s.LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE FROM Stock
sWHERE s.LISTED_ON_EXCHANGE=m.RIC);
+-------------------------+
| NAME |
+-------------------------+
| Tokyo Stock Exchange |
| NASDAQ |
| New York Stock Exchange |
| Bombay Stock Exchange |
+-------------------------+
4 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
Here inner query will execute for every Market as RIC will be changed for every market.
Difference between Correlated and NonCorrelated Subquery
Now we have seen correlated and noncorrelated subqueries and there example its much easier to
understand difference between correlated vs noncorrelated queries. By the way this is also one of the popular sql
interview question and its good to know few differences:
1.In case of correlated subquery inner query depends on outer query while in case of noncorrelated query inner
query or subquery doesn't depends on outer query and run by its own.
2.In case of correlated subquery, outer query executed before inner query or subquery while in case of
NonCorrelated subquery inner query executes before outer query.
3.Correlated Sub-queries are slower than non correlated subquery and should be avoided in favor of sql joins.
4.Common example of correlated subquery is using exits and not exists keyword while non correlated query mostly
use IN or NOT IN keywords.
SubQuery vs Join in SQL
Any information which you retrieve from database using subquery can be retrieved by using different types os joins
also. Since SQL is flexible and it provides different way of doing same thing. Some people find SQL Joins confusing
and subquery specially noncorrelated more intuitive but in terms of performance SQL Joins are more efficient than
subqueries.
Important points about SubQuery in DBMS
1.Almost whatever you want to do with subquery can also be done using join, it just matter of choice
subquery seems more intuitive to many user.
2.Subquery normally return an scaler value as result or result from one column if used along with
IN Clause.
3.You can use subqueries in four places: subquery as a column in select clause,
4.In case of correlated subquery outer query gets processed before inner query.
Difference between Primary key vs Foreign key in table SQL database
tutorial
Main difference between Primary key and Foreign key in a table is that, its the same column which behaves as
primary key in parent table and as foreign key in child table. For example
in Customer and Order relationship, customer_id is primary key in Customer table but foreign key
in Order table. By the way what is foreign key in a table and difference between Primary and Foreign key are some
of the popular SQL interview questions, much like truncate vs delete in SQL or difference between correlated and
noncorrelated subquery. We have been learning key SQL concepts along with these frequently asked SQL questions
and in this SQL tutorial we will discuss about what is foreign key in SQL and purpose of foreign key in any table. By
the way this is the third article related to primary key in SQL, other being difference between primary and unique
keyand How to find second highest salary in SQL. If you are preparing for any technical job interview where you
expect some SQL questions, check out these questions, they are worth preparing.
What is Foreign key in a table
Foreign key is a column in one table which is primary key on another table. Foreign key and Primary key is
used to define relationship between two tables in relational database. For example in Employee and Department
relationship, we have two tables Department(dept_id, dept_name) and Employee (emp_id, emp_name,
dept_id). dept_id is primary key in Department table and foreign key in Employee table. Though its not require
that name of foreign key must be same with primary key, we have kept it same as per standard SQL best practices.
Foreign key in a table enforce Referential Integrity constraint, which can be used to implement business rules e.g.
referential integrity can stop you from creating an Employee with a non existent department. This kind of check
maintains integrity of data in a relationship. As discussed in our post What is referential integrity in MySQL database,
we have seen that it's implemented as foreign key constraint and can allow CASCADE UPDATE and DELETE. These
referential action delete or update matching column in child table ( foreign key table) when corresponding row from
parent table (primary key table ) is deleted or updated to maintain integrity of data.
Difference between Primary key and Foreign key in SQL
Here are some important difference between primary and foreign keys in a table which is worth remembering both on
SQL interview point of view and knowledge point of view.
1) Name of foreign key can be different than the name of primary key it represent in other table. For example in
our Employeeand Department relationship, Primary key in Department table is dept_id and we have used
same name in Employeetable to create foreign key. It could have been different e.g. departmentId or
departmentID t etc.
2) Another difference between primary and foreign key is that unlike primary key, foreign key can be null e.g. in our
example you can have an Employee record for which dept_id can be null, this shows that no corresponding record
inDepartment table.
3) One more difference between primary key and foreign key is that foreign key can be duplicate opposite to
primary key which is always unique.
4) By using foreign key constraints, we can introduce referential integrity in multiple table relationship in SQL.
Referential integrity guarantees data integrity, see benefits of Referential Integrity in SQL to know more.
5) Foreign key mostly work as link between two table when we join tables using INNER JOIN and OUTER JOIN. For
example when we INNER JOIN both Employee with Department table, we can use dept_id as joining column.
SeeHow to join three tables in SQL for more details.
6) Table on which a column is declared as primary key is known as parent table in relationship and foreign
key table is known as child table in relationship. For example
in Employee and Department relationship, Department is parent table because dept_id is primary key there
and Employee is child table because dept_id is foreign key in this table.
Primary key and Foreign key Example in SQL
One of the best example to understand Primary key and Foreign key in a table
is Employee and Department relationship or Customer and Order relationship. You can
create Order and Customer table in MySQL as following to create primary and foreign keys :
CREATE TABLE Customer (cust_id INT NOT NULL,
cust_name VARCHAR(256),
PRIMARY KEY (cust_id)) ENGINE=INNODB;
CREATE TABLE ORDER (order_id INT NOT NULL,
amount INT NOT NULL,
cust_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (cust_id) REFERENCES Customer(cust_id)
ON DELETE CASCADE) ENGINE=INNODB;
Now cust_id is primary key in Customer table and foreign key in Order table. If we try to insert an Order for
whichcust_id is something which is invalid in Customer table, MySQL database will reject such INSERT or
UPDATE. This is one of the benefit of using Referential Integrity. It also allow to CASCADE
UPDATE and DELETE operation which first delete or update a row in parent table e.g. Customer and then delete or
update all matching rows in child table e.g. Order table.
That's all on what is foreign key in a table and difference between primary and foreign key in SQL. I suggest to create
some table by yourself and try to test foreign key constraint by violating it and see how database e.g. Oracle, MySQL
or SQL Server behaves. To understand more try ON DELETE CASCADE and ON DELETE UPDATE to see how
database maintains foreign key constraint. You can also see my post on Referential Integrity example on MySQL
database
Difference between primary key vs Candidate Key in table -
SQL database
Primary key vs Candidate Key
What is difference between primary key and candidate key is another popular SQL and database interview questions
which appears in various programming interviews now and then. Concept of primary key and candidate key is not just
important from interview point of view but also on designing database and normalization. By the way this is my
second post in primary key, In last one we have seen comparison of primary key vs unique key, which is also
happens to be one of the frequently asked database question. By definition primary key is a column or collection of
columns, which uniquely define a row in a table. Candidate keys are keys which can be primary key and also able to
uniquely identify any row in table. In simply terms you may have couple of Candidate keys and you have choose one
of them as primary key. This selection part is the most important skill in database design. Since only primary key can
have clustered index in table while unique keys can have Nonclustered index, its important to choose right column or
collection of columns as primary key. Often I select a column which is most frequently used in Where clause of
SELECT query. If you preparing for SQL interview or looking for some good SQL interview question than you can
also check difference between Correlated and Noncorrelated subqueries and When to use truncate vs delete in SQL.
Difference between Candidate Key vs Primary Key
Before seeing difference between Candidate key and Primary key let's see some similarities between them
in bullets points.
1) Both Primary and Candidate keys can uniquely identify records in a table on database.
2) Both Primary and Candidate keys are has constraints UNIQUE and NOT NULL.
3) Primary key or Candidate keys can be either single column or combination of multiple columns in a table.
Now from interview point of view here is difference between Candidate key and primary key in SQL table on point
format for easy to remember :
1) There can be multiple Candidate keys in a table in relation database e.g. Oracle, MySQL, Sybase or MSSQL but
only one primary key is permitted.
2) An example of Primary key and Candidate key can be ID and SSN number in a Employee table, Since both can
identify each employee uniquely they are candidate key and any one can become primary key. Now if you have to
choose between them as primary key, I will go ID as primary key because SSN is sensitive information and may not
be allow/not safe to use as String in queries as frequently as ID. Second reason of choosing ID over SSN as primary
key can be use of ID as primary tracking ID within organization and its frequent use all over the place. Once you
choose a primary key, All candidate key are like unique keys.
That's all on difference between Primary key and Candidate key in a table. If you understand election well than you
can think primary key as elected member among all candidate keys.
Question 1: SQL Query to find second highest salary of Employee
Answer : There are many ways to find second highest salary of Employee in SQL, you can either use SQL Join or
Subquery to solve this problem. Here is SQL query using Subquery :
select MAX(Salary) from Employee WHERE Salary NOT IN (select MAX(Salary) from Employee );
See How to find second highest salary in SQL for more ways to solve this problem.
Question 2: SQL Query to find Max Salary from each department.
Answer :
SELECT DeptID, MAX(Salary) FROM Employee GROUP BY DeptID.
Question 3:Write SQL Query to display current date.
Ans:SQL has built in function called GetDate() which returns current timestamp.
SELECT GetDate();
Question 4:Write an SQL Query to check whether date passed to Query is date of given format or not.
Ans: SQL has IsDate() function which is used to check passed value is date or not of specified format ,it returns
1(true) or 0(false) accordingly.
SELECT ISDATE('1/08/13') AS "MM/DD/YY";
It will return 0 because passed date is not in correct format.
Question 5: Write a SQL Query to print the name of distinct employee whose DOB is between 01/01/1960 to
31/12/1975.
Ans:
SELECT DISTINCT EmpName FROM Employees WHERE DOB BETWEEN 01/01/1960 AND 31/12/1975;
Question 6:Write an SQL Query find number of employees according to gender whose DOB is between
01/01/1960 to 31/12/1975.
Answer : SELECT COUNT(*), sex from Employees WHERE DOB BETWEEN 01/01/1960 ' AND
31/12/1975 GROUP BY sex;
Question 7:Write an SQL Query to find employee whose Salary is equal or greater than 10000.
Answer : SELECT EmpName FROM Employees WHERE Salary>=10000;
Question 8:Write an SQL Query to find name of employee whose name Start with M
Ans: SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE EmpName like 'M%';
Question 9: find all Employee records containing the word "Joe", regardless of whether it was stored as JOE,
Joe, or joe.
Answer : SELECT * from Employees WHERE upper(EmpName) like upper('joe%');
Question 10: Write a SQL Query to find year from date.
Answer : SELECT YEAR(GETDATE()) as "Year";
Difference between Self and Equi Join in SQL - INNER Join
example MySQL
Main difference between Self Join and Equi Join is that, In Self Join we join one table to itself rather than joining two
tables. Both Self Join and Equi Join are types of INNER Join in SQL but there is subtle difference between two. Any
INNER Join with equal as join predicate is known as Equi Join. SQL Joins are fundamental concept of SQL similar
to correlated and noncorrelated subqueries or using group by clause and good understanding of various types of SQL
join is must for any programmer. By the way If you have written INNER join using where clause than using
comparison operator as = will be known as equi join. Equi join or Self join are not a formal join or part of syntax,
instead they are just popular way to refer certain join examples. One of the best example of Self Join, I have seen in
SQL Interview questions is "How do you find all Employees who are Managers in Employee table", which is
commonly asked along with another popular question how to find second highest salary of employee or questions
related to join three tables in one sql query. In this SQL tutorial we will learn self join by example while solving this
SQL query.
Self Join Example in SQL
In order to solve this query let's first see schema and data of Employee table.
mysql> select * from employee;
+--------+----------+---------+--------+--------+
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_id | salary | mgr_id |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+--------+
| 103 | Jack | 2 | 1400 | 104 |
| 104 | John | 2 | 1450 | 104 |
| 105 | Johnny | 3 | 1050 | 104 |
| 108 | Alan | 3 | 1150 | 104 |
| 106 | Virat | 4 | 850 | 105 |
| 107 | Vina | 4 | 700 | 105 |
| 109 | joya | 4 | 700 | 105 |
+--------+----------+---------+--------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
In above table all employees who are managers has there emp_id as mgr_id in other employees and by using
SELF JOIN i.e. join two instance of employee table and comparing, we can find all employees who are managers.
Here is the SELECT query exampleusing self join :
mysql> select distinct e.emp_id, e.emp_name from employee e join employee
m on e.emp_id=m.mgr_id;
+--------+----------+
| emp_id | emp_name |
+--------+----------+
| 104 | John |
| 105 | Johnny |
+--------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
In this example of Self Join, we have joined employee table to itself by using two table aliases e and m. We
have also used distinct keyword to remove duplicates here. You can also say this is an example of EQUI JOIN
because in join predicate we have used = or equal condition. In fact this one is example of INNER Join, SELF Join
and EQUI Join at same time.
Self Join vs Equi Join
In short major difference between Self Join and Equi Join in SQL is that Self Join requires only one table while most
of Equi join is condition used in join predicate. Since Equi Join is based on condition for comparison, it can occur in
any INNER, OUTER or SELF join in SQL.
Thats all on difference between Self Join and Equi Join in SQL. Self Join is one of the important technique to solve
many SQL query related problem where two columns of table contains same type of data e.g. here emp_id and
dept_id are essentially same data.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- MF 5460Document586 paginiMF 5460Maximiliano Hitschfeld100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Data MiningDocument14 paginiData MiningAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAN KPI MonitorDocument8 paginiRAN KPI MonitorOmer WaqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecco ADocument5 paginiEcco Aouzun852Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical Slip Mcs Sem 3 Pune UniversityDocument4 paginiPractical Slip Mcs Sem 3 Pune UniversityAtul Galande0% (1)
- 13 - MCA I ScienceDocument35 pagini13 - MCA I ScienceashokshindepatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular 8 Nutrition Plan EveningDocument3 paginiMuscular 8 Nutrition Plan Eveningapi-325755907Încă nu există evaluări
- M.C.A Data Structures Question Paper: Madras UniversityDocument2 paginiM.C.A Data Structures Question Paper: Madras UniversityAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagram of Intel 8086Document5 paginiBlock Diagram of Intel 8086Ritesh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Language Basic QuestionDocument64 paginiC Language Basic QuestionAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corruption in IndiaDocument3 paginiCorruption in IndiaNoopur NagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 - MCA I ScienceDocument35 pagini13 - MCA I ScienceashokshindepatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Strcture NotesDocument94 paginiData Strcture NotesAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Faculty of SciencesDocument2 pagini2 - Faculty of SciencesAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45-Document SummaryDocument66 pagini45-Document SummarySneha AngreÎncă nu există evaluări
- MatrixDocument196 paginiMatrixAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Cs CDocument6 paginiMCQ Cs CAtul GalandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMC Core JavaDocument12 paginiCMC Core JavaAtul Galande100% (1)
- Positive Leadership and Adding Value - A Lifelong Journey: June 2017Document7 paginiPositive Leadership and Adding Value - A Lifelong Journey: June 2017CescSalinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - Gherkin An OverviewDocument19 pagini03 - Gherkin An OverviewArunkumar KrishnamoorthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 paginiGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridaySheilaMarB.Esteban100% (1)
- Wheel Radial Fatigue Test MachineDocument1 paginăWheel Radial Fatigue Test MachineAlex NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorine (Free or Total) Manual For Test Kits CN-70, CN-70F, CN-70TDocument6 paginiChlorine (Free or Total) Manual For Test Kits CN-70, CN-70F, CN-70TDemétrius Ivo FernandesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snel White Paper 2020Document18 paginiSnel White Paper 2020Zgodan NezgodanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting and Configuring Crontab in CygwinDocument2 paginiStarting and Configuring Crontab in CygwinSamir BenakliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5: Attention and PerformanceDocument10 paginiChapter 5: Attention and Performancerebela29Încă nu există evaluări
- Rosalind FranklinDocument1 paginăRosalind FranklinMichael SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 10 - WHLP - Q1 - Module 3Document3 paginiEnglish 10 - WHLP - Q1 - Module 3Mar Florence SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area Manager ChecklistDocument7 paginiArea Manager ChecklistUtkarsh RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philips 170v7fbDocument95 paginiPhilips 170v7fbaposticaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Resilience Philippines Urban PoorDocument16 paginiBuilding Resilience Philippines Urban PoorYasmin Pheebie BeltranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5054 s09 QP 1Document20 pagini5054 s09 QP 1Hany ElGezawyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis Sagar Project - A Study On The Need of CRM in OrganizatonDocument3 paginiSynopsis Sagar Project - A Study On The Need of CRM in OrganizatonViraja GuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usg Sheetrock® Brand Acoustical SealantDocument3 paginiUsg Sheetrock® Brand Acoustical SealantHoracio PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Large Generator Protection enDocument14 paginiLarge Generator Protection enNguyen Xuan TungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ty 9900Document4 paginiTy 9900Samir DarweshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Five Forces: Submitted by Subham Chakraborty PGDMDocument5 paginiPorter's Five Forces: Submitted by Subham Chakraborty PGDMSubham ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationDocument19 paginiElon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationBDApp StarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sick GM31Document54 paginiSick GM31Magdy SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter 2 Original TestDocument6 paginiPhysics Chapter 2 Original TestJanina OrmitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Channel Line Up 2018 Manual TVDocument1 paginăChannel Line Up 2018 Manual TVVher Christopher DucayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Languages and CommunicationDocument17 paginiLanguages and CommunicationDERICK REBAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Document3 paginiDuplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Mushfiqur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idea of CultureDocument28 paginiIdea of CultureGustavo Dias VallejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How many times do clock hands overlap in a dayDocument6 paginiHow many times do clock hands overlap in a dayabhijit2009Încă nu există evaluări