Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
11.fiber Optics
Încărcat de
Achilles AldaveDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
11.fiber Optics
Încărcat de
Achilles AldaveDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING PART 11
FIBER OPTICS
Multiple Choice: Encircle the letter that corresponds to your
answer.
1. A transparent material along which we can transmit light is
called:
a. a fiber optic
b. a flashlight
c. an optic fiber
d. a xenon bulb
2. A simple fiber optic system would consist of:
a. a light source, an optic fiber and a photo-electric cell
b. a laser, an optic fiber and an LED
c. a copper coaxial cable, a laser and a photo-electric cell
d. an LED, a cathode ray tube and a light source
3. Optic fiber is normally made from:
a. coherent glass and xenon
b. copper
c. water
d. silica glass or plastic
4. It is not true that:
a. endoscopes use coherent bundles of fibers
b. silica glass is used because of its clarity
c. photocell converts light into electric current
d. plastic fiber is normally used for long distance
communications
5. The number of fibers in a typical endoscope is about:
a. 1870
b. 300
c. 50,000
d. 60
6. The speed of light in a transparent material:
a. is always the same regardless of the material chosen
b. is never greater than the speed of light in free space
c. increases if the light enters a material with a higher
refractive index
d. is slowed down by a factor of a million within the first 60
meters
7. A ray of light in a transparent material of refractive index 1.5
is approaching a material with a refractive index of 1.48. At
the boundary, the critical angle is:
a. 90
b. 9.4
c. 75.2
d. 80.6
8. If a ray of light approaches a material with a greater
refractive index:
a. The angle of incidence will be greater than the angle of
refraction
b. TIR will always occur
c. The speed of the light will increase immediately as it
crosses the boundary
d. The angle of refraction will be greater than the angle of
incidence
9. If a light ray crosses the boundary between two materials
with different refractive indices:
a. no refraction would take place if the angle of incidence
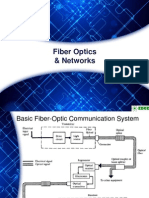
was 0
b. refraction will always occur
c. the speed of the light will not change if the incident ray is
traveling along the normal
d. the speed of light never changes
10. The common windows used in fiber optic communications
are centered on wavelengths of:
a. 300 nm, 1550 nm and 850 nm
b. 850 nm, 1500 nm and 1300 nm
c. 1350 nm, 1500 nm and 850 nm
d. 800 nm, 1300 nm and 1550 nm
11. A wavelength of 660 nm is often used for visible light
transmission. The frequency of this light in free space would
be:
a. 660 x 10
9
Hz
b. 4.5 x 10
14
Hz
c. 300 x 10
8
Hz
d. 45 x 10
12
Hz
12. In free space, light travels at approximately:
a. 180,000 ms
-1
b. 3 x 109 ms
-1
c. 300 ms
-1
d. 0.3 meters per nanosecond
13. The window with the longest wavelength operates at a
wavelength of approximately:
a. 850 nm
b. 1550 m
c. 1350 nm
d. 1.55 m
14. The 850 nm window remains popular because it:
a. uses visible light and this allows plastic fibers to be used
b. the fiber is less expensive to install and has lower losses
than any other windows
c. the system is less expensive and easier to install
d. allows higher data transmission rates
15. No material could have a refractive index of:
a. 1.5
b. 1.3
c. 1.1
d. 0.9
16. As the meridional ray is propagated along the optic fiber it:
a. travels in a sort of spiral shape
b. stays in the center of the fiber
c. passes repeatedly through the center of the core
d. is reflected off the the inside surface of the primary
buffer. This is called TIR
17. If the refractive index of the core of an optic fiber was 1.47
and that of the cladding was 1.44, the cone of acceptance
would have an angle of approximately:
a. 17.19
b. 72.82
c. 78.4
d. 34.36
18. An active fiber detector:
a. is used to prevent accidental exposure to invisible light
b. is a communication system used during installation
c. detects movement of fiber in security systems
d. can be used to weigh objects
19. If light leaves a material of refractive index 1.45 and crosses
an abrupt into a material of refractive index 1.0, the Fresnel
loss would be:
a. 0.346 dB
b. 0.149 dB
c. 1.613 dB
d. 3 dB
20. Absorption loss is caused by:
a. insufficient stirring of the ingredients during manufacture
b. changes in the density of the fiber due to uneven rates of
cooling
c. microscopic cracks in the cladding which allow leakage
of the vacuum in the core
d. impurities in the fiber
21. Rayleigh scatter is most severe:
a. in light with a short wavelength
b. in blue light on the Earth and black light on the moon
c. in low frequency light
d. at sunset
22. Bending losses:
a. always result in breakage of the fiber
b. can be caused by microbends and macrobends
c. are used to detect the length of fiber on a drum
d. are caused by the difference in the operating
temperature of the core compared with the cladding on
active fibers
23. Dispersion:
a. causes the core to spread out and get wider as the pulse
is transmitted along the fiber
b. results in the wavelength of the light increasing along the
fiber
c. is the lengthening of light pulses as they travel down the
fiber
d. cannot occur with a laser light source
24. An SI MM fiber has a core of 62.5 m diameter and a
numerical aperture of 0.2424. The number of modes that
would occur using a light of wavelength of 865 nm would be:
a. 1
b. 378
c. 1513.78
d. 1513
25. Intramodal dispersion:
a. only occurs in multimode fiber
b. is also called chromatic dispersion
c. does not occur in multimode fiber
d. could not occur in an all plastic fiber
26. If the wavelength of the transmitted light were to be
decreased, the number of modes would:
a. increase
b. decrease
c. remain the same
d. halve in a graded index fiber
27. The refractive index of a GI fiber
a. is at its highest value at the center of the core
b. is usually higher in the cladding than in the core
c. increases as we move away from the center of the core
d. has a value of 4 instead of the 2 common in step index
fibers
28. A cable containing both optic fiber and copper conductors is
called:
a. an armored cable
b. a dehydrated cable
c. tight jacketed cable
d. a hybrid cable
29. LSOH means low smoke:
a. zero halogen
b. zero heat
c. optic fibers of hybrid design
d. or heat
30. Spiral galvanized wires are sometimes added to a cable to:
a. conduct electricity
b. allow the cable to stretch more to relieve stress
c. improve crush resistance
d. allow the fibers to be upgraded as necessary
31. Blown fiber allows:
a. easy removal of the fibers to clean the ducts
b. the diameter of the fiber to be increased by filling it with
compressed air
c. easy removal of any water in the fiber
d. easy replacement of any damaged fiber
32. Within buildings:
a. both tight buffered and loose jacketed cables are used
b. only loose jacketed cables are used
c. only armored cables can be used
d. only tight buffered cables are used
33. If light is launched from a fiber with a core diameter of 50 m
into a fiber of core 62.5 m diameter, the loss would be:
a. +1.9 dB
b. zero
c. 1.9 dB
d. 16.8 dB
34. Cleaving is the process of:
a. removing the cladding before connecting fibers together
b. cutting the end of the fiber in preparation for connecting
two fibers
c. cleaning the surface of optic fibers
d. inspecting fibers for flaws
35. A tang is most likely to give rise to:
a. increased values of NA
b. eccentricity
c. excessive amplification
d. gap loss
36. The core of a typical monomode fiber would have a diameter
of:
a. 50 m
b. 50 nm
c. 8 m
d. 1 mm
37. Stripping off the primary buffer can be achieved by:
a. chemical or mechanical means
b. cleaving the buffer off
c. isopropyl alcohol
d. brushing on index matching gel then wiping off with lint
free cloth
38. Too much overfeed whilst splicing will cause:
a. waisting
b. a bubble being formed due to air being trapped inside
the fiber
c. a bulge in the fiber
d. runback
39. The main fusing arc is likely to have a duration of:
a. 15 s
b. 62.5 ns
c. 10-20 minutes
d. less than a second
40. PAS stands for:
a. position adjustment system
b. profile alignment standard
c. plane alignment system
d. profile alignment system
41. For viewing the splicing process, a CCD camera is
preferable to a microscope because:
a. higher magnification can be achieved
b. better resolution is possible
c. there is no risk of eye damage
d. a CCD camera can operate at very low light levels
42. A splice protector:
a. provides more flexibility at the mechanical joint
b. is not needed inside an enclosure
c. protects against unauthorized copying of data
d. provides mechanical protection to the fusion splice
43. The three basic designs used for mechanical splices are:
a. vee-groove, bent tube and precision hole
b. vee-groove, PAS and LID
c. fusion splice, mechanical splice and enclosures
d. UV curing epoxy, index matching gel and isopropyl
alcohol
44. A typical value for the insertion loss for a mechanical splice
is:
a. 50 dB
b. 0.2 dB
c. 12 mm
d. 3 dB
45. Mechanical splices have the advantage that they:
a. are easily mistaken for splice protectors
b. have lower losses than fusion splices
c. are quick and easy to fit
d. are waterproof
46. An elastomeric splice:
a. has losses which are about one thousandth of a fusion
splice
b. uses a flexible plastic to align the fibers
c. is based upon the bent tube principle
d. cannot be re-used
47. Some designs of mechanical splice can be easily mistaken
for:
a. an enclosure
b. a PAS splicer
c. a splice protector
d. an all plastic fiber
48. Two fibers can be joined by:
a. two adapters plugged into each end of a connector
b. a bare fiber connector
c. two connectors and one adapter
d. a single connector
49. A connector with a keyed ferrule and secured by a screw
thread is likely to be an:
a. SC
b. FCPC
c. STPC
d. SMA 906
50. A PC finish:
a. reduces both the return loss and the insertion loss
b. makes physical contact but damages the end of the fiber
c. is the result of polishing on a hard surface
d. is the result of using an incorrect dolly
51. A full length Delrin sleeve:
a. converts the ferrule of an SMA 905 connector to be
compatible with the SMA 906
b. can be used instead of an adapter
c. is a popular choice of connector with cable television
companies
d. reduces the insertion loss of SMA 906 connectors
52. During polishing of a silica fiber, final inspection reveals a
large scratch running right across the fiber. A likely cause of
this is:
a. contamination of the final lapping film with some coarse
grit from a previous stage of the polishing
b. using diamond lapping film instead of aluminum oxide
film
c. using the wrong dolly
d. water laying on the surface of the fiber. Simply wipe it
off with lint-free tissue
53. A 4 x 4 coupler would have a total of:
a. 16 ports
b. 4 ports
c. 9 ports
d. 8 ports
54. The main advantage of using a star coupler to connect a
large number of terminals is that:
a. more cable would be used and hence system reliability
would increase
b. the power loss is lower than would be the case if tee
couplers were to be used
c. higher levels of data errors could be tolerated
d. less cable is used
55. Coupling ratio is also known as:
a. directional loss
b. coupling loss
c. splitting ratio
d. directivity ratio
56. The output connection which carries the highest power level
is the:
a. tap port
b. power port
c. star
d. throughput port
57. The safest type of laser is referred to as:
a. infrared
b. class 1
c. pulsed
d. class 4
58. A typical value for the spectral width of a laser is:
a. 1310 nm
b. 3 nm
c. 850 nm
d. 30 nm
59. An APD:
a. can produce visible light as well as infrared light at 850
nm, 1300 nm and 1550 nm
b. has good electrical output in low light conditions
c. has a lower dynamic range than a PIN diode
d. is cheaper than a PIN diode
60. LEDs are not used as the light source for high speed
telecommunications because of their:
a. higher cost
b. poor reliability
c. inability to provide a visible light output
d. slow switching speed and higher spectral width
61. A typical value of t
r
for a laser would be:
a. 3.5 ns
b. 3 nm
c. 90%
d. 0.3 ns
62. For contract purposes, test equipment should:
a. have a valid certificate of calibration
b. be left switched on at all times
c. be powered by internal batteries
d. be manufactured by the same company as produced the
fiber
63. Light sources often include a tone output. This enables:
a. the length of the fiber to be calculated
b. our eyes to see the infrared light more easily
c. longer fibers to be tested
d. easy identification of the fiber being tested
64. For detailed examination of a very short length of optic fiber
cable, the OTDR should use the:
a. shortest possible wavelength
b. shortest possible pulsewidth
c. longest available pulsewidth
d. highest available power
65. The averaging facility of an OTDR can be switched off:
a. to provide a real time response
b. to remove noise and clean up the display of information
c. to allow the peak power to be used
d. if simultaneous measurements on more than one fiber
system are required
66. Reducing the length of a multimode fiber would:
a. decrease the transmitter rise time
b. decrease the system bandwidth
c. increase the bandwidth of the system
d. increase the system rise time
67. Changing the spectral width of the light source would affect
the:
a. fiber bandwidth in a singlemode system
b. system bandwidth of a multimode system but not a
singlemode one
c. aging losses
d. number of likely repairs
68. If the transmitter and the receiver rise times were 0.5 ns and
1.5 ns respectively, and the fiber rise time was 25 ps, the
system rise time would be approximately:
a. 25.05 ns
b. 1.42 ns
c. 1.58 ns
d. 5.19 ns
69. If the dispersion figure for a singlemode fiber is known to be
44 ps, the bandwidth of the fiber would be:
a. 10 GHz
b. 7.95 GHz
c. 100 MHz
d. 795 MHz
70. The following are the advantages of optical fiber system
except
a. greater capacity
b. crosstalk immunity
c. safer to handle
d. lower initial cost of installation
71. Plastic fibers have the following advantages over glass fiber
except
a. flexibility
b. ease of installation
c. ruggedness
d. low attenuation
72. This explains how a light may react when it meets the
interface of two transmission materials that have different
indices of refraction.
a. Huygen's Law
b. Nyquist's Theorem
c. Len's Law
d. Snell's Law
73. In optical fibers
a. the core and cladding have the same index of refraction
b. the core and cladding have the same area
c. the core surrounds the cladding
d. the cladding surround the core
74. A type of fiber whereby light rays take many paths between
the source and the receiver
a. monomode
b. multimode
c. single mode
d. step Index
75. A figure of merit used to measure the light gathering or light
collection ability of the optical fiber.
a. acceptance angle
b. numerical aperture
c. acceptance core
d. critical angle
76. The Basic Optical Fiber Communication System consist of
the following except
a. optical source
b. photodetector
c. transmission medium
d. 48 volts power supply
77. Optical fibers can be made out of
a. glass
b. plastic
c. combination of glass and plastic
d. any of these
78. In ____________ , the core has index of refraction that
changes continuously from the center to the outside
a. step index fiber
b. graded index fiber
c. monomode
d. multimode
79. The following are causes of attenuation and loss of optical
power within the fiber except
a. microbending loss
b. connector loss
c. splicing loss
d. ohmic loss
80. For a signal to be propagated through the optical fiber, the
angle of incidence should be __________ the critical angle.
a. greater than
b. less than
c. equal to
d. none of these
81. Scattering loss is caused by:
a. insufficient stirring of the ingredients during manufacture
b. changes in the density of the fiber due to uneven rates of
cooling
c. microscopic cracks in the cladding which allow leakage
of the vacuum in the core
d. impurities in the fiber
82. Cleaving is the process of
a. removing the cladding before connecting fibers together
b. cutting the end of the fiber in preparation for connecting
two fibers
c. cleaning the surface of optic fibers
d. inspecting fibers for flaws
83. The following are light detectors in Fiber Optic
Communications System except
a. ILD
b. PIN diode
c. APD
d. NOTA
84. The following are the three distinct regions of an optical fiber
except
a. core
b. cladding
c. jacket
d. coating
85. Which of the following combinations is impossible for optical
fibers
a. plastic core and cladding
b. glass core and cladding
c. plastic core and glass cladding
d. glass core and plastic cladding
86. The scientist who coined the term fiber optics
a. H.H. Hopkins
b. C.W. Hansel
c. N.S. Kapany
d. A.C. Van Heel
87. That dielectric material of an optical fiber surrounding the
core
a. cladding
b. armor
c. shield
d. cover
88. Approximately what is the frequency limit of the optical fiber?
a. 20 GHz
b. 1 MHz
c. 100 MHz
d. 40 MHz
89. A single fiber can handle as many voice channels as
a. a pair of copper conductors
b. a 1500 pair cable
c. a 500 pair cable
d. a 1000 pair cable
90. An incident ray can be defined as
a. a light ray reflected from a flat surface
b. a light ray directed toward a surface
c. a diffused light ray
d. a light ray that happens periodically
91. It is made from semiconductor material such as aluminum-
gallium-arsenide or gallium-arsenide-phosphide.
a. APD
b. Injection laser diode
c. Light emitting diode
d. Positive-intrinsic-negative
92. An absorption loss caused by valence electrons in the silica
material from which fibers are manufactured.
a. ultraviolet absorption
b. ion resonance absorption
c. modal dispersion
d. infrared absorption
93. The loss in signal power as light travels down a fiber is
a. attenuation
b. scattering
c. propagation
d. absorption
94. An object farther from a converging lens than its focal point
always has an __________ image.
a. inverted
b. virtual
c. smaller size
d. the same in size
95. The refractive index number is
a. a number which compares the transparency of a
material with that of air
b. a number assigned by the manufacturer to the fiber in
question
c. a number which determines the core diameter
d. a term for describing core elasticity
96. The mechanical splice is best suited for
a. quicker installation under ideal conditions
b. minimum attenuation losses
c. field service conditions
d. situations in which cost of equipment is not a factor
97. The cladding which surrounds the core
a. is used to reduce optical interference
b. is used to protect the fiber
c. acts to help guide the light in the core
d. ensures that the refractive index remains constant
98. The different angles of entry of light into an optical fiber
when the diameter of the core is many times the wavelength
of the light transmitted is known as __________.
a. refraction
b. emitter
c. mode
d. sensor
99. Proposed the use of a clad glass fiber as a dielectric
waveguide
a. Kao and Keck
b. Karpon and Keck
c. Bockham and Kao
d. Karpon and Brockham
100. The wavelength of light has no role in
a. polarization
b. interference
c. diffraction
d. resolving power
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 11-Fiber Optics2Document10 pagini11-Fiber Optics2Jesther LiwagÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEC3203 GEMINIANO Assignment-5Document10 paginiNEC3203 GEMINIANO Assignment-5JOSEFCARLMIKHAIL GEMINIANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- EST Sample Problems 05Document9 paginiEST Sample Problems 05Genesis PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMMS 7 - Fiber OpticsDocument4 paginiCOMMS 7 - Fiber OpticsfeelingsoflyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber OpticsDocument26 paginiFiber OpticsCherry Ebreo OlaivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberDocument6 paginiMultiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberERMIAS AmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optics Fundamentals Quiz Answers Light Propagation Reflection RefractionDocument50 paginiFiber Optics Fundamentals Quiz Answers Light Propagation Reflection RefractionMark JasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberDocument3 paginiMultiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberERMIAS AmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberDocument3 paginiMultiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberSneha SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toaz - Info Multiple Choice Questions in Optical Fiber PRDocument3 paginiToaz - Info Multiple Choice Questions in Optical Fiber PRERMIAS AmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberDocument3 paginiMultiple Choice Questions in Optical Fibersuresh100% (1)
- OPTICAL FIBER MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZDocument3 paginiOPTICAL FIBER MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZBhuvaneswari AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optics QuestionnaireDocument9 paginiFiber Optics QuestionnaireLorenz ArdienteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optics ExamDocument4 paginiFiber Optics Examrs lagrimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fiber and Antenna Fundamentals QuizDocument7 paginiOptical Fiber and Antenna Fundamentals Quizsadke213Încă nu există evaluări
- OPTICAL FIBER MCQSDocument3 paginiOPTICAL FIBER MCQSDenaiya Watton Leeh71% (14)
- WCMJT Radiography Interpretation CourseDocument6 paginiWCMJT Radiography Interpretation CourseSaut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (2)
- Optical MCQDocument9 paginiOptical MCQkavitha saravananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otdr Sample PaperDocument8 paginiOtdr Sample Paperapeksha sinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.fiber Optics2Document7 pagini11.fiber Optics2Spencer HayesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESAT - Optical FiberDocument71 paginiESAT - Optical FiberJoanna Grace JamillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDGE Fiber OpticsDocument117 paginiEDGE Fiber OpticsjinkoloyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fiber Questions on Total Internal Reflection, FDDI Standard, and Limitations (39Document26 paginiOptical Fiber Questions on Total Internal Reflection, FDDI Standard, and Limitations (39Mayur BundelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optics Refresher GuideDocument8 paginiFiber Optics Refresher GuidespidyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Box The Letter of The Best Answer. NO ERASUREDocument4 paginiMULTIPLE CHOICE: Box The Letter of The Best Answer. NO ERASUREsadke213Încă nu există evaluări
- Radiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Document8 paginiRadiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Saut Maruli Tua SamosirÎncă nu există evaluări
- MINA-Christian-H-Cellular-Mobile-Communications-and-Fiber-Optics-Communication-2Document9 paginiMINA-Christian-H-Cellular-Mobile-Communications-and-Fiber-Optics-Communication-2Chrissa Mea PadolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibre optics V3Document5 paginiFibre optics V3Benito PalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs in Fiber Optics Communications Part I - PinoyBIX - Engineering Review PDFDocument12 paginiMCQs in Fiber Optics Communications Part I - PinoyBIX - Engineering Review PDFSumeet Bhardwaj50% (2)
- Reviewer in TransmiDocument1 paginăReviewer in TransmiMoneth LozanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fiber Communication MCQsDocument37 paginiOptical Fiber Communication MCQsshamsundar kulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical TechnologyDocument5 paginiOptical Technologysolvedcare0% (1)
- RI CW 2Document6 paginiRI CW 2Saut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (1)
- Powerful Est 6Document4 paginiPowerful Est 6Dianne LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level 2 Ques (1) RTDocument34 paginiLevel 2 Ques (1) RTVishal Sharma100% (1)
- Sheet 6 - CH 7Document4 paginiSheet 6 - CH 7priyasingh1682Încă nu există evaluări
- OCDocument216 paginiOCpriyadharshini priyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 For Industrial RadiographyDocument2 paginiAssignment 1 For Industrial RadiographySuresh Senanayake100% (2)
- BE (E&TC) BCS (404190) Credits: 04 UNIT-I: Light Wave System ComponentsDocument13 paginiBE (E&TC) BCS (404190) Credits: 04 UNIT-I: Light Wave System ComponentsGaurav MunjewarÎncă nu există evaluări
- POI QuestionsDocument7 paginiPOI QuestionsAly CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soalan RT Free Set 1 3Document13 paginiSoalan RT Free Set 1 3AjimKe'enÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiography Level 1 & 2 TheoryDocument1 paginăRadiography Level 1 & 2 TheoryMohammed Al-leswas100% (1)
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION GUIDEDocument23 paginiOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION GUIDEAnkit JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scie 5 PTDocument9 paginiScie 5 PTsaldieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question of Radiation SafetyDocument4 paginiQuestion of Radiation SafetySuresh Senanayake100% (1)
- 8.1 ASNT Ultrasonic Testing Level - II Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagini8.1 ASNT Ultrasonic Testing Level - II Questions and AnswersGururaja G86% (21)
- Group Study - Microwaves Answer KeyDocument10 paginiGroup Study - Microwaves Answer KeySheehan Kayne De CardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Document5 paginiRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Mangalraj MadasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reg - No.:: Question Paper Code: 7004Document9 paginiReg - No.:: Question Paper Code: 7004pro . tech worldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optic ComponentsDocument7 paginiFiber Optic Componentsmangesh kharateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic NDT - RT QB - 1Document17 paginiBasic NDT - RT QB - 1prabhakaran.S100% (1)
- Radiographic Interpretation Assessment Multiple Choice ExamDocument5 paginiRadiographic Interpretation Assessment Multiple Choice ExamSaut Maruli Tua Samosir50% (2)
- Ultrasonic Testing Definitions and QuestionsDocument27 paginiUltrasonic Testing Definitions and QuestionskingstonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Fiber Optics: Theory and ApplicationsDe la EverandHandbook of Fiber Optics: Theory and ApplicationsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Optoelectronic Line Transmission: An Introduction to Fibre OpticsDe la EverandOptoelectronic Line Transmission: An Introduction to Fibre OpticsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksDe la EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering ReviewerDocument7 paginiMechanical Engineering Revieweredu_canete100% (4)
- Mechanical Engineering ReviewerDocument7 paginiMechanical Engineering Revieweredu_canete100% (4)
- Dubbel Handbook of Mechanical Engineering PDFDocument918 paginiDubbel Handbook of Mechanical Engineering PDFprajakt_pie50% (4)
- Philippine Mechanical Code 2008Document441 paginiPhilippine Mechanical Code 2008Mark Gonzales79% (43)
- Advances in Mechanical Engineering by Alexander EvgrafovDocument193 paginiAdvances in Mechanical Engineering by Alexander Evgrafovjazosebno100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Reviewer-Machine Design PDFDocument5 paginiMechanical Engineering Reviewer-Machine Design PDFedu_canete75% (4)
- Handbook of Mechanical Alloy Design (Mechanical Engineering (Marcell Dekker) )Document748 paginiHandbook of Mechanical Alloy Design (Mechanical Engineering (Marcell Dekker) )Husen Taufiq100% (6)
- Mechanical Properties of Engineered Materials Mechanical EngineeringDocument584 paginiMechanical Properties of Engineered Materials Mechanical EngineeringEnis Sevim100% (12)
- Alien Contact More Likely by "MailDocument5 paginiAlien Contact More Likely by "MailAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 paginiCode of Mechanical Engineeringrolly_acul50% (2)
- Mechanical Engineering ManufacturingDocument276 paginiMechanical Engineering ManufacturingAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- OLEDDocument1 paginăOLEDAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- MechanicalDocument20 paginiMechanicalIonut Daniel Epure67% (3)
- Irving H. Shames-Engineering Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics) - (1996)Document1.100 paginiIrving H. Shames-Engineering Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics) - (1996)yashwanth77% (31)
- Refrigeration - Mechanical Engineering ReviewDocument402 paginiRefrigeration - Mechanical Engineering Reviewanon_990889030% (2)
- MaydayDocument2 paginiMaydayAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of IranDocument33 paginiHistory of IranAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP3Document5 paginiMP3Achilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- How USB Ports WorkDocument5 paginiHow USB Ports WorkAchilles Aldave100% (1)
- MP2Document1 paginăMP2Achilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barroso, Niko Angelo M. Broadcast Engineering: Current LoudspeakerDocument3 paginiBarroso, Niko Angelo M. Broadcast Engineering: Current LoudspeakerAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document1 paginăGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Achilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- InternetDocument5 paginiInternetAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microphones LecDocument4 paginiMicrophones LecAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCDDocument5 paginiLCDAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- JpegDocument4 paginiJpegAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTMLDocument3 paginiHTMLAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definitions of GPRS On The WebDocument2 paginiDefinitions of GPRS On The WebAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSDPADocument1 paginăHSDPAAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Space OpticsDocument1 paginăFree Space OpticsAchilles AldaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Lines-Basic Principles 01515900Document13 paginiTransmission Lines-Basic Principles 01515900Sachin1091Încă nu există evaluări
- HC110110023 Link AggregationDocument12 paginiHC110110023 Link Aggregationmangla\Încă nu există evaluări
- DS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishDocument16 paginiDS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishJosé AdelinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baremos Espanoles CBCL6-18 PDFDocument24 paginiBaremos Espanoles CBCL6-18 PDFArmando CasillasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH Probe For The PIC Temperature ControllerDocument6 paginiPH Probe For The PIC Temperature ControllerMohamad ZikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- D000-EL-701 Rev 4Document19 paginiD000-EL-701 Rev 4Sardar PerdawoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17 Refutation Concession InstructionsDocument4 pagini17 Refutation Concession InstructionsfiahstoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- NASA Technical Paper 3675: A Survey of Theoretical and Experimental Coaxial Rotor Aerodynamic ResearchDocument34 paginiNASA Technical Paper 3675: A Survey of Theoretical and Experimental Coaxial Rotor Aerodynamic ResearchThomas MouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PVC Pipe Longevity ReportDocument24 paginiPVC Pipe Longevity ReportUnibellÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08 CastingDocument6 pagini08 CastinguzairmetallurgistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philips DoseRight 2.0 CT Dose ControlDocument4 paginiPhilips DoseRight 2.0 CT Dose Controlsombrero61Încă nu există evaluări
- Candlescript IntroductionDocument26 paginiCandlescript IntroductionLucasLavoisierÎncă nu există evaluări
- CamlabDocument22 paginiCamlabviswamanojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposed Changes to IRS-T-29-2000 CMS Crossing Manufacturing StandardsDocument11 paginiProposed Changes to IRS-T-29-2000 CMS Crossing Manufacturing StandardsShipra MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Database Architecture and Concepts ExplainedDocument17 paginiDatabase Architecture and Concepts Explainedshabbirjamali0% (1)
- Basic Principles of Counseling ProcessDocument2 paginiBasic Principles of Counseling ProcessBhavna SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extractor de Pasadores de OrugaDocument2 paginiExtractor de Pasadores de OrugaErik MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissertation Grosser 2012 PDFDocument359 paginiDissertation Grosser 2012 PDFPanos Sp0% (1)
- Operations and Maintenance Manual MAN-10000946 Elmar Grease Injection Equipment AssemblyDocument56 paginiOperations and Maintenance Manual MAN-10000946 Elmar Grease Injection Equipment AssemblyAbhinav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific American - February 2019Document112 paginiScientific American - February 2019Frankling AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- App Disply Rgrming PDFDocument776 paginiApp Disply Rgrming PDFGnaneshwar Rao SirikondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minimum drilling supplies stockDocument3 paginiMinimum drilling supplies stockAsif KhanzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Visualization Nanodegree Program Syllabus PDFDocument4 paginiData Visualization Nanodegree Program Syllabus PDFsergio paredesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CWI TEST FlashcardsDocument30 paginiCWI TEST FlashcardsLuis Jaramillo100% (3)
- BC Zong ProjectDocument25 paginiBC Zong Projectshahbaz awanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meetings Bloody MeetingsDocument4 paginiMeetings Bloody MeetingsMostafa MekawyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsDocument13 paginiCH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsArun GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Armstrong Ambience Plus 8 MMDocument30 paginiArmstrong Ambience Plus 8 MMPreethi RajendranÎncă nu există evaluări
- QKNA For Mining GeologistDocument10 paginiQKNA For Mining GeologistAchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toyota 1ZZ FE 3ZZ FE Engine Repair Manual RM1099E PDFDocument141 paginiToyota 1ZZ FE 3ZZ FE Engine Repair Manual RM1099E PDFJhorwind Requena87% (15)