Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Diabetes Presentation
Încărcat de
api-256331558Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Diabetes Presentation
Încărcat de
api-256331558Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ENDOCRI NE SYSTEM
DI SEASE
BY SEI CHANG, MI RAE KI M, J UNWON L EE
DI ABETES MELLI TUS
BASI C TERMI NOLOGY
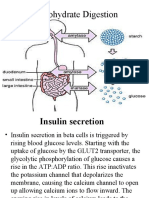
Endocrine System: body system in
which glands make hormones that
spread chemicals across the human
body
Glucose: sugar you consume when
eating food
Insulin: hormone that helps the glucose
get into your cells to give them energy,
produced by the pancreas gland
Pancreas
CAUSE OF DI SEASE
1. blood sugar/glucose levels are high
Pancreas not functioning
Type 1 Diabetes: body does not
make insulin
Type 2 Diabetes: insulin is not used
well
2. Effects on blood, therefore affects many
systems
***Without insulin, sugar stays in the blood,
pressure rises
CONSEQUENCES
1. Possible damage to the following organs:
eyes
heart stroke
kidneys
nerves
limbs (sometimes, you need to remove them)
HI STORY
HOW PEOPLE FROM PAST
DI SCOVERED DI ABETES
Diabetes first described by Ancient Egyptians
three-thousand years ago
1776- Dobson (Britain) confirmed the presence
of excess sugar in urine and blood as a cause
of their sweetness
1857- Claude Bernard (France) had concept
that diabetes is due to excess glucose
production
1955- Marketed the first treatments to diabetes
Claude Bernard
WHERE DOES THI S
FREQUENTLY
OCCUR I N THE U. S?
BASI C GEOGRAPHY
Key/Legend
darker colors =
higher diabetes rates
darkest color = more
than 10.6% of
population
HOW DO WE CURE
DI ABETES?
DI ABETES MEDI CATI ON
Diabetes medication: lowers blood glucose levels
Function: every type is different. Ex) type 2 diabetes,
may need medication including insulin.
Diabetes medication cannot cure diabetes
Most people will have to take it for the rest of their
lives.
I NSULI N DOSE
Insulin: necessary for everyone with Type 1
diabetes
Three groups of Insulin:
1. Animal
2. Human (not from humans, but
synthesized to match human insulin)
3. Analogues (similar to insulin)
Must inject insulin under skin (not into
muscle or vein)
FUTURE TREATMENTS I N
SCI ENTI FI C RESEARCH
I SLET TRANSPLANT
Islet: cluster of cells that work together to
regulate blood sugar
Type 1 diabetes results from the destruction
of insulin-producing cells in the islets of
pancreas.
Transplantation: extracting islet cells from the
pancreas of deceased donor; implanting them
in the liver.
Procedure performed 2/patient
2013, 95 islet transplants performed in 65
people in UK
Microscopic
images of islets
ARTI FI CI AL PANCREAS
Funding research into the artificial
pancreas
Articial Pancreas: combination of
electronic devices that work together
to monitor and adjust insulin levels
Tests successful in clinic
If tests at home successful, treatment
can be tested in large number of
people
Artificial Pancreas
THEORY/ CONCEPT FOR FUTURE
Vision to end Type 1 diabetes once and for all
Use vaccine-type treatments to prevent diabetes
from developing
Take much longer than other future methods
Key focus for research over next decade
Landmark discovery
ANSWER KEY FOR
ULTI MATE PUZZLE!
( DO I T FI RST)
ANSWERS
1a: glucose
1d: insulin
2a: animal
2d: islet
3a: diabetes
3d: rises
4a: vaccine
4d: limbs
WORKS CI TED
http://jonathaninthedistance.blogspot.kr/2011/02/obesity-diabetes-
physical-activity-and.html
https://www.diabetes.org.uk/Guide-to-diabetes/What-is-diabetes/
Diabetes-treatments/
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11953758
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/diabetes.html
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/endocrinediseases.html
http://license.umn.edu/technologies/z02003_implantable-microvalve-
device-for-controlled-insulin-delivery-in-type-1-diabetes-patients
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Unit 2 Power PointDocument21 paginiUnit 2 Power PointRyan WaltersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifeDe la EverandSolutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Genetic Landscape of Diabetes PDFDocument135 paginiThe Genetic Landscape of Diabetes PDFSC NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: Statistics Symptoms Causes Diagnosis PreventionDocument67 paginiDiabetes: Statistics Symptoms Causes Diagnosis PreventionShanthi_KVÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Sugar Control 1Document19 pagini4 Sugar Control 1JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIABETESDocument16 paginiDIABETESmariam miladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eli Lilly Insulin & DiabetesDocument4 paginiEli Lilly Insulin & Diabetesm_dattaiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DiabetesDocument13 paginiIntroduction To DiabetesNEW GENERATIONSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin TherapyDocument8 paginiInsulin TherapyHakima Hadji DaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MellitusDocument62 paginiDiabetes MellitusPrabhuswamyChowdiah100% (1)
- Diabetes MellitusDocument7 paginiDiabetes MellitusAlison ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- TreatmentDocument4 paginiTreatmentNor Ashikin IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type 1&2 DiabetesDocument2 paginiType 1&2 Diabetesterry johnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Diabetes: A Treatise For The General PublicDocument6 paginiUnderstanding Diabetes: A Treatise For The General PublicRaghuvir Keni Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Common Endocrine Disorders: Iril I. Panes, RN, MANDocument63 paginiCommon Endocrine Disorders: Iril I. Panes, RN, MANJona Phie Domingo MonteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: DR Patrick Commettant Beau Vallon Health CentreDocument26 paginiDiabetes: DR Patrick Commettant Beau Vallon Health CentrePatrick CommettantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type 1 Parents Resource Pack Sept 2019Document42 paginiType 1 Parents Resource Pack Sept 2019Piers BrandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 10Document5 paginiCase 10T LolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 2Document6 paginiPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 2jennmoyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes-Cho 2023 3rd Yr.Document37 paginiDiabetes-Cho 2023 3rd Yr.abdulrahmanbelewa96Încă nu există evaluări
- ORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Document5 paginiORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Aubrey Unique EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabete Mellitus HandoutsDocument7 paginiDiabete Mellitus HandoutsSittie Nashieva A. UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is DiabetesDocument9 paginiWhat Is Diabeteskdubb90Încă nu există evaluări
- Scenario Based QuestionsDocument7 paginiScenario Based QuestionsPraty SawadenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument11 paginiNursing Care of Patients With Diabetes MellitusMarcus, RN100% (32)
- Diabetes Type I Powerpoint 2Document10 paginiDiabetes Type I Powerpoint 2api-317440960Încă nu există evaluări
- Insulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32Document16 paginiInsulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32deryaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Name:A.F.M Sadman Fiaz Student Id: 2010324 Course Section: 4 Course Title: Discoveries in Biology Course Code: BIO 100 Date: 30/04/2021Document6 paginiStudent Name:A.F.M Sadman Fiaz Student Id: 2010324 Course Section: 4 Course Title: Discoveries in Biology Course Code: BIO 100 Date: 30/04/2021Sadman FiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document14 paginiDiabetes Mellitus Type 1John Karl Garcia RazalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiabetesDocument38 paginiDiabetesaquakumbh75% (4)
- Diabetes Project 1 PDFDocument10 paginiDiabetes Project 1 PDFDinesh Kumar100% (2)
- A Hormone Produced in The Pancreas by The Islets of LangerhansDocument11 paginiA Hormone Produced in The Pancreas by The Islets of LangerhansAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of PancreaticDocument61 paginiPhysiology of PancreaticMuhammad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus DiseaseDocument5 paginiDiabetes Mellitus DiseaseristaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Course: Team-Based Learning: Today's Clinical Case 1: Type I Diabetes MellitusDocument3 paginiSpecial Course: Team-Based Learning: Today's Clinical Case 1: Type I Diabetes MellitusAnanda DitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin - Structure, Discovery and Obtaining ItDocument61 paginiInsulin - Structure, Discovery and Obtaining Itsushant pawaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurse Delegation 2Document344 paginiNurse Delegation 2Jhon Albert RobledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Diabetes Project 1 DDDocument10 paginiPDF Diabetes Project 1 DDAshu SarasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MilletusDocument31 paginiDiabetes MilletusMary Joy SumandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus: The Honeyed Siphon: Past, Present, and FutureDocument7 paginiDiabetes Mellitus: The Honeyed Siphon: Past, Present, and FutureRoderick RichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEM CELL TherapyDocument23 paginiSTEM CELL Therapycamila hartmann100% (1)
- Diabetes The Basics An IntroductionDocument1 paginăDiabetes The Basics An Introductiondebabrata5976Încă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes The Basics An IntroductionDocument1 paginăDiabetes The Basics An Introductiondebabrata5976Încă nu există evaluări
- Definition of DiabetesDocument6 paginiDefinition of DiabetesSuyi PhoebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper - DiabetesDocument10 paginiResearch Paper - Diabetesapi-312645878Încă nu există evaluări
- Disorders in The Ovaries and PancreasDocument49 paginiDisorders in The Ovaries and PancreaswyneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin: Critical Thinking and Science Processs SkillDocument6 paginiInsulin: Critical Thinking and Science Processs SkillmistikarjunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Overflow TranscriptDocument11 paginiDiabetes Overflow TranscriptJonhangel UtreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomaterials: Body Part: PancreasDocument4 paginiBiomaterials: Body Part: PancreasroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: by Wenzel BurtonDocument2 paginiDiabetes: by Wenzel Burtonwburton236Încă nu există evaluări
- 1GP - Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagini1GP - Anaphy NoteseriannenabazengÎncă nu există evaluări
- IDDMDocument19 paginiIDDMZam PeaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiabetesDocument30 paginiDiabetesNopy QienahÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM Brochure For NCM 106Document12 paginiDM Brochure For NCM 106Kimsha ConcepcionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin Resistance and DiabetesDocument3 paginiInsulin Resistance and DiabetesPrecious C. MamaradloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: Two Main Types of Diabetes Type 1 (Also Known As Juvenile & Insulin Dependent Diabetes)Document4 paginiDiabetes: Two Main Types of Diabetes Type 1 (Also Known As Juvenile & Insulin Dependent Diabetes)flockychehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Brief DescriptionDocument20 paginiFinal Brief DescriptionKathleen Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act Assessment Practice Reading PassageDocument3 paginiAct Assessment Practice Reading PassageThanh HàÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument43 paginiNursing Care of Patients With Diabetes MellitusRashida RuwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Diabetes Patients in SurgeryDocument28 paginiManagement of Diabetes Patients in Surgerylow_sernÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.rohani Emleyat Sabq: 3. Rohani Emleyat Sabq No 3 Nade Ali or Sora Ekhlas or Dowa e Sefi Ke Amal Karny Ka TariqaDocument5 pagini2.rohani Emleyat Sabq: 3. Rohani Emleyat Sabq No 3 Nade Ali or Sora Ekhlas or Dowa e Sefi Ke Amal Karny Ka TariqaMuhammed Sarwar Hussin RosunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestational Diabetes ACOG 2013 PDFDocument11 paginiGestational Diabetes ACOG 2013 PDFCecilia TriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1Document5 paginiQuiz 1P PpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes HandbookDocument198 paginiDiabetes HandbookKeerthana SivarasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Practical Guide To Insulin TherapyDocument42 paginiA Practical Guide To Insulin Therapyseun williams100% (2)
- Acute Complications of Diabetes MellitusDocument1 paginăAcute Complications of Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (1)
- Brand Plan For Metformin: Presented By: Sanket Umredkar Sharan Shah Nita Tamboli Preeti Suryavanshi Kajal GajfodeDocument47 paginiBrand Plan For Metformin: Presented By: Sanket Umredkar Sharan Shah Nita Tamboli Preeti Suryavanshi Kajal GajfodeSanket UmredkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verify Study For VildagliptinDocument7 paginiVerify Study For VildagliptinDhaval PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin ChartDocument1 paginăInsulin ChartIrena O'Brien100% (3)
- Testing Blood For Glucose or HemoglucotestDocument3 paginiTesting Blood For Glucose or Hemoglucotestma simbajonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2022: 9. Pharmacologic Approaches To Glycemic TreatmentDocument19 paginiStandards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2022: 9. Pharmacologic Approaches To Glycemic TreatmentAdina SimionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fornas GPDocument2 paginiFornas GPyosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For: Diabetes, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, DKA, Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For: Diabetes, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, DKA, Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceFhai EscioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4209 ArticleText 15346 1 10 202101142020Document15 pagini4209 ArticleText 15346 1 10 202101142020Selmitha SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basal Insulin Versus Premixed Insulin For The Treatment of T2DmDocument98 paginiBasal Insulin Versus Premixed Insulin For The Treatment of T2DmMaya SwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 11648 J Ijde 20200502 12Document4 pagini10 11648 J Ijde 20200502 12AdemoluÎncă nu există evaluări
- 516 FullDocument5 pagini516 FullAndreea ŞtefănescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentDocument8 paginiTypes of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentChander KantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications in Najaf City, IraqDocument6 paginiDiabetes Mellitus and Its Complications in Najaf City, IraqYaman HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nyicil Borang Poli Penyakit DalamDocument3 paginiNyicil Borang Poli Penyakit Dalamrachma rfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka: Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. 2011 3:49-53Document2 paginiDaftar Pustaka: Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. 2011 3:49-53Dina Ikrama PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auspar Insulin Detemir Rys 140328 PiDocument18 paginiAuspar Insulin Detemir Rys 140328 Piali1922Încă nu există evaluări
- Efektifitas Perawatan LukaDocument9 paginiEfektifitas Perawatan LukaNur Rahmawati SalasahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefi Assignment 2Document29 paginiPrefi Assignment 2Joanne Bernadette AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallyDocument12 pagini15 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallyJ SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acog Practice Bulletin No 201 2018Document21 paginiAcog Practice Bulletin No 201 2018Rosalia Hernandez100% (1)
- Hubungan Tingkat StresDocument8 paginiHubungan Tingkat StresAri SuhartantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- T 2 DMDocument129 paginiT 2 DMTeuku Fadli SaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ask 34 1083 KDocument44 paginiAsk 34 1083 KanggrainiÎncă nu există evaluări