Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bartholin Cyst
Încărcat de
Chong Hui Chek0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
242 vizualizări2 paginiBartholin Cyst
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentBartholin Cyst
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
242 vizualizări2 paginiBartholin Cyst
Încărcat de
Chong Hui ChekBartholin Cyst
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
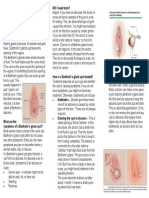
Bartholin's Gland Cyst
What is a Bartholin's gland cyst?
A Bartholin's gland cyst is a fluid-filled swelling of a Bartholin's gland. Bartholin's glands are two small
glands on each side of the opening of the vagina (birth canal). These glands are called Bartholin's glands.
They each have a small duct (tube) that opens to the outside. The glands produce a fluid that helps protect the
tissues around the vagina and provides lubrication during sexual intercourse. Normally these glands cannot
be felt or seen.
How does it occur?
A cyst may develop when the duct of one of the glands becomes swollen and blocked. Injury, irritation, or
infection may cause a buildup of fluid and swelling that blocks the duct.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms are:
swelling
tenderness
sometimes pain.
How is it diagnosed?
Your health care provider will ask about your symptoms and will see a swollen area at the opening of the
vagina. The swelling will be diagnosed as a cyst if it is not painful. If it is painful and infected, it is called a
Bartholin's gland abscess.
How is it treated?
Sometimes the cyst will go away if you put warm, moist cloths (compresses) on it or sit in warm baths. The
moist heat can help unblock the opening so that the fluid can drain out. Nonprescription medicine such as
aspirin, acetaminophen, or ibuprofen may help relieve the pain.
Your health care provider may make a small cut over the gland, making an opening so fluid can
drain out from the cyst. Your provider may then sew the opening in a way that leaves it open but
helps prevent it from tearing and getting bigger. This is usually done with a local anesthetic so that
you don't feel pain during the procedure. This treatment is called marsupialization.
Your health care provider may make a tiny cut in the cyst and insert a catheter (a very small tube)
into the cyst for a few weeks. The catheter helps form a passageway for fluid produced by the gland.
Ask your health care provider about any precautions you should take while the catheter is in place.
Your provider will remove the catheter in 4 to 6 weeks. The passageway should stay open after the
catheter is removed, preventing another cyst.
A cyst may become infected. It may form an abscess and become very painful. If a cyst is infected,
your health care provider may drain it and prescribe an antibiotic.
Sometimes the whole gland needs to be surgically removed, especially if the cyst often comes back.
The Bartholin's gland can be removed without damage to that area of the vaginal opening. You can
have sexual intercourse without the gland.
How can I help take care of myself?
Follow your health care provider's instructions. Call your health care provider if you have any of these signs
of infection:
redness around the cyst
fever
pain
more swelling.
How long will the effects last?
With the treatment of warm compresses, the cyst may go away in 3 to 5 days. Sometimes the cyst
does not go away with this treatment.
The cyst usually goes away almost immediately after your health care provider makes an incision for
drainage.
A cyst may recur over and over again if the whole gland is not removed.
How can I help prevent a Bartholin's gland cyst?
Make sure you keep the area of the vagina clean with mild soap and warm water.
Avoid hard or deep rubbing in the area around the opening of the vagina.
If you take long bike rides or ride horses a lot, try to protect your genital area by cushioning it with
soft padding.
Published by McKesson Health Solutions LLC. The information is intended to informand educate and is not a replacement for medical evaluation,
advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Written by Anthony Angello, MD. Copyright 2003 McKesson Health Solutions LLC.
All rights reserved. Copyright 2004 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Special Instructions:
Copyright Clinical Reference Systems 2004
Women's Health Advisor
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bartholin Cyst PDFDocument2 paginiBartholin Cyst PDFijmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholins Abscess Word CatheterDocument2 paginiBartholins Abscess Word CatheterCha DhichadherÎncă nu există evaluări
- B Bartholins Abscess - Word CatheterDocument2 paginiB Bartholins Abscess - Word CatheterMuhammadUsriYusranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin's Cyst-Abscess NBT002320Document8 paginiBartholin's Cyst-Abscess NBT002320Muhammad FadhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide To Bartholin Cyst, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide To Bartholin Cyst, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Symptoms of A Bartholin IndonesiaDocument3 paginiSymptoms of A Bartholin IndonesiaApryanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Bartholin Gland Procedure + Inform ConsentDocument4 pagini03 Bartholin Gland Procedure + Inform ConsentelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin CystDocument6 paginiBartholin CystCokorda Istri Devi LarayanthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin Cyst or Abscess v2 Apr 14Document2 paginiBartholin Cyst or Abscess v2 Apr 14Teguh Imana NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treating A Bartholins Cyst or Abscess Patient InformationDocument6 paginiTreating A Bartholins Cyst or Abscess Patient InformationRezaFArthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage of Bartholin Cyst Abscess ML46071Document4 paginiDrainage of Bartholin Cyst Abscess ML46071elenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin's Cyst or Abscess TreatmentDocument4 paginiBartholin's Cyst or Abscess TreatmentRezaFArthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholins Jul11Document3 paginiBartholins Jul11Maria PattyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CircumcisionDocument18 paginiCircumcisionTriciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 102 Bartholin's CystDocument12 pagini12 102 Bartholin's CystYuliana Eka SintaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inserting A Word Catheter To Treat A Bartholins Cyst or AbscessDocument2 paginiInserting A Word Catheter To Treat A Bartholins Cyst or AbscessMuhammad FadhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information From The British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) About Bladder CathetersDocument6 paginiInformation From The British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) About Bladder CathetersralphholingsheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of The Perineum After The Birth of Your Baby: Oxford University HospitalsDocument8 paginiCare of The Perineum After The Birth of Your Baby: Oxford University HospitalsSharief SkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin CuystDocument2 paginiBartholin CuystAgungLaksanaDharmantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISC Female PDFDocument4 paginiISC Female PDFralphholingsheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Points: Information From The British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) About Self-CatheterisationDocument4 paginiKey Points: Information From The British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) About Self-CatheterisationralphholingsheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- MedicinesDocument6 paginiMedicinesTriciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catheter Care TrainingDocument15 paginiCatheter Care TrainingAndrada MateiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interstitial Cystitis & Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Guide For WomenDocument2 paginiInterstitial Cystitis & Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Guide For Womencateterdoblejota100% (1)
- Teaching Plan For A Post Partum MotherDocument12 paginiTeaching Plan For A Post Partum Motherpatrickarvin100% (2)
- Bartholin Cyst or Abscess v2 Apr 14 PDFDocument2 paginiBartholin Cyst or Abscess v2 Apr 14 PDFTeguh Imana NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5960 1 Hartmanns ProcedureDocument8 pagini5960 1 Hartmanns ProcedurecosmicdaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FistomologyDocument11 paginiFistomologyKevin Fernandez MendioroÎncă nu există evaluări
- PD 6660 Orchiectomy SurgeryDocument4 paginiPD 6660 Orchiectomy SurgeryIndra WibawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anal Fissure, (Break in the Anus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandAnal Fissure, (Break in the Anus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- 06 40 Vesico-Vaginal FistulaDocument12 pagini06 40 Vesico-Vaginal FistulaHosny M IsseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document PDFDocument2 paginiDocument PDFSuneel Kumar PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cystoscopy: A Guide For WomenDocument2 paginiCystoscopy: A Guide For Womenmonir61Încă nu există evaluări
- DijaDocument6 paginiDijakanukhadijatu22Încă nu există evaluări
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument9 paginiPeritoneal Dialysismu_crÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIN0638 Female Incontinence v1Document5 paginiPIN0638 Female Incontinence v1Shamsuddin HasnaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Having A Sitz Bath at Home PDFDocument7 paginiHaving A Sitz Bath at Home PDFAvizam CahyonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Cystoscopy?Document3 paginiWhat Is A Cystoscopy?Harley Justiniani Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Marsupialization of A Bartholin's Cyst or AbscessDocument2 paginiMarsupialization of A Bartholin's Cyst or Abscesskyle31Încă nu există evaluări
- Taking Care of Your PerineumDocument16 paginiTaking Care of Your PerineumZuliana RazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open CholecystectomyDocument7 paginiOpen CholecystectomyMonique CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- BABC038 Sphincter Repair Operation May 2021Document4 paginiBABC038 Sphincter Repair Operation May 20212016satyendrakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Instructions For Hemorrhoid Surgery: Home CareDocument2 paginiDischarge Instructions For Hemorrhoid Surgery: Home CareKath ReignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholinitis 1Document9 paginiBartholinitis 1Muskan TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholinitis 1Document9 paginiBartholinitis 1Muskan TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- VaginitisDocument2 paginiVaginitisMardatillah WiranataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Instructions After FistulotomyDocument3 paginiDischarge Instructions After FistulotomyUsername374100% (1)
- 5960 1 Hartmanns ProcedureDocument8 pagini5960 1 Hartmanns ProcedureZakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument17 paginiPeritoneal DialysisIan Benedict GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- VaginaDocument5 paginiVaginaBrett DawsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- EpisiotomyDocument7 paginiEpisiotomyJalajarani Aridass100% (1)
- Dilation and Curettage: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsDocument2 paginiDilation and Curettage: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsDellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemorrhoidsDocument2 paginiHemorrhoidsadadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pi Care of Third and Fourth Degree Tears OasiDocument6 paginiPi Care of Third and Fourth Degree Tears OasiPetros Akin-NibosunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduced Bladder EmptyingDocument2 paginiReduced Bladder EmptyingThe Saloniti BabiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian CystDocument4 paginiOvarian CystBinita PoudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternity - Perineal TearsDocument4 paginiMaternity - Perineal TearsJunarto Butar ButarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureDocument9 paginiWhat Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureYusephAwangSanaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health EducationDocument41 paginiHealth EducationChong Hui ChekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health EducationDocument41 paginiHealth EducationChong Hui ChekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Document2 paginiRd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Chong Hui ChekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crop CirclesDocument1 paginăCrop CirclesChong Hui ChekÎncă nu există evaluări
- ManagementDocument1 paginăManagementChong Hui ChekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin Scraping ProcedureDocument2 paginiSkin Scraping ProcedureTi Ga VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universitas Tidar: Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu PendidikanDocument7 paginiUniversitas Tidar: Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu PendidikanTheresia Calcutaa WilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 Composition Rules For Photos That ShineDocument20 pagini18 Composition Rules For Photos That Shinemahfuzkhan100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536Document4 paginiSafety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536BanyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultracold Atoms SlidesDocument49 paginiUltracold Atoms SlideslaubbaumÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Level 4 COCDocument2 paginiIT Level 4 COCfikru tesefaye0% (1)
- Best Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondDocument17 paginiBest Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondPrateekÎncă nu există evaluări
- PETAL Sentence StartersDocument1 paginăPETAL Sentence StartersSnip x Hunt manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvo BL 71 ManualDocument280 paginiVolvo BL 71 ManualAlberto G.D.100% (2)
- Case Study - Suprema CarsDocument5 paginiCase Study - Suprema CarsALFONSO PATRICIO GUERRA CARVAJALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qpeak L-g4.2 360-370 2017-10 Rev02 NaDocument2 paginiHanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qpeak L-g4.2 360-370 2017-10 Rev02 NazulfikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction CompilerDocument47 paginiIntroduction CompilerHarshit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- KLA28 ProductsapplicationpresetDocument2 paginiKLA28 ProductsapplicationpresetcarxmozÎncă nu există evaluări
- CATaclysm Preview ReleaseDocument52 paginiCATaclysm Preview ReleaseGhaderalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review Template DownloadDocument4 paginiLiterature Review Template Downloadaflsigfek100% (1)
- A Literature Review of Retailing Sector and BusineDocument21 paginiA Literature Review of Retailing Sector and BusineSid MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magic Bullet Theory - PPTDocument5 paginiMagic Bullet Theory - PPTThe Bengal ChariotÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMD Question Bank II 2Document4 paginiEMD Question Bank II 2Soham MisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highlights ASME Guides Preheat PWHT IDocument4 paginiHighlights ASME Guides Preheat PWHT IArul Edwin Vijay VincentÎncă nu există evaluări
- G2 Rust Grades USA PDFDocument2 paginiG2 Rust Grades USA PDFSt3fandragos4306Încă nu există evaluări
- The Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsDocument58 paginiThe Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsWael HaidarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Sat) - 072023Document7 pagini(Sat) - 072023DhananjayPatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukDocument3 paginiUniversal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukPhilip EgyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeDocument84 paginiEducationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeAnna ModebadzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2500 Valve BrochureDocument12 pagini2500 Valve BrochureJurie_sk3608Încă nu există evaluări
- I M Com QT Final On16march2016Document166 paginiI M Com QT Final On16march2016Khandaker Sakib Farhad0% (1)
- Active Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023Document119 paginiActive Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023jagdeepchkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject OrientationDocument15 paginiSubject OrientationPearl OgayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer System Validation - Definition and Requirements - MustRead PDFDocument3 paginiComputer System Validation - Definition and Requirements - MustRead PDFtraining validÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Studocu Com in N 29646569 Sid 01682568219Document1 paginăWWW Studocu Com in N 29646569 Sid 01682568219Nivetha SelvamuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXDocument4 paginiNote!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXAdityaArnas0% (1)