Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BIOLOGY 12 Final Review
Încărcat de
wickedsickofrealityDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BIOLOGY 12 Final Review
Încărcat de
wickedsickofrealityDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BIOLOGY 12
Final Review
Biochemistry
Macromolecules:
o Carbs sugar
o Lipids fatty acids + glycerol
o Proteins - Amino Acids
o Nucleic Acids nucleotides
Protein
o Chemical messengers, enzymes, antibodies
o 4 levels of structure
o Denaturation is caused by heat/changes in pH (protein changes shape and stops
functioning)
Carbohydrates (CHO)
o Starch: storage in plants
o Glycogen: storage in liver and muscles
o Cellulose: rigidity of plant cell walls
Lipids
o Energy storage, mobilization, insulation
o Steroids: immune response
o Triglycerides: insulation
o Phospholipids: form bilayer of cell membranes
o Saturated fatty acids dont have double covalent bond
Nucleic Acids
o AG - purines
o TC pyrimidines
o RNA ribose instead of deoxyribose & uracil instead of thymine
o ATP = energy
Cell Parts and Functions
Cell membrane: phospholipid bilayer, protection, regulation of materials in and out of cell
Cytoplasm: provides support for organelles
SER: detox
RER: dispatch of proteins
Golgi: PMS (package modify sort macromolecules)
Lysosome: recycling
Mitochondria: creates ATP
Ribosomes: make proteins
Nucleus: DNA, brain
Nucleolus: ribosome subunits are made
Transport Methods
By proteins:
o Facilitated: with concentration gradient, no ATP
o Active: against concentration gradient, protein carrier
By vesicles (requires ATP)
o Vesicles come from golgi body and contain proteins
o They move to cell membrane (EXOCYTOSIS)
Digestive System
Functions
o Ingesting food
o Secreting enzymes & hormones
o Digestion
o Absorption
o Elimination
Mechanical Digestion: large pieces made smaller (mouth & stomach)
Chemical Digestion: enzymes break macromolecules down
Parts
o Mouth
Receives food
Mechanical: Teeth chew
Chemical: Salivary glands produce saliva which moistens food
Tongue creates bolus
o Pharynx
Air from nasal cavity
Food from mouth to pharynx to esophagus
Soft palate moves back during swallowing to close the nasopharynx
Epiglottis stops food from passing into larynx
o Esophagus
Carries food from pharynx to stomach
Peristalsis
o Stomach
Stores food
Cardiac Sphincter: esophagus stomach
Pyloric Sphincter: Stomach Sm. Intestine
Mechanical: layers of wall churn food
Chemical: Gastric juice, mucus make chime
o Small Intestine
Digestion: long length, enzymes digest food
Absorption: Villi absorb nutrients
Duodenum, Jejunum, Illeum
o Hepatic Portal vein
Carries blood from sm. Intestine to liver
Liver detoxifies food
o Large Intestine
Feces
Absorbs water, salts, vitamin
Enzymes:
o Mouth: Salivary Amylase (starch maltose)
o Stomach: Pepsin (protein peptide)
o Small Intestine:
Pancreatic Amylase (starch maltose)
Trypsin (Protein peptide)
Lipase (Fat droplets Glycerol + FA)
Peptidase (peptides AA)
Maltase (maltose glucose + glucose)
Nuclease (DNA Nucleotides)
Nucleosidase (Nucleotide base sugar phosphate)
o Stomach: Pepsinogen activated by HCl into pepsin.
o Liver/Gall Bladder: produces bile - stored in gall bladder
Bile emulsifies fat
o Pancreas
Insulin when glucose is too high
Glucagon opposite
Sm Intestine to liver is HPV
Liver to Heart is HV
Lungs to Liver is HA
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument28 paginiPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsJohn Michael Lopez100% (1)
- Female RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFDocument129 paginiFemale RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFsusdoctor100% (1)
- PG Syllabus 2nd Year PDFDocument95 paginiPG Syllabus 2nd Year PDFDevrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of ECGDocument32 paginiBasics of ECGNachiket Vijay PotdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical and Personal Development in The Arts: Quarter 1 The Anatomy of An Artist: Integumentary SystemDocument13 paginiPhysical and Personal Development in The Arts: Quarter 1 The Anatomy of An Artist: Integumentary SystemCarl Benedict RevillaÎncă nu există evaluări
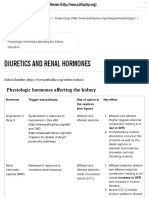
- Diuretics and Renal Hormones - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDocument4 paginiDiuretics and Renal Hormones - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewSandra MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR Rashmi S R Consultant NephrologyDocument1 paginăDR Rashmi S R Consultant Nephrologyanant chauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh: DidapatDocument54 paginiSistem Pertahanan Tubuh: DidapatNur JaziLahÎncă nu există evaluări
- B A M SDocument166 paginiB A M SParvathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Year Anatomy Guidelines - AIMC ACADEMIADocument29 paginiSecond Year Anatomy Guidelines - AIMC ACADEMIAMazen KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pex 02 02Document13 paginiPex 02 02Febriano SuwartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How The Brain Works - DK PDFDocument224 paginiHow The Brain Works - DK PDFHai Quang Ha95% (38)
- LECTURE 2 Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument74 paginiLECTURE 2 Biological Basis of BehaviorColossal HeartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System WebquestDocument3 paginiNervous System Webquestsilrub8015Încă nu există evaluări
- Medical Report: Eyes: Right Eye (V) HematologiDocument7 paginiMedical Report: Eyes: Right Eye (V) HematologimaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System Development: Ob NotesDocument2 paginiReproductive System Development: Ob NotesLykee PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal 4 Uji Jalan 6 MenitDocument10 paginiJurnal 4 Uji Jalan 6 MenitSandy Tama Okvan YudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20 - 1 Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument10 paginiChapter 20 - 1 Fluid and Electrolyte Balancekristinaf1224Încă nu există evaluări
- CH - 7 Control and CoordinationDocument8 paginiCH - 7 Control and CoordinationHARSHIT JAINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument22 paginiAlcoholic Liver DiseaseRaju NiraulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Quiz NCM 101Document11 paginiLong Quiz NCM 101Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Chronic Alcohol UseDocument11 paginiOverview of Chronic Alcohol UseMargarida SolizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glands 1Document20 paginiGlands 1Faith ChepoghishoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 18 Class 11 (MCQ)Document7 paginiChapter 18 Class 11 (MCQ)Ashok KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FST (Boys) 2023Document3 paginiFST (Boys) 2023Abdul qadoosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothalamus and Thalamus .PhysiologyDocument33 paginiHypothalamus and Thalamus .Physiologybareqgassan100% (1)
- Class Reptilia: Powerpoint Templates Powerpoint TemplatesDocument59 paginiClass Reptilia: Powerpoint Templates Powerpoint TemplatesChi Ziri100% (1)
- Chapter II - Bodies of Fire - The Accupuncture MeridiansDocument41 paginiChapter II - Bodies of Fire - The Accupuncture MeridiansScott Canter100% (1)
- Regions of The BrainDocument14 paginiRegions of The BrainSean pokemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Learning Topics On Biomedical EquipmentsDocument37 paginiShort Learning Topics On Biomedical EquipmentsAtif Aslam100% (1)