Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BS en 756-96 PDF
Încărcat de
Ahmet MemişDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BS en 756-96 PDF
Încărcat de
Ahmet MemişDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BRITISH STANDARD
BS EN
756 : 1996
The European Standard EN 756 : 1995 has the status of a
British Standard
ICS 25.160.20
NO COPYING WITHOUT BSI PERMISSION EXCEPT AS PERMITTED BY COPYRIGHT LAW
Welding consumables
Wire electrodes and wire-flux
combinations for submerged
arc welding of non alloy and
fine grain steels
Classification
This British Standard, having
been prepared under the
direction of the Engineering
Sector Board, was published
under the authority of the
Standards Board and comes into
effect on
15 August 1996
BSI 1996
The following BSI references
relate to the work on this
standard:
Committee reference WEE/39
Draft for comment 92/76973 DC
ISBN 0 580 25760 6
BS EN 756 : 1996
Amendments issued since publication
Amd. No. Date Text affected
Committees responsible for this
British Standard
The preparation of this British Standard was entrusted to Technical Committee
WEE/39, Welding consumables, upon which the following bodies were represented:
Aluminium Federation
Associated Offices Technical Committee
Association of Welding Distributors
British Association for Brazing and Soldering
British Compressed Gases Association
British Constructional Steelwork Association Ltd.
British Iron and Steel Producers' Association
Electricity Association
Engineering Equipment and Materials Users' Association
Lloyd's Register of Shipping
Magnesium Industry Council
Power Generation Contractors Association (PGCA (BEAMA Ltd.))
Process Plant Association
Stainless Steel Wire Industry Association
Welding Institute
Welding Manufacturers' Association (BEAMA Ltd.)
BS EN 756 : 1996
BSI 1996 i
Contents
Page
Committees responsible Inside front cover
National foreword ii
EN foreword 2
Text of EN 756 3
ii BSI 1996
BS EN 756 : 1996
National foreword
This British Standard has been prepared by Technical Committee WEE/39 and is the
English language version of EN 756 : 1995 Welding consumables Wire electrodes and
wire-flux combinations for submerged arc welding of non alloy and fine grain
steels Classification published by the European Committee for Standardization
(CEN).
EN 756 was produced as a result of international discussions in which the United
Kingdom took an active part.
BS EN 756 : 1996 partially supersedes BS 4165 : 1984 which will be withdrawn upon
publication of BS EN 760.
Compliance with a British Standard does not of itself confer immunity
from legal obligations.
CEN
European Committee for Standardization
Comite Europe en de Normalisation
Europa isches Komitee fu r Normung
Central Secretariat: rue de Stassart 36, B-1050 Brussels
1995 All rights of reproduction and communication in any form and by any means reserved in all countries to
CEN and its members
Ref. No. EN 756 : 1995 E
EUROPEAN STANDARD
EN 756
NORME EUROPE
ENNE
EUROPA
ISCHE NORM
October 1995
ICS 25.160.20
Descriptors: Arc welding, welding fluxes, welding electrodes, scale: corrosion, alloy steels, unalloyed steels, manganese steels,
classifications, symbols, mechanical tests, chemical composition
English version
Welding consumables Wire electrodes and wire-flux
combinations for submerged arc welding of non alloy and fine
grain steels Classification
Produits consommables pour le soudage
Fils-electrodes et couples fils-flux pour le soudage a
l'arc sous flux des aciers non allies et a grains
fins Classification
Schweizusatze Drahtelektroden und
Draht-Pulver-Kombinationen zum
Unterpulverschweien von unlegierten Stahlen und
Feinkornstahlen Einteilung
This European Standard was approved by CEN on 1995-08-27. CEN members are
bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations which stipulate the
conditions for giving this European Standard the status of a national standard
without any alteration.
Up-to-date lists and bibliographical references concerning such national standards
may be obtained on application to the Central Secretariat or to any CEN member.
This European Standard exists in three official versions (English, French, German).
A version in any other language made by translation under the responsibility of a
CEN member into its own language and notified to the Central Secretariat has the
same status as the official versions.
CEN members are the national standards bodies of Austria, Belgium, Denmark,
Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands,
Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom.
Page 2
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
Foreword
This European Standard was prepared by the Technical
Committee CEN/TC 121, Welding, of which the
secretariat is held by DS.
This European Standard shall be given the status of a
national standard, either by publication of an identical
text or by endorsement, at the latest by April 1996, and
conflicting national standards shall be withdrawn at
the latest by April 1996.
According to the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations,
the following countries are bound to implement this
European Standard: Austria, Belgium, Denmark,
Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland,
Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal,
Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom.
Contents
Page
Foreword 2
0 Introduction 3
1 Scope 3
2 Normative references 3
3 Classification 3
4 Symbols and requirements 3
4.1 Symbol for the product/process 3
4.2 Symbol for tensile properties 3
4.3 Symbol for impact properties of
all-weld metal or two-run welded joint 4
4.4 Symbol for type of welding flux 4
4.5 Symbol for the chemical composition
of wire electrodes 4
5 Mechanical tests 5
5.1 Multi-run technique 5
5.2 Two-run technique 6
6 Chemical analysis 6
7 Technical delivery conditions 6
8 Designation 6
Annex
A (informative) Bibliography 7
Page 3
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
0 Introduction
This standard proposes a classification in order to
designate wire electrodes by chemical analyses and
wire-flux combinations in terms of the yield strength,
tensile strength and elongation of the all-weld metal.
The ratio of yield to tensile strength of weld metal is
generally higher than that of parent material. Users
should note that matching weld metal yield strength to
parent material yield strength will not necessarily
ensure that the weld metal tensile strength matches
that of the parent material. Where the application
requires matching tensile strength, therefore, selection
of the consumable should be made by reference to
column 3 of table 1.
Although combinations of wires and fluxes supplied by
individual companies may have the same grading, the
individual wires and fluxes from different companies
are not interchangeable unless verified according to
this standard.
It should be noted that the mechanical properties of
all-weld metal test specimens used to classify the
wire-flux combinations will vary from those obtained
in production joints because of differences in welding
procedures such as electrode size and parent material
composition.
1 Scope
This standard specifies requirements for classification
of wire-flux combinations and all-weld metal in the
as-welded condition for submerged arc welding of
non-alloy and fine grain steels with a minimum yield
strength of up to 500 N/mm
2
. One flux may be
classified with different wire electrodes. The wire
electrode is also classified separately based on its
chemical composition.
Fluxes for the single-run and two-run techniques are
classified on the basis of the two-run technique.
2 Normative references
This European Standard incorporates by dated or
undated reference, provisions from other publications.
These normative references are cited at the
appropriate places in the text and the publications are
listed hereafter. For dated references, subsequent
amendments to or revisions of any of these
publications apply to this European Standard only
when incorporated in it by amendment or revision. For
undated references the latest edition of the publication
referred to applies.
prEN 759 Welding consumables Technical
delivery conditions for welding filler
metals Type of product,
dimensions, tolerances and marking
prEN 760 Welding consumables Fluxes for
submerged arc welding
Classification
prEN1258 Welding Measurement of
preheating temperature, interpass
temperature and preheat
maintenance temperature during
welding
prEN 1597-1 Welding consumables Testing for
classification
Part 1 : Test assembly for all-weld
metal test specimens in steel, nickel
and nickel alloys
prEN 1597-2 Welding consumables Testing for
classification
Part 2 : Preparation of test assembly
for single and two run technique test
specimens in steel
ISO 31-0 : 1992 Quantities and units
Part 0 : General principles
3 Classification
The classification includes all-weld metal properties
obtained with a manufacturer's specific wire-flux
combination as given below. A wire electrode may be
separately classified with the symbol for its chemical
composition in table 5.
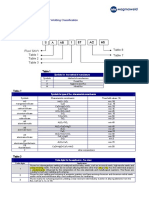
The classification is divided into five parts:
1) the first part gives a symbol indicating the
product/process to be identified;
2) the second part gives a symbol indicating the
strength and elongation of all-weld metal for
multi-run technique or the strength of the parent
material used in classification for the two-run
technique;
3) the third part gives a symbol indicating the
impact properties of all-weld metal or welded
joint;
4) the fourth part gives a symbol indicating the
type of flux used;
5) the fifth part gives a symbol indicating the
chemical composition of the wire electrode used.
4 Symbols and requirements
4.1 Symbol for the product/process
The symbol for a wire electrode and/or a wire-flux
combination used in the submerged arc welding
process shall be the letter S.
4.2 Symbol for tensile properties
4.2.1 Multi-run technique
The symbol in table 1 indicates yield strength, tensile
strength and elongation of the all-weld metal in the
as-welded condition determined in accordance
with 5.1.
Page 4
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
Table 1. Symbol for tensile properties by
multi-run technique
Symbol Minimum yield
strength
1)
Tensile
strength
Minimum
elongation
2)
N/mm
2
N/mm
2
%
35 355 440 to 570 22
38 380 470 to 600 20
42 420 500 to 640 20
46 460 530 to 680 20
50 500 560 to 720 18
1)
For yield strength the lower yield (R
eL
) shall be used when
yielding occurs, otherwise the 0,2 % proof strength (R
p0,2
) shall
be used.
2)
Gauge length is equal to five times the specimen diameter.
4.2.2 Two-run technique
The symbol indicates strength of the welded joint in
relation to strength of the parent material used in
two-run welding tests satisfactorily completed in
accordance with 5.2.
Table 2. Symbol for tensile properties by
two-run technique
Symbol Minimum parent
material yield
strength
Minimum tensile
strength of the
welded joint
N/mm
2
N/mm
2
2T 275 370
3T 355 470
4T 420 520
5T 500 600
4.3 Symbol for impact properties of all-weld
metal or two-run welded joint
The symbol in table 3 indicates the temperature at
which an average impact energy of 47 J is achieved
under the conditions given in clause 5. Three
specimens shall be tested. Only one individual value
may be lower than 47 J but not lower than 32 J. When
a wire-flux combination has been classified for a
certain temperature, it automatically covers any higher
temperature in table 3.
Table 3. Symbol for impact
properties of all-weld metal or
two-run welded joint
Symbol Temperature for minimum
average impact energy of
47 J
C
Z No requirements
A +20
0 0
2 220
3 230
4 240
5 250
6 260
7 270
8 280
4.4 Symbol for type of welding flux
The symbol in table 4 indicates type of welding flux as
described in EN 760.
Table 4. Symbol for type of welding flux
Type of flux Symbol
Manganese-silicate MS
Calcium-silicate CS
Zirconium-silicate ZS
Rutile-silicate RS
Aluminate-rutile AR
Aluminate-basic AB
Aluminate-silicate AS
Aluminate-fluoride basic AF
Fluoride-basic FB
Any other type Z
4.5 Symbol for the chemical composition of
wire electrodes
The symbol in table 5 indicates the chemical
composition of the wire electrode and includes an
indication of characteristic alloying elements.
The chemical composition of the weld metal is
dependent on the chemical composition of the wire
electrode and the metallurgical behaviour of the flux
(see EN 760).
Page 5
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
Table 5. Chemical composition of wire electrodes for submerged arc welding, percentage by mass
Symbol Chemical composition(%) (m/m)
1)2)3)
C Si Mn P S Mo Ni Cr
S0 Any other agreed composition
S1 0,05 to 0,15 0,15 0,35 to 0,60 0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S2 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 0,80 to 1,30 0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S3 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 >1,30 to
1,75
0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S4 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 >1,75 to
2,25
0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S1Si 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 to 0,40 0,35 to 0,60 0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S2Si 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 to 0,40 0,80 to 1,30 0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S2Si2 0,07 to 0,15 0,40 to 0,60 0,80 to 1,30 0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S3Si 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 to 0,40 >1,30 to
1,85
0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S4Si 0,07 to 0,15 0,15 to 0,40 >1,85 to
2,25
0,025 0,025 0,15 0,15 0,15
S1Mo 0,05 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,35 to 0,60 0,025 0,025 0,45 to 0,65 0,15 0,15
S2Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,025 0,025 0,45 to 0,65 0,15 0,15
S3Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 >1,30 to
1,75
0,025 0,025 0,45 to 0,65 0,15 0,15
S4Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 >1,75 to
2,25
0,025 0,025 0,45 to 0,65 0,15 0,15
S2Ni1 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,020 0,020 0,15 0,80 to 1,20 0,15
S2Ni1,5 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,020 0,020 0,15 >1,20 to
1,80
0,15
S2Ni2 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,020 0,020 0,15 >1,80 to
2,40
0,15
S2Ni3 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,020 0,020 0,15 >2,80 to
3,70
0,15
S2Ni1Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 0,80 to 1,30 0,020 0,020 0,45 to 0,65 0,80 to 1,20 0,20
S3Ni1,5 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 >1,30 to
1,70
0,020 0,020 0,15 >1,20 to
1,80
0,20
S3Ni1Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 >1,30 to
1,80
0,020 0,020 0,45 to 0,65 0,80 to 1,20 0,20
S3Ni1,5Mo 0,07 to 0,15 0,05 to 0,25 1,20 to 1,80 0,020 0,020 0,30 to 0,50 1,20 to 1,80 0,20
1)
Finished product chemical composition, Cu inclusive of copper coating # 0,30 %, Al # 0,030 %.
2)
Single values shown in the table are maximum values.
3)
The results shall be rounded to the same number of significant figures as in the specified value using the rules in accordance with
annex B, Rule A of ISO 31-0 : 1992.
5 Mechanical tests
5.1 Multi-run technique
Tensile and impact tests and any required retests shall
be carried out on weld metal in the as-welded
condition using an all-weld metal test assembly type 3
in accordance with EN 1597-1 using 4,0 mm or 3,2 mm
(3,0 mm) diameter wire electrodes whichever is the
larger size being supplied.
Welding conditions (single wire welding) and details of
the test assembly shall be selected from table 6.
Preheating is not required; welding may start from
room temperature.
The interpass temperature shall be measured using
temperature indicator crayons, surface thermometers
or thermocouples, see EN 1258.
The interpass temperature shall not exceed the
interpass temperature indicated in table 6. If, after any
pass, the interpass temperature is exceeded, the test
assembly shall be cooled in air to a temperature within
the indicated range.
Page 6
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
Table 6. Welding conditions for multi-run
single wire welding
Conditions
1) 2)
Wire electrode diameter
mm
3,2 4,0
Length of weld deposit, mm min. 200 min. 200
Type of current d.c. d.c.
Welding current, A 440
20 580
20
Welding voltage, V 27
1 29
1
Welding speed, mm/min 400
50 550
50
Interpass temperature range,
C (no preheat)
150
50 150
50
Electrode extension, mm 30
5 30
5
1)
If a.c. and d.c. operations are claimed, test welding shall be
carried out using a.c. only.
2)
a.c. means alternating current; d.c. means direct current.
5.2 Two-run technique
Tensile and impact tests and any required retests shall
be carried out on weld metal in the as-welded
condition using a test assembly type 4 in accordance
with EN 1597-2. Welding conditions shall be within the
range recommended by the manufacturer and shall be
recorded to demonstrate compliance with this
standard.
6 Chemical analysis
Chemical analysis shall be performed on specimens of
the wire electrode. Any analytical technique may be
used, but in case of dispute reference shall be made to
established published methods.
NOTE. See annex A.
7 Technical delivery conditions
Technical delivery conditions shall meet the
requirements in EN 759.
8 Designation
The designation of the wire electrode and the wire-flux
combination shall follow the principle given in the
examples below:
EXAMPLE 1:
A wire-flux combination for submerged arc welding for
multi-run technique deposits a weld metal with a
minimum yield strength of 460 N/mm
2
(46) and a
minimum average impact energy of 47 J at 230 C (3)
produced with an aluminate-basic flux (AB) and a
wire S2 is designated:
Wire-flux combination EN 756 S 46 3 AB S2
where:
EN 756 = standard number;
S = wire electrode and/or wire-flux
combination/submerged arc welding
(see 4.1);
46 = the tensile properties (see tables 1 and 2);
3 = impact properties (see table 3);
AB = type of welding flux (see table 4);
S2 = chemical composition of wire electrode
(see table 5).
EXAMPLE 2:
A wire-flux combination for submerged arc welding
using two-run technique demonstrated in accordance
with the manufacturer's recommendation in a parent
metal with minimum yield strength 420 N/mm
2
(4T)
achieving a weld metal with transverse tensile strength
> 520 N/mm
2
and impact energy 47 J at 220 C (2) with
an aluminate-basic flux (AB) and a wire electrode
S2Mo is designated:
Wire-flux combination EN 756 S 4T 2 AB S2Mo
EXAMPLE 3:
A wire electrode complying with the chemical
requirement of S2Mo in table 5 is designated:
Wire electrode EN 756 S2Mo
Page 7
EN 756 : 1995
BSI 1996
Annex A (informative)
Bibliography
A.1 Handbuch fu r das Eisenhu ttenlaboratorium, VdEh, Du sseldorf
A.2 BS 6200-3 Sampling and analysis of iron, steel and other ferrous metals Part 3: Methods of analysis
A.3 CEN/CR 10261 ECISS Information Circular 11 Iron and Steel Review of available methods of
chemical analysis
BSI
389 Chiswick High Road
London
W4 4AL
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BSI British Standards Institution
BSI is the independent national body responsible for preparing British Standards. It
presents the UK view on standards in Europe and at the international level. It is
incorporated by Royal Charter.
Revisions
British Standards are updated by amendment or revision. Users of British Standards
should make sure that they possess the latest amendments or editions.
It is the constant aim of BSI to improve the quality of our products and services. We
would be grateful if anyone finding an inaccuracy or ambiguity while using this
British Standard would inform the Secretary of the technical committee responsible,
the identity of which can be found on the inside front cover. Tel: 0181 996 9000.
Fax: 0181 996 7400.
BSI offers members an individual updating service called PLUS which ensures that
subscribers automatically receive the latest editions of standards.
Buying standards
Orders for all BSI, international and foreign standards publications should be
addressed to Customer Services. Tel: 0181 996 9001. Fax: 0181 996 7001.
In response to orders for international standards, it is BSI policy to supply the BSI
implementation of those that have been published as British Standards, unless
otherwise requested.
Information on standards
BSI provides a wide range of information on national, European and international
standards through its Library and its Technical Help to Exporters Service. Various
BSI electronic information services are also available which give details on all its
products and services. Contact the Information Centre. Tel: 0181 996 7111.
Fax: 0181 996 7048.
Subscribing members of BSI are kept up to date with standards developments and
receive substantial discounts on the purchase price of standards. For details of
these and other benefits contact Membership Administration. Tel: 0181 996 7002.
Fax: 0181 996 7001.
Copyright
Copyright subsists in all BSI publications. BSI also holds the copyright, in the UK, of
the publications of the international standardization bodies. Except as permitted
under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 no extract may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic,
photocopying, recording or otherwise without prior written permission from BSI.
This does not preclude the free use, in the course of implementing the standard, of
necessary details such as symbols, and size, type or grade designations. If these
details are to be used for any other purpose than implementation then the prior
written permission of BSI must be obtained.
If permission is granted, the terms may include royalty payments or a licensing
agreement. Details and advice can be obtained from the Copyright Manager.
Tel: 0181 996 7070.
BSI
389 Chiswick High Road
London
W4 4AL
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BSI British Standards Institution
BSI is the independent national body responsible for preparing British Standards. It
presents the UK view on standards in Europe and at the international level. It is
incorporated by Royal Charter.
Revisions
British Standards are updated by amendment or revision. Users of British Standards
should make sure that they possess the latest amendments or editions.
It is the constant aim of BSI to improve the quality of our products and services. We
would be grateful if anyone finding an inaccuracy or ambiguity while using this
British Standard would inform the Secretary of the technical committee responsible,
the identity of which can be found on the inside front cover. Tel: 020 8996 9000.
Fax: 020 8996 7400.
BSI offers members an individual updating service called PLUS which ensures that
subscribers automatically receive the latest editions of standards.
Buying standards
Orders for all BSI, international and foreign standards publications should be
addressed to Customer Services. Tel: 020 8996 9001. Fax: 020 8996 7001.
In response to orders for international standards, it is BSI policy to supply the BSI
implementation of those that have been published as British Standards, unless
otherwise requested.
Information on standards
BSI provides a wide range of information on national, European and international
standards through its Library and its Technical Help to Exporters Service. Various
BSI electronic information services are also available which give details on all its
products and services. Contact the Information Centre. Tel: 020 8996 7111.
Fax: 020 8996 7048.
Subscribing members of BSI are kept up to date with standards developments and
receive substantial discounts on the purchase price of standards. For details of
these and other benefits contact Membership Administration. Tel: 020 8996 7002.
Fax: 020 8996 7001.
Copyright
Copyright subsists in all BSI publications. BSI also holds the copyright, in the UK, of
the publications of the international standardization bodies. Except as permitted
under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 no extract may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic,
photocopying, recording or otherwise without prior written permission from BSI.
This does not preclude the free use, in the course of implementing the standard, of
necessary details such as symbols, and size, type or grade designations. If these
details are to be used for any other purpose than implementation then the prior
written permission of BSI must be obtained.
If permission is granted, the terms may include royalty payments or a licensing
agreement. Details and advice can be obtained from the Copyright Manager.
Tel: 020 8996 7070.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- En 1320-Fracture TestDocument17 paginiEn 1320-Fracture TestMadley RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 440-95 PDFDocument14 paginiBS en 440-95 PDFAhmet Memiş100% (2)
- En 14700 2005Document14 paginiEn 14700 2005Adil Malkic75% (4)
- prEN 14700-FD-2013-11-Consumiveis para Revestimentos DurosDocument15 paginiprEN 14700-FD-2013-11-Consumiveis para Revestimentos DurosRicardo FernandesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 15614-13Document24 paginiIso 15614-13Marija IvanovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshDocument36 paginiEN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshNiranjan Rajavel TigerÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en Iso 15609-3-2004Document14 paginiBS en Iso 15609-3-2004burak ücebakanÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 10025-2Document4 paginiEn 10025-2Sebastián Araya MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 9606 4 1999Document11 paginiIso 9606 4 1999Lino Alves InácioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO - 683 - 4 - 2016 - EN - PDF 7 PagesDocument11 paginiISO - 683 - 4 - 2016 - EN - PDF 7 PagesKALIDASS KÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN ISO 17639: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormDocument17 paginiEN ISO 17639: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormИван Иванов100% (1)
- Iso-Tr 17671-3-2002Document28 paginiIso-Tr 17671-3-2002Anbarasan Perumal100% (1)
- BS en 1708-3-12Document22 paginiBS en 1708-3-12gaso99Încă nu există evaluări
- BS en 00287-6-2010Document26 paginiBS en 00287-6-2010Shan Sandaruwan AbeywardeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIN EN 14700: Welding Consumables For Hard-FacingDocument14 paginiDIN EN 14700: Welding Consumables For Hard-FacingHany Elsayed100% (1)
- Fracture Testing According EN 9017Document3 paginiFracture Testing According EN 9017Anil100% (1)
- Iso 15609-1-2019Document19 paginiIso 15609-1-2019HarikeshRana100% (2)
- Iso 23277-2006 PDFDocument8 paginiIso 23277-2006 PDFAtim SahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steel.Document6 paginiEN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steel.Alin DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument15 paginiPDFkumarkk1969Încă nu există evaluări
- DIN en 1708-1-1999 Welding Basic Welded Joint Details in Steel Part 1 Pressurized ComponentsDocument73 paginiDIN en 1708-1-1999 Welding Basic Welded Joint Details in Steel Part 1 Pressurized Componentsmehmacar100% (2)
- En 1011-1Document14 paginiEn 1011-1nkpong849005Încă nu există evaluări
- ISO 15510 - Part 1Document5 paginiISO 15510 - Part 1Zdenko MahacekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minfm32202 Din 17445 Grade G X5crni13 4 Quenched and Tempered qt1Document3 paginiMinfm32202 Din 17445 Grade G X5crni13 4 Quenched and Tempered qt1Biraj SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 17640 2017 en PDFDocument11 paginiIso 17640 2017 en PDFTanveer Ahmed Quadri100% (1)
- En 10149-2Document19 paginiEn 10149-2singaravelan narayanasamy100% (1)
- BS en 10025-3Document28 paginiBS en 10025-3yasser awadallhÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO - TR - 15608 - Welding Guide Line PDFDocument10 paginiISO - TR - 15608 - Welding Guide Line PDFDacher DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN 760 (Flux-SAW)Document2 paginiEN 760 (Flux-SAW)HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application DIN 2303Document8 paginiApplication DIN 2303Marcelle Poll100% (1)
- En 10164-2005 PDFDocument15 paginiEn 10164-2005 PDFUmut HızırÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en - 14532 2 2004 PDFDocument26 paginiBS en - 14532 2 2004 PDFPacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 10029 PDFDocument1 paginăEn 10029 PDFJan AmersfÎncă nu există evaluări
- En ISO 14341-2008 Wire Electrodes MIG - MAG of Non Alloy and Fine Grain SteelsDocument4 paginiEn ISO 14341-2008 Wire Electrodes MIG - MAG of Non Alloy and Fine Grain SteelsAlessandro CamozzatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 10139Document2 paginiEn 10139releone11Încă nu există evaluări
- Iso DTR 20172Document66 paginiIso DTR 20172weldnoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSI Standards PublicationDocument40 paginiBSI Standards PublicationQuality Team100% (1)
- En 10088 Steel NumberDocument3 paginiEn 10088 Steel Numberrvieira659Încă nu există evaluări
- BS en 10204 2004 - 05Document12 paginiBS en 10204 2004 - 05EsakkirajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS EN 10028 3 2009, Flat ProductsDocument20 paginiBS EN 10028 3 2009, Flat ProductsgopalvivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 754 1Document7 paginiEn 754 1Amrut Kanungo0% (1)
- BS en Iso 9606-5 - 2000Document26 paginiBS en Iso 9606-5 - 2000jesoneliteÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 1412-2016Document12 paginiBS en 1412-2016S TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 2560-2009 PDFDocument7 paginiIso 2560-2009 PDFfebby farizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 10061-2003 (2008)Document10 paginiBS en 10061-2003 (2008)Martijn GrootÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF EN 10028-3-EnglishDocument17 paginiNF EN 10028-3-Englishhakan gecerÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS EN 14700-2014 - (Welding Consumables For Hard Facing)Document18 paginiBS EN 14700-2014 - (Welding Consumables For Hard Facing)HuiFrankyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 439-94 PDFDocument12 paginiBS en 439-94 PDFAhmet Memiş100% (2)
- Iso14341 ADocument2 paginiIso14341 AAluculesei Ciprian100% (1)
- B455Document3 paginiB455basha100% (1)
- Iso 9606-3Document30 paginiIso 9606-3Aleksandar StojanovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 764-4-2002Document44 paginiEn 764-4-2002Marija IvanovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cen Iso 17844 - 2004 PDFDocument80 paginiCen Iso 17844 - 2004 PDFANÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 757-97 PDFDocument14 paginiBS en 757-97 PDFAhmet Memiş100% (1)
- BS en 758-97 PDFDocument16 paginiBS en 758-97 PDFAhmet Memiş100% (1)
- En 876-Longitudinal Tensile TestDocument12 paginiEn 876-Longitudinal Tensile TestMadley RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische Norm: Draft Pren 10138-1Document21 paginiEuropean Standard Norme Européenne Europäische Norm: Draft Pren 10138-1gguardianangel100% (1)
- PrEN 10138-1 - 2000 - Prestressing Steels Part 1 - General RequirementsDocument21 paginiPrEN 10138-1 - 2000 - Prestressing Steels Part 1 - General RequirementsDang LuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 12072-2000 Welding Consumables - Wire Electrodes, Wires and Rods For Arc Welding of Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steels - ClassificationDocument12 paginiBS en 12072-2000 Welding Consumables - Wire Electrodes, Wires and Rods For Arc Welding of Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steels - Classificationnikidragon4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 1418-1998Document12 paginiEn 1418-1998apostolidis83Încă nu există evaluări
- Magnet Made of Rare-Earth MetalsDocument44 paginiMagnet Made of Rare-Earth MetalsbmomeraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stewmac: Two-Tone Fender Sunburst in The Pre-1956 StyleDocument4 paginiStewmac: Two-Tone Fender Sunburst in The Pre-1956 StyleAlexandre KlüppelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM A747-Standard-Specification-For-Steel-Castings-Stainless-Precipitation-Hardening PDFDocument4 paginiASTM A747-Standard-Specification-For-Steel-Castings-Stainless-Precipitation-Hardening PDFRaul Dela Rosa Malanog100% (1)
- Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysts For Multicomponent ReactionsDocument43 paginiHomogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysts For Multicomponent Reactionswakanda foreverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Removal of Impurities From ClayDocument5 paginiRemoval of Impurities From ClayPuturrú De FuáÎncă nu există evaluări
- D D Khedkar Evaluation of Suitability of Ambanala Water, Amravati, For IrrigationDocument4 paginiD D Khedkar Evaluation of Suitability of Ambanala Water, Amravati, For IrrigationDr. Dinesh D KhedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFDocument4 paginiInspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFSAIIN khodirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document44 paginiScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1cyril coscos57% (7)
- 1 The Haber ProcessDocument5 pagini1 The Haber ProcessLeses MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Conservation in Liquid IronDocument2 paginiHeat Conservation in Liquid Ironarnaldorcr8646Încă nu există evaluări
- Sandvik Pipe - Tube - Bar - Hollow Bar: Stock Program in StainlessDocument26 paginiSandvik Pipe - Tube - Bar - Hollow Bar: Stock Program in Stainlessalbejo_r9Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Topografi Permukaan Dan Kontak Antar PermukaanDocument37 pagini2 Topografi Permukaan Dan Kontak Antar PermukaanSarah FadliillahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toughened Glass Data SheetsDocument2 paginiToughened Glass Data SheetsAr Aayush GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eab2103 Construction Science-1 PDFDocument111 paginiEab2103 Construction Science-1 PDFJoshua KiptooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam - 5Document13 paginiExam - 5Stanley AlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Study of Natural Rubber Shock Attenuation DevicesDocument10 paginiExperimental Study of Natural Rubber Shock Attenuation DevicesMeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BQ - SewerageDocument3 paginiBQ - SewerageZak HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis On Biofuel ProductionDocument5 paginiThesis On Biofuel Productionaflpaftaofqtoa100% (2)
- Isolation of Caffeine From Tea Leaves - Lab ExperimentDocument11 paginiIsolation of Caffeine From Tea Leaves - Lab ExperimentMiera Ismail100% (1)
- Design of Boiler Forced Draft FanDocument5 paginiDesign of Boiler Forced Draft FanAu TagolimotÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM A 514 - A 514-00. Standard Specification For High-YieldDocument3 paginiASTM A 514 - A 514-00. Standard Specification For High-YieldHo Le QuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- GN042Document43 paginiGN042Riko Chy MakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Analysis of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Aircraft WinDocument4 paginiNumerical Analysis of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Aircraft WinSiva BhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abecote 352Document3 paginiAbecote 352engramir07Încă nu există evaluări
- LPG Storage and Piping SystemsDocument6 paginiLPG Storage and Piping SystemsAhmed Mohamed FarahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcite 2c ReportDocument23 paginiCalcite 2c ReportBhewill SermoniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Термостатический регулятор температуры VTA500 - VTS500 - 98140345 - utgC - lrDocument8 paginiТермостатический регулятор температуры VTA500 - VTS500 - 98140345 - utgC - lrDenisÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Lignin Structure, Pretreatments, Fermentation Reactions and Biorefinery PotentialDocument11 paginiA Review On Lignin Structure, Pretreatments, Fermentation Reactions and Biorefinery PotentialLidiane LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Possibility of Production of Bricks Using Waste Materials & Natural Binding Materials in Sri LankaDocument25 paginiPossibility of Production of Bricks Using Waste Materials & Natural Binding Materials in Sri LankaRohantha RukshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2024 RedoxDocument4 pagini2024 Redoxjoshualiew06Încă nu există evaluări