Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Total Productive Maintenance
Încărcat de
ROKOV ZHASA0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
37 vizualizări18 paginiThis was one the ppt I delivered as part of my 2 year MBA course at SMS-NU
Titlu original
TOTAL PRODUCTIVE MAINTENANCE
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis was one the ppt I delivered as part of my 2 year MBA course at SMS-NU
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
37 vizualizări18 paginiTotal Productive Maintenance
Încărcat de
ROKOV ZHASAThis was one the ppt I delivered as part of my 2 year MBA course at SMS-NU
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 18
Total Productive Management (TPM)
Presenter : Rokov N. Zhasa
(NU Reg. No.- 111291 of 2011-2012)
Course :
MGT 401 Total Quality Management
Course Instructor : Mr. Hriyo Kayina
Date/ Time : April 17, 2013/ 0900 hr
M M X I I I - M M I V
School of
Management Studies
Nagaland University
CONTENT
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
1.1 TPM An Introduction
1.2 Objectives of TPM
1.3 Wastes Eliminated in TPM
1.4 Equipment Maintenance Techniques
Reference
1.5 Benefits of TPM
1.6 Performance Measures of Maintenance System
1.7 VIII Pillars of TPM
1.8 Conclusion
Important
This topic is covered under UNIT V of
MGT 401 TQM, NU MBA Old syllabus.
While discussing 8 Pillars of TPM follow
the sequence !
Its coming in exam so pay attention!
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
1.1 TPM An Introduction
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
TPM Optimize Productivity
All Levels of Employees
Management System
Seiichi Nakajima
Institute of Plant Management, Japan
50s
Repair after breakdown
Productive
Maintenance
70s
1.2 Objectives of TPM
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Why TPM was launched?
Create a Collective culture
Maximum
Efficiency
Accidents
Defects Breakdowns
Losses
0
1.3 Waste Eliminated in TPM
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Break Down
Setup/ Changeovers
Idling/ Minor Stopover
Reduced Eqpt. Speed
Defects & Rework
Start-up
6
Big
Losses
1.4
Equipment Maintenance Techniques
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Preventive Maintenance
Corrective Maintenance
Time Based Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance
Maintenance prevention
Break down Maintenance
1.5
Performance Measures of Maintenance System
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
OEE % =uptime % x Speed % x Quality %
Uptime % =
(MTBF-MTTR)
X 100
MTBF
MTBF =
Total Running Time
No. of failures
Speed (%) Efficiency =
Actual cycle time
X 100
Design cycle time
Quality (%) Efficiency
=
Good parts produced
X 100
Total parts produced
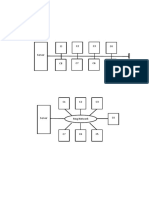
1.6 The 8 Pillars of TPM
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
TPM
VII Pillars
5
S
J
i
s
h
u
H
o
z
e
n
K
a
i
z
e
n
P
l
a
n
n
e
d
M
a
i
n
t
e
n
a
n
c
e
Q
u
a
l
i
t
y
M
a
i
n
t
e
n
a
n
c
e
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
O
f
f
i
c
e
T
P
M
S
a
f
e
t
y
,
H
e
a
l
t
h
&
E
n
v
i
r
o
n
m
e
n
t
1.6.1 5 S
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
5 S
1. SEIRI (Sort out)
5. SHITSUKE
(Self-discipline)
2. SEITON (Organise)
3. SEISO
(Shine the work place)
4. SEIKETSU
(Standardization)
1.6.2
Jishu Hozen (Autonomous maintenance)
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Purpose
Prepare the operators to take care of routine maintenance tasks
Steps in JH
1. Preparation of employees
2. Initial clean-up
3. Taking counter measures for the inaccessible areas of the
machine
4. Fixing tentative JH standards
5. General inspection training for employees
6. Autonomous inspection
7. Standardization
8. Achieve OPE and OEE and other TPM targets through Kaizen
1.6.3
Kaizen
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Meaning
Change for better
Focus
Foundation (5 Elements)
1. Team work,
2. Personnel discipline,
3. Improved morale,
4. Quality Circles
5. Suggestions for improvement
Philosophy
Incremental Change
1. Zero losses
2. Cost reduction in all resources
3. Improvement of overall plant
effectiveness
4. Use of PM analysis
5. Easy handling of operators
6. 30% manufacturing cost
reduction
Losses
Impede equipment
efficiency
Impede human work
efficiency
Impede effective use
of production
resources.
1.6.4 Planned Maintenance
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Purpose
Have trouble free machines/ equipment to produce defect free products
Steps in Planned Maintenance
1. Evaluate equipment and record its present status.
2. Restore from deterioration of equipment and minimize its
weaknesses.
3. Build up information management system.
4. Prepare time based information system, select equipement
parts and memebers and map out plan.
5. Prepare predictive maintenance
6. Evaluate planned maintenance.
Types
Preventive
Maintenance
Corrective
Maintenance
Maintenance
Prevention
Breakdown
Maintenance
1.6.5 Quality maintenance
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Purpose
Educating operators to upgrade their skill
Focus
1. Focus on improvement of knowledge, skills and techniques.
2. Creating a training environment for self-learning based on felt
needs.
3. Training curriculum/ tools/ assessment, etc. conductive to
employee revitalization.
4. Training to remove employees fatigue and make work
enjoyable.
1.6.8 Safety, health and environment
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Purpose
Have zero accident, zero health damage and zero fires
How to achieve?
Creating a safe work place
Creating a surrounding area that is not damaged by
the processes and procedures.
Creating awareness among employees
Conclusion
Develop a globally competitive Industrial
Base in our State (Nagaland) and NER
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
Our Mission
1. We must
Learn, Adopt, Adapt and Deploy TPM in our Conditions
and as per our needs
2. We must
Strive for
Excellence in the Working methods/ style needed
Excellence in the quality of our Products
Excellence in the quality of our Services
References
Panneerselvam, R. Production and
Operations Management, 2
nd
Edition, PHI
(2010)
MS 96 Total Quality Management, IGNOU
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
End of Presentation
School of Management Studies, Nagaland University
And I am open to queries
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Business EnvironementDocument34 paginiBusiness EnvironementROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Typolopgy DiagramDocument2 paginiNetwork Typolopgy DiagramROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delegation, Centralization and DecentralizationDocument31 paginiDelegation, Centralization and DecentralizationROKOV ZHASA50% (2)
- Country Risk Analysis Cra Write Up R N ZhasaDocument12 paginiCountry Risk Analysis Cra Write Up R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutual Fund Rokov N Zhasa 2Document18 paginiMutual Fund Rokov N Zhasa 2ROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bamboo Entrepreneurship Presentation 1Document27 paginiBamboo Entrepreneurship Presentation 1ROKOV ZHASA100% (2)
- Administrative Reforms CommissionDocument102 paginiAdministrative Reforms CommissionRahulRajRanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Governance PPT R N ZhasaDocument17 paginiCorporate Governance PPT R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutual Fund Write Up Rokov N ZhasaDocument16 paginiMutual Fund Write Up Rokov N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Country Risk Analysis CRA PPT by R N ZhasaDocument17 paginiCountry Risk Analysis CRA PPT by R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Governance PPT R N ZhasaDocument17 paginiCorporate Governance PPT R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delegation, Centralization and DecentralizationDocument31 paginiDelegation, Centralization and DecentralizationROKOV ZHASA50% (2)
- Technology Intelligence PPT R N ZhasaDocument19 paginiTechnology Intelligence PPT R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Governance Write Up R N ZhasaDocument21 paginiCorporate Governance Write Up R N ZhasaROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutual Fund Rokov N Zhasa 2Document18 paginiMutual Fund Rokov N Zhasa 2ROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counselling in The Work PlaceDocument12 paginiCounselling in The Work PlaceROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internet, HTML, Network Topology ReportDocument17 paginiInternet, HTML, Network Topology ReportROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna HazareDocument14 paginiAnna HazareROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Household Saving RateDocument8 pagini2 Household Saving RateROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liberalisation 1991Document5 paginiLiberalisation 1991ROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- C#.NET 2005 BasicsDocument71 paginiC#.NET 2005 Basicssanoj100% (26)
- Counselling in The Work PlaceDocument12 paginiCounselling in The Work PlaceROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Unions Act 1926Document21 paginiTrade Unions Act 1926ROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Productive MaintenanceDocument11 paginiTotal Productive MaintenanceROKOV ZHASA100% (1)
- Trade Unions Act 1926Document21 paginiTrade Unions Act 1926ROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hightlight of National Drug PolicyDocument1 paginăHightlight of National Drug PolicyROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Following GodDocument3 paginiFollowing GodROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenges of Inflationary Policy in India - Wikipedia The FreeDocument4 paginiChallenges of Inflationary Policy in India - Wikipedia The FreeROKOV ZHASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Cascadable Broadband Gaas Mmic Amplifier DC To 10Ghz: FeaturesDocument9 paginiCascadable Broadband Gaas Mmic Amplifier DC To 10Ghz: Featuresfarlocco23Încă nu există evaluări
- Resultados de La Web: GDDS - Traducción Al Español - Ejemplos Inglés - Reverso ..Document3 paginiResultados de La Web: GDDS - Traducción Al Español - Ejemplos Inglés - Reverso ..Jo PaterninaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Bubble Sheet Template Customize This WordDocument3 paginiMultiple Choice Bubble Sheet Template Customize This WordAl Bin0% (1)
- Muhammad Ajmal: Electrical EngineerDocument1 paginăMuhammad Ajmal: Electrical EngineerMuhammad AbrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizational Structure and ProfilesDocument178 paginiOrganizational Structure and ProfilesImran Khan NiaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylindrical Plug Gage DesignsDocument3 paginiCylindrical Plug Gage DesignskkphadnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magazine 55 EnglishPartDocument50 paginiMagazine 55 EnglishPartAli AwamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- C146-94a (2014) Standard Test Methods For Chemical Analysis of Glass SandDocument12 paginiC146-94a (2014) Standard Test Methods For Chemical Analysis of Glass SandAhmed AlzubaidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department Electrical Engineering Management IV Assignment 1 Semester 1, 2020Document2 paginiDepartment Electrical Engineering Management IV Assignment 1 Semester 1, 2020samuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Illustration Q3 Week3Document6 paginiGrade 10 Illustration Q3 Week3NetsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Novik NeoDocument32 paginiCatalogo Novik NeorafaelciceliniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubrics (Introduction To Human Resource Management) (HRM533)Document5 paginiRubrics (Introduction To Human Resource Management) (HRM533)norshaheeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- KV Sainik Vihar Class 6 Science Holidays HomeworkDocument7 paginiKV Sainik Vihar Class 6 Science Holidays HomeworkABYAN ShaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP 13 General Annexes - Horizon 2023 2024 - enDocument43 paginiWP 13 General Annexes - Horizon 2023 2024 - enLuchianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Gasification, Liquid Fuel Conversion (CTL), and CogenerationDocument66 paginiCoal Gasification, Liquid Fuel Conversion (CTL), and CogenerationVăn Đại - BKHNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noritz N-063 Installation ManualDocument66 paginiNoritz N-063 Installation ManualbondsupplyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers Et Al - Clear and Present ThinkingDocument214 paginiMyers Et Al - Clear and Present ThinkingAEÎncă nu există evaluări
- VUCG Guia de Instalacion y Comisionamiento en Ingles 1ZSC000562-AAY en Rev 1 - LowDocument56 paginiVUCG Guia de Instalacion y Comisionamiento en Ingles 1ZSC000562-AAY en Rev 1 - Lowarmandoa71565Încă nu există evaluări
- 2219 Aluminium Alloy - WikipediaDocument2 pagini2219 Aluminium Alloy - WikipediaVysakh VasudevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Contents: MechatronicsDocument45 paginiTable of Contents: MechatronicsFabo Barajas100% (1)
- Mockups Showeet (Standard)Document46 paginiMockups Showeet (Standard)Palo Alto Turismo y EntretenimientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doping Effects of Zinc On LiFePO4 Cathode MaterialDocument5 paginiDoping Effects of Zinc On LiFePO4 Cathode MaterialMarco Miranda RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reliance - Formulas & Calculations PDFDocument5 paginiReliance - Formulas & Calculations PDFkrishbistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of FlightDocument1 paginăMechanics of FlightMoh Flit25% (4)
- C ProgDocument29 paginiC ProgaishwaryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahusay Module 4 Acc3110Document2 paginiMahusay Module 4 Acc3110Jeth MahusayÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACP160DDocument14 paginiACP160Dinbox934Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment (40%) : A) Formulate The Problem As LPM B) Solve The LPM Using Simplex AlgorithmDocument5 paginiAssignment (40%) : A) Formulate The Problem As LPM B) Solve The LPM Using Simplex Algorithmet100% (1)
- Concept MappingDocument8 paginiConcept MappingRashid LatiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ata 47-NGS R25Document148 paginiAta 47-NGS R25NadirÎncă nu există evaluări