Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cylinder (Geometry) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Încărcat de
Shyamol BoseDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cylinder (Geometry) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Încărcat de
Shyamol BoseDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 1/6
Cylinder (geometry)
A right circular cylinder with
radius rand height h.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A cylinder (from Greek
kulindros, "roller, tumbler"
[1]
) is one of
the most basic curvilinear geometric
shapes, the surface formed by the points
at a fixed distance from a given line
segment, theaxis of the cylinder. The
solid enclosed by this surface and by two
planes perpendicular to the axis is also
called a cylinder. The surface area and
the volumeof a cylinder have been
known since deep antiquity.
In differential geometry, a cylinder is
defined more broadly as any ruled
surfacespanned by a one-parameter
family of parallel lines. A cylinder
whose cross section is an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola is called an elliptic
cylinder,parabolic cylinder, or hyperbolic cylinder respectively.
The open cylinder is topologically equivalent to both the open annulus and
thepunctured plane.
Contents [hide]
1 Common use
2 Volume
3 Surface area
4 Cylindric section
5 Other types of cylinders
6 About an arbitrary axis
7 Projective geometry
8 Related polyhedra
9 See also
10 References
11 External links
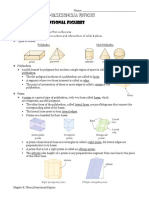
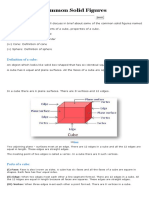
Common use [edit]
In common use a cylinder is taken to mean a finite section of a right circular
cylinder, i.e., the cylinder with the generating lines perpendicular to the bases,
with its ends closed to form two circular surfaces, as in the figure (right). If the
cylinder has a radius r and length (height) h, then its volume is given by
V = r
2
h
and its surface area is:
Article Talk
Read Edit View history
Search
Main page
Contents
Featured content
Current events
Random article
Donate to Wikipedia
Wikimedia Shop
Interaction
Help
About Wikipedia
Community portal
Recent changes
Contact page
Tools
What links here
Related changes
Upload file
Special pages
Permanent link
Page information
Data item
Cite this page
Print/export
Create a book
Download as PDF
Printable version
Languages
Asturianu
Aymar aru
Azrbaycanca
()%E2%
80%8E
Catal
etina
ChiShona
Dansk
Deutsch
Eesti
Espaol
Create account Log in
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 2/6
the area of the top (r
2
) +
the area of the bottom (r
2
) +
the area of the side (2rh).
Therefore without the top or bottom (lateral area), the surface area is:
A = 2rh.
With the top and bottom, the surface area is:
A = 2r
2
+ 2rh = 2r(r + h) = d(r + h),
where d is the diameter.
For a given volume, the cylinder with the smallest surface area has h = 2r. For a
given surface area, the cylinder with the largest volume has h = 2r, i.e. the
cylinder fits snugly in a cube (height = diameter).
Volume [edit]
Having a right circular cylinder with a height h units and a base of radius r units
with the coordinate axes chosen so that the origin is at the center of one base
and the height is measured along the positive x-axis. A plane section at a
distance of xunits from the origin has an area of A(x) square units where
or
An element of volume, is a right cylinder of base area Aw
i
square units and a
thickness of
i
x units. Thus if V cubic units is the volume of the right circular
cylinder, by Riemann sums,
Using cylindrical coordinates, the volume can be calculated by integration over
Surface area [edit]
The formula for finding the surface area of a cylinder is, with h as height, r as
radius, and S as surface area is Or, with B as base area
and L as lateral area,
Esperanto
Euskara
Franais
Galego
Hrvatski
Ido
Bahasa Indonesia
slenska
Italiano
Basa Jawa
Latina
Latvieu
Lietuvi
Magyar
Bahasa Melayu
Nederlands
Nordfriisk
Norsk bokml
Norsk nynorsk
Occitan
Piemontis
Polski
Portugus
Romn
Runa Simi
Scots
Shqip
Sicilianu
Simple English
Slovenina
Slovenina
Soomaaliga
/ srpski
Srpskohrvatski /
Basa Sunda
Suomi
Svenska
Trke
Ting Vit
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 3/6
Tycho Brahe Planetarium building,
its roof being an example of a cylindric
section
Cylindric section.
An elliptic cylinder with the half-
axesa and b for the surface ellipse and
the height h.
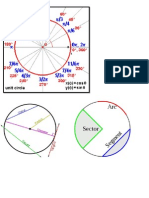
Cylindric section [edit]
Cylindric sections
are the
intersections of
cylinders with
planes. For a
right circular
cylinder, there
are four
possibilities. A
plane tangent to the cylinder, meets the cylinder in a single straight line. Moved
while parallel to itself, the plane either does not intersect the cylinder or
intersects it in two parallel lines. All other planes intersect the cylinder in an
ellipse or, when they are perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder, in a circle.
[2]
Eccentricity e of the cylindric section and semi-major axis aof the cylindric section
depend on the radius of the cylinder r and the angle between the secant plane
and cylinder axis in the following way:
Other types of cylinders [edit]
An elliptic cylinder is a quadric surface,
with the following equation in Cartesian
coordinates:
This equation is for an elliptic cylinder,
a generalization of the ordinary, circular
cylinder (a = b). Elliptic cylinders are
also known as cylindroids, but that
name is ambiguous, as it can also refer
to thePlcker conoid. The volume of an
elliptic cylinder with height h is
. Even more
general than the elliptic cylinder is the generalized cylinder: the cross-
sectioncan be any curve.
The cylinder is a degenerate quadric because at least one of the coordinates (in
this case z) does not appear in the equation.
An oblique cylinder has the top and bottom surfaces displaced from one
another.
There are other more unusual types of cylinders. These are the imaginary elliptic
Edit links
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 4/6
cylinders:
the hyperbolic cylinder:
and the parabolic cylinder:
About an arbitrary axis [edit]
Consider an infinite cylinder whose axis lies along the vector
We make use of spherical coordinates:
These variables can be used to define A and B, the orthogonal vectors that form
the basis for the cylinder:
With these defined, we may use the familiar formula for a cylinder:
where R is the radius of the cylinder. These results are usually derived
usingrotation matrices.
Projective geometry [edit]
In projective geometry, a cylinder is simply a cone whose apex is at infinity.
This is useful in the definition ofdegenerate conics, which require considering
the cylindrical conics.
Related polyhedra [edit]
A cylinder can be seen as a polyhedrallimiting case of an n-
gonal prism where napproaches infinity. It can also be seen as a dual of
a bicone as an infinite-sidedbipyramid.
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 5/6
In projective geometry, a cylinder is
simply a cone whose apex is at infinity,
which corresponds visually to a cylinder
in perspective appearing to be a cone
towards the sky.
Family of uniform prisms
Symmetry 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
[2n,2]
[n,2]
[2n,2
+
]
Image
As spherical polyhedra
Image
See also [edit]
Cylindrical coordinate system
Steinmetz solid, the intersection of two or three perpendicular cylinders
References [edit]
1. ^ , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on
Perseus
2. ^ "MathWorld: Cylindric section" .
5/29/2014 Cylinder (geometry) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cylinder_(geometry) 6/6
This page was last modif ied on 19 May 2014 at 19:26.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered trademark
of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-prof it organization.
Wikimedia Commons has
media related to Cylinder
(geometry).
Wikisource has the text of
the1911 Encyclopdia
Britannica article Cylinder.
Look up cylinder in
Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
External links [edit]
Surface area of a cylinder at
MATHguide
Volume of a cylinder at MATHguide
Categories: Quadrics Elementary shapes Euclidean solid geometry
Surfaces
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cylinder Shape Guide: Properties, Formulas & Types in 40 CharactersDocument39 paginiCylinder Shape Guide: Properties, Formulas & Types in 40 CharactersNaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steinmetz Solid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 paginiSteinmetz Solid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Construct Platonic, Archimedean and Stellated PolyhedraDe la EverandHow to Construct Platonic, Archimedean and Stellated PolyhedraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abcd Abcd Trapezoid Trapezium Trapezoid Trapèze Trapezio Trapez Trapezium Trapezium Trapézion Trápeza Tetrás Péza Trapezoid TrapézoeideDocument17 paginiAbcd Abcd Trapezoid Trapezium Trapezoid Trapèze Trapezio Trapez Trapezium Trapezium Trapézion Trápeza Tetrás Péza Trapezoid TrapézoeideSam Angelo EstrellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Riemannian Submersions, Riemannian Maps in Hermitian Geometry, and their ApplicationsDe la EverandRiemannian Submersions, Riemannian Maps in Hermitian Geometry, and their ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Geometry: 3D Figures and Their MeasurementsDocument16 paginiSolid Geometry: 3D Figures and Their MeasurementsJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths ProjectDocument7 paginiMaths ProjectHadiya KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexDocument9 paginiThree-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexAlí PabónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ellipsoid - Geometrìa DescriptivaDocument2 paginiEllipsoid - Geometrìa DescriptivaSolange PaihuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conics 1 Cut ConeDocument11 paginiConics 1 Cut ConeMarc LambertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cone Development Plane Area FormulasDocument9 paginiCone Development Plane Area FormulasManeesh BangaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vessel Head - WikiDocument2 paginiVessel Head - Wikiglh00Încă nu există evaluări
- CylinderDocument10 paginiCylinderSara XhaferiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conic SectionDocument12 paginiConic SectionAqilah MansorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Archimedean_spiralDocument3 paginiArchimedean_spiralLawathe M. EidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedDocument16 paginiSphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedAndreGuilhermeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Square Drilling with Reuleaux Triangle AttachmentDocument9 paginiSquare Drilling with Reuleaux Triangle AttachmentTanviÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Centroids: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiList of Centroids: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry Three-Dimensional Square Facets Vertex Regular Hexahedron Platonic SolidsDocument7 paginiGeometry Three-Dimensional Square Facets Vertex Regular Hexahedron Platonic SolidsAnonymous TpzPlptB5VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Geometry PrismsDocument17 paginiAnalytic Geometry PrismsCarl Kristopher Pelonia100% (1)
- 8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: ObjectivesDocument18 pagini8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: Objectiveszakaria shineeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Areas and VolumesDocument18 paginiSurface Areas and VolumesAjay BharatiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise NotesDocument3 paginiClass X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise NotesROOPAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ogive - Wikipedia PDFDocument10 paginiOgive - Wikipedia PDFNurul KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 paginiCircle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMahaveerprasad GotarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Project - PrantarDocument12 paginiMaths Project - Prantarprantarchakraborty.2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Jeecup2017 PDFDocument9 paginiJeecup2017 PDFGaurav PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle: Circumference of A Sphere Is The Circumference, or Length, of Any One of ItsDocument10 paginiCircle: Circumference of A Sphere Is The Circumference, or Length, of Any One of ItsSukhveen 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Sphere - WikipediaDocument72 paginiSphere - WikipediaNaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Shape of Drainage by Shinta Novia 2PJJADocument16 paginiThe Shape of Drainage by Shinta Novia 2PJJAShinta NoviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strakes & Spiral Staircase - Differential GeometryDocument5 paginiStrakes & Spiral Staircase - Differential GeometryBoby ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConeDocument6 paginiConeNaeem RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationDocument4 paginiA Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationAnjana mohandas WarrierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDocument5 paginiCylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDeviana DarmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid MensurationDocument5 paginiSolid MensurationDelfin MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curvature Extrema and Four-Vertex Theorems ForDocument13 paginiCurvature Extrema and Four-Vertex Theorems ForAnsui ZakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logarithmic SpiralDocument21 paginiLogarithmic SpiralSingh AshutoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reuleaux Triangle: ConstructionDocument4 paginiReuleaux Triangle: ConstructionAekanshÎncă nu există evaluări
- In MathematicsDocument2 paginiIn MathematicsRupa GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 CylinderDocument30 paginiWeek 7 CylinderJulius Patrick Mallanao100% (1)
- Euclid's Elements in Greek and EnglishDocument692 paginiEuclid's Elements in Greek and Englishjohn_tramp_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Hexagonal Dihexagonal Dipyramidal Class Axial ConfigurationDocument5 paginiHexagonal Dihexagonal Dipyramidal Class Axial Configurationbagz_555Încă nu există evaluări
- Angle Sum Property of A QuadrilateralDocument3 paginiAngle Sum Property of A Quadrilateralapi-174391216Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Volume FormulasDocument9 paginiCalculating Volume FormulasvvvvvvyyyyyyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical Guide to Quadric SurfacesDocument2 paginiMathematical Guide to Quadric SurfacesCarlo Tac-anÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Conic SectionsDocument10 paginiHistory of Conic SectionsJunna Mae GimongalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Geometry-3d PDFDocument27 paginiSolid Geometry-3d PDFpraveenshridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Solid FiguresDocument6 paginiCommon Solid FiguresERLIZA ROSETEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Formulas for Surface Area and VolumeDocument6 paginiImportant Formulas for Surface Area and Volumebhai ki gameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mensuration ProjectDocument4 paginiMensuration ProjectJatin NayyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cycloid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiCycloid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShivaanshh ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry and shapes in Euclidean spaceDocument2 paginiGeometry and shapes in Euclidean spaceJohn Matthew . SUYATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Conic SectionDocument23 paginiApplication of Conic Sectionsubbramaniam ramesh shunmugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- CirclesDocument6 paginiCirclesBrent Garcia OrdillanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alok Quadric Surfaces FinalDocument17 paginiAlok Quadric Surfaces FinalAlok Kumar OjhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DESCRIBE SHAPES Tugas Bhs InggrisDocument69 paginiDESCRIBE SHAPES Tugas Bhs InggrisZaCk D. ZogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conic Sections and Its Real Life ApplicationsDocument13 paginiConic Sections and Its Real Life Applicationstanwarabhinav2Încă nu există evaluări
- Epi CycloidDocument4 paginiEpi CycloidKishalaya KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deformation Mech2Document5 paginiDeformation Mech2Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Languages of India2Document12 paginiLanguages of India2Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superhuman: Human Enhancement and AdvancementDocument3 paginiSuperhuman: Human Enhancement and AdvancementShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction to SpidersDocument22 paginiAn Introduction to SpidersShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Languages of India1Document7 paginiLanguages of India1Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gene Libraries: Test Document (GGG)Document3 paginiGene Libraries: Test Document (GGG)Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhairavi - WikipediaDocument2 paginiBhairavi - WikipediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deformation MechDocument7 paginiDeformation MechShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of A Good Business PlanDocument19 paginiElements of A Good Business PlanShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angkor Wat: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 paginiAngkor Wat: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HarappaDocument5 paginiHarappaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiome: Copied and Pasted Remedy ThisDocument2 paginiPhysiome: Copied and Pasted Remedy ThisShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indus Valley Civilisation 1Document8 paginiIndus Valley Civilisation 1Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HelixDocument41 paginiHelixShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alhambra: Alhambra, Generalife and Albayzín, GranadaDocument12 paginiAlhambra: Alhambra, Generalife and Albayzín, GranadaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acropolis of AthensDocument10 paginiAcropolis of AthensShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cybernetics (Disambiguation)Document13 paginiCybernetics (Disambiguation)Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greeting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiGreeting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology 1Document6 paginiPhysiology 1Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant PhysiologyDocument10 paginiPlant PhysiologyShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metabolome: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 paginiMetabolome: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetabolomicsDocument11 paginiMetabolomicsShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of PhysiologistsDocument5 paginiList of PhysiologistsShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insect Physiology: Digestive SystemDocument8 paginiInsect Physiology: Digestive SystemShyamol Bose100% (1)
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument12 paginiExercise PhysiologyShyamol Bose100% (1)
- Fish Physiology 1Document17 paginiFish Physiology 1Shyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defense Physiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 paginiDefense Physiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurophysiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 paginiNeurophysiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurophysiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 paginiNeurophysiology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cy To ArchitectureDocument3 paginiCy To ArchitectureShyamol BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Std09 Maths TM 2 PDFDocument160 paginiStd09 Maths TM 2 PDFTNPSCbooksmaterials100% (1)
- FYUGP MathematicsDocument51 paginiFYUGP MathematicsISHA BANDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical solution transient Couette flow time-dependent pressureDocument7 paginiAnalytical solution transient Couette flow time-dependent pressureandresmendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 2.3Document10 paginiExercise 2.3Hendri Johan Tambunan11100% (2)
- Continuity Differentiation AssignmentDocument3 paginiContinuity Differentiation AssignmentGanesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Help AnClimDocument12 paginiHelp AnClimhcsrecsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Wildon - Representation Theory of The Symmetric Group (Lecture Notes) (2015)Document34 paginiMark Wildon - Representation Theory of The Symmetric Group (Lecture Notes) (2015)Satyam Agrahari0% (1)
- Nucl - Phys.B v.603Document578 paginiNucl - Phys.B v.603buddy72Încă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Kavita Gupta FinalDocument46 paginiDr. Kavita Gupta FinalMadhu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wksheet Calculus 1 Differentiation For Ch. 7 P1 & P2 PDFDocument39 paginiWksheet Calculus 1 Differentiation For Ch. 7 P1 & P2 PDFMs MsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProcrustesDistances.sasDocument3 paginiProcrustesDistances.sasMirQuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Formulas: Ca Foundation MathematicsDocument114 paginiAll Formulas: Ca Foundation MathematicsHimanshu SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Associated Legendre FunctionsDocument14 paginiAssociated Legendre FunctionsJuan Carlos TrujilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Fort Magsaysay National High School (Formerly Barangay Militar High School)Document10 paginiDepartment of Education: Fort Magsaysay National High School (Formerly Barangay Militar High School)Ciara Mae PrincesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01a - Course Outline of BS and MSC Mathematics Only For Fall 2020Document37 pagini01a - Course Outline of BS and MSC Mathematics Only For Fall 2020zaheer abbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Egorov's Theorem, A Detailed ProofDocument2 paginiEgorov's Theorem, A Detailed ProofpeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Non-Prismatic Semi-Rigid FramesDocument7 paginiAnalysis of Non-Prismatic Semi-Rigid FramesMhnd Al-SherrawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Survey On The Dai-Liao Family of Nonlinear Conjugate Gradient MethodsDocument16 paginiA Survey On The Dai-Liao Family of Nonlinear Conjugate Gradient Methodsهشام محمد خضرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Srinivasa RamanujanDocument10 paginiSrinivasa Ramanujangeena123Încă nu există evaluări
- Modal AnalysisDocument25 paginiModal AnalysisMuralitclÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Products and Factorization in 40 CharactersDocument39 paginiSpecial Products and Factorization in 40 CharactersHamza KahemelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Using Numerical Measures To Describe DataDocument72 paginiChapter 3 Using Numerical Measures To Describe Dataterzi eyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIU - EGM3311 - Syllabus Summer 2015Document3 paginiFIU - EGM3311 - Syllabus Summer 2015angelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes on "Modern Quantum MechanicsDocument24 paginiNotes on "Modern Quantum MechanicsPiLiGonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 2 OnlineDocument25 pagini4 2 Onlineapi-234934912Încă nu există evaluări
- 4MA0 4H Que 20170117Document28 pagini4MA0 4H Que 20170117abhayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimality Test - MODI Method PDFDocument2 paginiOptimality Test - MODI Method PDFKiruba ShankerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fung Resistance and Bales Seakeeping Optimization ModelDocument32 paginiFung Resistance and Bales Seakeeping Optimization ModelKivanc Ali ANILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trig Functions Domain & RangeDocument7 paginiInverse Trig Functions Domain & RangeArya NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Analysis: Prof. Dr. Patrick Dondl Adapted From Lecture Notes by Josias Reppekus (TU-München) 23rd July 2016Document73 paginiFunctional Analysis: Prof. Dr. Patrick Dondl Adapted From Lecture Notes by Josias Reppekus (TU-München) 23rd July 2016EDU CIPANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDe la EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDe la EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishDe la EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDe la EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDe la EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDe la EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (500)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe la EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDe la EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceDe la EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe la EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)De la EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (155)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDe la EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDe la EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (125)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDe la EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDe la EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (75)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDe la EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (94)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDe la EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationDe la EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (158)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesDe la EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (139)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsDe la EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityDe la EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe la EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)