Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Outline Based On Wwi PPT Fill in Blank
Încărcat de
api-2568706990 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
286 vizualizări10 paginiTitlu original
outline based on wwi ppt fill in blank
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
286 vizualizări10 paginiOutline Based On Wwi PPT Fill in Blank
Încărcat de
api-256870699Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
Renton Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _____
Chapter 12: World War I
Ch. 12 World War I: The Road to War
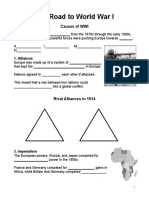
Long Term Causes of WWI
1. Imperialism - _____________________ nations dominating _____________________ nations
a. Scramble for ________________________ in late 1800s
b. 1910 most wanted colonies taken
c. Competition led to ________________________
d. ________________________ envied Britain and France
i. Only way for Germany to expand take colonies from other
countries in Africa.
2. Militarism - a policy under which nations built up their ___________________ forces
a. Preparation for _____________
b. Build up of arms
c. Giving ________________________ more authority
d. Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia
3. Nationalism ________________________ to the interests and culture of ones nation
a. Led to ______________________________ rivalries among nations
i. Many feared ________________________ growing power
b. Ethnic groups resent those controlling them & desire_____________________
i. Russia considered itself protector of Europes Slavic peoples
ii. _________________ Slavic people, under rule of Austria-Hungary
iii. Russia and Austria-Hungary rivals over ________________________
4. Alliance System by 1907 defense ________________________ form in Europe.
a. Complicated system to bolster ________________________
i. Bound great powers to come to one anothers _______ if attacked.
b. Germany and Austria Hungary treaty
c. Russia and France Treaty
d. Great Britain and France loose alliance
An Assassination Leads to War
1. Interest in the Balkan Peninsula
a. Russia wanted for Mediterranean Sea access
b. Germany wanted for rail link to Ottoman Empire
c. Austria-Hungary taken control of Bosnia accuses Serbia of subverting
its rule
2. Archduke Franz Ferdinand __________________________________
a. Heir to ________________________ throne, shot while driving through the
Bosnian capital Sarajevo by Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip
(member of Black Hand promoted Serbian nationalism)
b. One nation after another pulled into the ________________________
Timeline of Events
1. One nation after another pulled into the conflict
a. July 28 Austria declares war on Serbia
b. August 1 treaty forces Germany to support Austria Hungry, declares
war on Russia (it supported Serbia)
c. August 3 Germany declares war on France
d. Germany invades Belgium
e. Britain declares war on Austria-Hungry
Central Powers vs. Allied Powers
1. Central Powers: ________________________ and ________________________
2. Allied Powers: ________________________, France, ________________________, Great Britain
Summary:
The Fighting Starts
1. The active fighting begins when ______________________ invades _____________________
a. The ultimate goal of The Schlieffen Plan was to take over Belgiums
capital. The plan called for Germany to attack the western powers of
Europe while troops held off the Russians in the east.
b. After ________________________ had fallen, all German forces would be
directed at defeating the ________________________ Czar
2. For more than three years, ________________________ warfare was used as the major
form of fighting on the western front.
a. Armies lined up and stationed behind fort like structures with an area
between them called ________________________________________________
i. Front line, support, & reserve
3. Millions died and little ground was gained At the First Battle of the Somme 1.2
million died in 7 months over _________ miles of land
4. Fighting is _______________________________ for two years.
Trench Warfare
1. Describe the pictures you see on the board below:
America Desires Neutrality
1. Neutrality is staying out of a ________________________ not supporting either side
2. America desired to stay neutral because of __________ & commercial investments
3. ________________________ leaders support neutrality
Americans Question Neutrality
1. Some feel ________________________ involved
2. More than 1/3 of Americans = ________________________
3. Favor Central Powers:
a. German American, Irish American & those with Hostility toward ________
4. Favor Allies
a. Many trace roots to Great Britain
i. Identify with history, literature, culture
b. Recent immigrants from Italy & parts of Austria-Hungary hope for
________________________ at home
c. German autocrat Wilhelm II ruler with unlimited power vs.
________________________
d. News reports of German ________________________
5. Propaganda _______________________
Summary:
Ch. 12 World War I: The War Begins
The War Hits Home
1. The British ________________________ Blockade the German coast to prevent
____________________, other military supplies & ________________ from getting through
a. Causes widespread ____________________________ in Germany
b. American ships dont reach destination Germany
c. Angry that the British blockade threatened freedom of the seas
German U-Boats
1. Germany deployed U-Boats (________________________) to prevent munitions & food
from reaching Britain
2. First rose to ______________________ to allow crew of merchant ships to abandon
3. Britain then ____________________ merchant ships to ____________ back at U-Boats
4. In response, Germany permitted U-Boats to fire ________________________ warning.
5. U-Boat enables Germany to ________________________ stalemate at sea
Britain Encourages Anti-German Sentiment (Feelings)
1. Shortly after war began Britain cut ____________________________________ cable
between U.S. and Germany
2. U.S. only receives _______________________________bias news
3. American people favor punishing Germany for use of ________________________.
The Lusitania (British Passenger Liner) : May 7, 1915
1. German U-Boat suspects Lusitania is carrying ___________ for allies correct
2. Fires upon liner
3. Lusitania _________
4. 1200 passengers dead 128 ________________________
5. Germans had warned Americans to ___________ _______ British ships.
6. Americas Response
a. Americans furious, Wilson asks Americans to be _________________
b. US demands Germany _______ submarine warfare & pay victims families
c. Germany replied the Lusitania was carrying _________________
d. Germany ____________ to stop sinking passenger ships without warning as
long as the ships crew offered no resistance to German search/seizure.
e. Germans continue to ________________________ Allied ships
f. U.S. threatens to cut diplomatic ties to ________________________
The Sussex Pledge
1. Germany Signs the Sussex Pledge
a. Promise by German govt. that U-boats would _______ ships before attack
2. Germany Breaks the Sussex Pledge
a. Germans ________________________ Sussex Pledge - January 31, 1917
b. February 3 U.S. broke off diplomatic relations with Germany
c. Few weeks later Wilson __________ American merchant ships.
The Zimmerman Note
1. British intercept a German ________________________
2. From Arthur Zimmermann, Germanys foreign secretary
a. Makes secret offer to ________________________
b. If Mexico declared war on U.S., Germany would reward Mexico with
American ________________________ in the southwest
3. Not taken seriously by Wilson or Mexico
a. Civil war in Mexico = could not have launched successful invasion
4. American people still ________________________
Summary:
The U.S. Declares War
1. German Provocation
a. ________________________________ note Telegram between German foreign
minister to the German ambassador in Mexico, intercepted by Great
Britain
i. Proposed an ______________________ between Germany and Mexico
if the U.S. got involved in the war promised to retrieve Texas
ii. Not taken seriously
b. The sinking of ______ American unarmed merchant ships 36 lives
i. Pushes the U.S. into ______________
2. Russia replaces its monarchy with a ______________________________ govt. - becomes
viewed as democracies vs. brutal monarchies
3. America Acts
a. April 2, 1917 President Wilson deliver war resolution
i. The world must be made safe for _________________________________
b. Neutrally finally shattered pave way for future order of peace and
freedom
Summary:
Ch. 12 World War I: Americans on the European Front
America Mobilizes: Raising an Army
1. _____________________________ Service Act required men to register with the
government in order to be randomly selected for military service = DRAFT
a. 24 million registered 3 million called through lottery
b. Wide ____________________________ of the draft
c. Viewed as the War to end all wars
d. Most did not attend high school; 1 in 5 foreign born
e. 400,000 African-Americans
America Mobilizes: The Convoy System
1. Developed to transport ______________________ overseas safely
2. May 1917 all merchant and troop ships traveled in a ______________________
a. Group of unarmed ships surrounded by a ring of destroyers, torpedo
boats, armed vessels with hydrophones
3. Between April and December 1917 _____________ marine losses dropped by half
4. Convoy system _______________________________ in carrying troops to Europe
America Mobilizes: Women Serve
1. 11,000 women served as nurses, drivers, and clerks
2. 14,000 women served abroad civilians working for govt. or private agencies
3. Women begin to have new _________________________________
a. Farms, Telegraph messengers, elevator operators, letter carriers, some
mgmt. positions
4. 400,000 women join _______________________________ work force.
America Mobilizes: African Americans
1. More than 300,000 African Americans volunteered or were drafted
2. Served in _________________________________ units
3. Most ___________ saw combat given lesser jobs
4. Many fought with _______________________________
5. Nearly 4,000 died or were wounded
6. 369
th
Regiment
a. 369
th
Regiment Harlem Hell Fighters
b. eager to fight
c. persuaded white officers to loan regiment to ______________________
d. French integrated regiment into French army
e. Entire regiment received Frances highest combat medal
America Turns the Tide
1. Convoy system, barrier of mines
2. Fighting in Europe
a. Allied forces tired, Americans ____________________ & enthusiastic
New Weapons
1. List them here:
The Final Toll: Influenza
1. ______________________ epidemic killed more people worldwide than all of the
wartime battles
2. American troops carried a new strain of influenza in 1918
3. Spread easily in crowded, unsanitary conditions
4. More American soldiers died from influenza than from ______________________
5. Over a half million Americans and perhaps 30 million people worldwide died
Summary:
American Troops Go on the Offensive
1. The Collapse of Germany
a. November 3, 1918 Austria-Hungary surrender to the Allies
b. 11
th
hour, 11
th
day, 11
th
month of 1918 ________________ signed armistice
The Final Toll
1. The Final Toll
a. 22 million deaths, 20 million wounded, 10 million refugees, cost $338
billion
b. United States 48,000 lost in battle, 62,000 died of disease, 200,000
wounded
i. The U.S. lost the ______________________ lives
Ch. 12 World War I: Americans on the Homefront
Raising Money for the War
1. Government borrowed money by selling ____________ _______ to support the Allies
a. Could be later redeemed for original value plus interest
b. Raised more than 20 billion $
2. War Financing
a. US spent $35.5 billion on the war effort
b. 1/3 raised through taxes; progressive income tax, war-profits tax,
excise tax on tobacco, liquor, and luxury goods.
c. 2/3 raised by selling Liberty Loan and Victory Loan bonds
3. Committee on Public Information
a. First propaganda agency, designed to influence peoples thoughts and
actions. George Creel head of CPI
b. Persuaded artists and advertising agencies to create thousands of
painting, posters, cartoons, and sculptures to promote the war.
c. Printed 25 million copies of How the War Came to America which
included Wilsons war message
d. Promoted war bonds
e. Promoted patriotism, but inflamed hatred and violations of the civil
liberties of certain ethnic groups and opponents of the war
Congress Gives Power to Wilson
1. War Economy
a. Wages ______________________
b. Company stock increased
c. ______________________ pay between labor and management, increasing
work hours, child labor, dangerous conditions, unions ___________________
2. National War Labor Board 1918 established to settle ______________________
between management and labor.
a. Refusing meant losing draft exemptions
b. Improved factory conditions, 8-hr work day, safety inspections, and
child labor ban
3. Food Administration
a. Under Herbert Hoover
b. Help produce and conserve food; gospel of the clean plate; one day a
week meatless, sweetless, two days wheatless, two days
porkless.
c. Victory Gardens
Americans Fear Immigrants
1. Americans fear immigrants spying
a. Might try to ___________________________ war by destroying transportation
or communication networks
b. Resulted in ___________________________on immigration
2. National Security League 100% Americanism
a. ______________________ Test for immigrants excluded those who could not
read English or any other language
i. Few failed the test
3. Americans most hostile toward ______________________ referred to as Huns
a. High schools stop teaching German
b. German authors removed from libraries
c. Change names of goods, things, etc.
d. Attacks on those of German descent
Summary:
4. Espionage and Sedition Acts a person could be fined up to $10,000 &
sentenced to 20 years in jail for interfering with the war effort or for saying
anything disloyal, profane, or abusive about the ______________________ or the
____________ __________________.
a. Violated the spirit of the _____________ Amendment
b. Over 2,000 prosecuted over half convicted
c. Targeted socialists (anti-war) and labor leaders (pro-worker)
i. Examples: Debs, Robert Goldstein The Spirit of 76
World War I: Changes in the Workforce
1. War virtually stops European ___________________________________
2. Young men out of labor pool
3. Need workers in war-related ______________________
a. Recruit African Americans and ______________________ Americans to fill jobs
4. African Americans and the War
a. W.E.B. DuBois believed African-Americans should support the war to
strengthen calls for racial ______________________
b. William Monroe Trotter opposed DuBois and felt victims of racism
should not support a ______________________ government.
c. Most African Americans ______________________________ the War.
d. The greatest effect WWI had on African Americans was that it
accelerated the ________________ ______________________:
i. Southern African Americans move to Northern ___________
ii. Contributing factors:
escape racial discrimination
boll weevil infestation (ruined cotton fields)
_________ opportunities WWI and less immigration
Free RR passes
5. Women in the War
a. Moved into jobs typically held by ________
i. Examples: RR workers, dockworkers, cooks, bricklayers
b. ______________________ Red Cross, encouraged the sale of
bonds/planting of victory gardens.
c. __________ Movement Jane Addams (Womens Peace Party
remained pacifist)
d. Bolsters support for womens ______________________ 19
th
amendment ratified in 1920
Ch. 12 World War I: Global Peacemaker
Paris Peace Conference
1. Big Four
a. Great Britain = David Lloyd ______________________
b. ______________________ = George Clemenceau
c. ______________________ = Vittorio Orlando
d. U.S. = ______________________
2. Big three (not U.S.) desired to make the Central Powers _____________ wanted
to divide ______________________ colonies
3. Russia ______________________
a. Civil war between Bolsheviks and armies loyal to old government
b. British, French, & Americans involved on side of those against Lenin
i. Lenin called for workers to overthrow their governments
ii. U.S. feared Bolshevik Russia
Wilsons Hopes
1. Wilson hoped the world would be made safe for democracy
2. Fourteen Points
a. End ______________________
b. Keep ______________________
c. Removal of ______________________ barriers
d. Reduction of ______________________ forces
e. Self-____________________________________________
3. The Allies ______________________ Wilsons Plan
a. Allied leaders angry, wanted to ______________________ Central Powers
b. Central Powers had no say
c. Wilson conceded on most of Fourteen Points in return for
______________________ of ______________________
Debating the Treaty of Versailles
1. Provisions of the Treaty
a. 9 new ______________________
b. France & Britain temporarily gain 4 areas of the Ottoman Empire
c. Germany has no ______________________ & forced to pay
___________________________________ of $33 billion to Allies
2. The Treatys Weaknesses
a. The _____________________ treatment of Germany fails to provide a lasting
peace; problems eventually led to WWII
b. Germany ___________________________; war-guilt clause; no way to pay
reparations due to lost territories
c. Russia excluded _______________ territory, wanted it back
d. Ignored claims of colonized people for ______________________________________
3. Opposition to the Treaty
a. Too ______________________ with dire economic consequences
b. Did not end __________________________________
c. Treaty did not satisfy self-determination demands of ethnic groups
4. Debate Over the League of Nations
a. A few thought it threatened the US foreign policy of ______________________
b. Conservative senators were suspicious of the provision for joint
economic and military action against aggression. Wanted the
constitutional right of Congress to declare war.
Summary:
5. Wilson Refuses to Compromise
a. Wilson set out on 8,000 mile ______________ giving 34 speeches explaining
why the US should join the League of Nations; suffered a stroke,
partially paralyzed for more than 2 months
b. Senate added amendments which qualified the terms under which the
US would enter the League of Nations; Senate ______________________ the
amendments, failed to ratify the treaty
c. Wilson refused to ________________________; Senate again ___________ to ratify
d. US signed separate treaty w/Germany in 1921 under President Harding
Germany Reacts to the Treaty
1. Germany was humiliated, angry, and felt betrayed
2. They insisted the treaty violated the Fourteen Points
3. Reluctantly signed under threat of a ______________________ invasion.
4. Treaty was signed at Versailles
The Legacy of War
1. United States
a. U.S. Businesses ______________________ during war
b. U.S. now worlds largest ______________________ nation
i. European countries owed estimated $11 billion to U.S.
c. U.S. in position of unexpected ______________________
d. Upon return home jobs were ______________________
2. Great Britain
a. Spent much ______________________ on war
b. Nations power ______________________
3. France
a. ______________________invasion devastated France
4. Germany
a. Weakened by the Treaty of Versailles
Summary:
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Fighting World War I 1Document4 paginiFighting World War I 1api-294843376Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 American Reactions To The Outbreak of ww2Document10 pagini2 American Reactions To The Outbreak of ww2api-301854263Încă nu există evaluări
- Fighting World War I: Name - Date - PDDocument3 paginiFighting World War I: Name - Date - PDapi-177192937Încă nu există evaluări
- WWI: The Road To "The Great War"Document4 paginiWWI: The Road To "The Great War"api-177192937Încă nu există evaluări
- 13 2Document2 pagini13 2MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treaty of Versailles Cloze NotesDocument2 paginiTreaty of Versailles Cloze NotesAPTeacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Paper For Canadian History Grade 11Document5 paginiTest Paper For Canadian History Grade 11Reynasol ButiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 36-World War IDocument2 pagini36-World War Ijaelajeanine326Încă nu există evaluări
- Road To WWI Guided NotesDocument4 paginiRoad To WWI Guided NotesAdam WilliamsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War 1 WorksheetDocument3 paginiWorld War 1 WorksheetDavid MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- More Destructive War Before It. It Involved Many CountriesDocument3 paginiMore Destructive War Before It. It Involved Many CountriesBaron VonVideoÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War II 1939-1942 Fill - in Goes With PowerpointDocument2 paginiWorld War II 1939-1942 Fill - in Goes With PowerpointJoseph ScottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reasons For Germany's Defeat WRKSHT (With Blanks)Document7 paginiReasons For Germany's Defeat WRKSHT (With Blanks)Maddie BeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 3Document2 pagini5 3MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wwi PracticeDocument13 paginiWwi Practicevesko191719Încă nu există evaluări
- World War One TestDocument5 paginiWorld War One Testperkins7Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 The U S Battlefront and Homefront in Wwi 1Document2 pagini4 The U S Battlefront and Homefront in Wwi 1api-301854263Încă nu există evaluări
- America's Response To World War IIDocument6 paginiAmerica's Response To World War IIRayhonna WalkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War II Outcome in Europe at a GlanceDocument2 paginiWorld War II Outcome in Europe at a GlanceGiovanni BurkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning of The Cold War TestmodDocument6 paginiBeginning of The Cold War Testmodapi-510348056Încă nu există evaluări
- 2122 3C History Lesson6Document3 pagini2122 3C History Lesson6Eden UwUÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument36 paginiUntitledgurnoorkaur sandhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Hist of Warfare Key EventsDocument29 paginiCambridge Hist of Warfare Key EventsUmairÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWII Notes: Key Events, Battles, Leaders & CausesDocument2 paginiWWII Notes: Key Events, Battles, Leaders & CausesLaurel HouleÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War II TestDocument4 paginiWorld War II TestnaspradleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- WwiiguidednotesDocument5 paginiWwiiguidednotesapi-249633565Încă nu există evaluări
- Causes of Wwi Noted HandoutDocument3 paginiCauses of Wwi Noted Handoutapi-404649392Încă nu există evaluări
- Copy of Copy of Crash Course US History 35 World War II, Part 1Document2 paginiCopy of Copy of Crash Course US History 35 World War II, Part 1dukethetoxic0Încă nu există evaluări
- Social Final Revision SheetDocument6 paginiSocial Final Revision SheetAhmed AzalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ushistory WwiDocument3 paginiUshistory Wwiapi-324796495Încă nu există evaluări
- Eoc Review ImperialismDocument7 paginiEoc Review Imperialismapi-252514619Încă nu există evaluări
- Guided NotesDocument1 paginăGuided Notesapi-318115175Încă nu există evaluări
- Version A - Wwii ExamDocument6 paginiVersion A - Wwii Examapi-340511893Încă nu există evaluări
- Origins of the Cold War LessonDocument1 paginăOrigins of the Cold War LessonMÎncă nu există evaluări
- The French and Indian War: Conflict over North American TerritoryDocument3 paginiThe French and Indian War: Conflict over North American Territoryschelbk75Încă nu există evaluări
- WWI Nearpod Notes PageDocument3 paginiWWI Nearpod Notes PageBrooke G. BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- WW1 and The Russian RevolutionDocument13 paginiWW1 and The Russian RevolutionNuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Summary 1B - Teacher's Version 2Document4 paginiChapter Summary 1B - Teacher's Version 2Hi hi ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 U S Foreign Policy and ImperialismDocument3 pagini1 U S Foreign Policy and Imperialismapi-301854263Încă nu există evaluări
- Causes of World War 1Document9 paginiCauses of World War 1vishnus1Încă nu există evaluări
- X-STD Social Science One Mark I. Fill in The BlanksDocument2 paginiX-STD Social Science One Mark I. Fill in The BlanksSundara MurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- WW II Mega ReviewDocument1 paginăWW II Mega Reviewapi-238106896Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 2Document2 pagini5 2MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of World War IDocument2 paginiCauses of World War IAlexis CarranzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of World War I: Name - Date - PDDocument2 paginiCauses of World War I: Name - Date - PDapi-177192937Încă nu există evaluări
- World War I Begins and the US Enters the ConflictDocument11 paginiWorld War I Begins and the US Enters the Conflictmaria fernanda ceperoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFDocument2 pagini1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFsashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Imperialism and the Changing Role of US Foreign Policy (1898-1914Document2 paginiAmerican Imperialism and the Changing Role of US Foreign Policy (1898-1914sashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empire of Japan Invading ChinaDocument4 paginiEmpire of Japan Invading Chinahaejoo jaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copy of Major European Battles of WWII Slotted Notes EditableDocument3 paginiCopy of Major European Battles of WWII Slotted Notes Editabledukethetoxic0Încă nu există evaluări
- c19 MiddleagesDocument8 paginic19 MiddleagesMÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument4 paginiUntitledapi-245498585Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 10 Review WWIIDocument2 paginiUnit 10 Review WWIImike766Încă nu există evaluări
- WorldWarII, 1939 1942Document2 paginiWorldWarII, 1939 1942Cristhian Silva CastellonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10Th Social Science English Medium 2023-24Document43 pagini10Th Social Science English Medium 2023-24ontamil2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Name:: Global History and Geography 10 MR - Smith's ClassDocument3 paginiName:: Global History and Geography 10 MR - Smith's ClassDipaliBatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWII Unit Test Key TermsDocument4 paginiWWII Unit Test Key TermszoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War II TestDocument2 paginiWorld War II TestjoeystrittmatterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Great Battles for Boys: WWI: Great Battles for BoysDe la EverandGreat Battles for Boys: WWI: Great Battles for BoysEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Submarine Warfare and the Entry of the United States into World War IDe la EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Submarine Warfare and the Entry of the United States into World War IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feudalism - Relationships ChartDocument2 paginiFeudalism - Relationships Chartapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- June 2014 Resume Updated No AddressDocument2 paginiJune 2014 Resume Updated No Addressapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Plan - Western Europe To 1500Document3 paginiUnit Plan - Western Europe To 1500api-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Peasants and KnightsDocument2 paginiPeasants and Knightsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Kirby Recommendation PDF 2Document1 paginăKirby Recommendation PDF 2api-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Achievements of Ancient Greece ProjectDocument1 paginăAchievements of Ancient Greece Projectapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Achievements of Ancient Greeks LetterDocument1 paginăAchievements of Ancient Greeks Letterapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Medieval Society - FeudalismDocument20 paginiMedieval Society - Feudalismapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Western Europe To 1500 - FeudalismDocument3 paginiWestern Europe To 1500 - Feudalismapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Greek Achievements Web NotesDocument1 paginăAncient Greek Achievements Web Notesapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Greek Project Note SheetDocument2 paginiAncient Greek Project Note Sheetapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- MG Thank YouDocument1 paginăMG Thank Youapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Achievements of Ancient Greeks Presentation RubricDocument2 paginiAchievements of Ancient Greeks Presentation Rubricapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Greece Project TimelineDocument2 paginiAncient Greece Project Timelineapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Achievements of Ancient GreeksDocument11 paginiAchievements of Ancient Greeksapi-256870699100% (1)
- Letter of RecDocument1 paginăLetter of Recapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Document Based QuestionsDocument8 paginiWwi Document Based Questionsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Krystal Renton Letter of Recommendation Trayce SchwartzDocument1 paginăKrystal Renton Letter of Recommendation Trayce Schwartzapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Stations Ws Adapted Minus Station 7Document5 paginiWwi Stations Ws Adapted Minus Station 7api-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- StatisticsDocument1 paginăStatisticsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Note CardsDocument5 paginiWwi Note Cardsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Class Description OjDocument1 paginăClass Description Ojapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 Study GuideDocument4 paginiChapter 12 Study Guideapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- War at Home Propaganda Activity UpdatedDocument2 paginiWar at Home Propaganda Activity Updatedapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Government Involvement in Wwi UpdatedDocument2 paginiGovernment Involvement in Wwi Updatedapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Propaganda PostersDocument5 paginiSample Propaganda Postersapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Technology Worksheet JigsawDocument2 paginiWwi Technology Worksheet Jigsawapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Zimmerman Note Analysis WsDocument1 paginăZimmerman Note Analysis Wsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Tech Jigsaw DocumentsDocument8 paginiWwi Tech Jigsaw Documentsapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Wwi Causes Organizer BlankDocument2 paginiWwi Causes Organizer Blankapi-256870699Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil v Common: Legal Systems ComparisonDocument3 paginiCivil v Common: Legal Systems ComparisonAlyk Tumayan CalionÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADR - Interim MeasuresDocument24 paginiADR - Interim MeasuresNitin SherwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cifra Club - Ed Sheeran - PhotographDocument2 paginiCifra Club - Ed Sheeran - PhotographAnonymous 3g5b91qÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bureau of Jail Management and PenologyDocument5 paginiBureau of Jail Management and PenologyChalymie QuinonezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Chattel MortgageDocument2 paginiDeed of Chattel MortgageInnoKal100% (1)
- Bulk Sales Law Not Violated by Foundry Shop SaleDocument2 paginiBulk Sales Law Not Violated by Foundry Shop SaleTukne SanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Affidavit of LossDocument2 paginiSample Affidavit of LossFerleneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Proposal Sex Addiction FinalDocument14 paginiResearch Proposal Sex Addiction Finalapi-296203840100% (1)
- The Naked Church 3rd EditionDocument256 paginiThe Naked Church 3rd EditionChikaokoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manacop vs. Equitable PCIBankDocument20 paginiManacop vs. Equitable PCIBankDenise DianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sumrak Saga Knjige PDF DownloadDocument2 paginiSumrak Saga Knjige PDF DownloadErika Božić14% (7)
- Constitutional Law MelDocument5 paginiConstitutional Law MelDanny MwaangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSES Fill in VerbsDocument2 paginiTENSES Fill in VerbsMayma Bkt100% (1)
- MCQS Chapter 3 Company Law 2017Document10 paginiMCQS Chapter 3 Company Law 2017BablooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodesign BH Sos BrasilandiaDocument22 paginiGeodesign BH Sos BrasilandiaAdriana SandreÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Vril Girls As An ApologyDocument8 paginiThe Vril Girls As An ApologylordlucasenÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCOUT OATH EXPLAINEDDocument8 paginiSCOUT OATH EXPLAINEDpiperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employer Contractor Claims ProcedureDocument2 paginiEmployer Contractor Claims ProcedureNishant Singh100% (1)
- Docslide - Us Chowan University Defense Defensive Line Fundamental Techniques Drills Ricky Coon Co Defensive CoordinatorDocument46 paginiDocslide - Us Chowan University Defense Defensive Line Fundamental Techniques Drills Ricky Coon Co Defensive CoordinatorChuck Milla MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jose Jr. V Michaelmar Phils. IncDocument2 paginiJose Jr. V Michaelmar Phils. IncJuno GeronimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vietnamese Foreign PolicyDocument32 paginiVietnamese Foreign Policysơn namÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marriage Annulment Case UpheldDocument4 paginiMarriage Annulment Case UpheldpyulovincentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freeboard: A. DefinitionsDocument9 paginiFreeboard: A. DefinitionsFairuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boarding PassDocument2 paginiBoarding PassRupèsh GundechäÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outlaw King' Review: Bloody Medieval Times and GutsDocument3 paginiOutlaw King' Review: Bloody Medieval Times and GutsPaula AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jissen Issue 6Document92 paginiJissen Issue 6Antoine Hoang100% (1)
- Oct. 18 2022 Duluth Public Schools SRO ContractDocument12 paginiOct. 18 2022 Duluth Public Schools SRO ContractJoe BowenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Put The Verbs in Brackets Into The Correct Form: Infinitive or Verb+ingDocument2 paginiPut The Verbs in Brackets Into The Correct Form: Infinitive or Verb+ingИван АндреевÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crimpro Codal BreakdownDocument13 paginiCrimpro Codal BreakdownsobranggandakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A A ADocument5 paginiA A AZeeshan Byfuglien GrudzielanekÎncă nu există evaluări