Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 22 - The Respiratory System
Încărcat de
Tony SnearlyDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 22 - The Respiratory System
Încărcat de
Tony SnearlyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 1
Chapter 22 - 1he kesp|ratory System
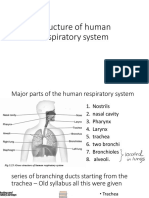
Iunct|ona| Anatomy of the kesp|ratory System
ConslsLs of Lhe resplraLory and conducLlng zones
8esplraLory zone
SlLe of gas exchange
Mlcroscoplc sLrucLures: resplraLory bronchloles, alveolar ducLs, and alveoll
ConducLlng zone
rovldes rlgld condulLs for alr Lo reach Lhe slLes of gas exchange
lncludes all oLher resplraLory sLrucLures (e.g., nose, nasal cavlLy, pharynx, Lrachea)
8esplraLory muscles - dlaphragm and oLher muscles LhaL promoLe venLllaLlon
Ma[or Iunct|ons of the kesp|ratory System
1o supply Lhe body wlLh oxygen and dlspose of carbon dloxlde
8esplraLlon - four dlsLlncL processes musL happen
ulmonary venLllaLlon (breaLhlng) - movlng alr lnLo and ouL of Lhe lungs
LxLernal resplraLlon - oxygen and carbon dloxlde exchange beLween Lhe lungs and Lhe blood
1ransporL - LransporL of oxygen and carbon dloxlde beLween Lhe lungs and Llssues vla blood
lnLernal resplraLlon - gas exchange beLween sysLemlc blood vessels and Llssues
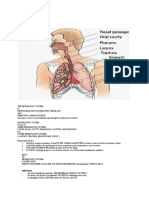
1he Nose and aranasa| S|nuses
Iunct|on of the Nose
1he only exLernally vlslble parL of Lhe resplraLory sysLem LhaL funcLlons by:
rovldlng an alrway for resplraLlon
MolsLenlng and warmlng Lhe enLerlng alr
lllLerlng lnsplred alr and cleanlng lL of forelgn maLLer
Servlng as a resonaLlng chamber for speech
Pouslng Lhe olfacLory recepLors
Structure of the Nose
1he nose ls dlvlded lnLo Lwo reglons
1. 1he exLernal nose, lncludlng Lhe rooL, brldge, dorsum nasl, and apex
hllLrum - a shallow verLlcal groove lnferlor Lo Lhe apex
1he exLernal nares (nosLrlls) are bounded laLerally by Lhe alae
2. 1he lnLernal nasal cavlLy, ln and posLerlor Lo Lhe exLernal nose
ls dlvlded by a mldllne nasal sepLum
Cpens posLerlorly lnLo Lhe nasal pharynx vla lnLernal nares
1he eLhmold and sphenold bones form Lhe roof
1he floor ls formed by Lhe hard and sofL palaLes
Nasa| Cav|ty
vesLlbule - nasal cavlLy superlor Lo Lhe nares
vlbrlssae - halrs LhaL fllLer coarse parLlcles from lnsplred alr
ClfacLory mucosa
Llnes Lhe superlor nasal cavlLy
ConLalns smell recepLors
8esplraLory mucosa
Llnes Lhe balance of Lhe nasal cavlLy
pp. 8o8
pp. 8o68o
2 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
Clands secreLe mucus conLalnlng lysozyme and defenslns Lo help desLroy bacLerla
lnsplred alr ls:
Pumldlfled by Lhe hlgh waLer conLenL ln Lhe nasal cavlLy
Warmed by rlch plexuses of caplllarles
ClllaLed mucosal cells remove conLamlnaLed mucus
Superlor, medlal, and lnferlor conchae:
roLrude medlally from Lhe laLeral walls
lncrease mucosal area
Lnhance alr Lurbulence and help fllLer alr
SenslLlve mucosa Lrlggers sneezlng when sLlmulaLed by lrrlLaLlng parLlcles
aranasa| S|nuses
Slnuses ln bones LhaL surround Lhe nasal cavlLy (fronLal, sphenold, eLhmold, maxlllary)
Slnuses llghLen Lhe skull and help Lo warm and molsLen Lhe alr
1he harynx
lunnel-shaped Lube of skeleLal muscle LhaL connecLs Lo Lhe:
nasal cavlLy and mouLh superlorly
Larynx and esophagus lnferlorly
LxLends from Lhe base of Lhe skull Lo Lhe level of Lhe slxLh cervlcal verLebra
lL ls dlvlded lnLo Lhree reglons:
nasopharynx
Cropharynx
Laryngopharynx
Nasopharynx
Lles posLerlor Lo Lhe nasal cavlLy, lnferlor Lo Lhe sphenold, and superlor Lo Lhe level of Lhe sofL
palaLe
SLrlcLly an alr passageway
Llned wlLh pseudosLraLlfled columnar eplLhellum
SofL palaLe and uvula closes durlng swallowlng Lo prevenL food from enLerlng Lhe nasal cavlLy
1he pharyngeal Lonsll (adenolds) lles hlgh on Lhe posLerlor wall
haryngoLympanlc (audlLory) Lubes open lnLo Lhe laLeral walls
Cropharynx
LxLends lnferlorly from Lhe level of Lhe sofL palaLe Lo Lhe eplgloLLls
Cpens Lo Lhe oral cavlLy vla an archway called Lhe fauces
Serves as a common passageway for food and alr
1he eplLhellal llnlng ls proLecLlve sLraLlfled squamous eplLhellum
alaLlne Lonslls lle ln Lhe laLeral walls of Lhe fauces
Llngual Lonsll covers Lhe base of Lhe Longue (posLerlor surface)
Laryngopharynx
Serves as a common passageway for food and alr
Lles posLerlor Lo Lhe uprlghL eplgloLLls
LxLends Lo Lhe larynx, where Lhe resplraLory and dlgesLlve paLhways dlverge (esophagus)
1he Larynx (Vo|ce 8ox)
ALLaches Lo Lhe hyold bone and opens lnLo Lhe laryngopharynx superlorly
ConLlnuous wlLh Lhe Lrachea posLerlorly
1he Lhree funcLlons of Lhe larynx are:
1o provlde a paLenL alrway
1o acL as a swlLchlng mechanlsm Lo rouLe alr and food lnLo Lhe proper channels
p. 8o
pp. 8o8z
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 3
1o funcLlon ln volce producLlon
Iramework of the Larynx
CarLllages (hyallne) of Lhe larynx are:
Shleld-shaped anLerosuperlor Lhyrold carLllage wlLh a mldllne laryngeal promlnence (Adam's
apple)
SlgneL rlng-shaped anLerolnferlor crlcold carLllage
1hree palrs of small aryLenold, cunelform, and cornlculaLe carLllages
LplgloLLls - elasLlc carLllage LhaL covers Lhe laryngeal lnleL durlng swallowlng
Voca| L|gaments
ALLach Lhe aryLenold carLllages Lo Lhe Lhyrold carLllage
Composed of elasLlc flbers LhaL form mucosal folds called ttoe vocol cotJs
1he medlal openlng beLween Lhem ls Lhe gloLLls
1hey vlbraLe Lo produce sound as alr rushes up from Lhe lungs
vesLlbular folds (false vocal cords)
Mucosal folds superlor Lo Lhe Lrue vocal cords
Pave no parL ln sound producLlon
Pelp Lo close Lhe gloLLls durlng swallowlng
Voca| roduct|on
Speech - lnLermlLLenL release of explred alr whlle openlng and closlng Lhe gloLLls
lLch - deLermlned by Lhe lengLh and Lenslon of Lhe vocal cords
Loudness - depends upon Lhe force aL whlch Lhe alr rushes across Lhe vocal cords
1he pharynx resonaLes, ampllfles, and enhances sound quallLy
Sound ls shaped" lnLo language by acLlon of Lhe pharynx, Longue, sofL palaLe, and llps
Sph|ncter Iunct|ons of the Larynx
8oLh Lhe eplgloLLls and Lhe vocal cords can close Lhe larynx
1he larynx ls closed durlng coughlng, sneezlng, and valsalva's maneuver
valsalva's maneuver
Alr ls Lemporarlly held ln Lhe lower resplraLory LracL by closlng Lhe gloLLls
Causes lnLra-abdomlnal pressure Lo rlse when abdomlnal muscles conLracL
LmpLles Lhe bladder or recLum
AcLs as a spllnL Lo sLablllze Lhe Lrunk when llfLlng heavy loads
1he 1rachea
llexlble and moblle Lube exLendlng from Lhe larynx lnLo Lhe medlasLlnum
Composed of Lhree layers
1. Mucosa - made up of gobleL cells and clllaLed pseudosLraLlfled eplLhellum
2. Submucosa - connecLlve Llssue deep Lo Lhe mucosa havlng seromucous glands
3. AdvenLlLla - ouLermosL layer made of C-shaped rlngs of hyallne carLllage
1rachealls muscle
ConnecLs posLerlor parLs of carLllage rlngs
ConLracLs durlng coughlng Lo expel mucus
Carlna
LasL Lracheal carLllage
olnL where Lrachea branches lnLo Lwo bronchl
4 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
1he 8ronch| and Subd|v|s|ons
Conduct|ng 2one: 8ronch|
1he carlna of Lhe lasL Lracheal carLllage marks Lhe end of Lhe Lrachea and Lhe beglnnlng of Lhe
rlghL and lefL bronchl
Alr reachlng Lhe bronchl ls:
Warm and cleansed of lmpurlLles
SaLuraLed wlLh waLer vapor
8ronchl subdlvlde lnLo secondary bronchl, each supplylng a lobe of Lhe lungs
Alr passages undergo 23 orders of branchlng ln Lhe lungs
Conduct|ng 2one: 8ronch|a| 1ree
1lssue walls of bronchl mlmlc LhaL of Lhe Lrachea
As conducLlng Lubes become smaller, sLrucLural changes occur
CarLllage supporL sLrucLures change
LplLhellum Lypes change
AmounL of smooLh muscle lncreases
8ronchloles
ConslsL of cuboldal eplLhellum
Pave a compleLe layer of clrcular smooLh muscle
Lack carLllage supporL and mucus-produclng cells
kesp|ratory 2one
ueflned by Lhe presence of alveoll, beglns as Lermlnal bronchloles feed lnLo resplraLory
bronchloles
8esplraLory bronchloles lead Lo alveolar ducLs, Lhen Lo Lermlnal clusLers of alveolar sacs
composed of alveoll
ApproxlmaLely 300 mllllon alveoll:
AccounL for mosL of Lhe lungs' volume
rovlde Lremendous surface area for gas exchange
kesp|ratory Membrane
1hls alr-blood barrler (~0.3-m-Lhlck) ls composed of:
Alveolar and caplllary walls
1helr fused basal lamlnas
Alveolar walls:
Are a slngle layer of Lype l eplLhellal cells
ermlL gas exchange by slmple dlffuslon
SecreLe ooqloteoslo coovettloq eozyme (ACL)
1ype ll cuboldal cells secreLe surfacLanL and anLlmlcroblal proLelns
A|veo||
Surrounded by flne elasLlc flbers
ConLaln open pores LhaL:
ConnecL ad[acenL alveoll
Allow alr pressure LhroughouL Lhe lung Lo be equallzed
Pouse macrophages LhaL keep alveolar surfaces sLerlle
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM S
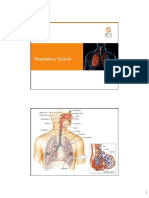
Gross Anatomy of the Lungs
Lungs occupy all of Lhe Lhoraclc cavlLy excepL Lhe medlasLlnum
8ooL - slLe of vascular and bronchlal aLLachmenLs
CosLal surface - anLerlor, laLeral, and posLerlor surfaces ln conLacL wlLh Lhe rlbs
Apex - narrow superlor Llp
8ase - lnferlor surface LhaL resLs on Lhe dlaphragm
Pllus - on medlasLlnal surface, lndenLaLlon LhaL conLalns pulmonary and sysLemlc blood
vessels, bronchl, lymphaLlc vessels, and nerves
1he Lungs and |eurae
Lungs
Cardlac noLch (lmpresslon) of lefL lung- concavlLy LhaL accommodaLes Lhe hearL
LefL lung - separaLed lnLo upper and lower lobes by Lhe obllque flssure, smaller
8lghL lung - separaLed lnLo Lhree lobes by Lhe obllque and horlzonLal flssures
1here are bronchopulmonary segmenLs ln each lung (10 rlghL, 8-9 lefL)
Lobules are Lhe smallesL subdlvlslons, served by bronchloles and Lhelr branches
8|ood Supp|y to Lungs
Lungs are perfused by Lwo clrculaLlons: pulmonary and bronchlal (low pressure, hlgh volume)
ulmonary arLerles - supply sysLemlc venous blood Lo be oxygenaLed
8ranch profusely, along wlLh bronchl
ulLlmaLely feed lnLo Lhe pulmonary caplllary neLwork surroundlng Lhe alveoll
ulmonary velns - carry oxygenaLed blood from resplraLory zones Lo Lhe hearL
8|ood Supp|y to Lungs
8ronchlal arLerles - provlde sysLemlc blood Lo Lhe lung Llssue
Arlse from aorLa and enLer Lhe lungs aL Lhe hllus
Supply all lung Llssue excepL Lhe alveoll
8ronchlal velns anasLomose wlLh pulmonary velns
ulmonary velns carry mosL venous blood back Lo Lhe hearL
|eurae
1hln, double-layered serosa
arleLal pleura
Covers Lhe Lhoraclc wall and superlor face of Lhe dlaphragm
ConLlnues around hearL and beLween lungs
vlsceral, or pulmonary, pleura
Covers Lhe exLernal lung surface
ulvldes Lhe Lhoraclc cavlLy lnLo Lhree chambers
o 1he cenLral medlasLlnum
o 1wo laLeral comparLmenLs, each conLalnlng a lung
Mechan|cs of 8reath|ng
8reaLhlng, or pulmonary venLllaLlon, conslsLs of Lwo phases
lnsplraLlon - alr flows lnLo Lhe lungs
LxplraLlon - gases exlL Lhe lungs
6 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
ressure ke|at|onsh|ps |n the 1horac|c Cav|ty
8esplraLory pressure ls always descrlbed relaLlve Lo aLmospherlc pressure
ALmospherlc pressure (
aLm
)
ressure exerLed by Lhe alr surroundlng Lhe body
negaLlve resplraLory pressure ls less Lhan
aLm
oslLlve resplraLory pressure ls greaLer Lhan
aLm
lnLrapulmonary pressure (
alv
) - pressure wlLhln Lhe alveoll
lnLrapleural pressure (
lp
) - pressure wlLhln Lhe pleural cavlLy
ressure ke|at|onsh|ps
lnLrapulmonary pressure and lnLrapleural pressure flucLuaLe wlLh Lhe phases of breaLhlng
lnLrapulmonary pressure always evenLually equallzes lLself wlLh aLmospherlc pressure
lnLrapleural pressure ls always less Lhan lnLrapulmonary pressure and aLmospherlc pressure
1wo forces acL Lo pull Lhe lungs away from Lhe Lhoraclc wall, promoLlng lung collapse
LlasLlclLy of lungs causes Lhem Lo assume smallesL posslble slze
Surface Lenslon of alveolar fluld draws alveoll Lo Lhelr smallesL posslble slze
Cpposlng force - elasLlclLy of Lhe chesL wall pulls Lhe Lhorax ouLward Lo enlarge Lhe lungs
Lung Co||apse
Caused by equallzaLlon of Lhe lnLrapleural pressure wlLh Lhe lnLrapulmonary pressure
1ranspulmonary pressure keeps Lhe alrways open
1ranspulmonary pressure - dlfference beLween Lhe lnLrapulmonary and lnLrapleural
pressures (
alv
-
lp
)
u|monary Vent||at|on
A mechanlcal process LhaL depends on volume changes ln Lhe Lhoraclc cavlLy
volume changes lead Lo pressure changes, whlch lead Lo Lhe flow of gases Lo equallze pressure
v l (flow of gases)
8oy|es Law
8oyles law - Lhe relaLlonshlp beLween Lhe pressure and volume of gases
1
v
1
=
2
v
2
= pressure of a gas ln mm Pg
v = volume ln cublc mllllmeLers
SubscrlpLs 1 and 2 represenL Lhe lnlLlal and resulLlng condlLlons, respecLlvely
Insp|rat|on
1he dlaphragm and exLernal lnLercosLal muscles (lnsplraLory muscles) conLracL and Lhe rlb cage
rlses
1he lungs are sLreLched and lnLrapulmonary volume lncreases
lnLrapulmonary pressure drops below aLmospherlc pressure (1 mm Pg)
Alr flows lnLo Lhe lungs, down lLs pressure gradlenL, unLll lnLrapleural pressure = aLmospherlc
pressure
Lxp|rat|on
lnsplraLory muscles relax and Lhe rlb cage descends due Lo gravlLy
1horaclc cavlLy volume decreases
LlasLlc lungs recoll passlvely and lnLrapulmonary volume decreases
lnLrapulmonary pressure rlses above aLmospherlc pressure (+1 mm Pg)
Cases flow ouL of Lhe lungs down Lhe pressure gradlenL unLll lnLrapulmonary pressure ls 0
pp. 88zo
pp. 8zo8zz
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 7
hys|ca| Iactors Inf|uenc|ng Vent||at|on
A|rway kes|stance
lrlcLlon ls Lhe ma[or nonelasLlc source of reslsLance Lo alrflow
1he relaLlonshlp beLween flow (l), pressure (), and reslsLance (8) ls:
l =
8
1he amounL of gas flowlng lnLo and ouL of Lhe alveoll ls dlrecLly proporLlonal Lo , Lhe pressure
gradlenL beLween Lhe aLmosphere and Lhe alveoll
= (
atm
-
alv
)
Cas flow ls lnversely proporLlonal Lo reslsLance wlLh Lhe greaLesL reslsLance belng ln Lhe medlum-
slzed bronchl
As alrway reslsLance rlses, breaLhlng movemenLs become more sLrenuous
Severely consLrlcLed or obsLrucLed bronchloles:
Can prevenL llfe-susLalnlng venLllaLlon
Can occur durlng acuLe asLhma aLLacks whlch sLops venLllaLlon
Lplnephrlne release vla Lhe sympaLheLlc nervous sysLem dllaLes bronchloles and reduces alr
reslsLance
A|veo|ar Surface 1ens|on
Surface Lenslon - Lhe aLLracLlon of llquld molecules for one anoLher aL a llquld-gas lnLerface
1he llquld coaLlng Lhe alveolar surface ls always acLlng Lo reduce Lhe alveoll Lo Lhe smallesL
posslble slze
SurfacLanL, a deLergenL-llke complex, reduces surface Lenslon and helps keep Lhe alveoll from
collapslng
Lung Comp||ance
1he ease wlLh whlch lungs can be expanded
Speclflcally, Lhe measure of Lhe change ln lung volume LhaL occurs wlLh a glven change ln
Lranspulmonary pressure
ueLermlned by Lwo maln facLors
ulsLenslblllLy of Lhe lung Llssue and surroundlng Lhoraclc cage
Surface Lenslon of Lhe alveoll
Iactors 1hat D|m|n|sh Lung Comp||ance
Scar Llssue or flbrosls LhaL reduces Lhe naLural reslllence of Lhe lungs
8lockage of Lhe smaller resplraLory passages wlLh mucus or fluld
8educed producLlon of surfacLanL
uecreased flexlblllLy of Lhe Lhoraclc cage or lLs decreased ablllLy Lo expand
Lxamples lnclude:
ueformlLles of Lhorax
CsslflcaLlon of Lhe cosLal carLllage
aralysls of lnLercosLal muscles
8 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
kesp|ratory Vo|umes and u|monary Iunct|on 1ests
kesp|ratory Vo|umes
1ldal volume (1v) - alr LhaL moves lnLo and ouL of Lhe lungs wlLh each breaLh (approxlmaLely 300
ml)
lnsplraLory reserve volume (l8v) - alr LhaL can be lnsplred forclbly beyond Lhe Lldal volume
(2100-3200 ml)
LxplraLory reserve volume (L8v) - alr LhaL can be evacuaLed from Lhe lungs afLer a Lldal
explraLlon (1000-1200 ml)
8esldual volume (8v) - alr lefL ln Lhe lungs afLer sLrenuous explraLlon (1200 ml)
kesp|ratory Capac|t|es
lnsplraLory capaclLy (lC) - LoLal amounL of alr LhaL can be lnsplred afLer a Lldal explraLlon
(l8v + 1v)
luncLlonal resldual capaclLy (l8C) - amounL of alr remalnlng ln Lhe lungs afLer a Lldal explraLlon
(8v + L8v)
vlLal capaclLy (vC) - Lhe LoLal amounL of exchangeable alr
(1v + l8v + L8v)
1oLal lung capaclLy (1LC) - sum of all lung volumes (approxlmaLely 6000 ml ln males)
Dead Space
AnaLomlcal dead space - volume of Lhe conducLlng resplraLory passages (130 ml)
Alveolar dead space - alveoll LhaL cease Lo acL ln gas exchange due Lo collapse or obsLrucLlon
1oLal dead space - sum of alveolar and anaLomlcal dead spaces
u|monary Iunct|on 1ests
SplromeLer - an lnsLrumenL conslsLlng of a hollow bell lnverLed over waLer, used Lo evaluaLe
resplraLory funcLlon
SplromeLry can dlsLlngulsh beLween:
CbsLrucLlve pulmonary dlsease - lncreased alrway reslsLance
8esLrlcLlve dlsorders - reducLlon ln LoLal lung capaclLy from sLrucLural or funcLlonal lung
changes
1oLal venLllaLlon - LoLal amounL of gas flow lnLo or ouL of Lhe resplraLory LracL ln one mlnuLe
lorced vlLal capaclLy (lvC) - gas forclbly expelled afLer Laklng a deep breaLh
lorced explraLory volume (lLv) - Lhe amounL of gas expelled durlng speclflc Llme lnLervals of Lhe
lvC
lncreases ln 1LC, l8C, and 8v may occur as a resulL of obsLrucLlve dlsease
8educLlon ln vC, 1LC, l8C, and 8v resulL from resLrlcLlve dlsease
A|veo|ar Vent||at|on
Alveolar venLllaLlon raLe (Av8) - measures Lhe flow of fresh gases lnLo and ouL of Lhe alveoll
durlng a parLlcular Llme
Slow, deep breaLhlng lncreases Av8 and rapld, shallow breaLhlng decreases Av8
Nonresp|ratory A|r Movements
MosL resulL from reflex acLlon
Lxamples lnclude: coughlng, sneezlng, crylng, laughlng, hlccuplng, and yawnlng
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 9
Gas Lxchanges 8etween the 8|ood, Lungs, and 1|ssues
8as|c ropert|es of Gases
Da|ton's Law of art|a| ressures
1oLal pressure exerLed by a mlxLure of gases ls Lhe sum of Lhe pressures exerLed lndependenLly
by each gas ln Lhe mlxLure
1he parLlal pressure of each gas ls dlrecLly proporLlonal Lo lLs percenLage ln Lhe mlxLure
nenry's Law
When a mlxLure of gases ls ln conLacL wlLh a llquld, each gas wlll dlssolve ln Lhe llquld ln
proporLlon Lo lLs parLlal pressure
1he amounL of gas LhaL wlll dlssolve ln a llquld also depends upon lLs solublllLy
varlous gases ln alr have dlfferenL solublllLles:
Carbon dloxlde ls Lhe mosL soluble
Cxygen ls 1/20
Lh
as soluble as carbon dloxlde
nlLrogen ls pracLlcally lnsoluble ln plasma
Compos|t|on of A|veo|ar Gas
1he aLmosphere ls mosLly oxygen and nlLrogen, whlle alveoll conLaln more carbon dloxlde and
waLer vapor
1hese dlfference resulL from:
Cas exchanges ln Lhe lungs - oxygen dlffuses from Lhe alveoll and carbon dloxlde dlffuses
lnLo Lhe alveoll
Alr ls humldlfled by Lhe conducLlng paLhways
1he mlxlng of alveolar gas occurs wlLh each breaLh
Lxterna| kesp|rat|on
u|monary Gas Lxchange
lacLors lnfluenclng Lhe movemenL of oxygen and carbon dloxlde across Lhe resplraLory
membrane
arLlal pressure gradlenLs and gas solublllLles
MaLchlng of alveolar venLllaLlon and pulmonary blood perfuslon
SLrucLural characLerlsLlcs of Lhe resplraLory membrane
art|a| ressure Grad|ents and Gas So|ub|||t|es
1he parLlal pressure oxygen (
C2
) of venous blood ls 40 mm Pg, Lhe parLlal pressure ln Lhe alveoll
ls 104 mm Pg
1hls sLeep gradlenL allows oxygen parLlal pressures Lo rapldly reach equlllbrlum (ln 0.23
seconds), and Lhus blood can move Lhree Llmes as qulckly (0.73 seconds) Lhrough Lhe
pulmonary caplllary and sLlll be adequaLely oxygenaLed
AlLhough carbon dloxlde has a lower parLlal pressure gradlenL:
lL ls 20 Llmes more soluble ln plasma Lhan oxygen
lL dlffuses ln equal amounLs wlLh oxygen
Vent||at|on-erfus|on Coup||ng
venLllaLlon - Lhe amounL of gas reachlng Lhe alveoll
erfuslon - Lhe blood flow reachlng Lhe alveoll
venLllaLlon and perfuslon musL be LlghLly regulaLed for efflclenL gas exchange
Changes ln
CC2
ln Lhe alveoll cause changes ln Lhe dlameLers of Lhe bronchloles
assageways servlclng areas where alveolar carbon dloxlde ls hlgh Jllote
1hose servlng area where alveolar carbon dloxlde ls low coosttlct
pp. 8z)8z8
p. 8z8
pp. 8z88o
10 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
Surface Area and 1h|ckness of the kesp|ratory Membrane
8esplraLory membranes:
Are only 0.3 Lo 1 m Lhlck, allowlng for efflclenL gas exchange
Pave a LoLal surface area (ln males) of 30-70 m
2
(40 Llmes LhaL of one's skln)
1hlcken lf lungs become waLerlogged and edemaLous, whereby gas exchange ls lnadequaLe
and oxygen deprlvaLlon resulLs
uecrease ln surface area wlLh emphysema, when walls of ad[acenL alveoll break
Interna| kesp|rat|on
1he facLors promoLlng gas exchange beLween sysLemlc caplllarles and Llssue cells are Lhe same as
Lhose acLlng ln Lhe lungs
1he parLlal pressures and dlffuslon gradlenLs are reversed
C2
ln Llssue ls always lower Lhan ln sysLemlc arLerlal blood
C2
of venous blood dralnlng Llssues ls 40 mm Pg and
CC2
ls 43 mm Pg
1ransport of kesp|ratory Gases by 8|ood
Cxygen 1ransport
Molecular oxygen ls carrled ln Lhe blood bound Lo hemoglobln (Pb) wlLhln 88Cs and dlssolved ln
plasma
Lach hemoglobln molecule blnds 4 oxygen ln a rapld and reverslble process
1he hemoglobln-oxygen comblnaLlon ls called oxybemoqloblo (PbC
2
)
Pemoglobln LhaL has released oxygen ls called teJoceJ bemoqloblo (PPb)
nemog|ob|n (nb)
SaLuraLed hemoglobln - when all four hemes of Lhe molecule are bound Lo oxygen
arLlally saLuraLed hemoglobln - when one Lo Lhree hemes are bound Lo oxygen
1he raLe ln whlch hemoglobln blnds and releases oxygen ls regulaLed by:
C2
, LemperaLure, blood pP,
CC2
, and Lhe concenLraLlon of 8C (an organlc chemlcal)
o 1hese facLors lnsure adequaLe dellvery of oxygen Lo Llssue cells
Inf|uence of
C2
on nemog|ob|n Saturat|on
Pemoglobln saLuraLlon ploLLed agalnsL
C2
produces a oxygen-hemoglobln dlssoclaLlon curve
98 saLuraLed arLerlal blood conLalns 20 ml oxygen per 100 ml blood (20 vol )
As arLerlal blood flows Lhrough caplllarles, 3 ml oxygen are released
1he saLuraLlon of hemoglobln ln arLerlal blood explalns why breaLhlng deeply lncreases Lhe
C2
buL has llLLle effecL on oxygen saLuraLlon ln hemoglobln
nemog|ob|n Saturat|on Curve
Pemoglobln ls almosL compleLely saLuraLed aL a
C2
of 70 mm Pg
lurLher lncreases ln
C2
produce only small lncreases ln oxygen blndlng
Cxygen loadlng and dellvery Lo Llssue ls adequaLe when
C2
ls below normal levels
Cnly 20-23 of bound oxygen ls unloaded durlng one sysLemlc clrculaLlon
lf oxygen levels ln Llssues drop:
More oxygen dlssoclaLes from hemoglobln and ls used by cells
8esplraLory raLe or cardlac ouLpuL need noL lncrease
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 11
Cther Iactors Inf|uenc|ng nemog|ob|n Saturat|on
1emperaLure, P
+
,
CC2
, and 8C:
Modlfy Lhe sLrucLure of hemoglobln and alLer lLs afflnlLy for oxygen
lncreases:
o uecrease hemoglobln's afflnlLy for oxygen
o Lnhance oxygen unloadlng from Lhe blood
uecreases acL ln Lhe opposlLe manner
1hese parameLers are all hlgh ln sysLemlc caplllarles where oxygen unloadlng ls Lhe goal
Iactors 1hat Increase ke|ease of Cxygen by nemog|ob|n
As cells meLabollze glucose, carbon dloxlde ls released lnLo Lhe blood causlng:
lncreases ln
CC2
and P
+
concenLraLlon ln caplllary blood
uecllnlng pP (acldosls) weakens Lhe hemoglobln-oxygen bond (8ohr effecL)
MeLabollzlng cells have heaL as a byproducL and Lhe rlse ln LemperaLure lncreases 8C synLhesls
All Lhese facLors lnsure oxygen unloadlng ln Lhe vlclnlLy of worklng Llssue cells
nemog|ob|n-N|tr|c Cx|de artnersh|p
nlLrlc oxlde (nC) ls a vasodllaLor LhaL plays a role ln blood pressure regulaLlon
Pemoglobln ls a vasoconsLrlcLor and a nlLrlc oxlde scavenger (heme desLroys nC)
Powever, as oxygen blnd Lo hemoglobln:
nlLrlc oxlde blnds Lo a cysLelne amlno acld on hemoglobln
8ound nlLrlc oxlde ls proLecLed from degradaLlon by hemoglobln's lron
nemog|ob|n-N|tr|c Cx|de artnersh|p
1he hemoglobln ls released as oxygen ls unloaded, causlng vasodllaLlon
As deoxygenaLed hemoglobln plcks up carbon dloxlde, lL also blnds nlLrlc oxlde and carrles Lhese
gases Lo Lhe lungs for unloadlng
Carbon D|ox|de 1ransport
Carbon dloxlde ls LransporLed ln Lhe blood ln Lhree forms:
ulssolved ln plasma - 7 Lo 10
Chemlcally bound Lo hemoglobln - 20 ls carrled ln 88Cs as carbamlnohemoglobln
8lcarbonaLe lon ln plasma - 70 ls LransporLed as blcarbonaLe (PCC
3
-
)
1ransport and Lxchange of Carbon D|ox|de
Carbon dloxlde dlffuses lnLo 88Cs and comblnes wlLh waLer Lo form carbonlc acld (P
2
CC
3
), whlch
qulckly dlssoclaLes lnLo hydrogen lons and blcarbonaLe lons
ln 88Cs, carbonlc anhydrase reverslbly caLalyzes Lhe converslon of carbon dloxlde and waLer Lo
carbonlc acld
AL Lhe Llssues:
8lcarbonaLe qulckly dlffuses from 88Cs lnLo Lhe plasma
Chlorlde shlfL - Lo counLerbalance Lhe ouLrush of negaLlve blcarbonaLe lons from Lhe 88Cs,
chlorlde lons (Cl
-
) move from Lhe plasma lnLo Lhe eryLhrocyLes
AL Lhe lungs, Lhese processes are reversed:
8lcarbonaLe lons move lnLo Lhe 88Cs and blnd wlLh hydrogen lons Lo form carbonlc acld
Carbonlc acld ls Lhen spllL by carbonlc anhydrase Lo release carbon dloxlde and waLer
Carbon dloxlde Lhen dlffuses from Lhe blood lnLo Lhe alveoll
12 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
na|dane Lffect
1he amounL of carbon dloxlde LransporLed ls markedly affecLed by Lhe
C2
Paldane effecL - Lhe lower Lhe
C2
and hemoglobln saLuraLlon wlLh oxygen, Lhe more carbon
dloxlde can be carrled ln Lhe blood
AL Lhe Llssues, as more carbon dloxlde enLers Lhe blood:
More oxygen dlssoclaLes from hemoglobln (8ohr effecL)
More carbon dloxlde comblnes wlLh hemoglobln, and more blcarbonaLe lons are formed
1hls slLuaLlon ls reversed ln pulmonary clrculaLlon
Inf|uence of Carbon D|ox|de on 8|ood pn
1he carbonlc acld-blcarbonaLe buffer sysLem reslsLs blood pP changes
lf hydrogen lon concenLraLlons ln blood begln Lo rlse, lL ls removed by comblnlng wlLh PCC
3
-
lf hydrogen lon concenLraLlons begln Lo drop, carbonlc acld dlssoclaLes, releaslng P
+
Changes ln resplraLory raLe can also:
AlLer blood pP
rovlde a fasL-acLlng sysLem Lo ad[usL pP when lL ls dlsLurbed by meLabollc facLors
Contro| of kesp|rat|on
Neura| Mechan|sms
Medu||ary kesp|ratory Centers
1he dorsal resplraLory group (u8C), or lnsplraLory cenLer:
ls locaLed near Lhe rooL of nerve lx
Appears Lo be Lhe paceseLLlng resplraLory cenLer
LxclLes Lhe lnsplraLory muscles and seLs eupnea (12-13 breaLhs/mlnuLe)
8ecomes dormanL durlng explraLlon
1he venLral resplraLory group (v8C) ls lnvolved ln forced lnsplraLlon and explraLlon
ons kesp|ratory Centers
ons cenLers:
lnfluence and modlfy acLlvlLy of Lhe medullary cenLers
SmooLh ouL lnsplraLlon and explraLlon LranslLlons and vlce versa
neumoLaxlc cenLer - conLlnuously lnhlblLs Lhe lnsplraLlon cenLer
ApneusLlc cenLer - conLlnuously sLlmulaLes Lhe medullary lnsplraLlon cenLer
kesp|ratory khythm
A resulL of reclprocal lnhlblLlon of Lhe lnLerconnecLed neuronal neLworks ln Lhe medulla
CLher Lheorles lnclude:
lnsplraLory neurons are pacemakers and have lnLrlnslc auLomaLlclLy and rhyLhmlclLy
SLreLch recepLors ln Lhe lungs esLabllsh resplraLory rhyLhm
Iactors Inf|uenc|ng 8reath|ng kate and Depth
lnsplraLory depLh ls deLermlned by how acLlvely Lhe resplraLory cenLer sLlmulaLes Lhe resplraLory
muscles
8aLe of resplraLlon ls deLermlned by how long Lhe lnsplraLory cenLer ls acLlve
8esplraLory cenLers ln Lhe pons and medulla are senslLlve Lo boLh exclLaLory and lnhlblLory
sLlmull
pp. 886
pp. 868
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 13
kef|exes
ulmonary lrrlLanL reflexes - lrrlLanLs promoLe reflexlve consLrlcLlon of alr passages
lnflaLlon reflex (Perlng-8reuer) - sLreLch recepLors ln Lhe lungs are sLlmulaLed by lung lnflaLlon
upon lnflaLlon, lnhlblLory slgnals are senL Lo Lhe medullary lnsplraLlon cenLer Lo end lnhalaLlon
and allow explraLlon
n|gher 8ra|n Centers
PypoLhalamlc conLrols - acL Lhrough Lhe llmblc sysLem Lo modlfy raLe and depLh of resplraLlon
Lxamples: breaLh holdlng LhaL occurs ln anger
A rlse ln body LemperaLure acLs Lo lncrease resplraLory raLe
CorLlcal conLrols - dlrecL slgnals from Lhe cerebral moLor corLex LhaL bypass medullary conLrols
Lxamples: volunLary breaLh holdlng, Laklng a deep breaLh
Carbon D|ox|de ressure (
CC2
)
Changlng
CC2
levels are monlLored by chemorecepLors of Lhe braln sLem
Carbon dloxlde ln Lhe blood dlffuses lnLo Lhe cerebrosplnal fluld where lL ls hydraLed
8esulLlng carbonlc acld dlssoclaLes, releaslng hydrogen lons
CC2
levels rlse (hypercapnla) resulLlng ln lncreased depLh and raLe of breaLhlng
PypervenLllaLlon - lncreased depLh and raLe of breaLhlng LhaL:
Culckly flushes carbon dloxlde from Lhe blood
Cccurs ln response Lo hypercapnla
1hough a rlse CC
2
acLs as Lhe orlglnal sLlmulus, conLrol of breaLhlng aL resL ls regulaLed by Lhe
hydrogen lon concenLraLlon ln Lhe braln
PypovenLllaLlon - slow and shallow breaLhlng due Lo abnormally low
CC2
levels
Apnea (breaLhlng cessaLlon) may occur unLll
CC2
levels rlse
ArLerlal oxygen levels are monlLored by Lhe aorLlc and caroLld bodles
SubsLanLlal drops ln arLerlal
C2
(Lo 60 mm Pg) are need before oxygen levels become a ma[or
sLlmulus for lncreased venLllaLlon
lf carbon dloxlde ls noL removed (e.g., as ln emphysema and chronlc bronchlLls), chemorecepLors
become unresponslve Lo
CC2
chemlcal sLlmull
ln such cases,
C2
levels become Lhe prlnclple resplraLory sLlmulus (hypoxlc drlve)
Arter|a| pn
Changes ln arLerlal pP can modlfy resplraLory raLe even lf carbon dloxlde and oxygen levels are
normal
lncreased venLllaLlon ln response Lo falllng pP ls medlaLed by perlpheral chemorecepLors
Acldosls may reflecL:
Carbon dloxlde reLenLlon
AccumulaLlon of lacLlc acld
Lxcess faLLy aclds ln paLlenLs wlLh dlabeLes melllLus
8esplraLory sysLem conLrols wlll aLLempL Lo ralse Lhe pP by lncreaslng resplraLory raLe and depLh
14 CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM
kesp|ratory Ad[ustments
Lxerc|se
8esplraLory ad[usLmenLs are geared Lo boLh Lhe lnLenslLy and duraLlon of exerclse
uurlng vlgorous exerclse:
venLllaLlon can lncrease 20 fold
8reaLhlng becomes deeper and more vlgorous, buL resplraLory raLe may noL be slgnlflcanLly
changed (hyperpnea)
Lxerclse-enhanced breaLhlng ls noL prompLed by an lncrease ln
CC2
nor a decrease
C2
or pP
1hese levels remaln surprlslngly consLanL durlng exerclse
As exerclse beglns:
venLllaLlon lncreases abrupLly, rlses slowly, and reaches a sLeady-sLaLe
When exerclse sLops:
venLllaLlon decllnes suddenly, Lhen gradually decreases Lo normal
neural facLors brlng abouL Lhe above changes, lncludlng:
sychlc sLlmull
CorLlcal moLor acLlvaLlon
LxclLaLory lmpulses from proprlocepLors ln muscles
n|gh A|t|tude
1he body responds Lo qulck movemenL Lo hlgh alLlLude (above 8000 fL) wlLh sympLoms of acuLe
mounLaln slckness - headache, shorLness of breaLh, nausea, and dlzzlness
AccllmaLlzaLlon - resplraLory and hemaLopoleLlc ad[usLmenLs Lo alLlLude lnclude:
lncreased venLllaLlon - 2-3 L/mln hlgher Lhan aL sea level
ChemorecepLors become more responslve Lo
CC2
SubsLanLlal decllne ln
C2
sLlmulaLes perlpheral chemorecepLors
nomeostat|c Imba|ances of the kesp|ratory System
Chron|c Cbstruct|ve u|monary D|sease (CCD)
Lxempllfled by chronlc bronchlLls and obsLrucLlve emphysema
aLlenLs have a hlsLory of:
Smoklng
uyspnea, where labored breaLhlng occurs and geLs progresslvely worse
Coughlng and frequenL pulmonary lnfecLlons
CCu vlcLlms develop resplraLory fallure accompanled by hypoxemla, carbon dloxlde reLenLlon,
and resplraLory acldosls
Asthma
CharacLerlzed by dyspnea, wheezlng, and chesL LlghLness
AcLlve lnflammaLlon of Lhe alrways precedes bronchospasms
Alrway lnflammaLlon ls an lmmune response caused by release of lL-4 and lL-3, whlch sLlmulaLe
lgL and recrulL lnflammaLory cells
Alrways Lhlckened wlLh lnflammaLory exudaLes magnlfy Lhe effecL of bronchospasms
p. 8
pp. 88qo
pp. 8qo8q
p. 8q
CnA1Lk 22 - kLSIkA1Ck SS1LM 1S
1ubercu|os|s
lnfecLlous dlsease caused by Lhe bacLerlum Mycoboctetlom tobetcolosls
SympLoms lnclude fever, nlghL sweaLs, welghL loss, a racklng cough, and spllLLlng headache
1reaLmenL enLalls a 12-monLh course of anLlbloLlcs
Lung Cancer
AccounLs for of all cancer deaLhs ln Lhe uS
90 of all paLlenLs wlLh lung cancer were smokers
1he Lhree mosL common Lypes are:
Squamous cell carclnoma (20-40 of cases) arlses ln bronchlal eplLhellum
Adenocarclnoma (23-33 of cases) orlglnaLes ln perlpheral lung area
Small cell carclnoma (20-23 of cases) conLalns lymphocyLe-llke cells LhaL orlglnaLe ln Lhe
prlmary bronchl and subsequenLly meLasLaslze
Deve|opmenta| Aspects
ClfacLory placodes lnvaglnaLes lnLo olfacLory plLs by Lhe 4
Lh
week
LaryngoLracheal buds are presenL by Lhe 3
Lh
week
Mucosae of Lhe bronchl and lung alveoll are presenL by Lhe 8
Lh
week
8y Lhe 28
Lh
week, a baby born premaLurely can breaLhe on lLs own
uurlng feLal llfe, Lhe lungs are fllled wlLh fluld and blood bypasses Lhe lungs
Cas exchange Lakes place vla Lhe placenLa
AL blrLh, resplraLory cenLers are acLlvaLed, alveoll lnflaLe, and lungs begln Lo funcLlon
8esplraLory raLe ls hlghesL ln newborns and slows unLll adulLhood
Lungs conLlnue Lo maLure and more alveoll are formed unLll young adulLhood
8esplraLory efflclency decreases ln old age
pp. 8q8qz
p. 8qz
pp. 8qz8q
8q6
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Textbook of Special Pathological Anatomy of Domestic AnimalsDe la EverandTextbook of Special Pathological Anatomy of Domestic AnimalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 23 - The Digestive SystemDocument15 paginiChapter 23 - The Digestive SystemTony SnearlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Prac QuizzesDocument7 paginiAnatomy Prac QuizzesTiffanie DickersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20 - The Lymphatic SystemDocument5 paginiChapter 20 - The Lymphatic SystemTony SnearlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument42 paginiAnatomy & PhysiologyArah Lyn ApiagÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesDocument31 paginiA&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesBethanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2Document115 paginiI. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2arielleortuosteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: Clarence L. Nuval, RMT, MDDocument121 paginiRespiratory System: Clarence L. Nuval, RMT, MDCla NuvalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System 1 Physiology 16-11-2018Document25 paginiRespiratory System 1 Physiology 16-11-2018Kangwa MasekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 118Responses-to-Altered-Ventilatory-FunctionDocument169 paginiNCM 118Responses-to-Altered-Ventilatory-FunctionAddah, Dhenaraiza H.Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument43 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemChristina GonezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratorysystem 101228012430 Phpapp01Document69 paginiRespiratorysystem 101228012430 Phpapp01Val Angelo BugayÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESPIRATORYDocument3 paginiRESPIRATORYKurt Adrian Z. TalagtagÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument62 paginiUntitledManaye MamuyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Respiratory SystemDocument25 paginiStructure of Respiratory SystemWijesiri D WÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Ent) - Lec5 Anatomy of The Pharynx & Esophagus - GonzalesDocument25 pagini(Ent) - Lec5 Anatomy of The Pharynx & Esophagus - GonzalesMark Loid Lucero AnlapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 paginiRespiratory Systemmehakapoor29Încă nu există evaluări
- PharynxDocument47 paginiPharynxAchraf RabadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument49 paginiRespiratory SystemVishal SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument84 paginiUntitledWardah AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Respiratory System and MechanicsDocument105 paginiHuman Respiratory System and MechanicsAbdul Qadir100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemhjhuDocument23 paginiRespiratory SystemhjhuSara AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Anatomy - Copy Edited 2022Document28 paginiRespiratory Anatomy - Copy Edited 2022celestelle247Încă nu există evaluări
- Functional Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument36 paginiFunctional Anatomy of Respiratory SystemshikhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Lower Respiratory TractDocument42 paginiHistology of Lower Respiratory TractRahma ShofiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument26 paginiBasic Functions of The Respiratory SystemMichael John CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiration SystemDocument49 paginiRespiration Systemfebe_aldellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument58 paginiAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinuseschambhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument68 pagini13 - Respiratory SystemNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument60 paginiRespiratory SystemSlindileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygenation-AnaPhysio HanakoRN PDFDocument69 paginiOxygenation-AnaPhysio HanakoRN PDFHanako Sasaki AranillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hhis221 Lab - Urinary SystemDocument48 paginiHhis221 Lab - Urinary SystemNel TinduganiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio CH8 F4 Studywithadmin PDFDocument16 paginiBio CH8 F4 Studywithadmin PDFMUHAMMAD FAREEZ HAIKAL MOHD SHAIFUDDINÎncă nu există evaluări
- The NoseDocument60 paginiThe NoseEdward Munyaradzi KutsanziraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect. 11 Respiratory SystemDocument43 paginiLect. 11 Respiratory Systemflex gyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS and RSDocument132 paginiCVS and RSclareawambuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory TractDocument49 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory TractshvnagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 Respiratory System 2022Document67 pagini16 Respiratory System 2022Yiannis AlatsathianosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument49 paginiRespiratory SystemSimply MiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise IxDocument27 paginiExercise IxShengrace GavinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Histology of Respiratory SystemDocument66 paginiComplete Histology of Respiratory Systemhassam qaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nasal Cavity, Larynx PDFDocument71 paginiNasal Cavity, Larynx PDFĄå DìÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System LecDocument49 paginiRespiratory System LecStef FieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System - ANATOMY HandoutDocument73 paginiRespiratory System - ANATOMY HandoutAmafel TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument351 paginiIlovepdf MergedSwara SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 paginiRespiratory Systemamulyajadhav119Încă nu există evaluări
- RespiratoryDocument62 paginiRespiratoryDerón Asbery HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: Gas ExchangeDocument28 paginiRespiratory System: Gas ExchangePinaka ShungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPD Final Exam: Head and NeckDocument16 paginiCPD Final Exam: Head and NeckSeeam Beanie HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 113 M1 Lesson 1Document10 paginiNCM 113 M1 Lesson 1Ryrl ShinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Lect IntroDocument15 paginiRespiratory Lect IntroAhmad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System (Anatomy)Document54 paginiRespiratory System (Anatomy)Juliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System 1Document29 paginiRespiratory System 1John SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Respiratory SystemDocument147 paginiThe Respiratory SystemAya SobhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument110 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemFarhin FarjenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Physio UsmleDocument61 paginiRespiratory Physio UsmleDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (2)
- Airway ClearanceDocument156 paginiAirway ClearancePriyasha TyagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System CopDocument44 paginiRespiratory System CopAsad KHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 paginiFunctions of The Respiratory Systemadelina.jianu9991Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformDocument367 paginiAnatomy and Physiology 2nd Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformMuhammad KashifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibreoptic IntubationDocument45 paginiFibreoptic IntubationArmaanjeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Build Your Own Warmup Revised 2 10 19Document7 paginiBuild Your Own Warmup Revised 2 10 19iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionDocument6 paginiCausticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionSuhas IngaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hoke Rachel InstructionalstrategyplanDocument36 paginiHoke Rachel Instructionalstrategyplanapi-422053279Încă nu există evaluări
- Vocal Cord Paralysis and Its Etiologies A Prospective StudyDocument4 paginiVocal Cord Paralysis and Its Etiologies A Prospective StudySheilla KhonadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drtbalu'S Otolaryngology Online: Acute LaryngitisDocument3 paginiDrtbalu'S Otolaryngology Online: Acute LaryngitisAnish RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro LarynxDocument4 paginiElectro LarynxHiroshi Osiris SugitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9D NLBA Illustrated Glossary 2015Document141 pagini9D NLBA Illustrated Glossary 2015galante81Încă nu există evaluări
- Speech Production MechanismDocument5 paginiSpeech Production MechanismAlyssa Crizel CalotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cha 24 Tortora Respiratory SystemDocument12 paginiCha 24 Tortora Respiratory Systemsrinivas ceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purpose of The LaryngosDocument13 paginiPurpose of The LaryngosdessriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning To SingDocument26 paginiLearning To SingDiane Hamel100% (13)
- Human Speech ArticulationDocument6 paginiHuman Speech ArticulationHaniefa AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posterior Cervical Triangle Anterior TrianglesDocument10 paginiPosterior Cervical Triangle Anterior TrianglesSaad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Document16 paginiRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Larynx1Document49 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Larynx1Enharmonic MelodiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Fundamentals of Speech CommunicationDocument12 pagini1 - Fundamentals of Speech CommunicationInga Budadoy NaudadongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excercise For The VoiceDocument16 paginiExcercise For The Voicehadibeigli100% (3)
- Matary Surgical Anatomy 2013 AllTebFamily ComDocument320 paginiMatary Surgical Anatomy 2013 AllTebFamily Comrusu_alexandra_4Încă nu există evaluări
- Kpbi 2010 Answer Respi SystemDocument38 paginiKpbi 2010 Answer Respi Systemwidyani rachimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laryngeal CleftDocument4 paginiLaryngeal CleftjuicyprunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- IyabodeOmolaraD 2011 CHAPTERTWO IntroductoryPhoneticsDocument10 paginiIyabodeOmolaraD 2011 CHAPTERTWO IntroductoryPhoneticsmiguelmrojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguDocument37 paginiEvaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguLavinia VictorÎncă nu există evaluări
- TheAnatomyofDirecting Final PDFDocument33 paginiTheAnatomyofDirecting Final PDFmike9and100% (2)
- Management of Ca LarynxDocument56 paginiManagement of Ca LarynxSatish Tripuraneni100% (1)
- The Origin of LanguageDocument14 paginiThe Origin of LanguageMorcosanu ConstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bontrager 9 EdicaoDocument339 paginiBontrager 9 EdicaoGerson Lopes100% (7)
- Voice Quality - EslingDocument5 paginiVoice Quality - EslingFelipe TabaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AliveDocument14 paginiThe Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AlivePeperoniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument20 paginiAnatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckTracie YWÎncă nu există evaluări