Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Boundaries of The Infratemporal Fossa
Încărcat de
Walter PowellTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The Boundaries of The Infratemporal Fossa
Încărcat de
Walter PowellDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
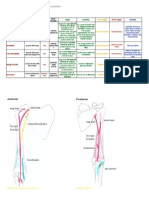
The boundaries of the infratemporal fossa
1. Moore, Keith L & Dalley, Arthur (2006). Clinically oriented anatomy (5th ed.), Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
Superior boundary (wall/roof): Infratemporal surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone
Anterior boundary (wall): The posterior, infratemporal surface of the body of the maxilla and the
adjacent anterior tissues of the pterygomandibular space (including the pterygomandibular raphe)
Posterior boundary (wall): The styloid process and diaphragm (including the styloid musculature and
related fascia) and the carotid sheath
Lateral wall: Ramus and coronoid process of the mandible
Medial boundary (wall): The lateral lamina (lateral pterygoid plate) of the pterygoid process of the
sphenoid bone.
Inferior boundary: Open communication with cervical tissue spaces
Contents of the infratemporal fossa
Muscles
Lower part of the Temporalis and masseter muscles (origin of massetar muscle:lower margin of the
inner surface of zygomatic bone insertion : outer surface of the ramus of the mandible )
Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
Vessels
The internal maxillary vessels, consisting of the maxillary artery originating from the external carotid
artery and its branches.
MAXILLARY ARTERY
The larger of the 2 terminal branches of the external carotid a. (supercial temporal a.)
Arises posterior to the condylar neck of the mandible within the parotid gland
Exits the parotid gland and passes anteriorly between the ramus of the mandible and the
sphenomandibular lig. within the infratemporal fossa
Takes a course that is either supercial or deep to the lateral pterygoid until reaching the
pterygopalatine fossa via the pterygomaxillary ssure
Supplies the deep structures of the face and may be divided into 3 parts as it passes medially
through the infratemporal fossa:
1. 1st partmandibular part
2. 2nd partpterygoid part
3. 3rd partpterygopalatine part
Veins
pterygoid venous plexus
Nerves
Mandibular nerve, inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve, buccal nerve, chorda tympani nerve, and
otic ganglion.
Mandibular nerve
Mandibular nerve which is the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3), also known as the
"inferior maxillary nerve", enters infratemporal fossa from middle cranial fossa through foramen
ovale.
Motor branches:
masseteric nerve
deep temporal nerve
lateral pterygoid nerve and medial pterygoid nerve
Its motor fibers innervate all the muscles of mastication plus the mylohyoid, anterior belly of the
digastric, and the tensores veli palati and tympani
Sensory innervation:
meningeal nerve
buccal nerve
auriculotemporal nerve
lingual nerve
inferior alveolar nerve
auricle
external acoustic meatus
tympanic membrane
temporal region
cheek
skin overlying the mandible (except at the angle of the mandible)
floor of mouth
lower teeth
gingiva
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Microbiology of Periodontal DiseaseDocument5 paginiMicrobiology of Periodontal DiseaseWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duraphat VarnishDocument1 paginăDuraphat VarnishWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set up a wireless Xbox hotspot on WindowsDocument1 paginăSet up a wireless Xbox hotspot on WindowsWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set up a wireless Xbox hotspot on WindowsDocument1 paginăSet up a wireless Xbox hotspot on WindowsWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuotesDocument4 paginiQuotesWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freestyle Program 1.8kmDocument1 paginăFreestyle Program 1.8kmWalter PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Fowlervs SORLreconstructionDocument6 paginiFowlervs SORLreconstructionAkbar GazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporomandibular Disorders: An Overview and Its Association With Parafunctional ActivityDocument72 paginiTemporomandibular Disorders: An Overview and Its Association With Parafunctional ActivityNaveen MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osce Summary - SystemsDocument9 paginiOsce Summary - Systemsnmc_nguyen82100% (6)
- Everyday Sports Injuries The Essential Step-By-Step Guide To Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument274 paginiEveryday Sports Injuries The Essential Step-By-Step Guide To Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentAnonymous f6goFflg3T100% (10)
- Buttonhole DislocationDocument13 paginiButtonhole DislocationHanif Andhika WardhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lateral EpicondylitisDocument12 paginiLateral EpicondylitisIshitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sba - Mrcs Past Year QDocument60 paginiSba - Mrcs Past Year QMohammad Husni Banisalman100% (1)
- Approach To Traumatic Orthopedic InjuriesDocument2 paginiApproach To Traumatic Orthopedic InjuriesZahid MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyzing the Phases and Components of Normal GaitDocument17 paginiAnalyzing the Phases and Components of Normal GaitDiego Cruces BustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collinear Reduction Clamp FLDocument8 paginiCollinear Reduction Clamp FLArhan MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomia MSKDocument1.249 paginiAnatomia MSKArthemizio Lopes100% (1)
- Foot Reflexology Complete How To Techniques & Step by Step Instructions!Document10 paginiFoot Reflexology Complete How To Techniques & Step by Step Instructions!Tony MickensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Made EasyDocument7 paginiMuscles of The Upper Limb Made Easynss92% (26)
- Anatomi Ankle 1Document114 paginiAnatomi Ankle 1Zera DirgantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedeul Putti PlatDocument7 paginiProcedeul Putti PlatLoredanaNovacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re-Visioning The Fascia As A Body-Wide Regulatory System: by Thomas MyersDocument4 paginiRe-Visioning The Fascia As A Body-Wide Regulatory System: by Thomas MyersAndrew LiebermannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mosby's Orthodontic Review (2nd Edition) Pages 92 - 96Document5 paginiMosby's Orthodontic Review (2nd Edition) Pages 92 - 96sillyazianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular System PDFDocument5 paginiMuscular System PDFgabri100167% (3)
- Kelompok 5 Skenario 1 Blok 7Document29 paginiKelompok 5 Skenario 1 Blok 7NATASYA SALSABILAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 paginiApplied Anatomy and PhysiologyLinet HuchuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CYRIAX TECHNIQUE: DEEP TRANSVERSE FRICTIONDocument38 paginiCYRIAX TECHNIQUE: DEEP TRANSVERSE FRICTIONAkanksha Kulvanshi100% (2)
- Test Bank For Joint Structure and Function A Comprehensive Analysis 5th EditionDocument11 paginiTest Bank For Joint Structure and Function A Comprehensive Analysis 5th EditionSergio BrownleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis - FractureDocument7 paginiCase Analysis - FractureMichelle TeodoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 - SkullDocument10 paginiChapter 11 - Skullwamaithamargaret257Încă nu există evaluări
- Healing Hamstring InjuriesDocument7 paginiHealing Hamstring Injuriesetelosztas108Încă nu există evaluări
- Idiopathic Toe Walking A Kinematic and Kinetic ProfileDocument8 paginiIdiopathic Toe Walking A Kinematic and Kinetic Profileyarimar hoyosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knee Injury Seminar GroupDocument96 paginiKnee Injury Seminar GroupAqilah Ab RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Tissue OutlineDocument4 paginiMuscle Tissue OutlinePeachy PieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 895 1993 1 SM PDFDocument9 pagini895 1993 1 SM PDFRahma TikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Above-Knee Prosthetics: The Knud Jansen LectureDocument15 paginiAbove-Knee Prosthetics: The Knud Jansen LecturerkÎncă nu există evaluări